Parrots on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Parrots, also known as psittacines (), are
 Psittaciform diversity in South America and Australasia suggests that the
Psittaciform diversity in South America and Australasia suggests that the 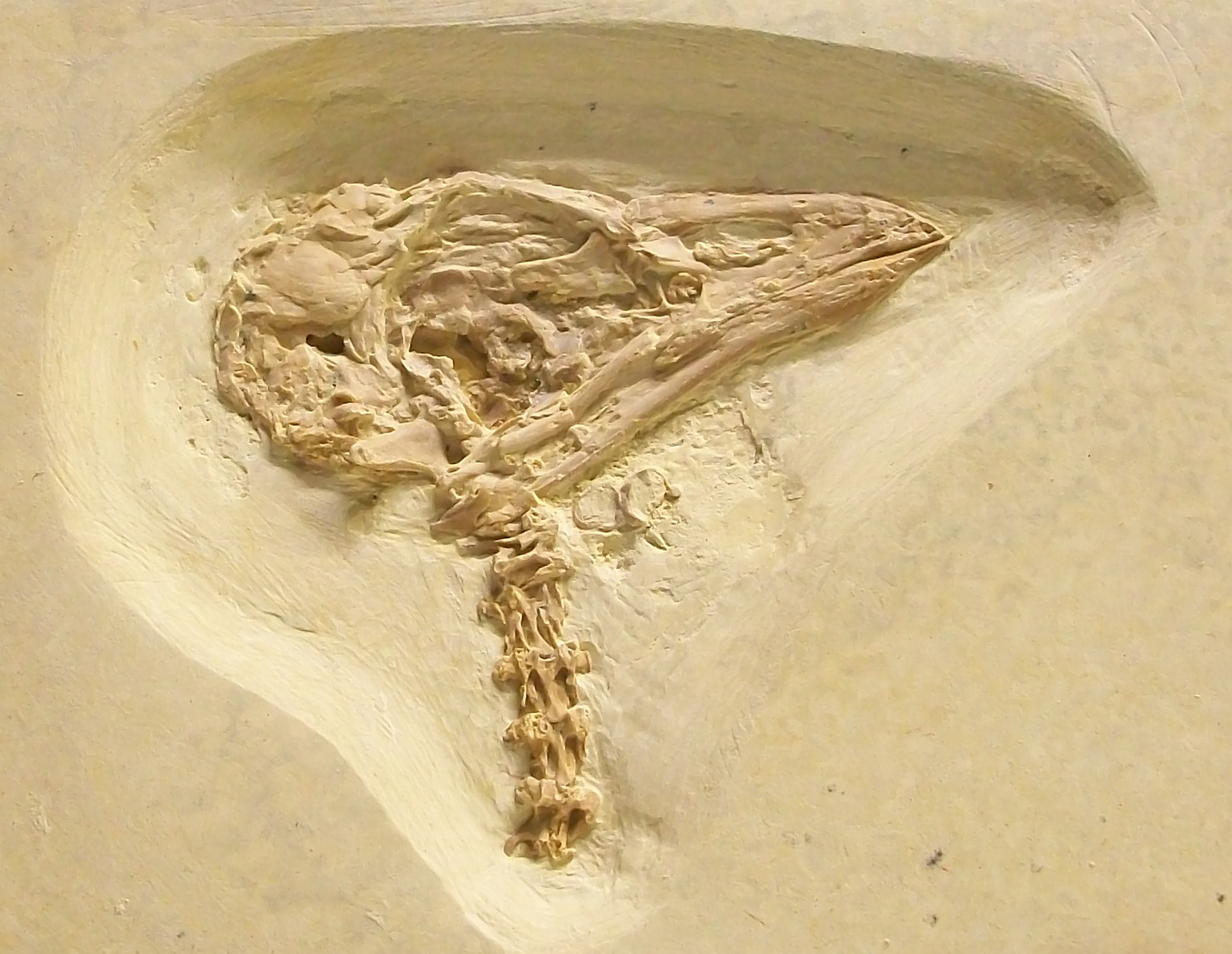 Several fairly complete skeletons of parrot-like birds have been found in England and Germany. These are probably not transitional fossils between ancestral and modern parrots, but rather lineages that evolved parallel to true parrots and cockatoos:
* '' Psittacopes''
* '' Serudaptus''
* Halcyornithidae
** '' Cyrilavis''
** '' Halcyornis''
** '' Pulchrapollia''
** '' Pseudasturides''
* Vastanavidae
** ''
Several fairly complete skeletons of parrot-like birds have been found in England and Germany. These are probably not transitional fossils between ancestral and modern parrots, but rather lineages that evolved parallel to true parrots and cockatoos:
* '' Psittacopes''
* '' Serudaptus''
* Halcyornithidae
** '' Cyrilavis''
** '' Halcyornis''
** '' Pulchrapollia''
** '' Pseudasturides''
* Vastanavidae
** ''
 Superfamily
Superfamily  Subfamily
Subfamily
 Living species range in size from the buff-faced pygmy parrot, at under in weight and in length, to the hyacinth macaw, at in length, and the kakapo, at in weight. Among the superfamilies, the three extant Strigopoidea species are all large parrots, and the cockatoos tend to be large birds, as well. The Psittacoidea parrots are far more variable, ranging the full spectrum of sizes shown by the family.
The most obvious physical characteristic is the strong, curved, broad bill. The upper mandible is prominent, curves downward, and comes to a point. It is not fused to the skull, which allows it to move independently, and contributes to the tremendous biting pressure the birds are able to exert. A large macaw, for example, has a bite force of , close to that of a large dog. The lower mandible is shorter, with a sharp, upward-facing cutting edge, which moves against the flat portion of the upper mandible in an anvil-like fashion. Touch receptors occur along the inner edges of the
Living species range in size from the buff-faced pygmy parrot, at under in weight and in length, to the hyacinth macaw, at in length, and the kakapo, at in weight. Among the superfamilies, the three extant Strigopoidea species are all large parrots, and the cockatoos tend to be large birds, as well. The Psittacoidea parrots are far more variable, ranging the full spectrum of sizes shown by the family.
The most obvious physical characteristic is the strong, curved, broad bill. The upper mandible is prominent, curves downward, and comes to a point. It is not fused to the skull, which allows it to move independently, and contributes to the tremendous biting pressure the birds are able to exert. A large macaw, for example, has a bite force of , close to that of a large dog. The lower mandible is shorter, with a sharp, upward-facing cutting edge, which moves against the flat portion of the upper mandible in an anvil-like fashion. Touch receptors occur along the inner edges of the  Cockatoo species have a mobile crest of feathers on the top of their heads, which they can raise for display, and retract. No other parrots can do so, but the Pacific lorikeets in the genera '' Vini'' and ''
Cockatoo species have a mobile crest of feathers on the top of their heads, which they can raise for display, and retract. No other parrots can do so, but the Pacific lorikeets in the genera '' Vini'' and ''
 Parrots are found on all tropical and subtropical continents and regions including
Parrots are found on all tropical and subtropical continents and regions including  Several parrots inhabit the cool,
Several parrots inhabit the cool,

 Numerous challenges are found in studying wild parrots, as they are difficult to catch and once caught, they are difficult to mark. Most wild bird studies rely on banding or wing tagging, but parrots chew off such attachments. Parrots also tend to range widely, and consequently many gaps occur in knowledge of their behaviour. Some parrots have a strong, direct flight. Most species spend much of their time perched or climbing in tree canopies. They often use their bills for climbing by gripping or hooking on branches and other supports. On the ground, parrots often walk with a rolling gait.
Numerous challenges are found in studying wild parrots, as they are difficult to catch and once caught, they are difficult to mark. Most wild bird studies rely on banding or wing tagging, but parrots chew off such attachments. Parrots also tend to range widely, and consequently many gaps occur in knowledge of their behaviour. Some parrots have a strong, direct flight. Most species spend much of their time perched or climbing in tree canopies. They often use their bills for climbing by gripping or hooking on branches and other supports. On the ground, parrots often walk with a rolling gait.
 Geographical range and body size predominantly explains diet composition of Neotropical parrots rather than phylogeny.
Lories, lorikeets,
Geographical range and body size predominantly explains diet composition of Neotropical parrots rather than phylogeny.
Lories, lorikeets,
 Some grey parrots have shown an ability to associate words with their meanings and form simple sentences. Along with
Some grey parrots have shown an ability to associate words with their meanings and form simple sentences. Along with
 Parrots may not make good pets for most people because of their natural wild instincts such as screaming and chewing. Although parrots can be very affectionate and cute when immature, they often become aggressive when mature (partly due to mishandling and poor training) and may bite, causing serious injury. For this reason, parrot rescue groups estimate that most parrots are surrendered and rehomed through at least five homes before reaching their permanent destinations or before dying prematurely from unintentional or intentional neglect and abuse. The parrots' ability to mimic human words and their bright colours and beauty prompt impulse buying from unsuspecting consumers. The domesticated budgerigar, a small parrot, is the most popular of all pet bird species. In 1992, the newspaper ''
Parrots may not make good pets for most people because of their natural wild instincts such as screaming and chewing. Although parrots can be very affectionate and cute when immature, they often become aggressive when mature (partly due to mishandling and poor training) and may bite, causing serious injury. For this reason, parrot rescue groups estimate that most parrots are surrendered and rehomed through at least five homes before reaching their permanent destinations or before dying prematurely from unintentional or intentional neglect and abuse. The parrots' ability to mimic human words and their bright colours and beauty prompt impulse buying from unsuspecting consumers. The domesticated budgerigar, a small parrot, is the most popular of all pet bird species. In 1992, the newspaper '' Parrots invariably require an enormous amount of attention, care, and intellectual stimulation to thrive, akin to that required by a three-year-old child, which many people find themselves unable to provide in the long term. Parrots that are bred for pets may be hand fed or otherwise accustomed to interacting with people from a young age to help ensure they become tame and trusting. However, even when hand fed, parrots revert to biting and aggression during hormonal surges and if mishandled or neglected. Parrots are not low-maintenance pets; they require feeding, grooming, veterinary care, training, environmental enrichment through the provision of toys, exercise, and social interaction (with other parrots or humans) for good health.
