|
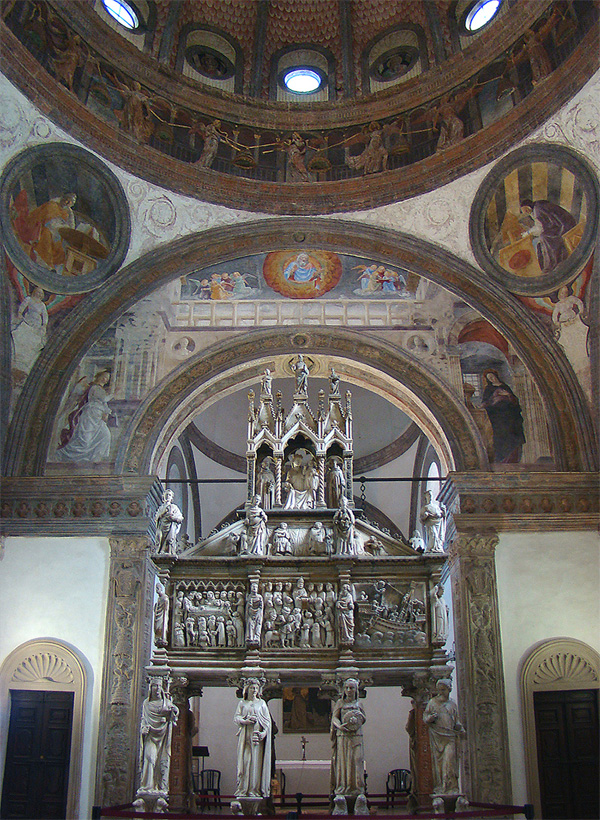
Church Of Sant'Eustorgio
The Basilica of Sant'Eustorgio is a church in Milan in northern Italy, which is in the Basilicas Park city park. It was for many years an important stop for pilgrims on their journey to Rome or to the Holy Land, because it was said to contain the tomb of the Three Magi or ''Three Kings''. Probably founded in the 4th century, its name refers to Eustorgius I, the bishop of Milan to whom is attributed the translation of the supposed relics of the Magi to the city from Constantinople in 344. In 1764, when an ancient pillar was removed, a Christian burial was discovered, housing coins of emperor Constans, the son of Constantine the Great. The church was later rebuilt in Romanesque style. In the 12th century, when Milan was sacked by Frederick Barbarossa, the relics of the Magi were appropriated and subsequently taken to Cologne. It was only in 1903/4 that fragments of the bones and garments were sent back to Sant'Eustorgio's. Nowadays they are in the Three Kings altar nearby the em ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Milan
Milan ( , , Lombard: ; it, Milano ) is a city in northern Italy, capital of Lombardy, and the second-most populous city proper in Italy after Rome. The city proper has a population of about 1.4 million, while its metropolitan city has 3.26 million inhabitants. Its continuously built-up urban area (whose outer suburbs extend well beyond the boundaries of the administrative metropolitan city and even stretch into the nearby country of Switzerland) is the fourth largest in the EU with 5.27 million inhabitants. According to national sources, the population within the wider Milan metropolitan area (also known as Greater Milan), is estimated between 8.2 million and 12.5 million making it by far the largest metropolitan area in Italy and one of the largest in the EU.* * * * Milan is considered a leading alpha global city, with strengths in the fields of art, chemicals, commerce, design, education, entertainment, fashion, finance, healthcar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
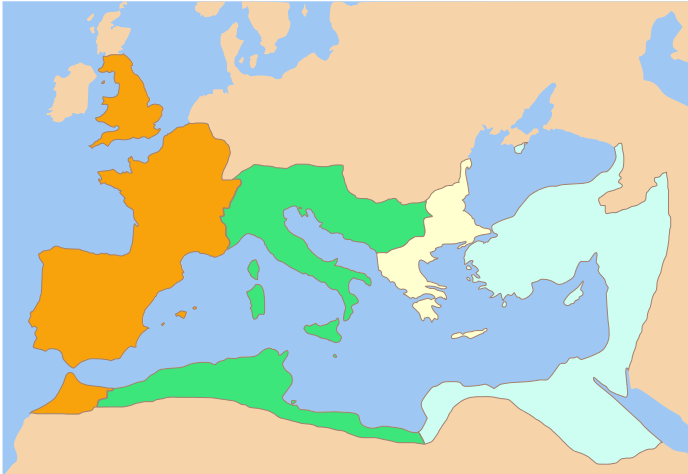
Constans
Flavius Julius Constans ( 323 – 350), sometimes called Constans I, was Roman emperor from 337 to 350. He held the imperial rank of ''caesar'' from 333, and was the youngest son of Constantine the Great. After his father's death, he was made ''augustus'' alongside his brothers in September 337. Constans was given the administration of the praetorian prefectures of Italy, Illyricum, and Africa. He defeated the Sarmatians in a campaign shortly afterwards. Quarrels over the sharing of power led to a civil war with his eldest brother and co-emperor Constantine II, who invaded Italy in 340 and was killed in battle with Constans's forces near Aquileia. Constans gained from him the praetorian prefecture of Gaul. Thereafter there were tensions with his remaining brother and co-''augustus'' Constantius II (), including over the exiled bishop Athanasius of Alexandria. In the following years he campaigned against the Franks, and in 343 he visited Roman Britain, the last legitimate emp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Visconti Of Milan
The Visconti of Milan are a noble Italian family. They rose to power in Milan during the Middle Ages where they ruled from 1277 to 1447, initially as Lords then as Dukes, and several collateral branches still exist. The effective founder of the Visconti Lordship of Milan was the Archbishop Ottone, who wrested control of the city from the rival Della Torre family in 1277. Origins The earliest members of the Visconti lineage appeared in Milan in the second half of the 11th century. The first evidence is on October 5, 1075, when Ariprando Visconti and his son Ottone ("Ariprandus Vicecomes", "Otto Vicecomes filius Ariprandi") attended and signed together some legal documents in Milan. Ariprando Visconti's family is believed to have pre-existed in Milan and obtained the title of viscount, which became hereditary throughout the male descent. In the years following 1075, Ottone Visconti is shown in the proximity of the Salian dynasty's sovereigns, Henry IV and his son Conrad. His d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Giotto
Giotto di Bondone (; – January 8, 1337), known mononymously as Giotto ( , ) and Latinised as Giottus, was an Italian painter and architect from Florence during the Late Middle Ages. He worked during the Gothic/Proto-Renaissance period. Giotto's contemporary, the banker and chronicler Giovanni Villani, wrote that Giotto was "the most sovereign master of painting in his time, who drew all his figures and their postures according to nature" and of his publicly recognized "talent and excellence".Bartlett, Kenneth R. (1992). ''The Civilization of the Italian Renaissance''. Toronto: D.C. Heath and Company. (Paperback). p. 37. Giorgio Vasari described Giotto as making a decisive break with the prevalent Byzantine style and as initiating "the great art of painting as we know it today, introducing the technique of drawing accurately from life, which had been neglected for more than two hundred years".Giorgio Vasari, ''Lives of the Artists'', trans. George Bull, Penguin Classics, (196 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ambrogio Bergognone
Ambrogio Borgognone (variously known as ''Ambrogio da Fossano'', ''Ambrogio di Stefano da Fossano'', ''Ambrogio Stefani da Fossano'' or as ''il Bergognone'' or ''Ambrogio Egogni'' By Gottardo Garollo, 1907, page 727. s1523/1524) was an Italian painter of the period active in and near . Biography While he was nearly contemporary with , he painted in a style more akin to the pre-Renaissance, Lomb ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triptych
A triptych ( ; from the Greek language, Greek adjective ''τρίπτυχον'' "''triptukhon''" ("three-fold"), from ''tri'', i.e., "three" and ''ptysso'', i.e., "to fold" or ''ptyx'', i.e., "fold") is a work of art (usually a panel painting) that is divided into three sections, or three Wood carving, carved panels that are hinged together and can be folded shut or displayed open. It is therefore a type of polyptych, the term for all multi-panel works. The middle panel is typically the largest and it is flanked by two smaller related works, although there are triptychs of equal-sized panels. The form can also be used for pendant jewelry. Beyond its association with art, the term is sometimes used more generally to connote anything with three parts, particularly if integrated into a single unit. In art The triptych form appears in early Christian art, and was a popular standard format for altar paintings from the Middle Ages onwards. Its geographical range was from the easter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
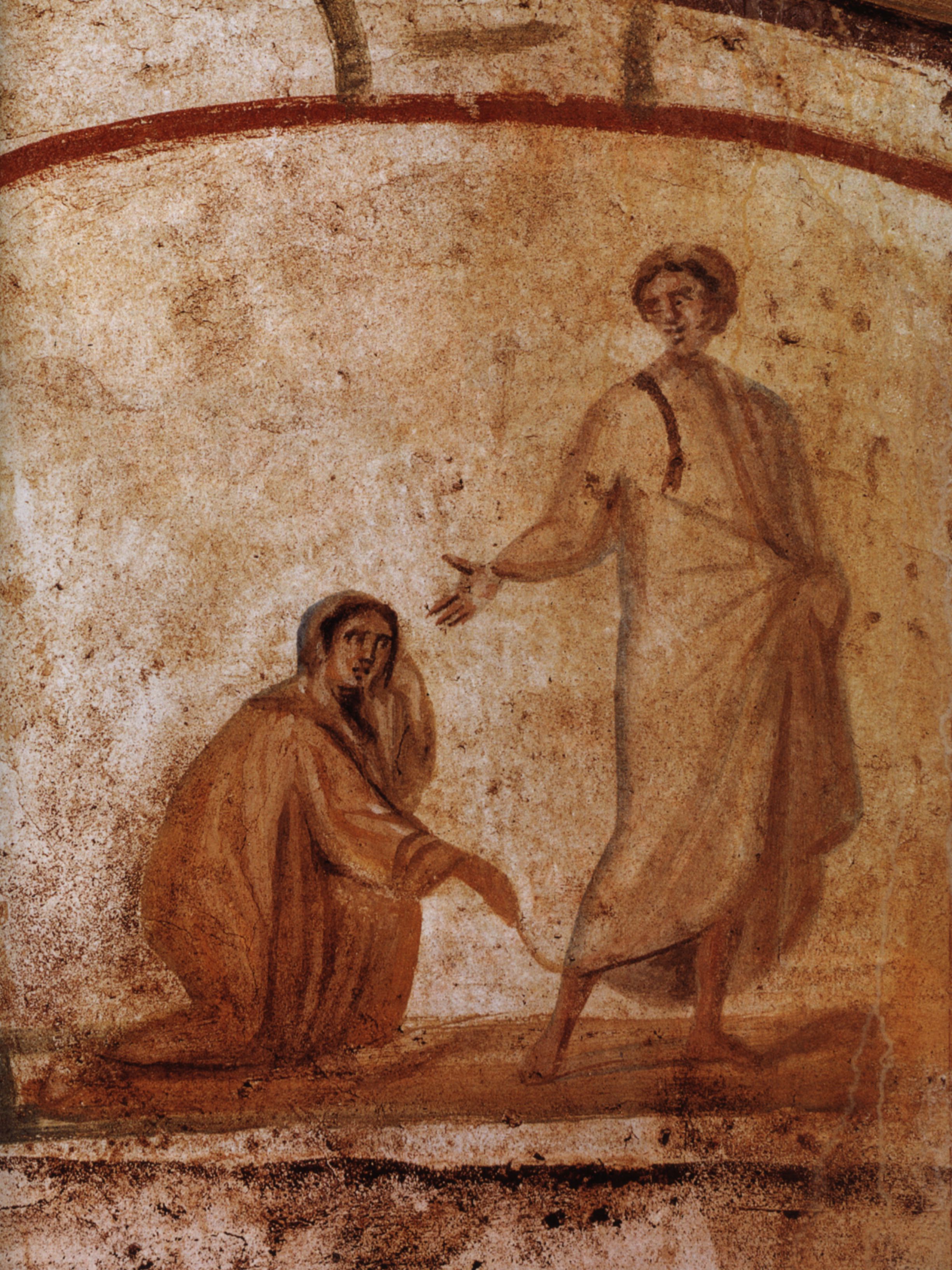
Early Christian Architecture
Early Christian art and architecture or Paleochristian art is the art produced by Christians or under Christian patronage from the earliest period of Christianity to, depending on the definition used, sometime between 260 and 525. In practice, identifiably Christian art only survives from the 2nd century onwards. After 550 at the latest, Christian art is classified as Byzantine, or of some other regional type. It is hard to know when distinctly Christian art began. Prior to 100, Christians may have been constrained by their position as a persecuted group from producing durable works of art. Since Christianity was largely a religion not well represented in the public sphere, the lack of surviving art may reflect a lack of funds for patronage, and simply small numbers of followers. The Old Testament restrictions against the production of graven (an idol or fetish carved in wood or stone) images (see also Idolatry and Christianity) may also have constrained Christians from producing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Groin Vault
A groin vault or groined vault (also sometimes known as a double barrel vault or cross vault) is produced by the intersection at right angles of two barrel vaults. Honour, H. and J. Fleming, (2009) ''A World History of Art''. 7th edn. London: Laurence King Publishing, p. 949. The word "groin" refers to the edge between the intersecting vaults. Sometimes the arches of groin vaults are pointed instead of round. In comparison with a barrel vault, a groin vault provides good economies of material and labor. The thrust is concentrated along the groins or arrises (the four diagonal edges formed along the points where the barrel vaults intersect), so the vault need only be abutted at its four corners. Groin vault construction was first exploited by the Romans, but then fell into relative obscurity in Europe until the resurgence of quality stone building brought about by Carolingian and Romanesque architecture. It was superseded by the more flexible rib vaults of Gothic architectur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
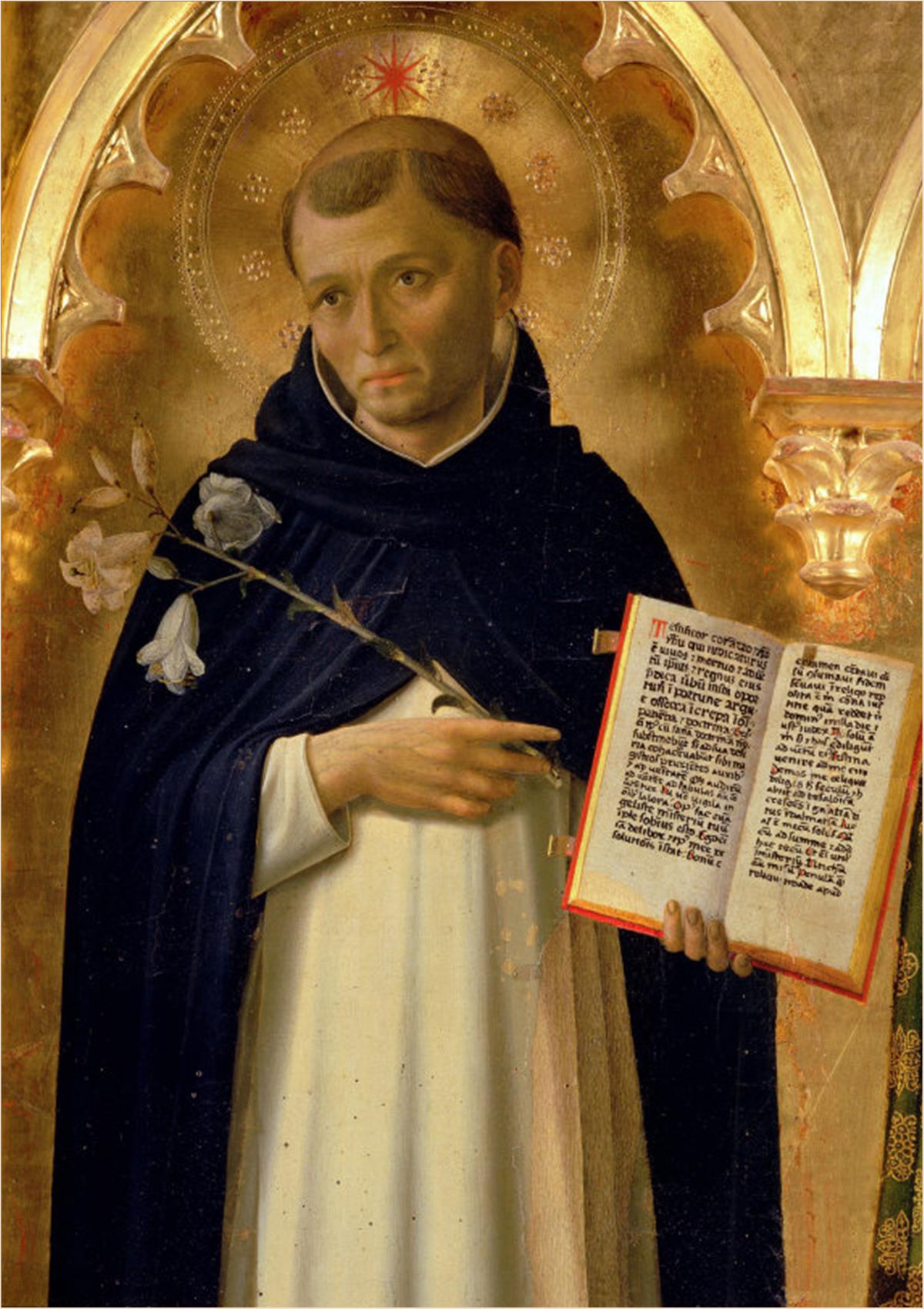
Dominican Order
The Order of Preachers ( la, Ordo Praedicatorum) abbreviated OP, also known as the Dominicans, is a Catholic mendicant order of Pontifical Right for men founded in Toulouse, France, by the Spanish priest, saint and mystic Dominic of Caleruega. It was approved by Pope Honorius III via the papal bull ''Religiosam vitam'' on 22 December 1216. Members of the order, who are referred to as ''Dominicans'', generally carry the letters ''OP'' after their names, standing for ''Ordinis Praedicatorum'', meaning ''of the Order of Preachers''. Membership in the order includes friars, nuns, active sisters, and lay or secular Dominicans (formerly known as tertiaries). More recently there has been a growing number of associates of the religious sisters who are unrelated to the tertiaries. Founded to preach the Gospel and to oppose heresy, the teaching activity of the order and its scholastic organisation placed the Preachers in the forefront of the intellectual life of the Middle Ag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antonius Fischer
Anton Hubert Fischer (Antonius Fischer) (30 May 1840, in Jülich, Rhine Province – 30 July 1912, in Neuenahr) was a Roman Catholic Archbishop of Cologne and Cardinal (Catholicism), Cardinal. Life The son of a professor, he was educated at the Friedrich Wilhelm Gymnasium at Cologne, making his theological studies at the University of Bonn and the Academy of Münster. Ordained priest, 2 September 1863, he was for twenty-five years professor of religion at the Gymnasium at Essen. In 1886, he received his doctorate at the University of Tübingen, his thesis being "De salute infidelium". He was preconized titular Bishop of Juliopolis, 14 February 1889, and was thenceforth associated in the administration of the Diocese of Cologne as assistant to the auxiliary Bishop Johann Anton Friedrich Baudri, then very old. When Baudri died (29 June 1893), Fischer succeeded him, and in 1895 he became Dean of Cologne Cathedral. In 1902 the See of Cologne became vacant by the death of Mgr. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cologne
Cologne ( ; german: Köln ; ksh, Kölle ) is the largest city of the German western States of Germany, state of North Rhine-Westphalia (NRW) and the List of cities in Germany by population, fourth-most populous city of Germany with 1.1 million inhabitants in the city proper and 3.6 million people in the Cologne Bonn Region, urban region. Centered on the left bank of the Rhine, left (west) bank of the Rhine, Cologne is about southeast of NRW's state capital Düsseldorf and northwest of Bonn, the former capital of West Germany. The city's medieval Catholic Cologne Cathedral (), the third-tallest church and tallest cathedral in the world, constructed to house the Shrine of the Three Kings, is a globally recognized landmark and one of the most visited sights and pilgrimage destinations in Europe. The cityscape is further shaped by the Twelve Romanesque churches of Cologne, and Cologne is famous for Eau de Cologne, that has been produced in the city since 1709, and "col ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
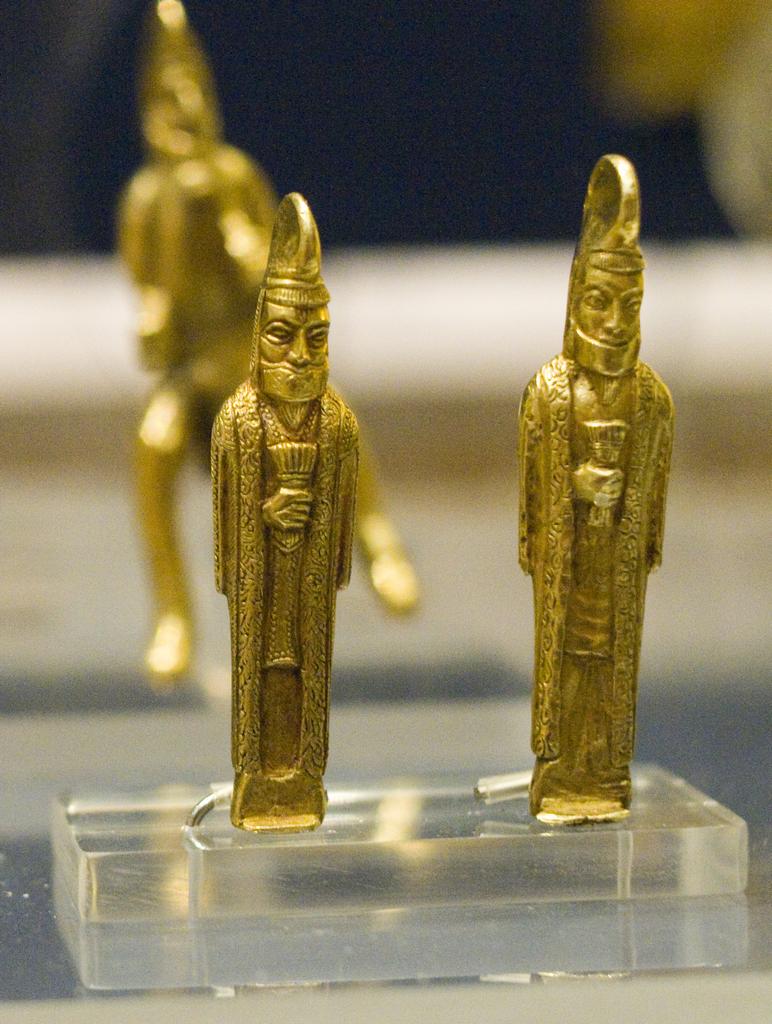
Magi
Magi (; singular magus ; from Latin ''magus'', cf. fa, مغ ) were priests in Zoroastrianism and the earlier religions of the western Iranians. The earliest known use of the word ''magi'' is in the trilingual inscription written by Darius the Great, known as the Behistun Inscription. Old Persian texts, predating the Hellenistic period, refer to a magus as a Zurvanic, and presumably Zoroastrian, priest. Pervasive throughout the Eastern Mediterranean and Western Asia until late antiquity and beyond, ''mágos'' (μάγος) was influenced by (and eventually displaced) Greek '' goēs'' (γόης), the older word for a practitioner of magic, to include astronomy/astrology, alchemy, and other forms of esoteric knowledge. This association was in turn the product of the Hellenistic fascination for Pseudo-Zoroaster, who was perceived by the Greeks to be the Chaldean founder of the Magi and inventor of both astrology and magic, a meaning that still survives in the modern-day words " ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




_MET_DP273206.jpg)



