|
Al-Batani Al-Sharqi
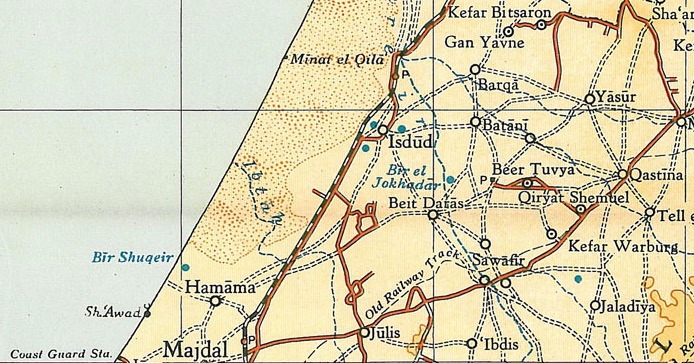
Al-Batani al-Sharqi ( ar, البطاني الشرقي) was a Palestinian Arab village in the Gaza Subdistrict, located northeast of Gaza situated in the flat terrain on the southern coastal plain of Palestine. It had a population of 650 in 1945. Al-Batani al-Sharqi was depopulated during the 1948 Arab-Israeli War.Khalidi, 1992, pp.84-85. History Ceramics from the Byzantine era have been found here, together with coins from reigns of Phocas and Constantine IV. One mention of al-Batani indicates that it was founded as a ranch by the Umayyad caliph Mu'awiyah I in the 8th century CE. Ottoman era Al-Batani al-Sharqi, like the rest of Palestine, was incorporated into the Ottoman Empire in 1517, and in the tax registers of 1596, it was a village in the ''nahiya'' of Gaza, east of Isdud, north of Bayt Daras and part of the Sanjak of Gaza with a population of 39. Al-Batani paid taxes on wheat, barley, fruit, beehives, goats, and vineyards. The whole population was Muslim. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mandatory Palestine
Mandatory Palestine ( ar, فلسطين الانتدابية '; he, פָּלֶשְׂתִּינָה (א״י) ', where "E.Y." indicates ''’Eretz Yiśrā’ēl'', the Land of Israel) was a geopolitical entity established between 1920 and 1948 in the region of Palestine under the terms of the League of Nations Mandate for Palestine. During the First World War (1914–1918), an Arab uprising against Ottoman rule and the British Empire's Egyptian Expeditionary Force under General Edmund Allenby drove the Ottoman Turks out of the Levant during the Sinai and Palestine Campaign. The United Kingdom had agreed in the McMahon–Hussein Correspondence that it would honour Arab independence if the Arabs revolted against the Ottoman Turks, but the two sides had different interpretations of this agreement, and in the end, the United Kingdom and France divided the area under the Sykes–Picot Agreementan act of betrayal in the eyes of the Arabs. Further complicating the issue was t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Defter
A ''defter'' (plural: ''defterler'') was a type of tax register and land cadastre in the Ottoman Empire. Description The information collected could vary, but ''tahrir defterleri'' typically included details of villages, dwellings, household heads (adult males and widows), ethnicity/religion (because these could affect tax liabilities/exemptions), and land use. The defter-i hakâni was a land registry, also used for tax purposes. Each town had a defter and typically an officiator or someone in an administrative role to determine whether the information should be recorded. The officiator was usually some kind of learned man who had knowledge of state regulations. The defter was used to record family interactions such as marriage and inheritance. These records are useful for historians because such information allows for a more in-depth understanding of land ownership among Ottomans. This is particularly helpful when attempting to study the daily affairs of Ottoman citizens. S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PEF Survey Of Palestine
The PEF Survey of Palestine was a series of surveys carried out by the Palestine Exploration Fund (PEF) between 1872 and 1877 for the Survey of Western Palestine and in 1880 for the Survey of Eastern Palestine. The survey was carried out after the success of the Ordnance Survey of Jerusalem by the newly-founded PEF, with support from the War Office. Twenty-six sheets were produced for "Western Palestine" and one sheet for "Eastern Palestine". It was the first fully scientific mapping of Palestine. Besides being a geographic survey the group collected thousands of place names with the objective of identifying Biblical, Talmudic, early Christian and Crusading locations. The survey resulted in the publication of a map of Palestine consisting of 26 sheets, at a scale of 1:63,360, the most detailed and accurate map of Palestine published in the 19th century. The PEF survey represented the peak of the cartographic work in Palestine in the nineteenth century. Although the holiness of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palestine Exploration Fund
The Palestine Exploration Fund is a British society based in London. It was founded in 1865, shortly after the completion of the Ordnance Survey of Jerusalem, and is the oldest known organization in the world created specifically for the study of the Levant region, also known as Palestine. Often simply known as the PEF, its initial objective was to carry out surveys of the topography and ethnography of Ottoman Palestine – producing the PEF Survey of Palestine – with a remit that fell somewhere between an expeditionary survey and military intelligence gathering. It had a complex relationship with Corps of Royal Engineers, and its members sent back reports on the need to salvage and modernise the region.Ilan Pappé (2004) A history of modern Palestine: one land, two peoples Cambridge University Press, pp 34-35 History Following the completion of the Ordnance Survey of Jerusalem, the Biblical archaeologists and clergymen who supported the survey financed the creation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Martin Hartmann
Martin Hartmann (9 December 1851, Breslau – 5 December 1918, Berlin) was a German orientalist, who specialized in Islamic studies. In 1875, he received his doctorate at the University of Leipzig as a student of Heinrich Leberecht Fleischer. From 1876 to 1887 he served as a dragoman at the German General Consulate in Beirut. From 1887 until his death in 1918 he taught classes at the Department of Oriental Languages in Berlin.Hartmann, Martin in: Neue Deutsche Biographie 7 (1966), S. 745 f. As a professor in Berlin he strove hard for the recognition of Islamic studies as an independent discipline. His numerous contributions to the field of Islamic studies were based on a sociological standpoint. Many of these works were published in the journal "'' |
Albert Socin
Albert Socin (13 October 1844 in Basel – 24 June 1899 in Leipzig) was a Swiss orientalist, who specialized in the research of Neo-Aramaic, Kurdish and contemporary Arabic dialects. He also made contributions to the geography, archaeology, religion, art and literature of the Middle East.Prof. Dr. phil. Albert Socin Professorenkatalog der Universität Leipzig He studied at the and Oriental studies at the universities of |
Adobe
Adobe ( ; ) is a building material made from earth and organic materials. is Spanish for '' mudbrick''. In some English-speaking regions of Spanish heritage, such as the Southwestern United States, the term is used to refer to any kind of earthen construction, or various architectural styles like Pueblo Revival or Territorial Revival. Most adobe buildings are similar in appearance to cob and rammed earth buildings. Adobe is among the earliest building materials, and is used throughout the world. Adobe architecture has been dated to before 5,100 B.C. Description Adobe bricks are rectangular prisms small enough that they can quickly air dry individually without cracking. They can be subsequently assembled, with the application of adobe mud to bond the individual bricks into a structure. There is no standard size, with substantial variations over the years and in different regions. In some areas a popular size measured weighing about ; in other contexts the size is weig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Victor Guérin
Victor Guérin (15 September 1821 – 21 Septembe 1890) was a French intellectual, explorer and amateur archaeologist. He published books describing the geography, archeology and history of the areas he explored, which included Greece, Asia Minor, North Africa, Lebanon, Syria and Palestine. Biography Guérin, a devout Catholic, graduated from the ''École normale supérieure'' in Paris in 1840. After graduation, he began working as a teacher of rhetoric and member of faculty in various colleges and high schools in France, then in Algeria in 1850, and 1852 he became a member of the French School of Athens. While exploring Samos, he identified the spring that feeds the Tunnel of Eupalinos and the beginnings of the channel. His doctoral thesis of 1856 dealt with the coastal region of Palestine, from Khan Yunis to Mount Carmel. With the financial help of Honoré Théodoric d'Albert de Luynes he was able to explore Greece and its islands, Asia Minor, Egypt, Nubia, Tunisia, and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edward Robinson (scholar)
Edward Robinson (April 10, 1794 – January 27, 1863) was an American biblical scholar known for his magnum opus, '' Biblical Researches in Palestine'', the first major work in Biblical Geography and Biblical Archaeology, which earned him the epithets "Father of Biblical Geography" and "Founder of Modern Palestinology." He studied in the United States and Germany, a center of biblical scholarship and exploration of the Bible as history. He translated scriptural works from classical languages, as well as German translations. His ''Greek and English Lexicon of the New Testament'' (1836; last revision, 1850) became a standard authority in the United States, and was reprinted several times in Great Britain. Biography Robinson was born in Southington, Connecticut, and raised on a farm. His father was a minister in the Congregational Church of the town for four decades. The younger Robinson taught at schools in East Haven and Farmington in 1810–11 to earn money for college. He ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pierre Jacotin
Pierre Jacotin (1765–1827) was the director of the survey for the '' Carte de l'Égypte (Description de l'Égypte)'', the first triangulation-based map of Egypt, Syria and Palestine. The maps were surveyed in 1799-1800 during the campaign in Egypt and Palestine of Napoleon. After his return from Egypt, Jacotin worked on preparing the plates for publication, but in 1808 Napoleon formally made them state secrets and forbade publication. This was apparently connected with Napoleon's efforts at the time to establish an alliance with the Ottomans. It was not until 1828-30 that the engraved plates could be published.Khatib, 2003, p211/ref> References Bibliography * Further reference * * * (Pierre Jacotin: pp437652, “Syria”: pp594609 ) External links * Jacotin maps at the David Rumsey Historical Map Collection The David Rumsey Historical Map Collection is a large private map collection with over 150,000 maps and cartographic items. The collection was created by David ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muslim
Muslims ( ar, المسلمون, , ) are people who adhere to Islam, a Monotheism, monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God in Abrahamic religions, God of Abraham (or ''Allah'') as it was revealed to Muhammad, the Muhammad in Islam, main Islamic prophet. The majority of Muslims also follow the teachings and practices of Muhammad (''sunnah'') as recorded in traditional accounts (''hadith''). With an estimated population of almost 1.9 billion followers as of 2020 year estimation, Muslims comprise more than 24.9% of the world's total population. In descending order, the percentage of people who identify as Muslims on each continental landmass stands at: 45% of Islam in Africa, Africa, 25% of Islam in Asia, Asia and Islam in Oceania, Oceania (collectively), 6% of Islam in Europe, Europe, and 1% of the Islam in the Americas, Americas. Addition ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gaza Sanjak
Gaza Sanjak ( ar, سنجق غزة) was a sanjak of the Damascus Eyalet, Ottoman Empire centered in Gaza. In the 16th century it was divided into ''nawahi'' (singular: ''nahiya''; third-level subdivisions): Gaza in the south and Ramla in the north. List of settlements In the 1596- daftar, the sanjak contained the following nahiyah and villages/town Gaza Nahiyah * Al-Sawafir al-Sharqiyya, Bayt Tima, Hamama,Hütteroth and Abdulfattah, 1977, p. 142 Al-Tina, Yibna, Isdud, Arab Suqrir,Hütteroth and Abdulfattah, 1977, p. 143 Deir al-Balah, Burayr, Jabalia, Beit Lahia, Al-Majdal, Askalan, Bayt 'Affa, Najd, Ni'ilya,Hütteroth and Abdulfattah, 1977, p. 144 Bayt Jirja, Hiribya, Qatra, Iraq Suwaydan, Kawkaba, Beit Jimal Monastery, Al-Batani al-Sharqi,Hütteroth and Abdulfattah, 1977, p. 145 Al-Qubayba, Al-Faluja, Bayt Daras, Al-Maghar,Hütteroth and Abdulfattah, 1977, p. 146 Hatta, Jusayr, Zikrin, Zayta, Barqa, Beit Hanoun, Dayr Sunayd, Simsim,Hütteroth and Abdulfatt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)
_1.jpg)

