|
Dhanurasana
Dhanurasana ( sa, धनुरासन, lit=Bow pose, translit=Dhanurāsana) is a back bending ''asana'' in ''hatha yoga'' and modern yoga as exercise. Etymology and origins The name comes from the Sanskrit words धनुर (dhanura) meaning " bow", and आसन (āsana) meaning "posture" or "seat". A similar pose named Nyubjasana, "the face-down asana", is described and illustrated in the 19th century ''Sritattvanidhi''. The pose is illustrated in half-tone in the 1905 ''Yogasopana Purvacatuska'' and named Dhanurāsana, quoting the ''Gheranda Samhitas description. It is unclear whether the asana is medieval, as although the name is used, the intended pose might be the sitting Akarna Dhanurasana rather than this backbend. The account of Dhanurasana in the 15th century ''Hatha Yoga Pradipika'' is ambiguous about whether the pose is reclining or sitting, stating The 17th century ''Gheranda Samhita'' is similarly ambiguous, stating Dhanurasana is used in the classical I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dhanurasana Yoga-Asana Nina-Mel
Dhanurasana ( sa, धनुरासन, lit=Bow pose, translit=Dhanurāsana) is a back bending '' asana'' in '' hatha yoga'' and modern yoga as exercise. Etymology and origins The name comes from the Sanskrit words धनुर (dhanura) meaning " bow", and आसन (āsana) meaning "posture" or "seat". A similar pose named Nyubjasana, "the face-down asana", is described and illustrated in the 19th century ''Sritattvanidhi''. The pose is illustrated in half-tone in the 1905 '' Yogasopana Purvacatuska'' and named Dhanurāsana, quoting the ''Gheranda Samhitas description. It is unclear whether the asana is medieval, as although the name is used, the intended pose might be the sitting Akarna Dhanurasana rather than this backbend. The account of Dhanurasana in the 15th century '' Hatha Yoga Pradipika'' is ambiguous about whether the pose is reclining or sitting, stating The 17th century '' Gheranda Samhita'' is similarly ambiguous, stating Dhanurasana is used in the class ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dhanurasana In Yogasopana Purvacatuska 1905
Dhanurasana ( sa, धनुरासन, lit=Bow pose, translit=Dhanurāsana) is a back bending '' asana'' in '' hatha yoga'' and modern yoga as exercise. Etymology and origins The name comes from the Sanskrit words धनुर (dhanura) meaning " bow", and आसन (āsana) meaning "posture" or "seat". A similar pose named Nyubjasana, "the face-down asana", is described and illustrated in the 19th century ''Sritattvanidhi''. The pose is illustrated in half-tone in the 1905 '' Yogasopana Purvacatuska'' and named Dhanurāsana, quoting the ''Gheranda Samhitas description. It is unclear whether the asana is