|
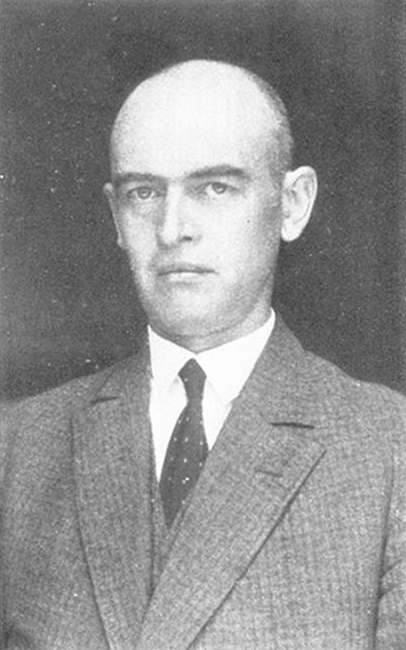
Albert Socin
Albert Socin (13 October 1844 in Basel – 24 June 1899 in Leipzig) was a Swiss orientalist, who specialized in the research of Neo-Aramaic, Kurdish and contemporary Arabic dialects. He also made contributions to the geography, archaeology, religion, art and literature of the Middle East.Prof. Dr. phil. Albert Socin Professorenkatalog der Universität Leipzig He studied at the and Oriental studies at the universities of |
Albert Socin - Taeschler Taeschler (18 Btv1b84499195 (cropped)
Albert may refer to: Companies * Albert (supermarket), a supermarket chain in the Czech Republic * Albert Heijn, a supermarket chain in the Netherlands * Albert Market, a street market in The Gambia * Albert Productions, a record label * Albert Computers, Inc., a computer manufacturer in the 1980s Entertainment * ''Albert'' (1985 film), a Czechoslovak film directed by František Vláčil * ''Albert'' (2015 film), a film by Karsten Kiilerich * ''Albert'' (2016 film), an American TV movie * ''Albert'' (Ed Hall album), 1988 * "Albert" (short story), by Leo Tolstoy * Albert (comics), a character in Marvel Comics * Albert (''Discworld''), a character in Terry Pratchett's ''Discworld'' series * Albert, a character in Dario Argento's 1977 film ''Suspiria'' Military * Battle of Albert (1914), a WWI battle at Albert, Somme, France * Battle of Albert (1916), a WWI battle at Albert, Somme, France * Battle of Albert (1918), a WWI battle at Albert, Somme, France People * Albert (given ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baedeker
Verlag Karl Baedeker, founded by Karl Baedeker on July 1, 1827, is a German publisher and pioneer in the business of worldwide travel guides. The guides, often referred to simply as " Baedekers" (a term sometimes used to refer to similar works from other publishers, or travel guides in general), contain, among other things, maps and introductions; information about routes and travel facilities; and descriptions of noteworthy buildings, sights, attractions and museums, written by specialists. History (1827−1948) Karl Baedeker 1827−1859: Karl Baedeker (1801-1859) descended from a long line of printers, booksellers and publishers from Essen. He was the eldest of ten children of Gottschalk Diederich Bädeker (1778–1841), who had inherited the publishing house founded by his own father, Zacharias Gerhard Bädeker (1750–1800). The company also published the local newspaper, the '' Essendische Zeitung'', and the family expected that Karl, too, would eventually join the firm. Karl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Academic Staff Of The University Of Tübingen
An academy (Attic Greek: Ἀκαδήμεια; Koine Greek Ἀκαδημία) is an institution of secondary or tertiary higher learning (and generally also research or honorary membership). The name traces back to Plato's school of philosophy, founded approximately 385 BC at Akademia, a sanctuary of Athena, the goddess of wisdom and skill, north of Athens, Greece. Etymology The word comes from the ''Academy'' in ancient Greece, which derives from the Athenian hero, ''Akademos''. Outside the city walls of Athens, the gymnasium was made famous by Plato as a center of learning. The sacred space, dedicated to the goddess of wisdom, Athena, had formerly been an olive grove, hence the expression "the groves of Academe". In these gardens, the philosopher Plato conversed with followers. Plato developed his sessions into a method of teaching philosophy and in 387 BC, established what is known today as the Old Academy. By extension, ''academia'' has come to mean the accumulation, de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Academic Staff Of Leipzig University
An academy ( Attic Greek: Ἀκαδήμεια; Koine Greek Ἀκαδημία) is an institution of secondary or tertiary higher learning (and generally also research or honorary membership). The name traces back to Plato's school of philosophy, founded approximately 385 BC at Akademia, a sanctuary of Athena, the goddess of wisdom and skill, north of Athens, Greece. Etymology The word comes from the ''Academy'' in ancient Greece, which derives from the Athenian hero, '' Akademos''. Outside the city walls of Athens, the gymnasium was made famous by Plato as a center of learning. The sacred space, dedicated to the goddess of wisdom, Athena, had formerly been an olive grove, hence the expression "the groves of Academe". In these gardens, the philosopher Plato conversed with followers. Plato developed his sessions into a method of teaching philosophy and in 387 BC, established what is known today as the Old Academy. By extension, ''academia'' has come to mean the accumulatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
People From Basel-Stadt
A person ( : people) is a being that has certain capacities or attributes such as reason, morality, consciousness or self-consciousness, and being a part of a culturally established form of social relations such as kinship, ownership of property, or legal responsibility. The defining features of personhood and, consequently, what makes a person count as a person, differ widely among cultures and contexts. In addition to the question of personhood, of what makes a being count as a person to begin with, there are further questions about personal identity and self: both about what makes any particular person that particular person instead of another, and about what makes a person at one time the same person as they were or will be at another time despite any intervening changes. The plural form "people" is often used to refer to an entire nation or ethnic group (as in "a people"), and this was the original meaning of the word; it subsequently acquired its use as a plural form of per ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1899 Deaths
Events January 1899 * January 1 ** Spanish rule ends in Cuba, concluding 400 years of the Spanish Empire in the Americas. ** Queens and Staten Island become administratively part of New York City. * January 2 – ** Bolivia sets up a customs office in Puerto Alonso, leading to the Brazilian settlers there to declare the Republic of Acre in a revolt against Bolivian authorities. **The first part of the Jakarta Kota–Anyer Kidul railway on the island of Java is opened between Batavia Zuid ( Jakarta Kota) and Tangerang. * January 3 – Hungarian Prime Minister Dezső Bánffy fights an inconclusive duel with his bitter enemy in parliament, Horánszky Nándor. * January 4 – **U.S. President William McKinley's declaration of December 21, 1898, proclaiming a policy of benevolent assimilation of the Philippines as a United States territory, is announced in Manila by the U.S. commander, General Elwell Otis, and angers independence activists who had fought agai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1844 Births
In the Philippines, it was the only leap year with 365 days, as December 31 was skipped when 1845 began after December 30. Events January–March * January 15 – The University of Notre Dame, based in the city of the same name, receives its charter from Indiana. * February 27 – The Dominican Republic gains independence from Haiti. * February 28 – A gun on the USS ''Princeton'' explodes while the boat is on a Potomac River cruise, killing two United States Cabinet members and several others. * March 8 ** King Oscar I ascends to the throne of Sweden–Norway upon the death of his father, Charles XIV/III John. ** The Althing, the parliament of Iceland, is reopened after 45 years of closure. * March 9 – Giuseppe Verdi's opera ''Ernani'' debuts at Teatro La Fenice, Venice. * March 12 – The Columbus and Xenia Railroad, the first railroad planned to be built in Ohio, is chartered. * March 13 – The dictator Carlos Antonio López becomes first President of Pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ma'lula
Maaloula or Maʿlūlā ( arc, ܡܥܠܘܠܐ in Eastern Aramaic Syriac script, ' in Western Aramaic Maalouli script; ar, مَعلُولَا) is a town in the Rif Dimashq Governorate in Syria. The town is located 56 km to the northeast of Damascus and built into the rugged mountainside, at an altitude of more than 1500 m. It is known as one of three remaining villages where Western Aramaic – said to be the language of Jesus – is spoken, the other two being the nearby, smaller villages of Jubb'adin and Bakhah. Etymology is said to derive from the Aramaic word ' (), meaning 'entrance'. The name is romanized in multiple different ways, e.g. Maaloula, Ma'loula, Maalula, Ma'lula, Malula. However, "Maaloula" is the most common one. Population In 1838, its inhabitants were Greek Orthodox Church of Antioch Christians, Melkite Greek Catholic Church Christians, and Sunni Muslim. Half a century ago, 15,000 people lived in Maaloula. According to the Syria Central Bureau of Stati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gotthelf Bergsträsser
Gotthelf Bergsträsser (5 April 1886, in Oberlosa, Plauen – 16 August 1933, near Berchtesgaden) was a German linguist specializing in Semitic studies, generally considered to be one of the greatest of the twentieth century. Bergsträsser was initially a teacher of classical languages before deciding to approach Semitic. He was a professor at Istanbul University during World War I, when he was an officer in the German army stationed in Turkey. While there, he studied the spoken dialects of Arabic and Aramaic in Syria and Palestine. One of his most well known works is the 29th (and final) edition of Wilhelm Gesenius' ''Hebrew Grammar'' (1918–1929), which remained incomplete, containing only phonology and morphology of the verb. Also widely admired was his ''Introduction to the Semitic Languages'' (1928, English 1983). These brought him international fame as a scholar. His last position was professor of Semitic languages at the University of Munich. Bergsträsser mostly eng ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karl Baedeker
Karl Ludwig Johannes Baedeker ( , ; 3 November 1801 – 4 October 1859) was a German publisher whose company, Baedeker, set the standard for authoritative guidebooks for tourists. Karl Baedeker was descended from a long line of printers, booksellers and publishers. He was the eldest of ten children of Gottschalk Diederich Bädeker (1778–1841), who had inherited the publishing house founded by his own father, Zacharias Gerhard Bädeker (1750–1800). The company also published the local newspaper, the ''Essendische Zeitung'', and the family expected that Karl, too, would eventually join the firm. Karl changed the spelling of the family name from Bädeker with the umlaut to Baedeker around 1850. Biography Karl Baedeker was born in Essen, then in the Kingdom of Prussia, on November 3, 1801. After his schooling in Hagen, he left home in 1817 to study humanities in Heidelberg where he also worked for a while at the leading local bookseller J.C.B. Mohr. Military service foll ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hans Stumme
Hans Stumme (3 November 1864 in Mittweida – 20 December 1936 in Dresden) was a German linguist, known for his research of Semitic and other Afroasiatic languages. He studied at the universities of Tübingen, Halle, Leipzig and Strasbourg, obtaining his habilitation in 1895. While a student at Leipzig, his teachers were Ludolf Krehl, Albert Socin and Friedrich Delitzsch.Hans Stumme Orientalisches Institut der Universität Leipzig In 1900 he became an associate professor of Oriental philology at Leipzig, where in 1909 he was named an honorary professor of Neo-Arabic and |
Diwan (poetry)
In Islamic cultures of the Middle East, North Africa, Sicily and South Asia, a Diwan ( fa, دیوان, ''divân'', ar, ديوان, ''dīwān'') is a collection of poems by one author, usually excluding his or her long poems ( mathnawī). The vast majority of Diwan poetry was lyric in nature: either ghazals or ''gazel''s (which make up the greatest part of the repertoire of the tradition), or ''kasîde''s. There were, however, other common genres, most particularly the ''mesnevî'', a kind of verse romance and thus a variety of narrative poetry; the two most notable examples of this form are the ''Layla and Majnun'' (ليلى و مجنون) of Fuzûlî and the ''Hüsn ü Aşk'' (حسن و عشق; "Beauty and Love") of Şeyh Gâlib. Originating in Persian literature, the idea spread to the Arab and Turkish worlds, and South Asia, and the term was sometimes used in Europe, not always in the same way. Etymology The English usage of the phrase "diwan poetry" comes from the Arab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)


_1938.jpg)

.jpg)