Some large parrot species, including large cockatoos, amazons, and macaws, have very long lifespans, with 80 years being reported, and record ages of over 100. Small parrots, such as lovebirds, hanging parrots, and budgies, have shorter lifespans up to 15–20 years. Some parrot species can be quite loud, and many of the larger parrots can be destructive and require a very large cage, and a regular supply of new toys, branches, or other items to chew up. The intelligence of parrots means they are quick to learn tricks and other behaviours—both good and bad—that get them what they want, such as attention or treats.
The popularity, longevity, and intelligence of many of the larger kinds of pet parrots and their wild traits such as screaming, has led to many birds needing to be rehomed during the course of their long lifespans. A common problem is that large parrots that are cuddly and gentle as juveniles mature into intelligent, complex, often demanding adults who can outlive their owners, and can also become aggressive or even dangerous. Due to an increasing number of homeless parrots, they are being euthanised like dogs and cats, and parrot adoption centres and sanctuaries are becoming more common. Parrots do not often do well in captivity, causing some parrots to go insane and develop repetitive behaviours, such as swaying and screaming, or they become riddled with intense fear. Feather destruction and self-mutilation, although not commonly seen in the wild, occur frequently in captivity.
Parrots invariably require an enormous amount of attention, care, and intellectual stimulation to thrive, akin to that required by a three-year-old child, which many people find themselves unable to provide in the long term. Parrots that are bred for pets may be hand fed or otherwise accustomed to interacting with people from a young age to help ensure they become tame and trusting. However, even when hand fed, parrots revert to biting and aggression during hormonal surges and if mishandled or neglected. Parrots are not low-maintenance pets; they require feeding, grooming, veterinary care, training, environmental enrichment through the provision of toys, exercise, and social interaction (with other parrots or humans) for good health.
Some large parrot species, including large cockatoos, amazons, and macaws, have very long lifespans, with 80 years being reported, and record ages of over 100. Small parrots, such as lovebirds, hanging parrots, and budgies, have shorter lifespans up to 15–20 years. Some parrot species can be quite loud, and many of the larger parrots can be destructive and require a very large cage, and a regular supply of new toys, branches, or other items to chew up. The intelligence of parrots means they are quick to learn tricks and other behaviours—both good and bad—that get them what they want, such as attention or treats.
The popularity, longevity, and intelligence of many of the larger kinds of pet parrots and their wild traits such as screaming, has led to many birds needing to be rehomed during the course of their long lifespans. A common problem is that large parrots that are cuddly and gentle as juveniles mature into intelligent, complex, often demanding adults who can outlive their owners, and can also become aggressive or even dangerous. Due to an increasing number of homeless parrots, they are being euthanised like dogs and cats, and parrot adoption centres and sanctuaries are becoming more common. Parrots do not often do well in captivity, causing some parrots to go insane and develop repetitive behaviours, such as swaying and screaming, or they become riddled with intense fear. Feather destruction and self-mutilation, although not commonly seen in the wild, occur frequently in captivity.
 The popularity of parrots as pets has led to a thriving—and often illegal—trade in the birds, and some species are now threatened with extinction. A combination of trapping of wild birds and damage to parrot habitats makes survival difficult or even impossible for some species of parrot. Importation of wild-caught parrots into the US and Europe is illegal after the Wild Bird Population Act was passed in 1992.
The scale of the problem can be seen in the
The popularity of parrots as pets has led to a thriving—and often illegal—trade in the birds, and some species are now threatened with extinction. A combination of trapping of wild birds and damage to parrot habitats makes survival difficult or even impossible for some species of parrot. Importation of wild-caught parrots into the US and Europe is illegal after the Wild Bird Population Act was passed in 1992.
The scale of the problem can be seen in the
 Parrots have featured in human writings, story, art, humor, religion, and music for thousands of years, such as
Parrots have featured in human writings, story, art, humor, religion, and music for thousands of years, such as
 Escaped parrots of several species have become established in the wild outside their natural ranges and in some cases outside the natural range of parrots. Among the earliest instances were pet red shining-parrots from Fiji, which established a population on the islands of southern
Escaped parrots of several species have become established in the wild outside their natural ranges and in some cases outside the natural range of parrots. Among the earliest instances were pet red shining-parrots from Fiji, which established a population on the islands of southern
 The principal threats of parrots are habitat loss and degradation, hunting, and, for certain species, the wild-bird trade. Parrots are persecuted because, in some areas, they are (or have been) hunted for food and feathers, and as
The principal threats of parrots are habitat loss and degradation, hunting, and, for certain species, the wild-bird trade. Parrots are persecuted because, in some areas, they are (or have been) hunted for food and feathers, and as  One of the largest parrot conservation groups is the World Parrot Trust, an international organisation. The group gives assistance to worthwhile projects, as well as producing a magazine (''PsittaScene'') and raising funds through donations and memberships, often from pet parrot owners. On a smaller scale, local parrot clubs raise money to donate to a conservation cause. Zoo and wildlife centres usually provide public education, to change habits that cause damage to wild populations. Conservation measures to conserve the habitats of some of the high-profile charismatic parrot species has also protected many of the less charismatic species living in the ecosystem. A popular attraction that many zoos employ is a feeding station for lories and lorikeets, where visitors feed them with cups of liquid food. This is usually done in association with educational signs and lectures.
One of the largest parrot conservation groups is the World Parrot Trust, an international organisation. The group gives assistance to worthwhile projects, as well as producing a magazine (''PsittaScene'') and raising funds through donations and memberships, often from pet parrot owners. On a smaller scale, local parrot clubs raise money to donate to a conservation cause. Zoo and wildlife centres usually provide public education, to change habits that cause damage to wild populations. Conservation measures to conserve the habitats of some of the high-profile charismatic parrot species has also protected many of the less charismatic species living in the ecosystem. A popular attraction that many zoos employ is a feeding station for lories and lorikeets, where visitors feed them with cups of liquid food. This is usually done in association with educational signs and lectures.
Parrot videos
on the Internet Bird Collection {{authority control Articles containing video clips Extant Ypresian first appearances
bird
Birds are a group of warm-blooded vertebrates constituting the class Aves (), characterised by feathers, toothless beaked jaws, the laying of hard-shelled eggs, a high metabolic rate, a four-chambered heart, and a strong yet lightweig ...
s of the roughly 398 species
In biology, a species is the basic unit of classification and a taxonomic rank of an organism, as well as a unit of biodiversity. A species is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriat ...
in 92 genera
Genus ( plural genera ) is a taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of living and fossil organisms as well as viruses. In the hierarchy of biological classification, genus comes above species and below family. In binomial nomenclat ...
comprising the order
Order, ORDER or Orders may refer to:
* Categorization, the process in which ideas and objects are recognized, differentiated, and understood
* Heterarchy, a system of organization wherein the elements have the potential to be ranked a number of ...
Psittaciformes (), found mostly in tropical
The tropics are the regions of Earth surrounding the Equator. They are defined in latitude by the Tropic of Cancer in the Northern Hemisphere at N and the Tropic of Capricorn in
the Southern Hemisphere at S. The tropics are also referred to ...
and subtropical
The subtropical zones or subtropics are geographical and climate zones to the north and south of the tropics. Geographically part of the temperate zones of both hemispheres, they cover the middle latitudes from to approximately 35° north a ...
regions. The order is subdivided into three superfamilies: the Psittacoidea
The true parrots are about 350 species of hook-billed, mostly herbivorous birds forming the superfamily Psittacoidea, one of the three superfamilies in the biological order Psittaciformes (parrots). True parrots are widespread, with species i ...
("true" parrots), the Cacatuoidea
A cockatoo is any of the 21 parrot species belonging to the family Cacatuidae, the only family in the superfamily Cacatuoidea. Along with the Psittacoidea ( true parrots) and the Strigopoidea (large New Zealand parrots), they make up the ...
(cockatoos), and the Strigopoidea
The New Zealand parrot family, Strigopidae,Nestoridae and Strigopidae are described in the same article, Bonaparte, C.L. (1849) ''Conspectus Systematis Ornithologiae''. Therefore, under rules of the ICZN, the first reviser determines priority, w ...
(New Zealand parrots). One-third of all parrot species are threatened by extinction
Extinction is the termination of a kind of organism or of a group of kinds (taxon), usually a species. The moment of extinction is generally considered to be the death of the Endling, last individual of the species, although the Functional ext ...
, with higher aggregate extinction risk ( IUCN Red List Index) than any other comparable bird group. Parrots have a generally pantropical
A pantropical ("all tropics") distribution is one which covers tropical regions of both hemispheres. Examples of species include caecilians, modern sirenians and the plant genera ''Acacia'' and '' Bacopa''.
