|
Animal Perception
Animal cognition encompasses the mental capacities of non-human animals including insect cognition. The study of animal conditioning and learning used in this field was developed from comparative psychology. It has also been strongly influenced by research in ethology, behavioral ecology, and evolutionary psychology; the alternative name cognitive ethology is sometimes used. Many behaviors associated with the term ''animal intelligence'' are also subsumed within animal cognition. Researchers have examined animal cognition in mammals (especially primates, cetaceans, elephants, dogs, cats, pigs, horses, cattle, raccoons and rodents), birds (including parrots, fowl, corvids and pigeons), reptiles (lizards, snakes, and turtles), fish and invertebrates (including cephalopods, spiders and insects). Historical background Earliest inferences The mind and behavior of non-human animals has captivated the human imagination for centuries. Many writers, such as Desc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
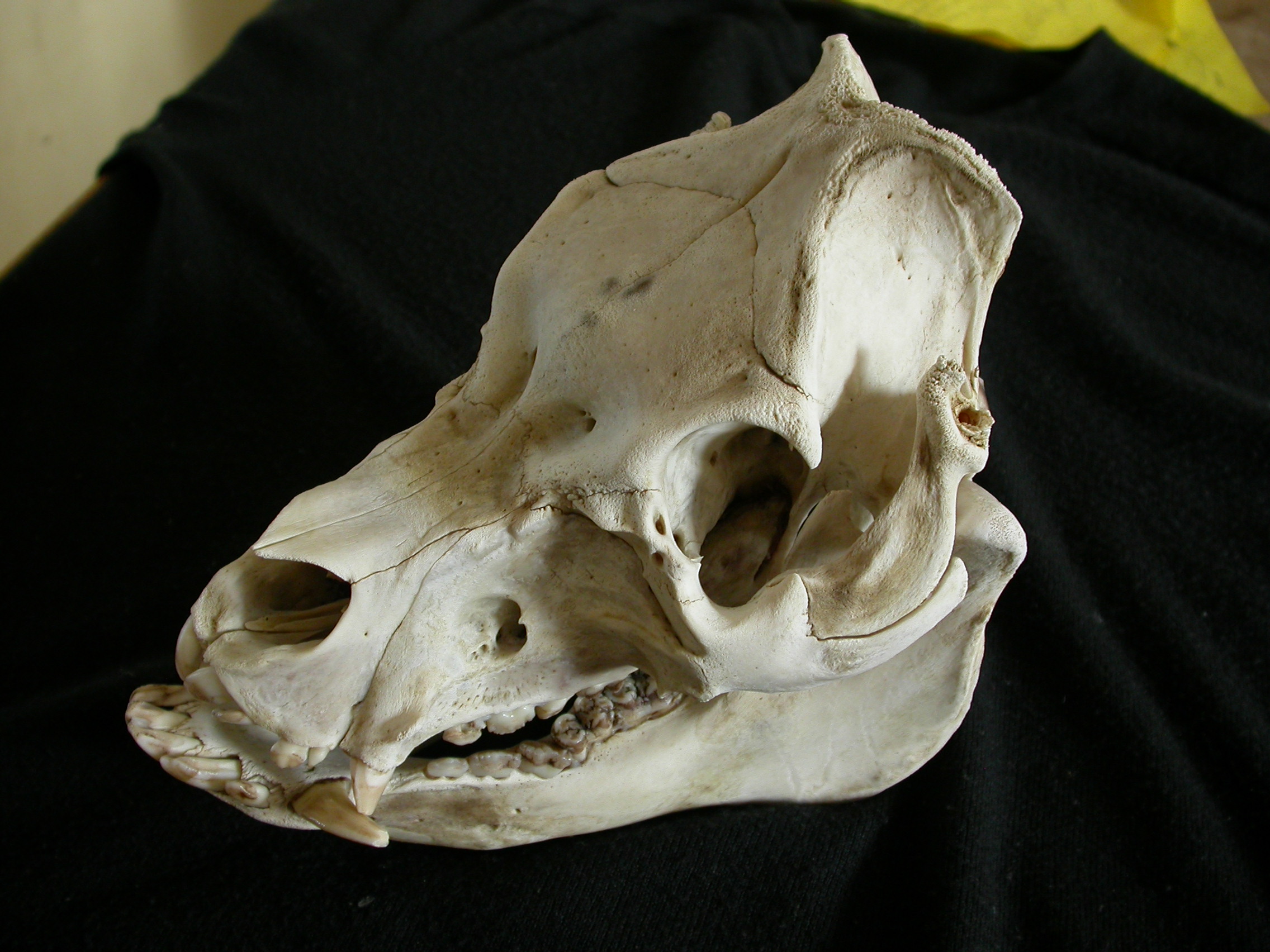
Domestic Pig
The pig (''Sus domesticus''), often called swine, hog, or domestic pig when distinguishing from other members of the genus '' Sus'', is an omnivorous, domesticated, even-toed, hoofed mammal. It is variously considered a subspecies of ''Sus scrofa'' (the wild boar or Eurasian boar) or a distinct species. The pig's head-plus-body length ranges from , and adult pigs typically weigh between , with well-fed individuals even exceeding this range. The size and weight of hogs largely depends on their breed. Compared to other artiodactyls, a pig's head is relatively long and pointed. Most even-toed ungulates are herbivorous, but pigs are omnivores, like their wild relative. Pigs grunt and make snorting sounds. When used as livestock, pigs are farmed primarily for the production of meat, called pork. A group of pigs is called a ''passel'', a ''team'', or a ''sounder''. The animal's bones, hide, and bristles are also used in products. Pigs, especially miniature breeds, are kept as pets ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turtle
Turtles are an order of reptiles known as Testudines, characterized by a special shell developed mainly from their ribs. Modern turtles are divided into two major groups, the Pleurodira (side necked turtles) and Cryptodira (hidden necked turtles), which differ in the way the head retracts. There are 360 living and recently extinct species of turtles, including land-dwelling tortoises and freshwater terrapins. They are found on most continents, some islands and, in the case of sea turtles, much of the ocean. Like other amniotes (reptiles, birds, and mammals) they breathe air and do not lay eggs underwater, although many species live in or around water. Turtle shells are made mostly of bone; the upper part is the domed carapace, while the underside is the flatter plastron or belly-plate. Its outer surface is covered in scales made of keratin, the material of hair, horns, and claws. The carapace bones develop from ribs that grow sideways and develop into broad flat plates th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Snakes
Snakes are elongated, limbless, carnivorous reptiles of the suborder Serpentes . Like all other squamates, snakes are ectothermic, amniote vertebrates covered in overlapping scales. Many species of snakes have skulls with several more joints than their lizard ancestors, enabling them to swallow prey much larger than their heads (cranial kinesis). To accommodate their narrow bodies, snakes' paired organs (such as kidneys) appear one in front of the other instead of side by side, and most have only one functional lung. Some species retain a pelvic girdle with a pair of vestigial claws on either side of the cloaca. Lizards have evolved elongate bodies without limbs or with greatly reduced limbs about twenty-five times independently via convergent evolution, leading to many lineages of legless lizards. These resemble snakes, but several common groups of legless lizards have eyelids and external ears, which snakes lack, although this rule is not universal (see Amphisbaenia, D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monitor Lizard