medieval, as although the name is used, the intended pose might be the sitting Akarna Dhanurasana rather than this backbend. The account of Dhanurasana in the 15th century '' Hatha Yoga Pradipika'' is ambiguous about whether the pose is reclining or sitting, stating The 17th century '' Gheranda Samhita'' is similarly ambiguous, stating Dhanurasana is used in the class ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
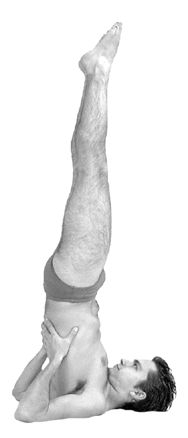
Urdhva Dhanurasana
Chakrasana ( sa, चक्रासन, lit=Wheel Pose, translit=Cakrāsana) or Urdhva Dhanurasana ( sa, ऊर्ध्वधनुरासन, lit=Upward-Facing Bow Pose, translit=Ūrdhvadhanurāsana) is a backbending asana in yoga as exercise. The one-legged variant is often chosen by yoga practitioners who wish to advertise themselves. Etymology and origins The name Chakrasana comes from the Sanskrit words चक्र ''chakra'', "wheel", and आसन ''āsana'', "posture" or "seat". The name Urdhva Dhanurasana comes from the Sanskrit ''urdhva'' ऊर्ध्व, upwards, and ''dhanura'' धनु, a bow (for shooting arrows). The pose is illustrated in the 19th century ''Sritattvanidhi'' as ''Paryaṇkāsana'', Couch Pose. Description In the general form of the asana, the practitioner has hands and feet on the floor, and the abdomen arches up toward the sky. It may be entered from a supine position or through a less rigorous supine backbend, such as Setu Bandha Sarva ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
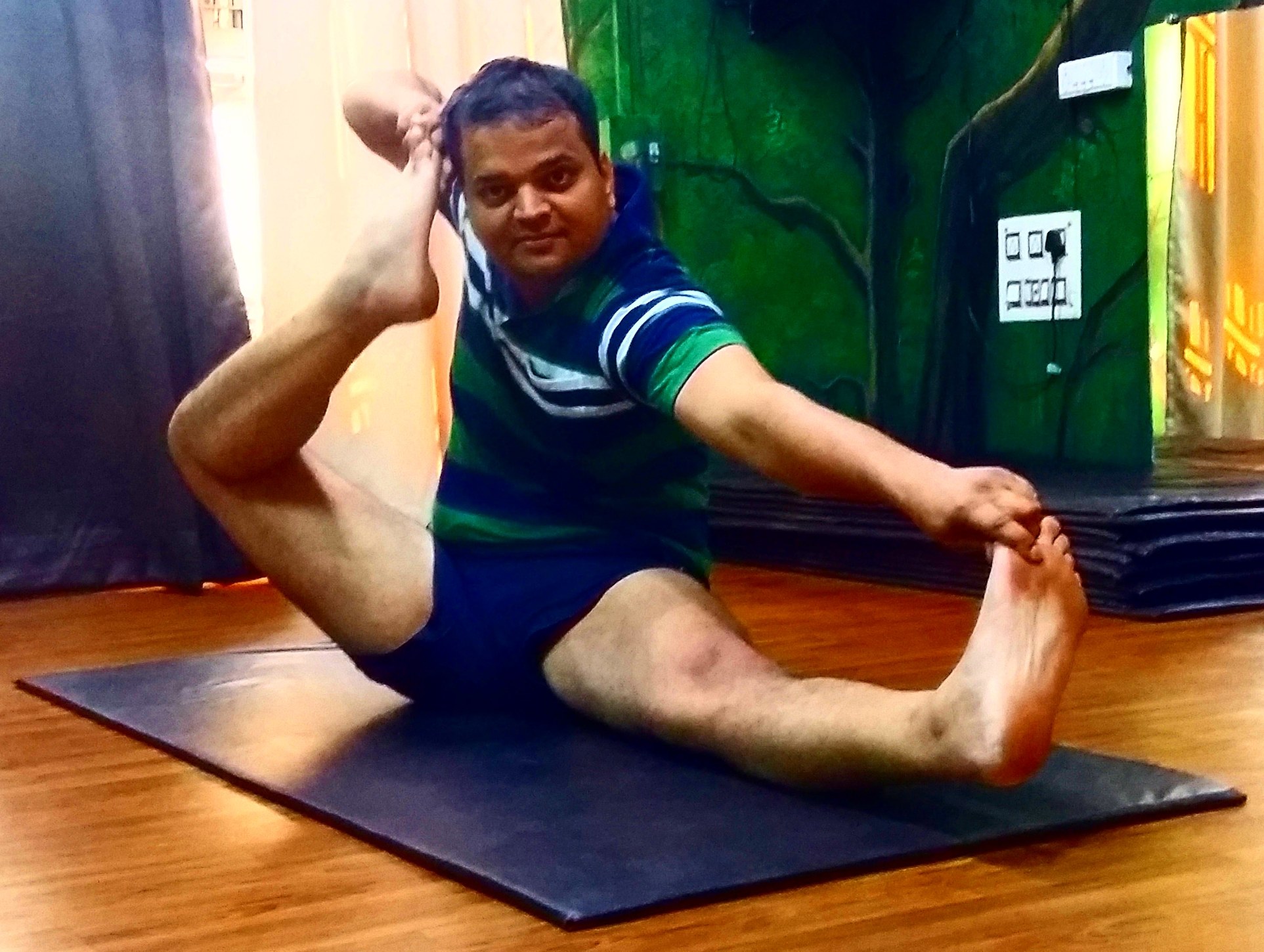
Akarna Dhanurasana
Akarna Dhanurasana ( sa, आकर्ण धनुरासन; IAST: ''Ākarṇa Dhanurāsana''), also called the Archer pose, Bow and Arrow pose, or Shooting Bow pose is an asana in hatha yoga and modern yoga as exercise. The posture resembles an archer about to release an arrow. Etymology and origins The name of the pose is from Sanskrit कर्ण ''Karṇa'', "ear" with the prefix ''Ā'', "towards" or "near". धनुर ''Dhanura'' means "bow" and आसन ''asana'' means "posture" or "seat". The name alludes to a myth in the Ramayana in which the infant Sita is able to lift Shiva's enormous bow, and when she reaches marriageable age, only Rama is able to wield it, and so become her husband. The pose is shown as ''Dhanurāsana'' in the 19th century ''Sritattvanidhi''. It has its modern name in the 1966 '' Light on Yoga''. File:Sritattvanidhi Akarna Dhanurasana.jpg, Pose labelled ''Dhanurāsana''in the 19th century ''Sritattvanidhi'' Description Akarna Dhanurasan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Balasana
Bālāsana ( sa, बालासन) or Child Pose, is a kneeling asana in modern yoga as exercise. Balasana is a counter asana for various asanas and is usually practiced before and after Sirsasana. Etymology and origins The name comes from the Sanskrit words बाल ''bala'', "child" and आसन ''āsana'', "posture" or "seat". Balasana is not described until the 20th century; a similar pose appears in Niels Bukh's 1924 ''Primary Gymnastics''. Ananda Balasana is illustrated as Kandukasana (Ball Pose) in the 19th century ''Sritattvanidhi''. Description From a kneeling position, bring the forehead to the floor and relax the arms alongside the body, palms upwards. Variations If need be, and during pregnancy, the knees can be spread. The arms may be stretched forward in front of the head. If there is discomfort in the neck and shoulders, a rolled blanket may be placed on the backs of the lower legs, and the forearms can be stacked and the forehead rested on them. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Complete Illustrated Book Of Yoga
''The Complete Illustrated Book of Yoga'' is a bestselling 1960 book by Swami Vishnudevananda, the founder of the Sivananda Yoga Vedanta Centres. It is an introduction to Hatha yoga, describing the ''Yoga Sutras of Patanjali'' and the ''Hatha Yoga Pradipika''. It contributed to the incorporation of Surya Namaskar (salute to the sun) into yoga as exercise. While some of its subject matter is the traditional philosophy of yoga, its detailed photographs of Vishnudevananda performing the asanas is modern, helping to market the Sivananda yoga brand to a global audience. Context The book was one of the first three reference works on asanas (yoga postures) in the development of yoga as exercise in the mid-20th century, the other two being Selvarajan Yesudian and Elisabeth Haich's 1941 ''Sport és Jóga'' (in Spanish: an English version appeared in 1953) and Theos Bernard's 1944 '' Hatha Yoga: The Report of a Personal Experience''. Its author, Vishnudevananda, was a student of Siv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Iyengar Way
''The'' () is a grammatical article in English, denoting persons or things that are already or about to be mentioned, under discussion, implied or otherwise presumed familiar to listeners, readers, or speakers. It is the definite article in English. ''The'' is the most frequently used word in the English language; studies and analyses of texts have found it to account for seven percent of all printed English-language words. It is derived from gendered articles in Old English which combined in Middle English and now has a single form used with nouns of any gender. The word can be used with both singular and plural nouns, and with a noun that starts with any letter. This is different from many other languages, which have different forms of the definite article for different genders or numbers. Pronunciation In most dialects, "the" is pronounced as (with the voiced dental fricative followed by a schwa) when followed by a consonant sound, and as (homophone of the archaic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yoga Dipika