''Neotropical'' is a zoogeographic te ...
distribution with several species inhabiting temperate
In geography, the temperate climates of Earth occur in the middle latitudes (23.5° to 66.5° N/S of Equator), which span between the tropics and the polar regions of Earth. These zones generally have wider temperature ranges throughout ...
regions in the Southern Hemisphere, as well. The greatest diversity of parrots is in South America
South America is a continent entirely in the Western Hemisphere and mostly in the Southern Hemisphere, with a relatively small portion in the Northern Hemisphere at the northern tip of the continent. It can also be described as the sou ...
and Australasia
Australasia is a region that comprises Australia, New Zealand and some neighbouring islands in the Pacific Ocean. The term is used in a number of different contexts, including geopolitically, physiogeographically, philologically, and ecologic ...
.
Characteristic features of parrots include a strong, curved bill
Bill(s) may refer to:
Common meanings
* Banknote, paper cash (especially in the United States)
* Bill (law), a proposed law put before a legislature
* Invoice, commercial document issued by a seller to a buyer
* Bill, a bird or animal's beak
Pla ...
, an upright stance, strong legs, and clawed zygodactyl feet. Many parrots are vividly coloured, and some are multi-coloured. Most parrots exhibit little or no sexual dimorphism
Sexual dimorphism is the condition where the sexes of the same animal and/or plant species exhibit different morphological characteristics, particularly characteristics not directly involved in reproduction. The condition occurs in most an ...
in the visual spectrum. They form the most variably sized bird order in terms of length.
The most important components of most parrots' diets are seeds, nuts, fruit, buds, and other plant material. A few species sometimes eat animals and carrion
Carrion () is the decaying flesh of dead animals, including human flesh.
Overview
Carrion is an important food source for large carnivores and omnivores in most ecosystems. Examples of carrion-eaters (or scavengers) include crows, vultures ...
, while the lories and lorikeets
Loriini is a tribe of small to medium-sized arboreal parrots characterized by their specialized brush-tipped tongues for feeding on nectar of various blossoms and soft fruits, preferably berries. The species form a monophyletic group within the ...
are specialised for feeding on floral nectar
Nectar is a sugar-rich liquid produced by plants in glands called nectaries or nectarines, either within the flowers with which it attracts pollinating animals, or by extrafloral nectaries, which provide a nutrient source to animal mutualist ...
and soft fruits. Almost all parrots nest in tree hollows (or nest boxes in captivity), and lay white eggs from which hatch altricial
In biology, altricial species are those in which the young are underdeveloped at the time of birth, but with the aid of their parents mature after birth. Precocial species are those in which the young are relatively mature and mobile from the mome ...
(helpless) young.
Parrots, along with ravens, crows, jays, and magpies, are among the most intelligent birds, and the ability of some species to imitate human speech enhances their popularity as pet
A pet, or companion animal, is an animal kept primarily for a person's company or entertainment rather than as a working animal, livestock, or a laboratory animal. Popular pets are often considered to have attractive appearances, intelligence ...
s. Trapping
Animal trapping, or simply trapping or gin, is the use of a device to remotely catch an animal. Animals may be trapped for a variety of purposes, including food, the fur trade, hunting, pest control, and wildlife management.
History
Neolithi ...
wild parrots for the pet trade, as well as hunting
Hunting is the human activity, human practice of seeking, pursuing, capturing, or killing wildlife or feral animals. The most common reasons for humans to hunt are to harvest food (i.e. meat) and useful animal products (fur/hide (skin), hide, ...
, habitat loss
Habitat destruction (also termed habitat loss and habitat reduction) is the process by which a natural habitat becomes incapable of supporting its native species. The organisms that previously inhabited the site are displaced or dead, thereby ...
, and competition
Competition is a rivalry where two or more parties strive for a common goal which cannot be shared: where one's gain is the other's loss (an example of which is a zero-sum game). Competition can arise between entities such as organisms, ind ...
from invasive species
An invasive species otherwise known as an alien is an introduced organism that becomes overpopulated and harms its new environment. Although most introduced species are neutral or beneficial with respect to other species, invasive species adv ...
, has diminished wild populations, with parrots being subjected to more exploitation than any other group of birds. As of 2021, about 50 million parrots (half of all parrots) live in captivity, with the vast majority of these living as pets in people's homes. Measures taken to conserve the habitats of some high-profile charismatic species have also protected many of the less charismatic species living in the same ecosystem
An ecosystem (or ecological system) consists of all the organisms and the physical environment with which they interact. These biotic and abiotic components are linked together through nutrient cycles and energy flows. Energy enters the syst ...
s.
Parrots are the only creatures that display true tripedalism, using their necks and beaks as limbs with propulsive forces equal to or greater than those forces generated by the forelimbs of primates
Primates are a diverse order of mammals. They are divided into the strepsirrhines, which include the lemurs, galagos, and lorisids, and the haplorhines, which include the tarsiers and the simians ( monkeys and apes, the latter including ...
when climbing vertical surfaces. They can travel with cyclical tripedal gaits when climbing.Melody W. Young, Edwin Dickinson, Nicholas D. Flaim and Michael C. Granatosky (2022). Overcoming a ‘forbidden phenotype’: the parrot’s head supports, propels and powers tripedal locomotion, ''Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences'', 20220245, https://doi.org/10.1098/rspb.2022.0245
Taxonomy
Origins and evolution
 Psittaciform diversity in South America and Australasia suggests that the
Psittaciform diversity in South America and Australasia suggests that the order
Order, ORDER or Orders may refer to:
* Categorization, the process in which ideas and objects are recognized, differentiated, and understood
* Heterarchy, a system of organization wherein the elements have the potential to be ranked a number of ...
may have evolved in Gondwana
Gondwana () was a large landmass, often referred to as a supercontinent, that formed during the late Neoproterozoic (about 550 million years ago) and began to break up during the Jurassic period (about 180 million years ago). The final sta ...
, centred in Australasia. The scarcity of parrots in the fossil record, however, presents difficulties in confirming the hypothesis. There is currently a higher amount of fossil remains from the northern hemisphere in the early Cenozoic.Mayr, G. (2009). Paleogene fossil birds. Springer. Molecular studies suggest that parrots evolved approximately 59 million years ago
The abbreviation Myr, "million years", is a unit of a quantity of (i.e. ) years, or 31.556926 teraseconds.
Usage
Myr (million years) is in common use in fields such as Earth science and cosmology. Myr is also used with Mya (million years ago ...
(Mya) (range 66–51 Mya) in Gondwana. The three major clades of Neotropical parrots originated about 50 Mya (range 57–41 Mya).
A single fragment from a large lower bill
Bill(s) may refer to:
Common meanings
* Banknote, paper cash (especially in the United States)
* Bill (law), a proposed law put before a legislature
* Invoice, commercial document issued by a seller to a buyer
* Bill, a bird or animal's beak
Pla ...
(UCMP
The University of California Museum of Paleontology (UCMP) is a paleontology museum located on the campus of the University of California, Berkeley.
The museum is within the Valley Life Sciences Building (VLSB), designed by George W. Kelham and ...
143274), found in deposits from the Lance Creek Formation in Niobrara County, Wyoming, had been thought to be the oldest parrot fossil and is presumed to have originated from the Late Cretaceous
The Late Cretaceous (100.5–66 Ma) is the younger of two epochs into which the Cretaceous Period is divided in the geologic time scale. Rock strata from this epoch form the Upper Cretaceous Series. The Cretaceous is named after ''creta'', ...
period, which makes it about 70 million years old. However, other studies suggest that this fossil is not from a bird, but from a caenagnathid
Caenagnathidae is a family of bird-like maniraptoran theropod dinosaurs from the Cretaceous of North America and Asia. They are a member of the Oviraptorosauria, and close relatives of the Oviraptoridae. Like other oviraptorosaurs, caenagnathids ...
oviraptorosaur (a non-avian dinosaur with a birdlike beak), as several details of the fossil used to support its identity as a parrot are not actually exclusive to parrots, and it is dissimilar to the earliest-known unequivocal parrot fossils.
It is generally assumed that the Psittaciformes were present during the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event
The Cretaceous–Paleogene (K–Pg) extinction event (also known as the Cretaceous–Tertiary extinction) was a sudden mass extinction of three-quarters of the plant and animal species on Earth, approximately 66 million years ago. With the ...
(K-Pg extinction), 66 mya. They were probably generalised arboreal
Arboreal locomotion is the locomotion of animals in trees. In habitats in which trees are present, animals have evolved to move in them. Some animals may scale trees only occasionally, but others are exclusively arboreal. The habitats pose nu ...
birds, and did not have the specialised crushing bills of modern species. Genomic analysis provides strong evidence that parrots are the sister group
In phylogenetics, a sister group or sister taxon, also called an adelphotaxon, comprises the closest relative(s) of another given unit in an evolutionary tree.
Definition
The expression is most easily illustrated by a cladogram:
Taxon A and ...
of passerine
A passerine () is any bird of the order Passeriformes (; from Latin 'sparrow' and '-shaped'), which includes more than half of all bird species. Sometimes known as perching birds, passerines are distinguished from other orders of birds by th ...
s, forming the clade Psittacopasserae
Psittacopasserae is a taxon of birds consisting of the Passeriformes (passerines, a large group of perching birds) and Psittaciformes (parrots). Per Ericson and colleagues, in analysing genomic DNA, revealed a lineage comprising passerines, psit ...
, which is the sister group of the falcons
Falcons () are birds of prey in the genus ''Falco'', which includes about 40 species. Falcons are widely distributed on all continents of the world except Antarctica, though closely related raptors did occur there in the Eocene.
Adult falcons ...
.
The first uncontroversial parrot fossils date to tropical Eocene
The Eocene ( ) Epoch is a geological epoch that lasted from about 56 to 33.9 million years ago (mya). It is the second epoch of the Paleogene Period in the modern Cenozoic Era. The name ''Eocene'' comes from the Ancient Greek (''ēṓs'', ...
Europe around 50 mya. Initially, a neoavian
Neoaves is a clade that consists of all modern birds (Neornithes or Aves) with the exception of Paleognathae (ratites and kin) and Galloanserae (ducks, chickens and kin). Almost 95% of the roughly 10,000 known species of extant birds belong to t ...
named ''Mopsitta tanta
''Mopsitta tanta'' is an extinct bird of uncertain taxonomic position from the Early Eocene of Denmark; its remains were recovered from the Fur Formation. So far, the holotype and only known specimen is a single humerus bone of rather large ...
'', uncovered in Denmark's Early Eocene
In the geologic timescale the Ypresian is the oldest age or lowest stratigraphic stage of the Eocene. It spans the time between , is preceded by the Thanetian Age (part of the Paleocene) and is followed by the Eocene Lutetian Age. The Ypresian ...
Fur Formation and dated to 54 mya, was assigned to the Psittaciformes. However, the rather nondescript bone is not unequivocally psittaciform, and it may rather belong to the ibis
The ibises () (collective plural ibis; classical plurals ibides and ibes) are a group of long-legged wading birds in the family Threskiornithidae, that inhabit wetlands, forests and plains. "Ibis" derives from the Latin and Ancient Greek word ...
genus ''Rhynchaeites
''Rhynchaeites'' is an extinct genus of Threskiornithidae related to modern ibises and has a single named species ''Rhynchaeites meselensis''. It lived in today's Germany during the mid-Eocene and its remains were found in the famous Messel pit. ...
'', whose fossil legs were found in the same deposits.
 Several fairly complete skeletons of parrot-like birds have been found in England and Germany. These are probably not transitional fossils between ancestral and modern parrots, but rather lineages that evolved parallel to true parrots and cockatoos:
* '' Psittacopes''
* '' Serudaptus''
* Halcyornithidae
** '' Cyrilavis''
** '' Halcyornis''
** '' Pulchrapollia''
** '' Pseudasturides''
* Vastanavidae
** ''
Several fairly complete skeletons of parrot-like birds have been found in England and Germany. These are probably not transitional fossils between ancestral and modern parrots, but rather lineages that evolved parallel to true parrots and cockatoos:
* '' Psittacopes''
* '' Serudaptus''
* Halcyornithidae
** '' Cyrilavis''
** '' Halcyornis''
** '' Pulchrapollia''
** '' Pseudasturides''
* Vastanavidae
** ''Vastanavis
''Vastanavis'' is a genus of parrot-like bird that lived in what is now western India in the Early Eocene.
Footnotes
Eocene birds
Fossil taxa described in 2007
Prehistoric birds of Asia
Prehistoric bird genera
{{paleo-bird-stub ...
''
* Quercypsittidae
''Quercypsitta'' is a genus of prehistoric bird from the Late Eocene (''circa'' 37-34 Mya) Quercy phosphorites in France.
Known from rather fragmentary remains (some foot and wing bones for the type species ''Q. sudrei'', three coracoids fo ...
** '' Quercypsitta''
* Messelasturidae
** ''Messelastur
''Messelastur'' is a genus of messelasturid bird. It is known from the Messel pit of Germany, which dates to the Eocene.Peters, D.S. (1994) ''Messelastur gratulator'' n. gen. n. spec., ein Greifvogel as der Grube Messel (Aves: Accipitridae). ' ...
''
** ''Tynskya
''Tynskya'' is a genus of messelasturid bird. It is known from a fossil of the North American Green River Formation and the London Clay Formation of England, both from the early Eocene
The Eocene ( ) Epoch is a geological epoch that lasted ...
''
The earliest records of modern parrots date to around 23–20 mya. The fossil record—mainly from Europe—consists of bones clearly recognisable as belonging to anatomically modern parrots. The Southern Hemisphere contains no known parrot-like remains earlier than the Early Miocene
The Early Miocene (also known as Lower Miocene) is a sub-epoch of the Miocene epoch (geology), Epoch made up of two faunal stage, stages: the Aquitanian age, Aquitanian and Burdigalian stages.
The sub-epoch lasted from 23.03 ± 0.05 annum, Ma to ...
around 20 mya.
Etymology
The name 'Psittaciformes' comes from theancient Greek
Ancient Greek includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Dark Ages (), the Archaic pe ...
for parrot, (), whose origin is unclear. Ctesias
Ctesias (; grc-gre, Κτησίας; fl. fifth century BC), also known as Ctesias of Cnidus, was a Greek physician and historian from the town of Cnidus in Caria, then part of the Achaemenid Empire.
Historical events
Ctesias, who lived in the fi ...
(5th century BCE) recorded the name after the Indian name for a bird, most likely a parakeet (now placed in the genus ''Psittacula
Members of the parrot genus ''Psittacula'' or Afro-Asian ring-necked parrots they are commonly known in aviculture originate from Africa to South-East Asia. It is a widespread group with a clear concentration of species in south Asia, but also ...
''). Pliny the Elder
Gaius Plinius Secundus (AD 23/2479), called Pliny the Elder (), was a Roman author, naturalist and natural philosopher, and naval and army commander of the early Roman Empire, and a friend of the emperor Vespasian. He wrote the encyclopedic ' ...
(23/24–79 CE) in his ''Natural History'' (book 10, chapter 58) noted that the Indians called the bird as "siptaces"; however, no matching Indian name has been traced.
Phylogeny
The Psittaciformes comprise three main lineages:Strigopoidea
The New Zealand parrot family, Strigopidae,Nestoridae and Strigopidae are described in the same article, Bonaparte, C.L. (1849) ''Conspectus Systematis Ornithologiae''. Therefore, under rules of the ICZN, the first reviser determines priority, w ...
, Psittacoidea
The true parrots are about 350 species of hook-billed, mostly herbivorous birds forming the superfamily Psittacoidea, one of the three superfamilies in the biological order Psittaciformes (parrots). True parrots are widespread, with species i ...
and Cacatuoidea
A cockatoo is any of the 21 parrot species belonging to the family Cacatuidae, the only family in the superfamily Cacatuoidea. Along with the Psittacoidea ( true parrots) and the Strigopoidea (large New Zealand parrots), they make up the ...
. The Strigopoidea were considered part of the Psittacoidea, but the former is now placed at the base of the parrot tree next to the remaining members of the Psittacoidea, as well as all members of the Cacatuoidea. The Cacatuoidea are quite distinct, having a movable head crest, a different arrangement of the carotid
In anatomy, the left and right common carotid arteries (carotids) (Entry "carotid"
in
gall bladder In vertebrates, the gallbladder, also known as the cholecyst, is a small hollow organ where bile is stored and concentrated before it is released into the small intestine. In humans, the pear-shaped gallbladder lies beneath the liver, although ...
, differences in the skull bones, and lack the in
gall bladder In vertebrates, the gallbladder, also known as the cholecyst, is a small hollow organ where bile is stored and concentrated before it is released into the small intestine. In humans, the pear-shaped gallbladder lies beneath the liver, although ...
Dyck texture
Feathers are epidermal growths that form a distinctive outer covering, or plumage, on both avian (bird) and some non-avian dinosaurs and other archosaurs. They are the most complex integumentary structures found in vertebrates and a premier ...
feathers that—in the Psittacidae—scatter light to produce the vibrant colours of so many parrots. Colourful feathers with high levels of psittacofulvin resist the feather-degrading bacterium
Bacteria (; singular: bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one biological cell. They constitute a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria were am ...
'' Bacillus licheniformis'' better than white ones. Lorikeets were previously regarded as a third family, Loriidae, but are now considered a tribe (Loriini
Loriini is a tribe of small to medium-sized arboreal parrots characterized by their specialized brush-tipped tongues for feeding on nectar of various blossoms and soft fruits, preferably berries. The species form a monophyletic group within the ...
) within the subfamily Loriinae
Loriinae is a subfamily of psittacine birds, one of the five subfamilies that make up the family Psittaculidae. It consists of three tribes, the lories and lorikeets ( Loriini), the budgerigar ( Melopsittacini) and the fig parrots ( Cyclopsittini ...
, family Psittaculidae. The two other tribes in the subfamily are the closely related fig parrots (two genera in the tribe Cyclopsittini
Fig parrots (Cyclopsittini) are a small tribe of Australasian parrots in the family Psittaculidae, made up of five species in two genera (''Cyclopsitta'' and '' Psittaculirostris''). Fig parrots are found on and around the island of New Guinea, ...
) and budgerigar
The budgerigar ( ; ''Melopsittacus undulatus''), also known as the common parakeet or shell parakeet, is a small, long-tailed, seed-eating parrot usually nicknamed the budgie ( ), or in American English, the parakeet. Budgies are the only spe ...
(tribe Melopsittacini).
Systematics
The order Psittaciformes consists of roughly 393 species belonging to 92 genera. Superfamily
Superfamily Strigopoidea
The New Zealand parrot family, Strigopidae,Nestoridae and Strigopidae are described in the same article, Bonaparte, C.L. (1849) ''Conspectus Systematis Ornithologiae''. Therefore, under rules of the ICZN, the first reviser determines priority, w ...
: New Zealand parrots
* Family Nestoridae: two genera with two living ( kea and New Zealand kaka) and several extinct species of the New Zealand region
* Family Strigopidae: the flightless, critically endangered kakapo of New Zealand
Superfamily Cacatuoidea
A cockatoo is any of the 21 parrot species belonging to the family Cacatuidae, the only family in the superfamily Cacatuoidea. Along with the Psittacoidea ( true parrots) and the Strigopoidea (large New Zealand parrots), they make up the ...
: cockatoos
* Family Cacatuidae
A cockatoo is any of the 21 parrot species belonging to the family Cacatuidae, the only family in the superfamily Cacatuoidea. Along with the Psittacoidea (true parrots) and the Strigopoidea (large New Zealand parrots), they make up the orde ...
** Subfamily Nymphicinae: one genus with one species, the cockatiel
The cockatiel (; ''Nymphicus hollandicus''), also known as weiro (also spelt weero), or quarrion, is a medium-sized parrot that is a member of its own branch of the cockatoo family endemic to Australia. They are prized as household pets and c ...
.
** Subfamily Calyptorhynchinae: the black cockatoos
** Subfamily Cacatuinae
The subfamily Cacatuinae consists of two tribes, the Microglossini with one species (palm cockatoo) and the Cacatuini
The tribe Cacatuini consists of four whitish, pinkish or greyish genera:
References
Bird tribes
Cacatuinae
{{pa ...
*** Tribe Microglossini
The palm cockatoo (''Probosciger aterrimus''), also known as the goliath cockatoo or great black cockatoo, is a large smoky-grey or black parrot of the cockatoo family native to New Guinea, Aru Islands, and Cape York Peninsula. It has a very l ...
: one genus with one species, the black palm cockatoo
The palm cockatoo (''Probosciger aterrimus''), also known as the goliath cockatoo or great black cockatoo, is a large smoky-grey or black parrot of the cockatoo family native to New Guinea, Aru Islands, and Cape York Peninsula. It has a ver ...
*** Tribe Cacatuini
The tribe Cacatuini consists of four whitish, pinkish or greyish genera:
References
Bird tribes
Cacatuinae
{{parrot-stub ...
: four genera of white, pink, and grey species
Superfamily Psittacoidea
The true parrots are about 350 species of hook-billed, mostly herbivorous birds forming the superfamily Psittacoidea, one of the three superfamilies in the biological order Psittaciformes (parrots). True parrots are widespread, with species i ...
: true parrots
* Family Psittacidae
The family Psittacidae or holotropical parrots is one of three families of true parrots. It comprises the roughly 10 species of subfamily Psittacinae (the Old World or Afrotropical parrots) and 157 of subfamily Arinae (the New World or Neotropi ...
** Subfamily Psittacinae: two African genera, '' Psittacus'' and '' Poicephalus''
** Subfamily Arinae
*** Tribe Arini: 18 genera
*** Tribe Androglossini: seven genera.
* Family Psittrichasiidae
Psittrichasiidae is a family of birds belonging to the superfamily of the true parrots (Psittacoidea).Leo Joseph, Alicia Toon, Erin E. Schirtzinger, Timothy F. Wright, Richard Schodde. 2012. A revised nomenclature and classification for family-gr ...
** Subfamily Psittrichasinae: one species, Pesquet's parrot
Pesquet's parrot (''Psittrichas fulgidus''), also known as the Dracula parrot or as the vulturine parrot (leading to easy confusion with '' Pyrilia vulturina'' from Brazil), is the only member of its genus. It is endemic to hill and montane rain ...
** Subfamily Coracopsinae: one genus with four species.
* Family Psittaculidae
Psittaculidae is a family containing Old World parrots. It consists of five subfamilies: Agapornithinae, Loriinae, Platycercinae, Psittacellinae and Psittaculinae.
This family has been accepted into '' The Clements Checklist of Birds of the W ...
** Subfamily Platycercinae
Platycercinae is a subfamily of birds belonging to the family Psittaculidae that inhabit Oceania. It consists of two tribes, the ground parrots and allies ( Pezoporini) and the many species of broad-tailed parrot ( Platycercini).
Genera
Tribe ...
*** Tribe Pezoporini: ground parrots and allies
*** Tribe Platycercini: broad-tailed parrots
** Subfamily Psittacellinae
Tiger parrots are members of the genus ''Psittacella'' (the only genus in the subfamily Psittacellinae) in the family Psittaculidae, named for their tiger-striped backs. Established by Hermann Schlegel in 1871, the genus contains the following s ...
: one genus (''Psittacella
Tiger parrots are members of the genus ''Psittacella'' (the only genus in the subfamily Psittacellinae) in the family Psittaculidae, named for their tiger-striped backs. Established by Hermann Schlegel in 1871, the genus contains the following ...
'') with several species
** Subfamily Loriinae
Loriinae is a subfamily of psittacine birds, one of the five subfamilies that make up the family Psittaculidae. It consists of three tribes, the lories and lorikeets ( Loriini), the budgerigar ( Melopsittacini) and the fig parrots ( Cyclopsittini ...
*** Tribe Loriini
Loriini is a tribe of small to medium-sized arboreal parrots characterized by their specialized brush-tipped tongues for feeding on nectar of various blossoms and soft fruits, preferably berries. The species form a monophyletic group within the ...
: lories and lorikeets
*** Tribe Melopsittacini: one genus with one species, the budgerigar
The budgerigar ( ; ''Melopsittacus undulatus''), also known as the common parakeet or shell parakeet, is a small, long-tailed, seed-eating parrot usually nicknamed the budgie ( ), or in American English, the parakeet. Budgies are the only spe ...
*** Tribe Cyclopsittini
Fig parrots (Cyclopsittini) are a small tribe of Australasian parrots in the family Psittaculidae, made up of five species in two genera (''Cyclopsitta'' and '' Psittaculirostris''). Fig parrots are found on and around the island of New Guinea, ...
: fig parrots
** Subfamily
Subfamily Agapornithinae
Agapornithinae is a subfamily of psittacine birds, one of the five subfamilies that make up the family Psittaculidae.Leo Joseph, Alicia Toon, Erin E. Schirtzinger, Timothy F. Wright, Richard Schodde. 2012. A revised nomenclature and classificati ...
: three genera
** Subfamily Psittaculinae
The parrot subfamily Psittaculinae consists of three tribes: the Polytelini with three genera, the Psittaculini or Asian psittacines, and the pygmy parrots of the Micropsittini tribe.Joseph L., Alicia Toon, Erin E. Schirtzinger, Timothy F. Wrig ...
*** Tribe Polytelini
The Polytelini tribe belongs to the parrot family Psittaculidae and consists of three genera.Joseph L., Alicia Toon, Erin E. Schirtzinger, Timothy F. Wright, Richard SchoddeA revised nomenclature and classification for family-group taxa of parrot ...
: three genera
*** Tribe Psittaculini
Psittaculini is a tribe of parrots of the family Psittaculidae. The subdivisions within the tribe are controversial.
Tribe Psittaculini
* Genus '' Psittinus''
** Blue-rumped parrot, ''Psittinus cyanurus''
** Simeulue parrot, ''Psittinus abbo ...
: Asian psittacines
*** Tribe Micropsittini: pygmy parrot
Pygmy parrots are the smallest members of the parrot order. The six species of pygmy parrots are all in the genus ''Micropsitta'', which is the only genus in the Micropsittini tribe.
Pygmy parrots are native to the forests of New Guinea and near ...
s
Morphology
keratin
Keratin () is one of a family of structural fibrous proteins also known as ''scleroproteins''. Alpha-keratin (α-keratin) is a type of keratin found in vertebrates. It is the key structural material making up Scale (anatomy), scales, hair, Nail ...
ised bill, which are collectively known as the "bill tip organ
The beak, bill, or rostrum is an external anatomical structure found mostly in birds, but also in turtles, non-avian dinosaurs and a few mammals. A beak is used for eating, preening, manipulating objects, killing prey, fighting, probing for food, ...
", allowing for highly dexterous manipulations. Seed-eating parrots have a strong tongue
The tongue is a muscular organ in the mouth of a typical tetrapod. It manipulates food for mastication and swallowing as part of the digestive process, and is the primary organ of taste. The tongue's upper surface (dorsum) is covered by taste ...
(containing similar touch receptors to those in the bill tip organ), which helps to manipulate seeds or position nuts in the bill so that the mandibles can apply an appropriate cracking force. The head is large, with eyes positioned high and laterally in the skull, so the visual field of parrots is unlike any other birds. Without turning its head, a parrot can see from just below its bill tip, all above its head, and quite far behind its head. Parrots also have quite a wide frontal binocular field for a bird, although this is nowhere near as large as primate binocular visual fields. Unlike humans, the vision of parrots is also sensitive to ultraviolet light.
Parrots have strong zygodactyl feet (two toes facing forward and two back) with sharp, elongated claws, which are used for climbing and swinging. Most species are capable of using their feet to manipulate food and other objects with a high degree of dexterity, in a similar manner to a human using their hands. A study conducted with Australian parrots has demonstrated that they exhibit "handedness
In human biology, handedness is an individual's preferential use of one hand, known as the dominant hand, due to it being stronger, faster or more dextrous. The other hand, comparatively often the weaker, less dextrous or simply less subject ...
", a distinct preference with regards to the foot used to pick up food, with adult parrots being almost exclusively "left-footed" or "right-footed", and with the prevalence of each preference within the population varying by species.