Monitor lizards are lizards in the genus ''Varanus,'' the only extant genus in the family Varanidae. They are native to Africa, Asia, and Oceania, and one species is also found in the Americas as an invasive species. About 80 species are recognized. Monitor lizards have long necks, powerful tails and claws, and well-developed limbs. The adult length of extant species ranges from in some species, to over in the case of the Komodo dragon, though the extinct varanid known as megalania (''Varanus priscus'') may have been capable of reaching lengths more than . Most monitor species are terrestrial, but arboreal and semiaquatic monitors are also known. While most monitor lizards are carnivorous, eating eggs, smaller reptiles, fish, birds, insects, and small mammals, some also eat fruit and vegetation, depending on where they live. Distribution The various species cover a vast area, occurring through Africa, the Indian subcontinent, to China, the Ryukyu Islands in southern Japan, s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reptiles
Reptiles, as most commonly defined are the animals in the Class (biology), class Reptilia ( ), a paraphyletic grouping comprising all sauropsid, sauropsids except birds. Living reptiles comprise turtles, crocodilians, Squamata, squamates (lizards and snakes) and rhynchocephalians (tuatara). As of March 2022, the Reptile Database includes about 11,700 species. In the traditional Linnaean taxonomy, Linnaean classification system, birds are considered a separate class to reptiles. However, crocodilians are more closely related to birds than they are to other living reptiles, and so modern Cladistics, cladistic classification systems include birds within Reptilia, redefining the term as a clade. Other cladistic definitions abandon the term reptile altogether in favor of the clade Sauropsida, which refers to all amniotes more closely related to modern reptiles than to mammals. The study of the traditional reptile Order (biology), orders, historically combined with that of modern amphi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pigeon Intelligence
Pigeons have featured in numerous experiments in comparative psychology, including experiments concerned with animal cognition, and as a result there is considerable knowledge of pigeon intelligence. Available data show, for example, that: *Pigeons have the capacity to share attention between different dimensions of a stimulus, but (like humans and other animals) their performance with multiple dimensions is worse than with a single stimulus dimension. *Pigeons can be taught relatively complex actions and response sequences, and can learn to make responses in different sequences. *Pigeons readily learn to respond in the presence of one simple stimulus and withhold responding in the presence of a different stimulus, or to make different responses in the presence of different stimuli. *Pigeons can discriminate between other individual pigeons, and can use the behaviour of another individual as a cue to tell them what response to make. *Pigeons readily learn to make discriminative res ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corvidae
Corvidae is a cosmopolitan family of oscine passerine birds that contains the crows, ravens, rooks, jackdaws, jays, magpies, treepies, choughs, and nutcrackers. In colloquial English, they are known as the crow family or corvids. Currently, 133 species are included in this family. The genus ''Corvus'', including the crows, rooks, and ravens, makes up over a third of the entire family. Corvids (ravens) are the largest passerines. Corvids display remarkable intelligence for animals of their size, and are among the most intelligent birds thus far studied. Specifically, members of the family have demonstrated self-awareness in mirror tests (European magpies) and tool-making ability (e.g. crows and rooks), skills which until recently were thought to be possessed only by humans and a few other higher mammals. Their total brain-to-body mass ratio is equal to that of non-human great apes and cetaceans, and only slightly lower than that of humans.Birding in India and South AsiaCor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fowl
