|
Cross-coupling Reaction
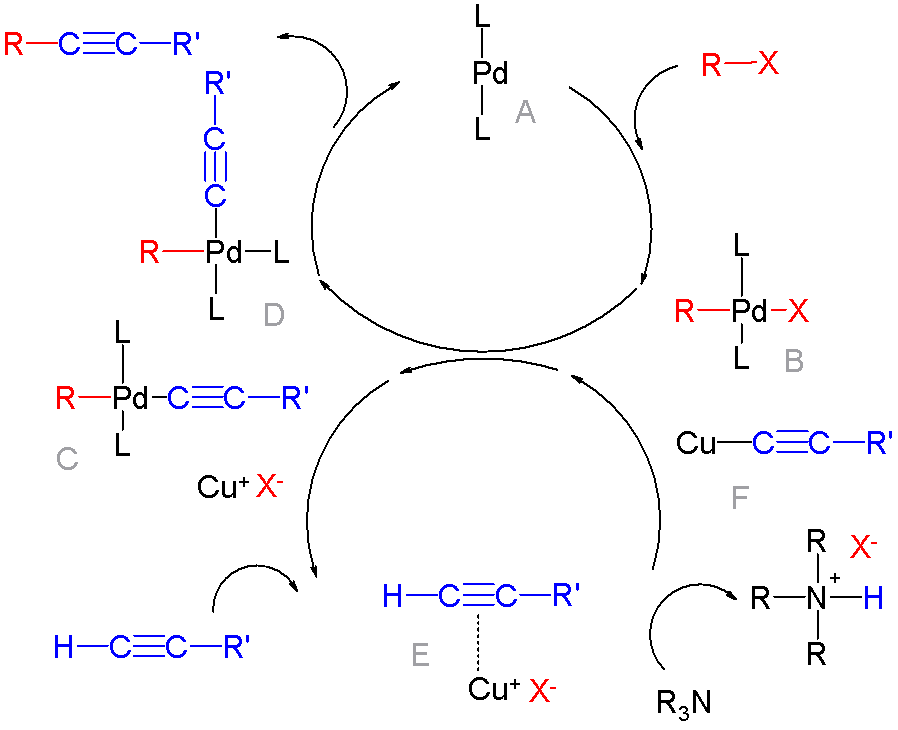
In organic chemistry, a cross-coupling reaction is a reaction where two fragments are joined together with the aid of a metal catalyst. In one important reaction type, a main group organometallic compound of the type R-M (R = organic fragment, M = main group center) reacts with an organic halide of the type R'-X with formation of a new carbon–carbon bond in the product R-R'. Cross-coupling reaction are a subset of coupling reactions. It is often used in arylations. Richard F. Heck, Ei-ichi Negishi, and Akira Suzuki were awarded the 2010 Nobel Prize in Chemistry for developing palladium-catalyzed coupling reactions. Mechanism The mechanism generally involves reductive elimination of the organic substituents R and R' on a metal complex of the type LnMR(R') (where L is some arbitrary spectator ligand). The crucial intermediate LnMR(R') is formed in a two step process from a low valence precursor Ln. The oxidative addition of an organic halide (RX) to LnM gives LnMR(X). Su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organic Chemistry
Organic chemistry is a subdiscipline within chemistry involving the science, scientific study of the structure, properties, and reactions of organic compounds and organic materials, i.e., matter in its various forms that contain carbon atoms.Clayden, J.; Greeves, N. and Warren, S. (2012) ''Organic Chemistry''. Oxford University Press. pp. 1–15. . Study of structure determines their structural formula. Study of properties includes Physical property, physical and Chemical property, chemical properties, and evaluation of Reactivity (chemistry), chemical reactivity to understand their behavior. The study of organic reactions includes the organic synthesis, chemical synthesis of natural products, drugs, and polymers, and study of individual organic molecules in the laboratory and via theoretical (in silico) study. The range of chemicals studied in organic chemistry includes hydrocarbons (compounds containing only carbon and hydrogen) as well as compounds based on carbon, but also con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transmetallation
Transmetalation (alt. spelling: transmetallation) is a type of organometallic reaction that involves the transfer of ligands from one metal to another. It has the general form: :M1–R + M2–R′ → M1–R′ + M2–R where R and R′ can be, but are not limited to, an alkyl, aryl, alkynyl, allyl, halogen, or pseudohalogen group. The reaction is usually an irreversible process due to thermodynamic and kinetic reasons. Thermodynamics will favor the reaction based on the electronegativities of the metals and kinetics will favor the reaction if there are empty orbitals on both metals. There are different types of transmetalation including redox-transmetalation and redox-transmetalation/ligand exchange. During transmetalation the metal-carbon bond is activated, leading to the formation of new metal-carbon bonds. Transmetalation is commonly used in catalysis, synthesis of main group complexes, and synthesis of transition metal complexes. Types of transmetalation There are two main ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boron
