|
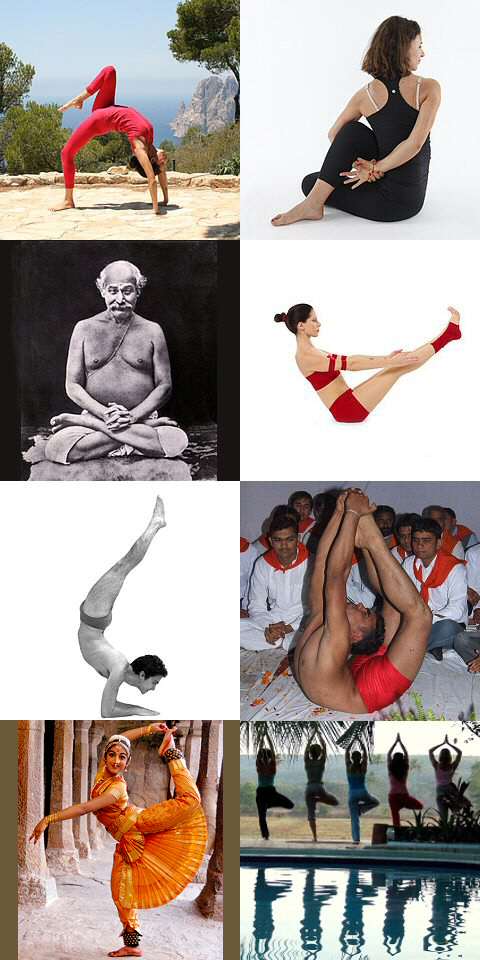
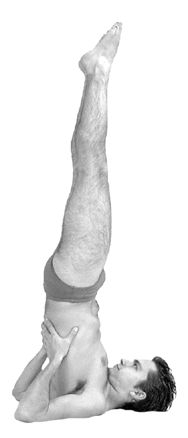
Sarvangasana
Sarvangasana ( sa, सर्वाङ्गासन, translit=sarvāṅgāsana), Shoulder stand, or more fully Salamba Sarvangasana (Supported Shoulder stand), is an inverted asana in modern yoga as exercise; similar poses were used in medieval hatha yoga as a mudra. Many named variations exist, including with legs in lotus position and Supta Konasana with legs wide apart, toes on the ground. ''Sarvāṅgāsana'' has been nicknamed the "queen" or "mother" of all the asanas. Etymology and origins The name comes from the Sanskrit सालम्ब ''Salamba'', "supported", सर्वाङ्ग ''Sarvāṅga'', "all limbs", i.e. "the whole body", and आसन ''Āsana'', "posture"," position", or "seat". The name Sarvangasana is modern, but similar inverted poses were in use in medieval hatha yoga as a mudra, Viparita Karani, which is documented in the 14th century '' Śiva Saṃhitā'' 4.45-47, the 15th century ''Haṭha Yoga Pradīpikā'' 3.78-81, the 17th century ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Asanas
An asana is a body posture, used in both medieval hatha yoga and modern yoga. The term is derived from the Sanskrit word for 'seat'. While many of the oldest mentioned asanas are indeed seated postures for meditation, asanas may be standing, seated, arm-balances, twists, inversions, forward bends, backbends, or reclining in prone or supine positions. The asanas have been given a variety of English names by competing schools of yoga. The traditional number of asanas is the symbolic 84, but different texts identify different selections, sometimes listing their names without describing them. Some names have been given to different asanas over the centuries, and some asanas have been known by a variety of names, making tracing and the assignment of dates difficult. For example, the name Muktasana is now given to a variant of Siddhasana with one foot in front of the other, but has also been used for Siddhasana and other cross-legged meditation poses. As another example, the headstand ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
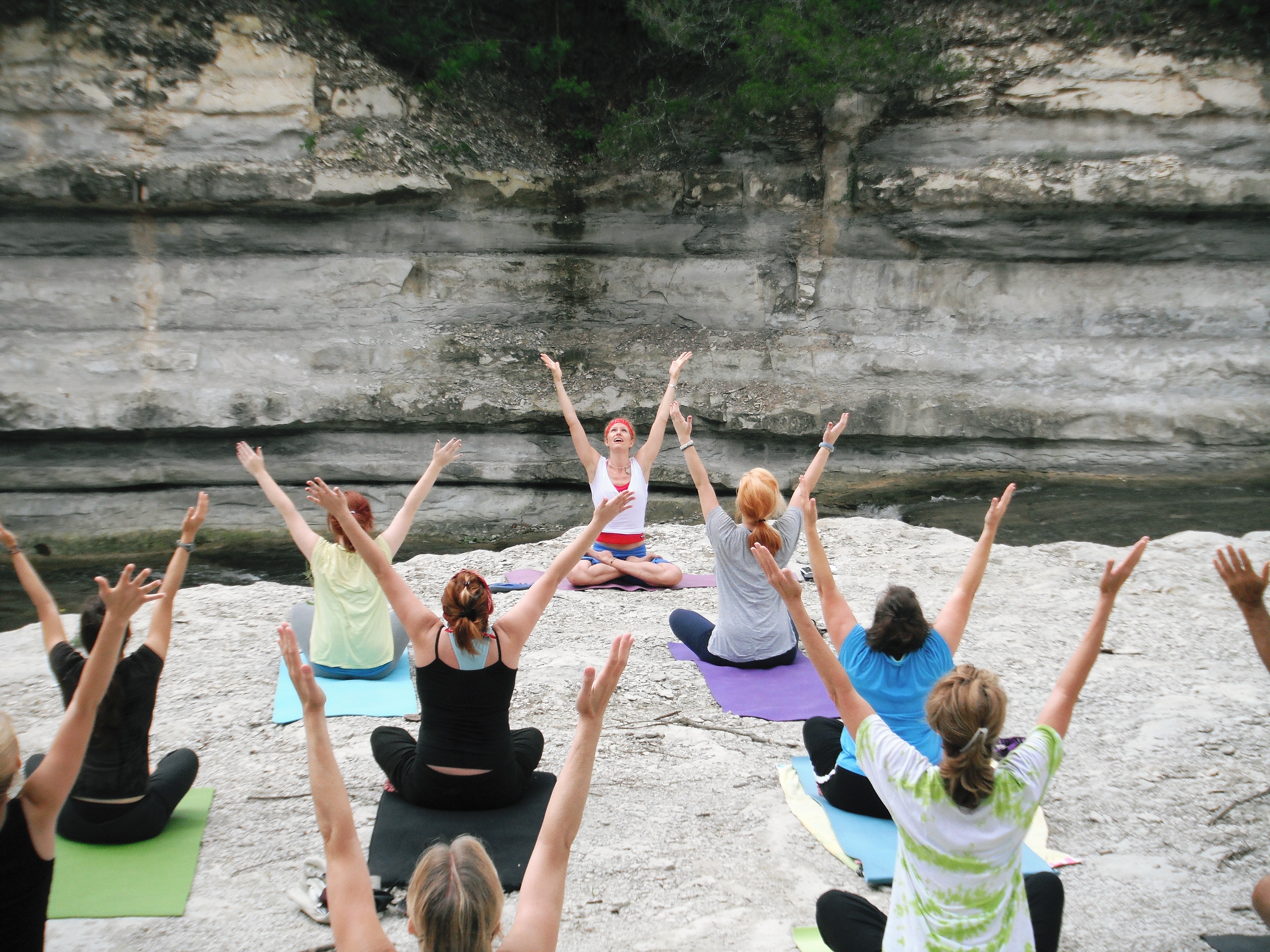
Yoga As Exercise