Fowl are birds belonging to one of two biological orders, namely the gamefowl or landfowl (Galliformes) and the waterfowl (Anseriformes). Anatomical and molecular similarities suggest these two groups are close evolutionary relatives; together, they form the fowl clade which is scientifically known as Galloanserae (initially termed Galloanseri) (Latin ''gallus'' (“rooster”) + ''ānser'' (“goose”)). This clade is also supported by morphological and DNA sequence data as well as retrotransposon presence/absence data. Terminology As opposed to "fowl", "poultry" is a term for any kind of domesticated bird or bird captive-raised for meat, eggs, or feathers; ostriches, for example, are sometimes kept as poultry, but are neither gamefowl nor waterfowl. In colloquial speech, however, the term "fowl" is often used near-synonymously with "poultry," and many languages do not distinguish between "poultry" and "fowl". Nonetheless, the fact that the Galliformes and Anseriformes most ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parrots
Parrots, also known as psittacines (), are birds of the roughly 398 species in 92 genus (biology), genera comprising the order (biology), order Psittaciformes (), found mostly in tropics, tropical and subtropics, subtropical regions. The order is subdivided into three superfamilies: the true parrot, Psittacoidea ("true" parrots), the Cockatoo, Cacatuoidea (cockatoos), and the New Zealand parrot, Strigopoidea (New Zealand parrots). One-third of all parrot species are threatened by extinction, with higher aggregate extinction risk (Red List Index, IUCN Red List Index) than any other comparable bird group. Parrots have a generally pantropical distribution with several species inhabiting temperateness, temperate regions in the Southern Hemisphere, as well. The greatest biodiversity, diversity of parrots is in South America and Australasia. Characteristic features of parrots include a strong, curved beak, bill, an upright stance, strong legs, and clawed Dactyly#In birds, zygodactyl f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bird Intelligence
The difficulty of defining or measuring intelligence in non-human animals makes the subject difficult to study scientifically in birds. In general, birds have relatively large brains compared to their head size. The visual and auditory senses are well developed in most species, though the tactile and olfactory senses are well realized only in a few groups. Birds communicate using visual signals as well as through the use of calls and song. The testing of intelligence in birds is therefore usually based on studying responses to sensory stimuli. The corvids ( ravens, crows, jays, magpies, etc.) and psittacines (parrots, macaws, and cockatoos) are often considered the most intelligent birds, and are among the most intelligent animals in general. Pigeons, finches, domestic fowl, and birds of prey have also been common subjects of intelligence studies. Studies Bird intelligence has been studied through several attributes and abilities. Many of these studies have been on birds such ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rodents
Rodents (from Latin , 'to gnaw') are mammals of the order Rodentia (), which are characterized by a single pair of continuously growing incisors in each of the upper and lower jaws. About 40% of all mammal species are rodents. They are native to all major land masses except for New Zealand, Antarctica, and several oceanic islands, though they have subsequently been introduced to most of these land masses by human activity. Rodents are extremely diverse in their ecology and lifestyles and can be found in almost every terrestrial habitat, including human-made environments. Species can be arboreal, fossorial (burrowing), saltatorial/richochetal (leaping on their hind legs), or semiaquatic. However, all rodents share several morphological features, including having only a single upper and lower pair of ever-growing incisors. Well-known rodents include mice, rats, squirrels, prairie dogs, porcupines, beavers, guinea pigs, and hamsters. Rabbits, hares, and pikas, whose incisors ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |