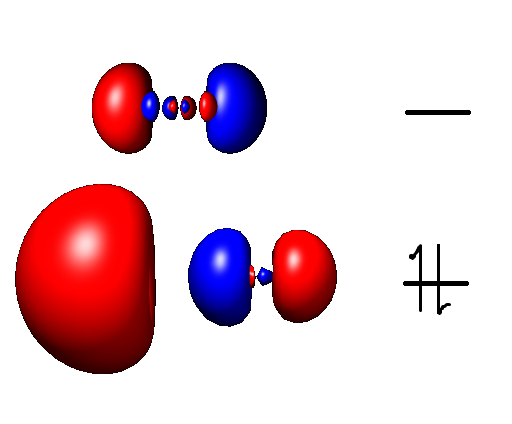|
Aluminium(I)
In chemistry, aluminium(I) refers to monovalent aluminium (+1 oxidation state) in both ionic and covalent bonds. Along with aluminium(II), it is an extremely unstable form of aluminium. While late Group 13 elements such as thallium and indium prefer the +1 oxidation state, aluminium(I) is rare. Aluminium does not experience the inert pair effect, a phenomenon where valence s electrons are poorly shielded from nuclear charge due to the presence of filled d and f orbitals. As such, aluminium (III) (Al^3+) is the much more common oxidation state for aluminium. Aluminium(I) compounds are both prone to disproportionation and difficult to prepare. At standard conditions, they readily oxidize to the aluminium(III) form. Characteristics Al(I) appears to be red, as solutions of AlBr and AlCl in organic solvents are both red. The presence of this color implies a relatively small HOMO/LUMO gap that is accessible by green light. The geometry of compounds can be determined by analysis o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
(Pentamethylcyclopentadienyl)aluminium(I)
(Pentamethylcyclopentadienyl)aluminium(I) is an organometallic compound with the formula Al(CMe) ("Me" is a methyl group; CH). The compound is often abbreviated to AlCp* or Cp*Al, where Cp* is the pentamethylcyclopentadienide anion (CMe). Discovered in 1991 by Dhmeier ''et al.'', AlCp* serves as the first ever documented example of a room temperature stable monovalent aluminium compound. In its isolated form, Cp*Al exists as the tetramer p*Al and is a yellow crystal that decomposes at temperatures above 100 °C but also sublimes at temperatures above 140 °C. Synthesis The earliest documented synthesis and characterization of Cp*Al was by Dohmeier ''et al.'' in 1991, where four equivalents of AlCl in toluene/diethyl ether is reacted with two equivalents of 2 g(Cp*)to give p*Alas yellow crystals: Despite the above synthetic scheme successfully producing tetrameters of p*Alat reasonable yields (44%), its use of AlCl proved problematic, as AlCl synthesis requires ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aluminium
Aluminium (aluminum in American and Canadian English) is a chemical element with the symbol Al and atomic number 13. Aluminium has a density lower than those of other common metals, at approximately one third that of steel. It has a great affinity towards oxygen, and forms a protective layer of oxide on the surface when exposed to air. Aluminium visually resembles silver, both in its color and in its great ability to reflect light. It is soft, non-magnetic and ductile. It has one stable isotope, 27Al; this isotope is very common, making aluminium the twelfth most common element in the Universe. The radioactivity of 26Al is used in radiodating. Chemically, aluminium is a post-transition metal in the boron group; as is common for the group, aluminium forms compounds primarily in the +3 oxidation state. The aluminium cation Al3+ is small and highly charged; as such, it is polarizing, and bonds aluminium forms tend towards covalency. The strong affinity tow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aluminium Monofluoride
Aluminium monofluoride, also known as fluoridoaluminium, is the chemical compound with the formula AlF. This elusive species is formed by the reaction between aluminium trifluoride and metallic aluminium at elevated temperatures but quickly reverts to the reactants when cooled. Clusters derived from related aluminium(I) halides can be stabilized using specialized ligands. This molecule has been detected in the interstellar medium, where molecules are so dilute that intermolecular collisions are unimportant. See also *Aluminium monobromide Aluminium monobromide is a chemical compound with the empirical formula AlBr. It forms from the reaction of HBr with Al metal at high temperature. It disproportionates near room temperature: :6/n " lBrsub>n" → Al2Br6 + 4 Al This reaction i ... * Aluminium monochloride * Aluminium monoiodide References Aluminium(I) compounds Fluorides Metal halides {{inorganic-compound-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