Yoga as exercise is a physical activity consisting mainly of postures, often connected by flowing sequences, sometimes accompanied by breathing exercises, and frequently ending with relaxation lying down or meditation. Yoga in this form has become familiar across the world, especially in America and Europe. It is derived from medieval Haṭha yoga, which made use of similar postures, but it is generally simply called "yoga". Academics have given yoga as exercise a variety of names, including modern postural yoga and transnational anglophone yoga. Posture is described in the ''Yoga Sutras'' II.29 as the third of the eight limbs, the ashtanga, of yoga. Sutra II.46 defines it as that which is ''steady and comfortable'', but no further elaboration or list of postures is given. Postures were not central in any of the older traditions of yoga; posture practice was revived in the 1920s by yoga gurus including Yogendra and Kuvalayananda, who emphasised its health benefits. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
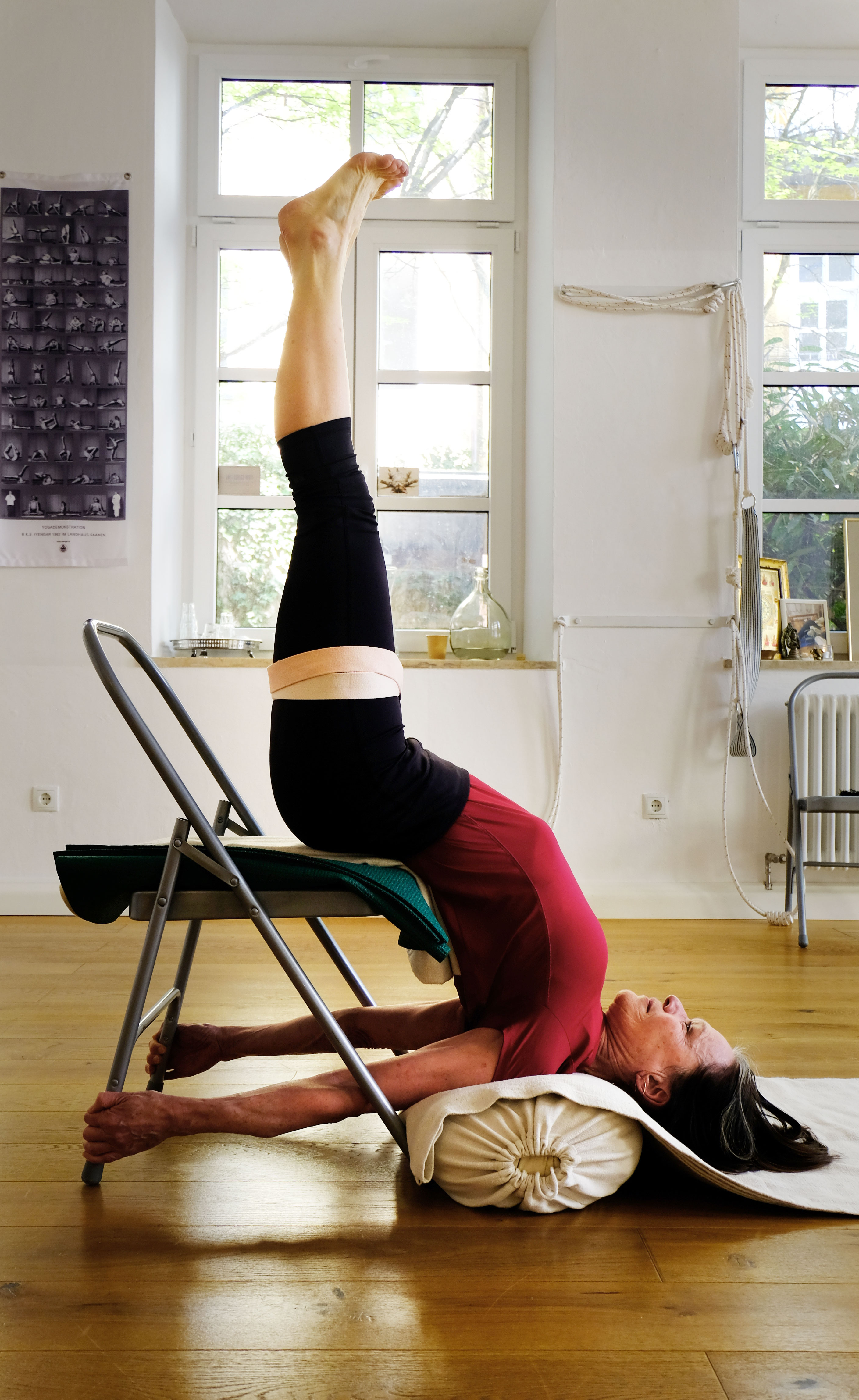
Yoga Using Props
Props used in yoga include chairs, blocks, belts, mats, blankets, bolsters, and straps. They are used in postural yoga to assist with correct alignment in an asana, for ease in mindful yoga practice, to enable poses to be held for longer periods in Yin Yoga, where support may allow muscles to relax, and to enable people with movement restricted for any reason, such as stiffness, injury, or arthritis, to continue with their practice. One prop, the yoga strap, has an ancient history, being depicted in temple sculptures and described in manuscripts from ancient and medieval times; it was used in ''Sopasrayasana'', also called ''Yogapattasana'', a seated meditation pose with the legs crossed and supported by the strap. In modern times, the use of props is associated especially with the yoga guru B. K. S. Iyengar; his disciplined style required props including belts, blocks, and ropes. History The ''yogapaṭṭa'' in sculpture The practice of yoga as exercise is modern, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
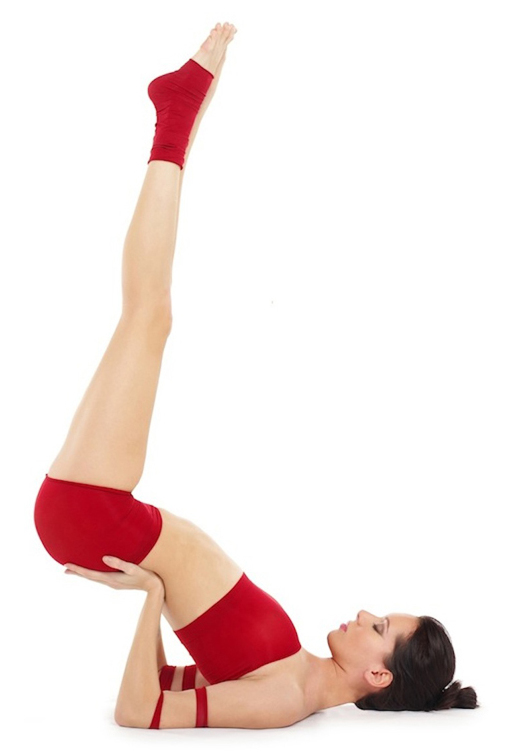
Karnapidasana
Halasana (Sanskrit: हलासन; IAST: ''halāsana'') or Plough pose is an inverted asana in hatha yoga and modern yoga as exercise. Its variations include Karnapidasana with the knees by the ears, and Supta Konasana with the feet wide apart. Etymology and origins The name Halasana comes from Sanskrit हला ''hala'', " plough" and आसन ''āsana'', "posture" or "seat". The pose is described and illustrated in the 19th century ''Sritattvanidhi'' as ''Lāṇgalāsana'', which also means plough pose in Sanskrit. Karnapidasana is not found in the medieval hatha yoga texts. It is described independently in Swami Vishnudevananda's 1960 '' Complete Illustrated Book of Yoga'' in the Sivananda Yoga tradition, and by '' B. K. S. Iyengar'' in his 1966 '' Light on Yoga'', implying that it may have older origins. The name comes from the Sanskrit words ''karṇa'' (कर्ण) meaning "ears", ''pīḍ'' (पीड्) meaning "to squeeze", and ''āsana'' (आसन) mea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Viparita Karani
Viparita Karani ( sa, विपरीतकरणी; ) or legs up the wall pose is both an asana and a mudra in hatha yoga. In modern yoga as exercise, it is commonly a fully supported pose using a wall and sometimes a pile of blankets, where it is considered a restful practice. As a mudra it was practised using any preferred inversion, such as a headstand or shoulderstand. The purpose of the mudra was to reverse the downward flow of vital fluid being lost from the head, using gravity. Etymology and origins The name comes from the Sanskrit words विपरीत ''viparīta'', "inverted" or "reversed", and करणी ''karaṇī'', "a particular type of practice". The practice is described in the 13th century ''Vivekamārtaṇḍa'' (verses 103-131) as a means of yogic withdrawal, pratyahara. The pose was practised from the 17th century onwards in hatha yoga under names such as Narakasana, Kapalasana and Viparitakaranasana; its purpose as a mudra was to reverse the do ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Light On Yoga
''Light on Yoga: Yoga Dipika'' (Sanskrit: योग दीपिका, "Yoga Dīpikā") is a 1966 book on the Iyengar Yoga style of modern yoga as exercise by B. K. S. Iyengar, first published in English. It describes more than 200 yoga postures or asanas, and is illustrated with some 600 monochrome photographs of Iyengar demonstrating these. The book has been described as the 'bible of modern yoga', and its presentation of the asanas has been called "unprecedented" and "encyclopedic". It has been translated into at least 23 languages and has sold over three million copies. Context Yoga is a group of physical, mental, and spiritual practices from ancient India, forming one of the six orthodox schools of Hindu philosophical traditions. In the Western world, however, yoga is often taken to mean a modern form of medieval Hatha yoga, practised mainly for exercise, consisting largely of the postures called asanas. B. K. S. Iyengar (1918-2014) was born in a poor family ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Halasana
Halasana (Sanskrit: हलासन; IAST: ''halāsana'') or Plough pose is an inverted asana in hatha yoga and modern yoga as exercise. Its variations include Karnapidasana with the knees by the ears, and Supta Konasana with the feet wide apart. Etymology and origins The name Halasana comes from Sanskrit हला ''hala'', "plough" and आसन ''āsana'', "posture" or "seat". The pose is described and illustrated in the 19th century ''Sritattvanidhi'' as ''Lāṇgalāsana'', which also means plough pose in Sanskrit. Karnapidasana is not found in the medieval hatha yoga texts. It is described independently in Swami Vishnudevananda's 1960 '' Complete Illustrated Book of Yoga'' in the Sivananda Yoga tradition, and by '' B. K. S. Iyengar'' in his 1966 ''Light on Yoga'', implying that it may have older origins. The name comes from the Sanskrit words ''karṇa'' (कर्ण) meaning "ears", ''pīḍ'' (पीड्) meaning "to squeeze", and ''āsana'' (आसन) meaning " ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Halasana
Halasana (Sanskrit: हलासन; IAST: ''halāsana'') or Plough pose is an inverted asana in hatha yoga and modern yoga as exercise. Its variations include Karnapidasana with the knees by the ears, and Supta Konasana with the feet wide apart. Etymology and origins The name Halasana comes from Sanskrit हला ''hala'', "plough" and आसन ''āsana'', "posture" or "seat". The pose is described and illustrated in the 19th century ''Sritattvanidhi'' as ''Lāṇgalāsana'', which also means plough pose in Sanskrit. Karnapidasana is not found in the medieval hatha yoga texts. It is described independently in Swami Vishnudevananda's 1960 '' Complete Illustrated Book of Yoga'' in the Sivananda Yoga tradition, and by '' B. K. S. Iyengar'' in his 1966 ''Light on Yoga'', implying that it may have older origins. The name comes from the Sanskrit words ''karṇa'' (कर्ण) meaning "ears", ''pīḍ'' (पीड्) meaning "to squeeze", and ''āsana'' (आसन) meaning " ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sirsasana
Shirshasana (Sanskrit: शीर्षासन, IAST: śīrṣāsana) Salamba Shirshasana, or Yoga Headstand is an inverted asana in modern yoga as exercise; it was described as both an asana and a mudra in classical hatha yoga, under different names. It has been called the king of all asanas. Its many variations can be combined into Mandalasana, in which the legs are progressively swept from one variation to the next in a full circle around the body. Etymology and origins The name Salamba Shirshasana comes from the Sanskrit words सालम्ब ''Sālamba'' meaning "supported", शीर्ष, ''Śīrṣa'' meaning "head", and आसन, ''Āsana'' meaning "posture" or "seat". The name ''Śīrṣāsana'' is relatively recent; the pose itself is much older, but had other names and purposes. Like other inversions, it was practised as Viparita Karani, described as a mudra in the 15th century ''Hatha Yoga Pradipika'' and other classical texts on haṭha yoga. Viparita Karani, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asana
An asana is a body posture, originally and still a general term for a sitting meditation pose,Verse 46, chapter II, "Patanjali Yoga sutras" by Swami Prabhavananda, published by the Sri Ramakrishna Math p. 111 and later extended in hatha yoga and modern yoga as exercise, to any type of position, adding reclining, standing, inverted, twisting, and balancing poses. The ''Yoga Sutras of Patanjali'' define "asana" as " position thatis steady and comfortable". Patanjali mentions the ability to sit for extended periods as one of the eight limbs of his system. Patanjali ''Yoga sutras'', Book II:29, 46 Asanas are also called yoga poses or yoga postures in English. The 10th or 11th century '' Goraksha Sataka'' and the 15th century '' Hatha Yoga Pradipika'' identify 84 asanas; the 17th century ''Hatha Ratnavali'' provides a different list of 84 asanas, describing some of them. In the 20th century, Indian nationalism favoured physical culture in response to colonialism. In that enviro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lotus Position
Lotus position or Padmasana ( sa, पद्मासन, translit=padmāsana) is a cross-legged sitting meditation pose from ancient India, in which each foot is placed on the opposite thigh. It is an ancient asana in yoga, predating hatha yoga, and is widely used for meditation in Hindu, Tantra, Jain, and Buddhist traditions. Variations include easy pose (Sukhasana), half lotus, bound lotus, and psychic union pose. Advanced variations of several other asanas including yoga headstand have the legs in lotus or half lotus. The pose can be uncomfortable for people not used to sitting on the floor, and attempts to force the legs into position can injure the knees. Shiva, the meditating ascetic God of Hinduism, Gautama Buddha, the founder of Buddhism, and the Tirthankaras in Jainism have been depicted in the lotus position, especially in statues. The pose is emblematic both of Buddhist meditation and of yoga, and as such has found a place in Western culture as a symbol of health ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Raja Sarvangasana
''Raja'' (; from , IAST ') is a royal title used for South Asian monarchs. The title is equivalent to king or princely ruler in South Asia and Southeast Asia. The title has a long history in South Asia and Southeast Asia, being attested from the Rigveda, where a ' is a ruler, see for example the ', the "Battle of Ten Kings". Raja-ruled Indian states While most of the Indian salute states (those granted a gun salute by the British Crown) were ruled by a Maharaja (or variation; some promoted from an earlier Raja- or equivalent style), even exclusively from 13 guns up, a number had Rajas: ; Hereditary salutes of 11-guns : * the Raja of Pindrawal * the Raja of Morni * the Raja of Rajouri * the Raja of Ali Rajpur * the Raja of Bilaspur * the Raja of Chamba * the Raja of Faridkot * the Raja of Jhabua * the Raja of Mandi * the Raja of Manipur * the Raja of Narsinghgarh * the Raja of Pudukkottai * the Raja of Rajgarh * the Raja of Sangli * the Raja of Sailana * the R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |








.jpg)