 Cockatoo species have a mobile crest of feathers on the top of their heads, which they can raise for display, and retract. No other parrots can do so, but the Pacific lorikeets in the genera '' Vini'' and ''
Cockatoo species have a mobile crest of feathers on the top of their heads, which they can raise for display, and retract. No other parrots can do so, but the Pacific lorikeets in the genera '' Vini'' and ''Phigys
The collared lory (''Vini solitaria'') is a species of parrot in the family Psittaculidae. It is endemic to the islands of Fiji. It is the only Fijian rainforest bird to adapt to urban landscapes and can be found in urban Suva. Measuring , i ...
'' can ruffle the feathers of the crown and nape, and the red-fan parrot
The red-fan parrot (''Deroptyus accipitrinus''), also known as the hawk-headed parrot, is a New World parrot hailing from the Amazon Rainforest. It is the only member of the genus ''Deroptyus''.
It dwells in Brazil, Suriname, Bolivia, Ecuador, ...
(or hawk-headed parrot) has a prominent feather neck frill
A neck frill is the relatively extensive margin seen on the back of the heads of reptiles with either a bony support such as those present on the skulls of dinosaurs of the suborder Marginocephalia or a cartilaginous one as in the frill-necke ...
that it can raise and lower at will. The predominant colour of plumage
Plumage ( "feather") is a layer of feathers that covers a bird and the pattern, colour, and arrangement of those feathers. The pattern and colours of plumage differ between species and subspecies and may vary with age classes. Within species, ...
in parrots is green, though most species have some red or another colour in small quantities. Cockatoos, however, are predominately black or white with some red, pink, or yellow. Strong sexual dimorphism
Sexual dimorphism is the condition where the sexes of the same animal and/or plant species exhibit different morphological characteristics, particularly characteristics not directly involved in reproduction. The condition occurs in most an ...
in plumage is not typical among parrots, with some notable exceptions, the most striking being the eclectus parrot. However it has been shown that some parrot species exhibit sexually dimorphic plumage in the ultraviolet spectrum, normally invisible to humans.
Distribution and habitat
 Parrots are found on all tropical and subtropical continents and regions including
Parrots are found on all tropical and subtropical continents and regions including Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a sovereign country comprising the mainland of the Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous smaller islands. With an area of , Australia is the largest country by ...
and Oceania
Oceania (, , ) is a geographical region that includes Australasia, Melanesia, Micronesia, and Polynesia. Spanning the Eastern and Western hemispheres, Oceania is estimated to have a land area of and a population of around 44.5 million ...
, South Asia
South Asia is the southern subregion of Asia, which is defined in both geographical and ethno-cultural terms. The region consists of the countries of Afghanistan, Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, Maldives, Nepal, Pakistan, and Sri Lanka.;;;;; ...
, Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia, also spelled South East Asia and South-East Asia, and also known as Southeastern Asia, South-eastern Asia or SEA, is the geographical south-eastern region of Asia, consisting of the regions that are situated south of mainland ...
, Central America
Central America ( es, América Central or ) is a subregion of the Americas. Its boundaries are defined as bordering the United States to the north, Colombia to the south, the Caribbean Sea to the east, and the Pacific Ocean to the west. ...
, South America
South America is a continent entirely in the Western Hemisphere and mostly in the Southern Hemisphere, with a relatively small portion in the Northern Hemisphere at the northern tip of the continent. It can also be described as the sou ...
, and Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent, after Asia in both cases. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of Earth's total surface area ...
. Some Caribbean and Pacific islands are home to endemic species
Endemism is the state of a species being found in a single defined geographic location, such as an island, state, nation, country or other defined zone; organisms that are indigenous to a place are not endemic to it if they are also found else ...
. By far the greatest number of parrot species come from Australasia and South America. The lories and lorikeets range from Sulawesi
Sulawesi (), also known as Celebes (), is an island in Indonesia. One of the four Greater Sunda Islands, and the world's eleventh-largest island, it is situated east of Borneo, west of the Maluku Islands, and south of Mindanao and the Sulu ...
and the Philippines
The Philippines (; fil, Pilipinas, links=no), officially the Republic of the Philippines ( fil, Republika ng Pilipinas, links=no),
* bik, Republika kan Filipinas
* ceb, Republika sa Pilipinas
* cbk, República de Filipinas
* hil, Republ ...
in the north to Australia and across the Pacific as far as French Polynesia
)Territorial motto: ( en, "Great Tahiti of the Golden Haze")
, anthem =
, song_type = Regional anthem
, song = "Ia Ora 'O Tahiti Nui"
, image_map = French Polynesia on the globe (French Polynesia centered).svg
, map_alt = Location of French ...
, with the greatest diversity being found in and around New Guinea
New Guinea (; Hiri Motu: ''Niu Gini''; id, Papua, or , historically ) is the world's second-largest island with an area of . Located in Oceania in the southwestern Pacific Ocean, the island is separated from Australia by the wide Torres ...
. The subfamily Arinae encompasses all the neotropical parrots, including the amazons, macaws, and conures, and ranges from northern Mexico
Mexico (Spanish language, Spanish: México), officially the United Mexican States, is a List of sovereign states, country in the southern portion of North America. It is borders of Mexico, bordered to the north by the United States; to the so ...
and the Bahamas
The Bahamas (), officially the Commonwealth of The Bahamas, is an island country within the Lucayan Archipelago of the West Indies in the North Atlantic. It takes up 97% of the Lucayan Archipelago's land area and is home to 88% of the a ...
to Tierra del Fuego
Tierra del Fuego (, ; Spanish for "Land of the Fire", rarely also Fireland in English) is an archipelago off the southernmost tip of the South American mainland, across the Strait of Magellan. The archipelago consists of the main island, Isla ...
in the southern tip of South America. The pygmy parrots, tribe Micropsittini, form a small genus restricted to New Guinea and the Solomon Islands. The superfamily Strigopoidea contains three living species of aberrant parrots from New Zealand. The broad-tailed parrots, subfamily Platycercinae
Platycercinae is a subfamily of birds belonging to the family Psittaculidae that inhabit Oceania. It consists of two tribes, the ground parrots and allies ( Pezoporini) and the many species of broad-tailed parrot ( Platycercini).
Genera
Tribe ...
, are restricted to Australia, New Zealand, and the Pacific islands as far eastwards as Fiji
Fiji ( , ,; fj, Viti, ; Fiji Hindi: फ़िजी, ''Fijī''), officially the Republic of Fiji, is an island country in Melanesia, part of Oceania in the South Pacific Ocean. It lies about north-northeast of New Zealand. Fiji consis ...
. The true parrot superfamily, Psittacoidea, includes a range of species from Australia and New Guinea to South Asia and Africa. The centre of cockatoo biodiversity is Australia and New Guinea, although some species reach the Solomon Islands
Solomon Islands is an island country consisting of six major islands and over 900 smaller islands in Oceania, to the east of Papua New Guinea and north-west of Vanuatu. It has a land area of , and a population of approx. 700,000. Its capit ...
(and one formerly occurred in New Caledonia
)
, anthem = ""
, image_map = New Caledonia on the globe (small islands magnified) (Polynesia centered).svg
, map_alt = Location of New Caledonia
, map_caption = Location of New Caledonia
, mapsize = 290px
, subdivision_type = Sovereign st ...
), Wallacea
Wallacea is a biogeographical designation for a group of mainly Indonesian islands separated by deep-water straits from the Asian and Australian continental shelves. Wallacea includes Sulawesi, the largest island in the group, as well as ...
and the Philippines.
 Several parrots inhabit the cool,
Several parrots inhabit the cool, temperate
In geography, the temperate climates of Earth occur in the middle latitudes (23.5° to 66.5° N/S of Equator), which span between the tropics and the polar regions of Earth. These zones generally have wider temperature ranges throughout ...
regions of South America and New Zealand
New Zealand ( mi, Aotearoa ) is an island country in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It consists of two main landmasses—the North Island () and the South Island ()—and over 700 smaller islands. It is the sixth-largest island coun ...
. Three species—the thick-billed parrot, the green parakeet
The green parakeet (''Psittacara holochlorus'') is a medium-sized parrot occurring in North and Central America, from the southernmost tip of Texas south to northern Nicaragua.
Description
The green parakeet is 32 cm in length, and is mos ...
, and the now-extinct Carolina parakeet—have lived as far north as the southern United States. Many parrots, especially monk parakeets, have been introduced to areas with temperate climates, and have established stable populations in parts of the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country Continental United States, primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 U.S. state, states, a Washington, D.C., ...
(including New York City
New York, often called New York City or NYC, is the List of United States cities by population, most populous city in the United States. With a 2020 population of 8,804,190 distributed over , New York City is also the L ...
), the United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotland, Wales and ...
, Belgium
Belgium, ; french: Belgique ; german: Belgien officially the Kingdom of Belgium, is a country in Northwestern Europe. The country is bordered by the Netherlands to the north, Germany to the east, Luxembourg to the southeast, France to ...
, Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = '' Plus ultra'' (Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, ...
and Greece
Greece,, or , romanized: ', officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the southern tip of the Balkans, and is located at the crossroads of Europe, Asia, and Africa. Greece shares land borders wi ...
. These birds can be quite successful in introduced areas, such as the non-native population of red-crowned amazons in the U.S. which may rival that of their native Mexico. The only parrot to inhabit alpine climate
Alpine climate is the typical weather (climate) for elevations above the tree line, where trees fail to grow due to cold. This climate is also referred to as a mountain climate or highland climate.