P4 And Nacnacal(I)
P4 may refer to: Computing * Intel Pentium 4, a 7th-generation processor design ** The P4 power connector introduced to power it and later CPUs in the ATX12V 1.0 standard * The i486DX (P4) model of the Intel 80486, a high-performance microprocessor * P4 (programming language), for describing packet forwarding * P4, the Perforce software command line client Media * P4 Radio Hele Norge (PFI), a Norwegian radio company ** Kanal 24 (Kanal 4), which acquired the Norwegian P4 channel from PFI * Sveriges Radio P4, a Swedish radio channel * '' Persona 4'', a 2008 video game * '' Periphery IV: Hail Stan'', 2019 album by American progressive metal band Periphery Military * Skaraborg Regiment (armoured), a Swedish army unit whose designation is P 4 * Peugeot P4, a vehicle used by the French Military Science * P4 laboratory, a biosafety level 4 facility * Tetraphosphorus (P4), an allotrope of phosphorus * Group p4, the plane symmetry group Wallpaper group p4 * Progesterone (Pregn-4-e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbene Versus Aluminum (I)
In organic chemistry, a carbene is a molecule containing a neutral carbon atom with a valence of two and two unshared valence electrons. The general formula is or where the R represents substituents or hydrogen atoms. The term "carbene" may also refer to the specific compound , also called methylene, the parent hydride from which all other carbene compounds are formally derived. Carbenes are classified as either singlets or triplets, depending upon their electronic structure. Most carbenes are very short lived, although persistent carbenes are known. One well-studied carbene is dichlorocarbene , which can be generated ''in situ'' from chloroform and a strong base. Structures and bonding The two classes of carbenes are singlet and triplet carbenes. Singlet carbenes are spin-paired. In the language of valence bond theory, the molecule adopts an sp2 hybrid structure. Triplet carbenes have two unpaired electrons. Most carbenes have a nonlinear triplet ground stat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbenes
In organic chemistry, a carbene is a molecule containing a neutral carbon atom with a valence of two and two unshared valence electrons. The general formula is or where the R represents substituents or hydrogen atoms. The term "carbene" may also refer to the specific compound , also called methylene, the parent hydride from which all other carbene compounds are formally derived. Carbenes are classified as either singlets or triplets, depending upon their electronic structure. Most carbenes are very short lived, although persistent carbenes are known. One well-studied carbene is dichlorocarbene , which can be generated ''in situ'' from chloroform and a strong base. Structures and bonding The two classes of carbenes are singlet and triplet carbenes. Singlet carbenes are spin-paired. In the language of valence bond theory, the molecule adopts an sp2 hybrid structure. Triplet carbenes have two unpaired electrons. Most carbenes have a nonlinear triplet ground stat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synthesis Of Nacnacal(i) Generic
Synthesis or synthesize may refer to: Science Chemistry and biochemistry *Chemical synthesis, the execution of chemical reactions to form a more complex molecule from chemical precursors ** Organic synthesis, the chemical synthesis of organic compounds ***Total synthesis, the complete organic synthesis of complex organic compounds, usually without the aid of biological processes ***Convergent synthesis or linear synthesis, a strategy to improve the efficiency of multi-step chemical syntheses **Dehydration synthesis, a chemical synthesis resulting in the loss of a water molecule * Biosynthesis, the creation of an organic compound in a living organism, usually aided by enzymes **Photosynthesis, a biochemical reaction using a carbon molecule to produce an organic molecule, using sunlight as a catalyst **Chemosynthesis, the synthesis of biological compounds into organic waste, using methane or an oxidized molecule as a catalyst **Amino acid synthesis, the synthesis of an amino ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chem Structure Of Hnacnac