Yoga (; sa, योग, lit=yoke' or 'union ) is a group of physical, mental, and spiritual practices or disciplines which originated in ancient India and aim to control (yoke) and still the mind, recognizing a detached witness-consciousness untouched by the mind ('' Chitta'') and mundane suffering ('' Duḥkha''). There is a wide variety of schools of yoga, practices, and goals in Hinduism, Buddhism, and Jainism,Stuart Ray Sarbacker, ''Samādhi: The Numinous and Cessative in Indo-Tibetan Yoga''. SUNY Press, 2005, pp. 1–2.Tattvarthasutra .1 see Manu Doshi (2007) Translation of Tattvarthasutra, Ahmedabad: Shrut Ratnakar p. 102. and traditional and modern yoga is practiced worldwide. Two general theories exist on the origins of yoga. The linear model holds that yoga originated in the Vedic period, as reflected in the Vedic textual corpus, and influenced Buddhism; according to author Edward Fitzpatrick Crangle, this model is mainly supported by Hindu scholars. Accor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salabhasana
Salabhasana or Purna Salabhasana ( sa, शलभासन; IAST: ''Śalabhāsana''), Locust pose, or Grasshopper pose is a prone back-bending asana in modern yoga as exercise. Etymology and origins The asana's name comes from the Sanskrit शलभा "shalabh" which means "grasshopper" or "locust". The pose is not found in the medieval hatha yoga texts. It is included in Yoga Ghamande's 1905 '' Yogasopana Purvacatuska'', the first yoga manual with printed illustrations, uniquely as halftone plates. It is described independently in Swami Vishnudevananda's 1960 '' Complete Illustrated Book of Yoga'' in the Sivananda Yoga tradition, and by '' B. K. S. Iyengar'' in his 1966 '' Light on Yoga'', implying that it may have older origins. A similar pose was found in Western gymnastics in '' The Bagot Stack Stretch-and-Swing System'', 1931, though Mary Bagot Stack had visited India. File:Salabhasana in Yogasopana 1905.jpg, Salabhasana in '' Yogasopana Purvacatuska'', 1905 File:Sc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sarvangasana
Sarvangasana ( sa, सर्वाङ्गासन, translit=sarvāṅgāsana), Shoulder stand, or more fully Salamba Sarvangasana (Supported Shoulder stand), is an inverted asana in modern yoga as exercise; similar poses were used in medieval hatha yoga as a mudra. Many named variations exist, including with legs in lotus position and Supta Konasana with legs wide apart, toes on the ground. ''Sarvāṅgāsana'' has been nicknamed the "queen" or "mother" of all the asanas. Etymology and origins The name comes from the Sanskrit सालम्ब ''Salamba'', "supported", सर्वाङ्ग ''Sarvāṅga'', "all limbs", i.e. "the whole body", and आसन ''Āsana'', "posture"," position", or "seat". The name Sarvangasana is modern, but similar inverted poses were in use in medieval hatha yoga as a mudra, Viparita Karani, which is documented in the 14th century '' Śiva Saṃhitā'' 4.45-47, the 15th century ''Haṭha Yoga Pradīpikā'' 3.78-81, the 17th century ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Halasana
Halasana (Sanskrit: हलासन; IAST: ''halāsana'') or Plough pose is an inverted asana in hatha yoga and modern yoga as exercise. Its variations include Karnapidasana with the knees by the ears, and Supta Konasana with the feet wide apart. Etymology and origins The name Halasana comes from Sanskrit हला ''hala'', "plough" and आसन ''āsana'', "posture" or "seat". The pose is described and illustrated in the 19th century ''Sritattvanidhi'' as ''Lāṇgalāsana'', which also means plough pose in Sanskrit. Karnapidasana is not found in the medieval hatha yoga texts. It is described independently in Swami Vishnudevananda's 1960 '' Complete Illustrated Book of Yoga'' in the Sivananda Yoga tradition, and by '' B. K. S. Iyengar'' in his 1966 ''Light on Yoga'', implying that it may have older origins. The name comes from the Sanskrit words ''karṇa'' (कर्ण) meaning "ears", ''pīḍ'' (पीड्) meaning "to squeeze", and ''āsana'' (आसन) meaning " ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
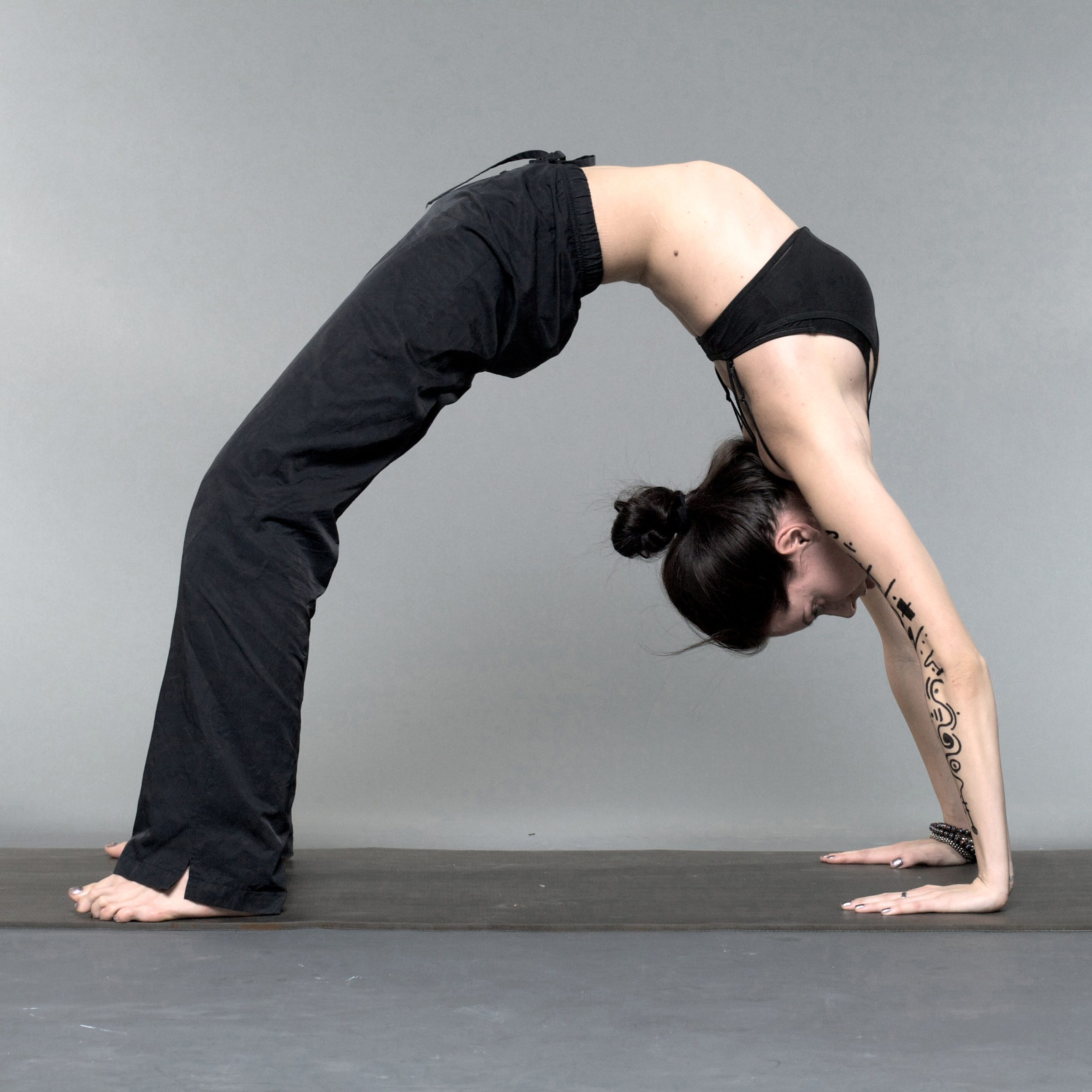
Backbend
A backbend is a gymnastics, contortion, dance and ice skating move, where the spine is bent backwards, and catching oneself with the hands. Throughout the move, the abdominal muscles, obliques, and legs are used to steady the performer while curving backwards. Modern yoga includes some backbending asanas. Backbending can be acquired from intense training or genetics. Overview The spine consists of 24 vertebrae and between the vertebrae are small cushions referred to as disks. The movement of the vertebrae and the compression ability of the disks give the spine its flexibility. It is easier to perform a backbend after mastering a bridge. A bridge helps familiarize the bones and muscles to the positions and movements of a backbend. There are over a dozen yoga positions that are variant of the backbend. A "rib thrust" is common and deleterious to a good yoga pose, and one of the more common of several errors associated with the backbend. Uses The backbend is important in gy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.png)

.jpg)