|
Aligner (semiconductor)
An aligner, or mask aligner, is a system that produces integrated circuits (IC) using the photolithography process. It holds the photomask over the silicon wafer while a bright light is shone through the mask and onto the photoresist. The "alignment" refers to the ability to place the mask over precisely the same location repeatedly as the chip goes through multiple rounds of lithography. Aligners were a major part of IC manufacture from the 1960s into the late 1970s, when they began to be replaced by the stepper. There are several distinct generations of aligner technology. The early contact aligners placed the mask in direct contact with the top surface of the wafer, which often damaged the pattern when the mask was lifted off again. Used only briefly, proximity aligners held the mask slightly above the surface to avoid this problem, but were difficult to work with and required considerable manual adjustment. Finally, the Micralign projection aligner, introduced by Perkin-Elmer i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Integrated Circuit
An integrated circuit or monolithic integrated circuit (also referred to as an IC, a chip, or a microchip) is a set of electronic circuits on one small flat piece (or "chip") of semiconductor material, usually silicon. Large numbers of tiny MOSFETs (metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistors) integrate into a small chip. This results in circuits that are orders of magnitude smaller, faster, and less expensive than those constructed of discrete electronic components. The IC's mass production capability, reliability, and building-block approach to integrated circuit design has ensured the rapid adoption of standardized ICs in place of designs using discrete transistors. ICs are now used in virtually all electronic equipment and have revolutionized the world of electronics. Computers, mobile phones and other home appliances are now inextricable parts of the structure of modern societies, made possible by the small size and low cost of ICs such as modern computer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photolithography
In integrated circuit manufacturing, photolithography or optical lithography is a general term used for techniques that use light to produce minutely patterned thin films of suitable materials over a substrate, such as a silicon wafer, to protect selected areas of it during subsequent etching, deposition, or implantation operations. Typically, ultraviolet light is used to transfer a geometric design from an optical mask to a light-sensitive chemical (photoresist) coated on the substrate. The photoresist either breaks down or hardens where it is exposed to light. The patterned film is then created by removing the softer parts of the coating with appropriate solvents. Conventional photoresists typically consists of three components: resin, sensitizer, and solvent. Photolithography processes can be classified according to the type of light used, such as ultraviolet, deep ultraviolet, extreme ultraviolet, or X-ray. The wavelength of light used determines the minimum feature si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photomask
A photomask is an opaque plate with holes or transparencies that allow light to shine through in a defined pattern. They are commonly used in photolithography and the production of integrated circuits (ICs or "chips") in particular. Masks are used to produce a pattern on a substrate, normally a thin slice of silicon known as a wafer in the case of chip manufacturing. Several masks are used in turn, each one reproducing a layer of the completed design, and together they are known as a mask set. Previously, photomasks used to be produced manually by using rubylith and mylar. As complexity continued to grow, manual processing of any sort became difficult. This was solved with the introduction of the optical pattern generator which automated the process of producing the initial large-scale pattern, and the step-and-repeat cameras that automated the copying of the pattern into a multiple-IC mask. The intermediate masks are known as reticles, and were initially copied to production mas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silicon Wafer
In electronics, a wafer (also called a slice or substrate) is a thin slice of semiconductor, such as a crystalline silicon (c-Si), used for the fabrication of integrated circuits and, in photovoltaics, to manufacture solar cells. The wafer serves as the substrate for microelectronic devices built in and upon the wafer. It undergoes many microfabrication processes, such as doping, ion implantation, etching, thin-film deposition of various materials, and photolithographic patterning. Finally, the individual microcircuits are separated by wafer dicing and packaged as an integrated circuit. History In the semiconductor or silicon wafer industry, the term wafer appeared in the 1950s to describe a thin round slice of semiconductor material, typically germanium or silicon. Round shape comes from single-crystal ingots usually produced using the Czochralski method. Silicon wafers were first introduced in the 1940s. By 1960, silicon wafers were being manufactured in the U.S. by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photoresist
A photoresist (also known simply as a resist) is a light-sensitive material used in several processes, such as photolithography and photoengraving, to form a patterned coating on a surface. This process is crucial in the electronic industry. The process begins by coating a substrate with a light-sensitive organic material. A patterned mask is then applied to the surface to block light, so that only unmasked regions of the material will be exposed to light. A solvent, called a developer, is then applied to the surface. In the case of a positive photoresist, the photo-sensitive material is degraded by light and the developer will dissolve away the regions that were exposed to light, leaving behind a coating where the mask was placed. In the case of a negative photoresist, the photosensitive material is strengthened (either polymerized or cross-linked) by light, and the developer will dissolve away only the regions that were not exposed to light, leaving behind a coating in areas w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stepper
A stepper is a device used in the manufacture of integrated circuits (ICs) that is similar in operation to a slide projector or a photographic enlarger. ''Stepper'' is short for step-and-repeat camera. Steppers are an essential part of the complex process, called photolithography, which creates millions of microscopic circuit elements on the surface of chips of silicon. These chips form the heart of ICs such as computer processors, memory chips, and many other devices. The stepper emerged in the late 1970s but did not become widespread until the 1980s. This was because it was replacing an earlier technology, the mask aligner. Aligners imaged the entire surface of a wafer at the same time, producing many chips in a single operation. In contrast, the stepper imaged only one chip at a time, and was thus much slower to operate. The stepper eventually displaced the aligner when the relentless forces of Moore's Law demanded that smaller feature sizes be used. Because the stepper im ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Micralign
The Perkin-Elmer Micralign was a family of aligners introduced in 1973. Micralign was the first projection aligner, a concept that dramatically improved semiconductor fabrication. According to the Chip History Center, it "literally made the modern IC industry". The Micralign addressed a significant problem in the early integrated circuit (IC) industry, that the vast majority of ICs printed contained defects that rendered them useless. On average, about 1 in 10 complex ICs produced would be operational, a 10% yield. The Micralign improved this to over 50%, and as great as 70% in many applications. In doing so, the price of microprocessors and dynamic RAM products fell about 10 times between 1974 and 1978, by which time the Micralign had become practically universal in the high-end market. Initially predicting to sell perhaps 50 units, Perkin-Elmer eventually sold about 2,000, making them the by far largest vendor in the semiconductor fabrication equipment space through the second h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perkin-Elmer
PerkinElmer, Inc., previously styled Perkin-Elmer, is an American global corporation focused in the business areas of diagnostics, life science research, food, environmental and industrial testing. Its capabilities include detection, imaging, informatics, and service. PerkinElmer produces analytical instruments, genetic testing and diagnostic tools, medical imaging components, software, instruments, and consumables for multiple end markets. PerkinElmer is part of the S&P 500 Index and operates in 190 countries. History Founding Richard Scott Perkin, Richard Perkin was attending the Pratt Institute in Brooklyn to study chemical engineering, but left after a year to try his hand on Wall Street. Still interested in the sciences, he gave public lectures on various topics. Charles Wesley Elmer, Charles Elmer ran a firm that supplied court reporters and was nearing retirement when he attended one of Perkin's lectures on astronomy being held at the Brooklyn Institute of Arts and Sci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
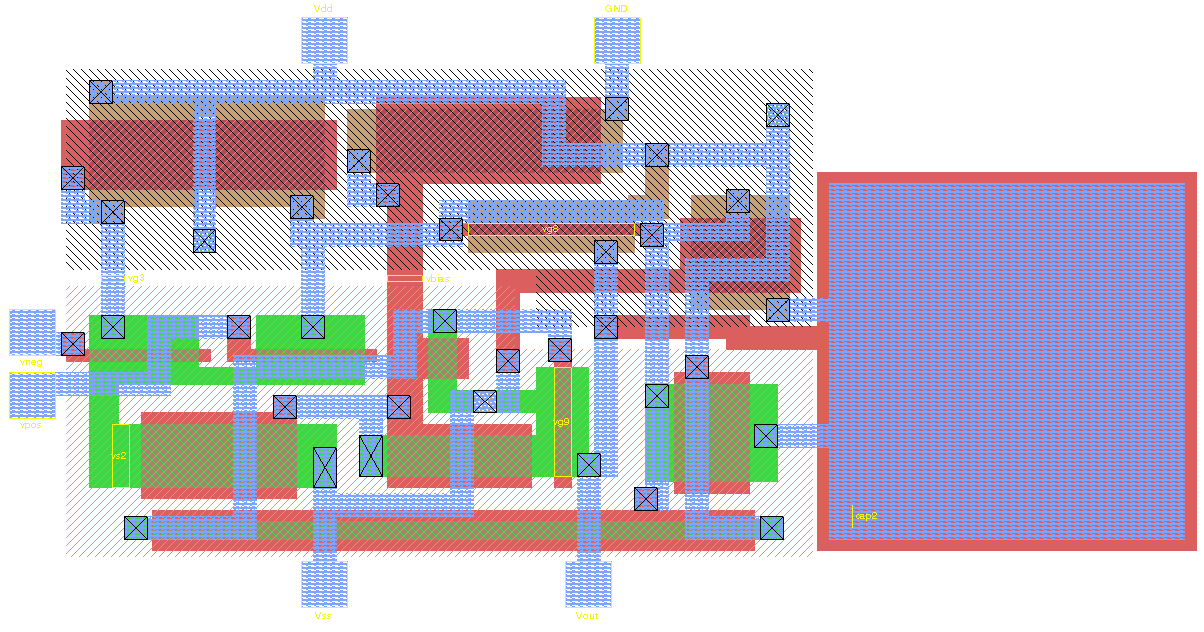
Integrated Circuit Layout
Integrated circuit layout, also known IC layout, IC mask layout, or mask design, is the representation of an integrated circuit in terms of planar geometric shapes which correspond to the patterns of metal, oxide, or semiconductor layers that make up the components of the integrated circuit. Originally the overall process was called tapeout as historically early ICs used graphical black crepe tape on mylar media for photo imaging (erroneously believed to reference magnetic data—the photo process greatly predated magnetic media). When using a standard process—where the interaction of the many chemical, thermal, and photographic variables is known and carefully controlled—the behaviour of the final integrated circuit depends largely on the positions and interconnections of the geometric shapes. Using a computer-aided layout tool, the layout engineer—or layout technician—places and connects all of the components that make up the chip such that they meet certain criteria ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minimum Feature Size
Semiconductor device fabrication is the process used to manufacture semiconductor devices, typically integrated circuit (IC) chips such as modern computer processors, microcontrollers, and memory chips such as NAND flash and DRAM that are present in everyday electrical and electronic devices. It is a multiple-step sequence of photolithographic and chemical processing steps (such as surface passivation, thermal oxidation, planar diffusion and junction isolation) during which electronic circuits are gradually created on a wafer made of pure semiconducting material. Silicon is almost always used, but various compound semiconductors are used for specialized applications. The entire manufacturing process takes time, from start to packaged chips ready for shipment, at least six to eight weeks (tape-out only, not including the circuit design) and is performed in highly specialized semiconductor fabrication plants, also called foundries or fabs. All fabrication takes place inside a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)