Chem may refer to: * Chemistry practical waali mam * Chemistry *Chemical * ''Chem'' (journal), a scientific journal published by Cell Press *Post apocalyptic slang for "drugs", medicinal or otherwise in the Fallout video game series. In Ancient Egyptian usage: * ''Khem'' (also spelt ''Chem''), the Egyptian word for "black" * Min (god), in the past erroneously named ''Khem'' CHEM may refer to : *A metabolic panel: for instance, CHEM-7, which is the basic metabolic panel *CHEM-DT CHEM-DT is the TVA owned-and-operated television station in Trois-Rivières, Quebec, Canada. It broadcasts a high-definition digital signal on VHF channel 8 from a transmitter on Rue Principale in Notre-Dame-du-Mont-Carmel. Owned by the Grou ..., a Canadian television channel See also * Chemo (other) * Kemi, a place in Finland {{disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abundance Of Elements In Earth's Crust
The abundance of elements in Earth's crust is shown in tabulated form with the estimated crustal abundance for each chemical element shown as mg/kg, or parts per million (ppm) by mass (10,000 ppm = 1%). Estimates of elemental abundance are difficult because (a) the composition of the upper and lower crust are quite different, and (b) the composition of the continental crust can vary drastically by locality. David KringComposition of Earth's continental crust as inferred from the compositions of impact melt sheets Lunar and Planetary Science XXVIII List of abundance by element See also * Abundances of the elements (data page) * Atmospheric chemistry * Clarke number — lists of historical data and terminology * List of chemical elements * Primordial nuclide In geochemistry, geophysics and nuclear physics, primordial nuclides, also known as primordial isotopes, are nuclides found on Earth that have existed in their current form since before Earth was formed. Pri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aluminium Fluoride
Aluminium fluoride refers to inorganic compounds with the formula AlF3·''x''H2O. They are all colorless solids. Anhydrous AlF3 is used in the production of aluminium metal. Several occur as minerals. Occurrence and production Aside from anhydrous AlF3, several hydrates are known. With the formula AlF3·''x''H2O, these compounds include monohydrate (''x'' = 1), two polymorphs of the trihydrate (''x'' = 3), a hexahydrate (''x'' = 6), and a nonahydrate (''x'' = 9). The majority of aluminium fluoride is produced by treating alumina with hydrogen fluoride at 700 °C: Hexafluorosilicic acid may also be used make aluminum fluoride. :H2SiF6 + Al2O3 + 3 H2O → 2 AlF3 + SiO2 + 4 H2O Alternatively, it is manufactured by thermal decomposition of ammonium hexafluoroaluminate. For small scale laboratory preparations, AlF3 can also be prepared by treating aluminium hydroxide or aluminium metal with hydrogen fluoride. Aluminium fluoride trihydrate is found in nature as the rare min ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Comproportionation
Comproportionation or synproportionation is a chemical reaction where two reactants containing the same element but with different oxidation numbers, form a compound having an intermediate oxidation number. It is the opposite of disproportionation.Shriver, D. F.; Atkins, P. W.; Overton, T. L.; Rourke, J. P.; Weller, M. T.; Armstrong, F. A. “Inorganic Chemistry” W. H. Freeman, New York, 2006. . Frost diagrams The tendency of two species to disproportionate or comproportionate can be determined by examining the Frost diagram of the oxidation states; if a species' value of Δ''G''/''F'' is lower than the line joining the two oxidation numbers on either side of it, then it is more stable and if in a solution, these two species will undergo comproportionation. A Frost Diagram is another way of displaying the reduction potentials for the various oxidation states of a given element, X. It shows nE against the oxidation number N: here, E is the reduction potential for the X(N)/X(0) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |