|
Cingulate
Cingulata, part of the superorder Xenarthra, is an order of armored New World placental mammals. Dasypodids and chlamyphorids, the armadillos, are the only surviving families in the order. Two groups of cingulates much larger than extant armadillos (maximum body mass of 45 kg (100 lb) in the case of the giant armadillo) existed until recently: pampatheriids, which reached weights of up to 200 kg (440 lb) and chlamyphorid glyptodonts, which attained masses of 2,000 kg (4,400 lb) or more. The cingulate order originated in South America during the Paleocene epoch about 66 to 56 million years ago, and due to the continent's former isolation remained confined to it during most of the Cenozoic. However, the formation of a land bridge allowed members of all three families to migrate to southern North America during the Pliocene or early Pleistocene as part of the Great American Interchange. After surviving for tens of millions of years, all of the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Armadillo
Armadillos (meaning "little armored ones" in Spanish) are New World placental mammals in the order Cingulata. The Chlamyphoridae and Dasypodidae are the only surviving families in the order, which is part of the superorder Xenarthra, along with the anteaters and sloths. Nine extinct genera and 21 extant species of armadillo have been described, some of which are distinguished by the number of bands on their armor. All species are native to the Americas, where they inhabit a variety of different environments. Armadillos are characterized by a leathery armor shell and long, sharp claws for digging. They have short legs, but can move quite quickly. The average length of an armadillo is about , including its tail. The giant armadillo grows up to and weighs up to , while the pink fairy armadillo has a length of only . When threatened by a predator, ''Tolypeutes'' species frequently roll up into a ball; they are the only species of armadillo capable of this. Etymology The wor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chlamyphoridae
Chlamyphoridae is a family of cingulate mammals. While glyptodonts have traditionally been considered stem-group cingulates outside the group that contains modern armadillos, there had been speculation that the extant family Dasypodidae could be paraphyletic based on morphological evidence. In 2016, an analysis of ''Doedicurus'' mtDNA found it was, in fact, nested within the modern armadillos as the sister group of a clade consisting of Chlamyphorinae and Tolypeutinae. For this reason, all extant armadillos but '' Dasypus'' were relocated to a new family. __TOC__ Classification Below is a taxonomy of the extant species of armadillos in this family. Family Chlamyphoridae * Subfamily Chlamyphorinae ** Genus '' Calyptophractus'' *** Greater fairy armadillo, ''Calyptophractus retusus'' ** Genus '' Chlamyphorus'' *** Pink fairy armadillo, ''Chlamyphorus truncatus'' * Subfamily Euphractinae ** Genus ''Euphractus'' ***Six-banded armadillo, ''Euphractus sexcinctus'' ** Genus ''Zaed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
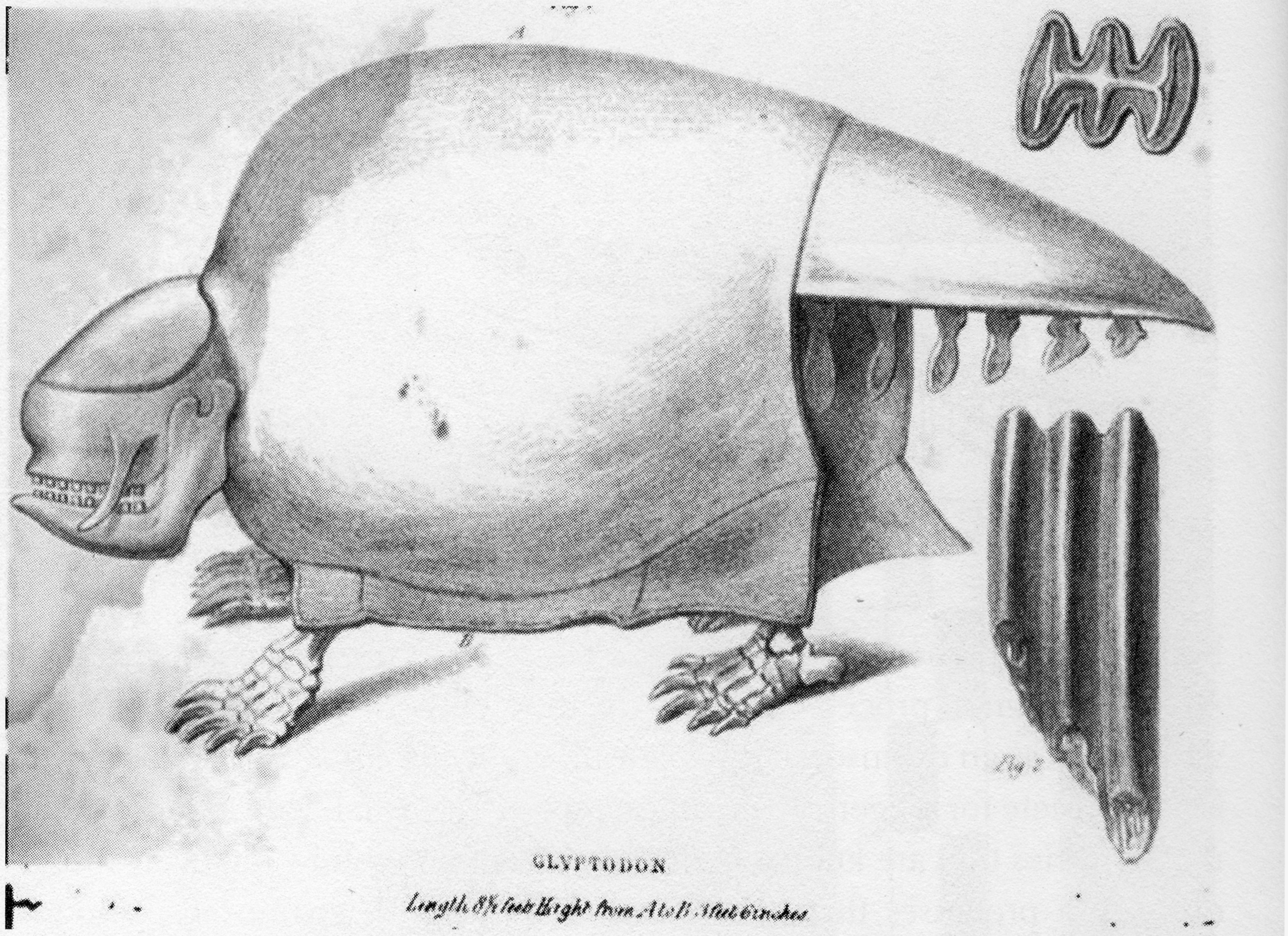
Glyptodon
''Glyptodon'' (from Greek for 'grooved or carved tooth': γλυπτός 'sculptured' and ὀδοντ-, ὀδούς 'tooth') is a genus of glyptodont (an extinct group of large, herbivorous armadillos) that lived from the Pleistocene, around 2.5 million years ago, to the Early Holocene, around 11,000 years ago, in Argentina, Uruguay, Paraguay, Bolivia, Peru, Brazil, and Colombia. It was the first named extinct cingulate and is the type genus of Glyptodontinae, and, or, Glyptodontinae. Many species have been named for the genus, though few are considered valid, and it is one of, if not the, best known genus of glyptodont. Hundreds of specimens have been referred to the genus, but the holotype, or name specimen, of the type species, ''G. clavipes'', was described in 1839 by notable British paleontologist Sir Richard Owen. It was roughly the same size and weight as a Volkswagen Beetle, 800–840 kg (1,760–1,850 lb). With its rounded, bony shell and squat limbs, it superfic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xenarthra
Xenarthra (; from Ancient Greek ξένος, xénos, "foreign, alien" + ἄρθρον, árthron, "joint") is a major clade of placental mammals native to the Americas. There are 31 living species: the anteaters, tree sloths, and armadillos. Extinct xenarthrans include the glyptodonts, pampatheres and ground sloths. Xenarthrans originated in South America during the late Paleocene about 60 million years ago. They evolved and diversified extensively in South America during the continent's long period of isolation in the early to mid Cenozoic Era. They spread to the Antilles by the early Miocene and, starting about 3 Mya, spread to Central and North America as part of the Great American Interchange. Nearly all of the formerly abundant megafaunal xenarthrans became extinct at the end of the Pleistocene. Xenarthrans share several characteristics not present in other placental mammals, which suggest their ancestors were subterranean diggers for insects. The name Xenarthra de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glyptodont
Glyptodonts are an extinct subfamily of large, heavily armoured armadillos. They arose in South America around 48 million years ago and spread to southern North America after the continents became connected several million years ago. The best-known genus within the group is ''Glyptodon''. While they were formerly considered to constitute the distinct family Glyptodontidae, in 2016, an analysis of ''Doedicurus'' Mitochondrial DNA (also known as mtDNA / mDNA) found that it was, in fact, nested within the modern armadillos as the sister group of a clade consisting of Chlamyphorinae and Tolypeutinae. For this reason, glyptodonts and all armadillos but '' Dasypus'' were relocated to a new family, Chlamyphoridae, and glyptodonts were demoted from the former family Glyptodontidae to a subfamily. Evolution Glyptodonts first evolved during the Eocene in South America, which remained their center of species diversity. For example, an Early Miocene glyptodont with many primitive feature ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pampatheriidae
Pampatheriidae ("Pampas beasts") is an extinct family of large plantigrade armored armadillos related to extant armadillos in the order Cingulata. However, pampatheriids have existed as a separate lineage since at least the middle Eocene Mustersan age, . Pampatheres evolved in South America during its long period of Cenozoic isolation. Although widespread, they were less diverse and abundant than the armadillos. ''Holmesina'' spread to North America after the formation of the Isthmus of Panama as part of the Great American Interchange. They finally disappeared on both continents in the end-Pleistocene extinctions, about 12,000 years ago. Description Pampatheres are believed to have attained a weight of up to . Like three-banded armadillos, and unlike glyptodonts, their armored shell was given some flexibility by three movable lateral bands of scutes. The osteoderms (bony plates in the skin comprising the armor) of pampatheres were each covered by a single keratinized scute, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Megafauna
In terrestrial zoology, the megafauna (from Greek μέγας ''megas'' "large" and New Latin ''fauna'' "animal life") comprises the large or giant animals of an area, habitat, or geological period, extinct and/or extant. The most common thresholds used are weight over see page 17 (i.e., having a mass comparable to or larger than a human) or over a tonne, (i.e., having a mass comparable to or larger than an ox). The first of these include many species not popularly thought of as overly large, and being the only few large animals left in a given range/area, such as white-tailed deer, Thomson's gazelle, and red kangaroo. In practice, the most common usage encountered in academic and popular writing describes land mammals roughly larger than a human that are not (solely) domesticated. The term is especially associated with the Pleistocene megafauna – the land animals often larger than their extant counterparts that are considered archetypical of the last ice age, such as mammoth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dasypodidae
Dasypodidae is a family of mostly extinct genera of armadillos. One genus, '' Dasypus'', is extant, with at least seven living species. __TOC__ Classification Below is a taxonomy of armadillos in this family. Family Dasypodidae *† Genus '' Acantharodeia'' *† Genus '' Amblytatus'' *† Genus '' Archaeutatus'' *† Genus ''Astegotherium'' *† Genus '' Barrancatatus'' *† Genus '' Chasicotatus'' *† Genus ''Chorobates'' *† Genus '' Coelutaetus'' *† Genus '' Eocoleophorus'' *† Genus '' Epipeltecoelus'' *† Genus ''Eutatus'' *† Genus '' Hemiutaetus'' *† Genus '' Isutaetus'' *† Genus '' Lumbreratherium'' *† Genus '' Macrochorobates'' *† Genus '' Mazzoniphractus'' *† Genus '' Meteutatus'' *† Genus '' Pedrolypeutes'' *† Genus '' Prodasypus'' *† Genus ''Proeutatus'' *† Genus '' Prostegotherium'' *† Genus '' Pucatherium'' *† Genus '' Punatherium'' *† Genus ''Stegotherium'' *† Genus '' Stenotatus'' *† Genus ''Utaetus'' * Subfamily Dasypodina ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quaternary Extinction Event
The Quaternary period (from 2.588 ± 0.005 million years ago to the present) has seen the extinctions of numerous predominantly megafaunal species, which have resulted in a collapse in faunal density and diversity and the extinction of key ecological strata across the globe. The most prominent event in the Late Pleistocene is differentiated from previous Quaternary pulse extinctions by the widespread absence of ecological succession to replace these extinct species, and the regime shift of previously established faunal relationships and habitats as a consequence. The earliest casualties were incurred at 130,000 BCE (the start of the Late Pleistocene), in Australia ~ 60,000 years ago, in Americas ~ 15,000 years ago, coinciding in time with the early human migrations. However, the great majority of extinctions in Afro-Eurasia and the Americas occurred during the transition from the Pleistocene to the Holocene epoch (13,000 BCE to 8,000 BCE). This extinction wave di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great American Interchange
The Great American Biotic Interchange (commonly abbreviated as GABI), also known as the Great American Interchange and the Great American Faunal Interchange, was an important late Cenozoic paleozoogeographic biotic interchange event in which land and freshwater fauna migrated from North America via Central America to South America and vice versa, as the volcanic Isthmus of Panama rose up from the sea floor and bridged the formerly separated continents. Although earlier dispersals had occurred, probably over water, the migration accelerated dramatically about 2.7 million years ( Ma) ago during the Piacenzian age. It resulted in the joining of the Neotropic (roughly South American) and Nearctic (roughly North American) biogeographic realms definitively to form the Americas. The interchange is visible from observation of both biostratigraphy and nature (neontology). Its most dramatic effect is on the zoogeography of mammals, but it also gave an opportunity for reptiles, amphibia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Holocene
The Holocene ( ) is the current geological epoch. It began approximately 11,650 cal years Before Present (), after the Last Glacial Period, which concluded with the Holocene glacial retreat. The Holocene and the preceding Pleistocene together form the Quaternary period. The Holocene has been identified with the current warm period, known as MIS 1. It is considered by some to be an interglacial period within the Pleistocene Epoch, called the Flandrian interglacial.Oxford University Press – Why Geography Matters: More Than Ever (book) – "Holocene Humanity" section https://books.google.com/books?id=7P0_sWIcBNsC The Holocene corresponds with the rapid proliferation, growth and impacts of the human species worldwide, including all of its written history, technological revolutions, development of major civilizations, and overall significant transition towards urban living in the present. The human impact on modern-era Earth and its ecosystems may be considered of global si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Springer Science+Business Media
Springer Science+Business Media, commonly known as Springer, is a German multinational publishing company of books, e-books and peer-reviewed journals in science, humanities, technical and medical (STM) publishing. Originally founded in 1842 in Berlin, it expanded internationally in the 1960s, and through mergers in the 1990s and a sale to venture capitalists it fused with Wolters Kluwer and eventually became part of Springer Nature in 2015. Springer has major offices in Berlin, Heidelberg, Dordrecht, and New York City. History Julius Springer founded Springer-Verlag in Berlin in 1842 and his son Ferdinand Springer grew it from a small firm of 4 employees into Germany's then second largest academic publisher with 65 staff in 1872.Chronology ". Springer Science+Business Media. In 1964, Springer expanded its business internationally, o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

_(cropped).jpg)