Boron is a chemical element with the symbol B and atomic number 5. In its crystalline form it is a brittle, dark, lustrous metalloid; in its amorphous form it is a brown powder. As the lightest element of the '' boron group'' it has three valence electrons for forming covalent bonds, resulting in many compounds such as boric acid, the mineral sodium borate, and the ultra-hard crystals of boron carbide and boron nitride. Boron is synthesized entirely by cosmic ray spallation and supernovae and not by stellar nucleosynthesis, so it is a low-abundance element in the Solar System and in the Earth's crust. It constitutes about 0.001 percent by weight of Earth's crust. It is concentrated on Earth by the water-solubility of its more common naturally occurring compounds, the borate minerals. These are mined industrially as evaporites, such as borax and kernite. The largest known deposits are in Turkey, the largest producer of boron minerals. Elemental boron is a meta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zinc
Zinc is a chemical element with the symbol Zn and atomic number 30. Zinc is a slightly brittle metal at room temperature and has a shiny-greyish appearance when oxidation is removed. It is the first element in group 12 (IIB) of the periodic table. In some respects, zinc is chemically similar to magnesium: both elements exhibit only one normal oxidation state (+2), and the Zn2+ and Mg2+ ions are of similar size.The elements are from different metal groups. See periodic table. Zinc is the 24th most abundant element in Earth's crust and has five stable isotopes. The most common zinc ore is sphalerite (zinc blende), a zinc sulfide mineral. The largest workable lodes are in Australia, Asia, and the United States. Zinc is refined by froth flotation of the ore, roasting, and final extraction using electricity ( electrowinning). Zinc is an essential trace element for humans, animals, plants and for microorganisms and is necessary for prenatal and postnatal development. It ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iodide
An iodide ion is the ion I−. Compounds with iodine in formal oxidation state −1 are called iodides. In everyday life, iodide is most commonly encountered as a component of iodized salt, which many governments mandate. Worldwide, iodine deficiency affects two billion people and is the leading preventable cause of intellectual disability. Structure and characteristics of inorganic iodides Iodide is one of the largest monatomic anions. It is assigned a radius of around 206 picometers. For comparison, the lighter halides are considerably smaller: bromide (196 pm), chloride (181 pm), and fluoride (133 pm). In part because of its size, iodide forms relatively weak bonds with most elements. Most iodide salts are soluble in water, but often less so than the related chlorides and bromides. Iodide, being large, is less hydrophilic compared to the smaller anions. One consequence of this is that sodium iodide is highly soluble in acetone, whereas sodium chloride is not ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bromide
A bromide ion is the negatively charged form (Br−) of the element bromine, a member of the halogens group on the periodic table. Most bromides are colorless. Bromides have many practical roles, being found in anticonvulsants, flame-retardant materials, and cell stains. Although uncommon, chronic toxicity from bromide can result in bromism, a syndrome with multiple neurological symptoms. Bromide toxicity can also cause a type of skin eruption, see potassium bromide. The bromide ion has an ionic radius of 196 pm. Natural occurrence Bromide is present in typical seawater (35 PSU) with a concentration of around 65 mg/L, which is about 0.2% of all dissolved salts. Seafood and deep sea plants generally have higher levels than land-derived foods. Bromargyrite—natural, crystalline silver bromide—is the most common bromide mineral known but is still very rare. In addition to silver, bromine is also in minerals combined with mercury and copper. Formation and rea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pseudohalide
Pseudohalogens are polyatomic analogues of halogens, whose chemistry, resembling that of the true halogens, allows them to substitute for halogens in several classes of chemical compounds. Pseudohalogens occur in pseudohalogen molecules, inorganic molecules of the general forms ''Ps''–''Ps'' or ''Ps''–X (where ''Ps'' is a pseudohalogen group), such as cyanogen; pseudohalide anions, such as cyanide ion; inorganic acids, such as hydrogen cyanide; as ligands in coordination complexes, such as ferouscyanide; and as functional groups in organic molecules, such as the nitrile group. Well-known pseudohalogen functional groups include cyanide, cyanate, thiocyanate, and azide. Common pseudohalogens and their nomenclature Many pseudohalogens are known by specialized common names according to where they occur in a compound. Well-known ones include (the true halogen chlorine is listed for comparison): Au− is considered to be a pseudohalogen ion due to its disproportionation reactio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tosylate
In organic chemistry, a toluenesulfonyl group (tosyl group, abbreviated Ts or Tos) is a univalent functional group with the chemical formula –. It consists of a tolyl group, –, joined to a sulfonyl group, ––, with the open valence on sulfur. This group is usually derived from the compound tosyl chloride, (abbreviated TsCl), which forms esters and amides of toluenesulfonic acid, (abbreviated TsOH). The para orientation illustrated (''p''-toluenesulfonyl) is most common, and by convention ''tosyl'' without a prefix refers to the ''p''-toluenesulfonyl group. The toluenesulfonate (or tosylate) group refers to the – (TsO–) group, with an additional oxygen attached to sulfur and open valence on an oxygen. In a chemical name, the term ''tosylate'' may either refer to the salts containing the anion of ''p''-toluenesulfonic acid, (M = alkali metal, , , etc), or it may refer to esters of ''p''-toluenesulfonic acid, TsOR (R = organyl group). Applications For SN2 re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triflate
In organic chemistry, triflate ( systematic name: trifluoromethanesulfonate), is a functional group with the formula and structure . The triflate group is often represented by , as opposed to −Tf, which is the triflyl group, . For example, ''n''-butyl triflate can be written as . The corresponding triflate anion, , is an extremely stable polyatomic ion; this comes from the fact that triflic acid () is a superacid; i.e. it is more acidic than pure sulfuric acid, already one of the strongest acids known. Applications A triflate group is an excellent leaving group used in certain organic reactions such as nucleophilic substitution, Suzuki couplings and Heck reactions. Since alkyl triflates are extremely reactive in SN2 reactions, they must be stored in conditions free of nucleophiles (such as water). The anion owes its stability to resonance stabilization which causes the negative charge to be spread symmetrically over the three oxygen atoms. An additional stabili ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
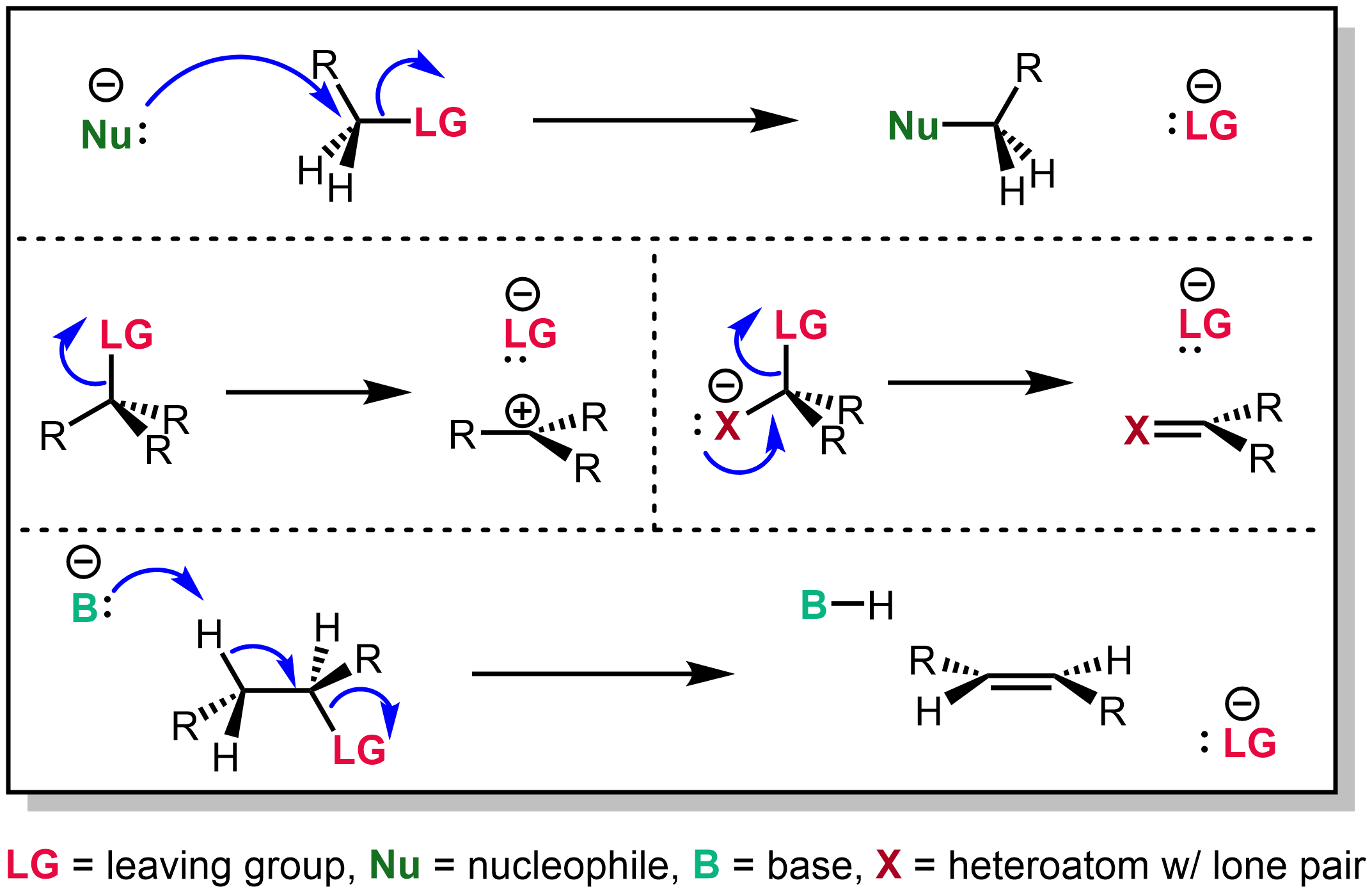
Leaving Group
In chemistry, a leaving group is defined by the IUPAC as an atom or group of atoms that detaches from the main or residual part of a substrate during a reaction or elementary step of a reaction. However, in common usage, the term is often limited to a fragment that departs with a pair of electrons in heterolytic bond cleavage. In this usage, a leaving group is a less formal but more commonly used synonym of the term ''nucleofuge''. In this context, leaving groups are generally anions or neutral species, departing from a neutral or cationic substrates, respectively, though in rare cases, cations leaving from a dicationic substrate are also known. A species' ability to serve as a leaving group depends on its ability to stabilize the additional electron density that results from bond heterolysis. Common anionic leaving groups are halides such as Cl−, Br−, and I−, and sulfonate esters such as tosylate (TsO−), while water (H2O), alcohols (HOR), and amines (R3N) are common neu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heterogeneous Catalyst
In chemistry, heterogeneous catalysis is catalysis where the phase of catalysts differs from that of the reactants or products. The process contrasts with homogeneous catalysis where the reactants, products and catalyst exist in the same phase. Phase distinguishes between not only solid, liquid, and gas components, but also immiscible mixtures (e.g. oil and water), or anywhere an interface is present. Heterogeneous catalysis typically involves solid phase catalysts and gas phase reactants. In this case, there is a cycle of molecular adsorption, reaction, and desorption occurring at the catalyst surface. Thermodynamics, mass transfer, and heat transfer influence the rate (kinetics) of reaction. Heterogeneous catalysis is very important because it enables faster, large-scale production and the selective product formation. Approximately 35% of the world's GDP is influenced by catalysis. The production of 90% of chemicals (by volume) is assisted by solid catalysts. The chemical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organopalladium
Organopalladium chemistry is a branch of organometallic chemistry that deals with organic palladium compounds and their reactions. Palladium is often used as a catalyst in the reduction of alkenes and alkynes with hydrogen. This process involves the formation of a palladium-carbon covalent bond. Palladium is also prominent in carbon-carbon coupling reactions, as demonstrated in tandem reactions. Organopalladium chemistry timeline * 1873 - A. N. Zaitsev reports reduction of benzophenone over palladium with hydrogen. * 1894 - Phillips reports that palladium(II) chloride reduces to palladium metal by contact with ethylene. * 1907 - Autoclave technology introduced by Vladimir Ipatieff makes it possible to carry out high pressure hydrogenation. * 1956 - In the Wacker process ethylene and oxygen react to acetaldehyde with catalyst PdCl2/CuCl2 * 1957 - Tetrakis(triphenylphosphine)palladium(0) is reported by Malatesta and Angoletta. * 1972 - The Heck reaction is a coupling ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |






sample.jpg)