Definition
There are multiple definitions o ...
s is the kea, which is endemic to the Southern Alps
The Southern Alps (; officially Southern Alps / Kā Tiritiri o te Moana) is a mountain range extending along much of the length of New Zealand's South Island, reaching its greatest elevations near the range's western side. The name "Southern ...
mountain range on New Zealand's South Island
The South Island, also officially named , is the larger of the two major islands of New Zealand in surface area, the other being the smaller but more populous North Island. It is bordered to the north by Cook Strait, to the west by the Tasman ...
.
Few parrots are wholly sedentary or fully migratory. Most fall somewhere between the two extremes, making poorly understood regional movements, with some adopting an entirely nomadic lifestyle. Only three species are migratory – the orange-bellied, blue-winged and swift parrots.
Behaviour

 Numerous challenges are found in studying wild parrots, as they are difficult to catch and once caught, they are difficult to mark. Most wild bird studies rely on banding or wing tagging, but parrots chew off such attachments. Parrots also tend to range widely, and consequently many gaps occur in knowledge of their behaviour. Some parrots have a strong, direct flight. Most species spend much of their time perched or climbing in tree canopies. They often use their bills for climbing by gripping or hooking on branches and other supports. On the ground, parrots often walk with a rolling gait.
Numerous challenges are found in studying wild parrots, as they are difficult to catch and once caught, they are difficult to mark. Most wild bird studies rely on banding or wing tagging, but parrots chew off such attachments. Parrots also tend to range widely, and consequently many gaps occur in knowledge of their behaviour. Some parrots have a strong, direct flight. Most species spend much of their time perched or climbing in tree canopies. They often use their bills for climbing by gripping or hooking on branches and other supports. On the ground, parrots often walk with a rolling gait.
Diet
The diet of parrots consists ofseed
A seed is an embryonic plant enclosed in a protective outer covering, along with a food reserve. The formation of the seed is a part of the process of reproduction in seed plants, the spermatophytes, including the gymnosperm and angiosper ...
s, fruit
In botany, a fruit is the seed-bearing structure in flowering plants that is formed from the ovary after flowering.
Fruits are the means by which flowering plants (also known as angiosperms) disseminate their seeds. Edible fruits in partic ...
, nectar
Nectar is a sugar-rich liquid produced by plants in glands called nectaries or nectarines, either within the flowers with which it attracts pollinating animals, or by extrafloral nectaries, which provide a nutrient source to animal mutualist ...
, pollen
Pollen is a powdery substance produced by seed plants. It consists of pollen grains (highly reduced microgametophytes), which produce male gametes (sperm cells). Pollen grains have a hard coat made of sporopollenin that protects the gametop ...
, buds, and sometimes arthropod
Arthropods (, (gen. ποδός)) are invertebrate animals with an exoskeleton, a segmented body, and paired jointed appendages. Arthropods form the phylum Arthropoda. They are distinguished by their jointed limbs and cuticle made of chiti ...
s and other animal prey. The most important of these for most true parrots and cockatoos are seeds; the large and powerful bill has evolved to open and consume tough seeds. All true parrots, except the Pesquet's parrot
Pesquet's parrot (''Psittrichas fulgidus''), also known as the Dracula parrot or as the vulturine parrot (leading to easy confusion with '' Pyrilia vulturina'' from Brazil), is the only member of its genus. It is endemic to hill and montane rain ...
, employ the same method to obtain the seed from the husk; the seed is held between the mandibles and the lower mandible crushes the husk, whereupon the seed is rotated in the bill and the remaining husk is removed. They may use their foot sometimes to hold large seeds in place. Parrots are granivore
Seed predation, often referred to as granivory, is a type of plant-animal interaction in which granivores (seed predators) feed on the seeds of plants as a main or exclusive food source,Hulme, P.E. and Benkman, C.W. (2002) "Granivory", pp. 132 ...
s rather than seed dispersers, and in many cases where they are seen consuming fruit, they are only eating the fruit to get at the seed. As seeds often have poisons that protect them, parrots carefully remove seed coats and other chemically defended fruit parts prior to ingestion. Many species in the Americas, Africa, and Papua New Guinea consume clay
Clay is a type of fine-grained natural soil material containing clay minerals (hydrous aluminium phyllosilicates, e.g. kaolin, Al2 Si2 O5( OH)4).
Clays develop plasticity when wet, due to a molecular film of water surrounding the clay pa ...
, which releases minerals and absorbs toxic compounds from the gut.
 Geographical range and body size predominantly explains diet composition of Neotropical parrots rather than phylogeny.
Lories, lorikeets,
Geographical range and body size predominantly explains diet composition of Neotropical parrots rather than phylogeny.
Lories, lorikeets, hanging parrot
Hanging parrots are birds in the genus ''Loriculus'', a group of small parrots from tropical southern Asia.
About long, hanging parrots are mostly green plumaged and short-tailed. Often head coloring helps to identify individual species. They a ...
s, and swift parrots are primarily nectar
Nectar is a sugar-rich liquid produced by plants in glands called nectaries or nectarines, either within the flowers with which it attracts pollinating animals, or by extrafloral nectaries, which provide a nutrient source to animal mutualist ...
and pollen
Pollen is a powdery substance produced by seed plants. It consists of pollen grains (highly reduced microgametophytes), which produce male gametes (sperm cells). Pollen grains have a hard coat made of sporopollenin that protects the gametop ...
consumers, and have tongues with brush tips to collect it, as well as some specialised gut adaptations. Many other species also consume nectar when it becomes available.
Some parrot species prey on animals, especially invertebrate larvae. Golden-winged parakeets prey on water snail
A snail is, in loose terms, a shelled gastropod. The name is most often applied to land snails, terrestrial pulmonate gastropod molluscs. However, the common name ''snail'' is also used for most of the members of the molluscan class ...
s, the New Zealand kea can, though uncommonly, hunt adult sheep, and the Antipodes parakeet, another New Zealand parrot, enters the burrows of nesting grey-backed storm petrels and kills the incubating adults. Some cockatoos and the New Zealand kaka excavate branches and wood to feed on grubs; the bulk of the yellow-tailed black cockatoo
The yellow-tailed black cockatoo (''Zanda funerea'') is a large cockatoo native to the south-east of Australia measuring in length. It has a short crest on the top of its head. Its plumage is mostly brownish black and it has prominent yello ...
's diet is made up of insects.
Some extinct parrots had carnivorous diets. Pseudasturids were probably cuckoo
Cuckoos are birds in the Cuculidae family, the sole taxon in the order Cuculiformes . The cuckoo family includes the common or European cuckoo, roadrunners, koels, malkohas, couas, coucals and anis. The coucals and anis are sometimes separ ...
- or puffbird-like insectivores, while messelasturids were raptor
Raptor or RAPTOR may refer to:
Animals
The word "raptor" refers to several groups of bird-like dinosaurs which primarily capture and subdue/kill prey with their talons.
* Raptor (bird) or bird of prey, a bird that primarily hunts and feeds on v ...
-like carnivores.
Breeding
With few exceptions, parrots aremonogamous
Monogamy ( ) is a form of dyadic relationship in which an individual has only one partner during their lifetime. Alternately, only one partner at any one time ( serial monogamy) — as compared to the various forms of non-monogamy (e.g., pol ...
breeders who nest in cavities and hold no territories
A territory is an area of land, sea, or space, particularly belonging or connected to a country, person, or animal.
In international politics, a territory is usually either the total area from which a state may extract power resources or a ...
other than their nesting sites. The pair bond
In biology, a pair bond is the strong affinity that develops in some species between a mating pair, often leading to the production and rearing of offspring and potentially a lifelong bond. Pair-bonding is a term coined in the 1940s that is freque ...
s of the parrots and cockatoos are strong and a pair remains close during the nonbreeding season, even if they join larger flocks. As with many birds, pair bond formation is preceded by courtship displays; these are relatively simple in the case of cockatoos. In Psittacidae parrots' common breeding displays, usually undertaken by the male, include slow, deliberate steps known as a "parade" or "stately walk" and the " eye-blaze", where the pupil of the eye constricts to reveal the edge of the iris. Allopreening is used by the pair to help maintain the bond. Cooperative breeding, where birds other than the breeding pair help raise the young and is common in some bird families, is extremely rare in parrots, and has only unambiguously been demonstrated in the El Oro parakeet and the golden parakeet
The golden parakeet or golden conure, (''Guaruba guarouba''), is a medium-sized golden-yellow Neotropical parrot native to the Amazon Basin of interior northern Brazil. It is the only species placed in the genus ''Guaruba''.
Its plumage is most ...
(which may also exhibit polygamous
Crimes
Polygamy (from Late Greek (') "state of marriage to many spouses") is the practice of marrying multiple spouses. When a man is married to more than one wife at the same time, sociologists call this polygyny. When a woman is marri ...
, or group breeding, behaviour with multiple females contributing to the clutch).
Only the monk parakeet and five species of lovebird
Lovebird is the common name for the genus ''Agapornis'', a small group of parrots in the Old World parrot family Psittaculidae. Of the nine species in the genus, all are native to the African continent, with the grey-headed lovebird being native ...
s build nests in trees, and three Australian and New Zealand ground parrots nest on the ground. All other parrots and cockatoos nest in cavities, either tree hollows or cavities dug into cliffs, banks, or the ground. The use of holes in cliffs is more common in the Americas. Many species use termite
Termites are small insects that live in colonies and have distinct castes ( eusocial) and feed on wood or other dead plant matter. Termites comprise the infraorder Isoptera, or alternatively the epifamily Termitoidae, within the order Blat ...
nests, possibly to reduce the conspicuousness of the nesting site or to create a favourable microclimate
A microclimate (or micro-climate) is a local set of atmospheric conditions that differ from those in the surrounding areas, often with a slight difference but sometimes with a substantial one. The term may refer to areas as small as a few squ ...
. In most cases, both parents participate in the nest excavation. The length of the burrow varies with species, but is usually between in length. The nests of cockatoos are often lined with sticks, wood chips, and other plant material. In the larger species of parrots and cockatoos, the availability of nesting hollows may be limited, leading to intense competition for them both within the species and between species, as well as with other bird families. The intensity of this competition can limit breeding success in some cases. Hollows created artificially by arborists have proven successful in boosting breeding rates in these areas. Some species are colonial, with the burrowing parrot
The burrowing parrot (''Cyanoliseus patagonus''), also known as the burrowing parakeet or the Patagonian conure, is a species of parrot native to Argentina and Chile. It belongs to the monotypic genus ''Cyanoliseus'', with four subspecies tha ...
nesting in colonies up to 70,000 strong. Coloniality is not as common in parrots as might be expected, possibly because most species adopt old cavities rather than excavate their own.
The eggs of parrots are white. In most species, the female undertakes all the incubation, although incubation is shared in cockatoos, the blue lorikeet, and the vernal hanging parrot. The female remains in the nest for almost all of the incubation period and is fed both by the male and during short breaks. Incubation varies from 17 to 35 days, with larger species having longer incubation periods. The newly born young are altricial
In biology, altricial species are those in which the young are underdeveloped at the time of birth, but with the aid of their parents mature after birth. Precocial species are those in which the young are relatively mature and mobile from the mome ...
, either lacking feathers or with sparse white down. The young spend three weeks to four months in the nest, depending on species, and may receive parental care for several months thereafter.
As typical of K-selected species, the macaws and other larger parrot species have low reproductive rates. They require several years to reach maturity, produce one or very few young per year, and do not necessarily breed every year.
Intelligence and learning
 Some grey parrots have shown an ability to associate words with their meanings and form simple sentences. Along with
Some grey parrots have shown an ability to associate words with their meanings and form simple sentences. Along with crow
A crow is a bird of the genus '' Corvus'', or more broadly a synonym for all of ''Corvus''. Crows are generally black in colour. The word "crow" is used as part of the common name of many species. The related term "raven" is not pinned scientifica ...
s, raven
A raven is any of several larger-bodied bird species of the genus '' Corvus''. These species do not form a single taxonomic group within the genus. There is no consistent distinction between " crows" and "ravens", common names which are assigne ...
s, and jays (family Corvidae
Corvidae is a cosmopolitan family of oscine passerine birds that contains the crows, ravens, rooks, jackdaws, jays, magpies, treepies, choughs, and nutcrackers. In colloquial English, they are known as the crow family or corvids. Cu ...
), parrots are considered the most intelligent of birds. The brain-to-body size ratio of psittacines and corvines is comparable to that of higher primates. Instead of using the cerebral cortex
The cerebral cortex, also known as the cerebral mantle, is the outer layer of neural tissue of the cerebrum of the brain in humans and other mammals. The cerebral cortex mostly consists of the six-layered neocortex, with just 10% consisting o ...
like mammals, birds use the mediorostral HVC for cognition. Not only have parrots demonstrated intelligence through scientific testing of their language-using ability, but also some species of parrots, such as the kea, are also highly skilled at using tools and solving puzzles.
Learning in early life is apparently important to all parrots, and much of that learning is social learning. Social interactions are often practised with siblings, and in several species, crèches are formed with several broods. Foraging behaviour is generally learnt from parents, and can be a very protracted affair. Generalists and specialists generally become independent of their parents much quicker than partly specialised species who may have to learn skills over long periods as various resources become seasonally available. Play forms a large part of learning in parrots; play can be solitary or social. Species may engage in play fights or wild flights to practice predator evasion. An absence of stimuli can delay the development of young birds, as demonstrated by a group of vasa parrots kept in tiny cages with domesticated chickens from the age of 3 months; at 9 months, these birds still behaved in the same way as 3-month-olds, but had adopted some chicken behaviour. In a similar fashion, captive birds in zoo collections or pets can, if deprived of stimuli, develop stereotyped
In social psychology, a stereotype is a generalized belief about a particular category of people. It is an expectation that people might have about every person of a particular group. The type of expectation can vary; it can be, for example ...
and harmful behaviours like self-plucking. Aviculturists working with parrots have identified the need for environmental enrichment to keep parrots stimulated.
Sound imitation and speech
Many parrots can imitate humanspeech
Speech is a human vocal communication using language. Each language uses phonetic combinations of vowel and consonant sounds that form the sound of its words (that is, all English words sound different from all French words, even if they are th ...
or other sounds. A study by scientist Irene Pepperberg
Irene Maxine Pepperberg (born April 1, 1949) is a scientist noted for her studies in animal cognition, particularly in relation to parrots. She has been a professor, researcher and/or lecturer at multiple universities, and she is currently a res ...
suggested a high learning ability in a grey parrot named Alex
Alex is a given name. It can refer to a shortened version of Alexander, Alexandra, Alexis.
People
Multiple
*Alex Brown (disambiguation), multiple people
*Alex Gordon (disambiguation), multiple people
*Alex Harris (disambiguation), multiple p ...
. Alex was trained to use words to identify objects, describe them, count them, and even answer complex questions such as "How many red squares?" with over 80% accuracy. N'kisi
N'kisi is a grey parrot (''Psittacus erithacus'') thought to exhibit advanced English talking skills and other abilities.
Accomplishments
According to news reports and websites, as of January 2004 N'kisi had a vocabulary of about 950 words and u ...
, another grey parrot, has been shown to have a vocabulary around a thousand words, and has displayed an ability to invent and use words in context in correct tenses.
Parrots do not have vocal cords, so sound is accomplished by expelling air across the mouth of the trachea
The trachea, also known as the windpipe, is a cartilaginous tube that connects the larynx to the bronchi of the lungs, allowing the passage of air, and so is present in almost all air- breathing animals with lungs. The trachea extends from t ...
in the organ called the syrinx
In classical Greek mythology, Syrinx ( Greek Σύριγξ) was a nymph and a follower of Artemis, known for her chastity. Pursued by the amorous god Pan, she ran to a river's edge and asked for assistance from the river nymphs. In answer, ...
. Different sounds are produced by changing the depth and shape of the trachea. Grey parrots are known for their superior ability to imitate sounds and human speech, which has made them popular pets since ancient times.
Although most parrot species are able to imitate, some of the amazon parrot
Amazon parrots are parrots in the genus ''Amazona''. They are medium-sized, short-tailed parrots native to the Americas, with their range extending from South America to Mexico and the Caribbean. ''Amazona'' is one of the 92 genera of parrots ...
s are generally regarded as the next-best imitators and speakers of the parrot world. The question of why birds imitate remains open, but those that do often score very high on tests designed to measure problem-solving ability. Wild grey parrots have been observed imitating other birds.
Song
Parrots are unusual among birds due to their learned vocalizations, a trait they share with onlyhummingbird
Hummingbirds are birds native to the Americas and comprise the Family (biology), biological family Trochilidae. With about 361 species and 113 genus, genera, they occur from Alaska to Tierra del Fuego, but the vast majority of the species are ...
s and songbird
A songbird is a bird belonging to the suborder Passeri of the perching birds (Passeriformes). Another name that is sometimes seen as the scientific or vernacular name is Oscines, from Latin ''oscen'', "songbird". The Passeriformes contains 5000 ...
s. The syrinx
In classical Greek mythology, Syrinx ( Greek Σύριγξ) was a nymph and a follower of Artemis, known for her chastity. Pursued by the amorous god Pan, she ran to a river's edge and asked for assistance from the river nymphs. In answer, ...
(vocal organ) of parrots, which aids in their ability to produce song, is located at the base of the trachea
The trachea, also known as the windpipe, is a cartilaginous tube that connects the larynx to the bronchi of the lungs, allowing the passage of air, and so is present in almost all air- breathing animals with lungs. The trachea extends from t ...
and consists of two complex syringeal muscles that allow for the production of sound vibrations, and a pair of lateral tympaniform membranes that control sound frequency. The position of the syrinx in birds allows for directed air flow into the interclavicular air sacs according to air sac pressure, which in turn creates a higher and louder tone in birds’ singing.
Cooperation
A 2011 study stated that some African grey parrots preferred to work alone, while others like to work together. With two parrots, they know the order of tasks or when they should do something together at once, but they have trouble exchanging roles. With three parrots, one parrot usually prefers to cooperate with one of the other two, but all of them are cooperating to solve the task.Relationship with humans
Pets
 Parrots may not make good pets for most people because of their natural wild instincts such as screaming and chewing. Although parrots can be very affectionate and cute when immature, they often become aggressive when mature (partly due to mishandling and poor training) and may bite, causing serious injury. For this reason, parrot rescue groups estimate that most parrots are surrendered and rehomed through at least five homes before reaching their permanent destinations or before dying prematurely from unintentional or intentional neglect and abuse. The parrots' ability to mimic human words and their bright colours and beauty prompt impulse buying from unsuspecting consumers. The domesticated budgerigar, a small parrot, is the most popular of all pet bird species. In 1992, the newspaper ''
Parrots may not make good pets for most people because of their natural wild instincts such as screaming and chewing. Although parrots can be very affectionate and cute when immature, they often become aggressive when mature (partly due to mishandling and poor training) and may bite, causing serious injury. For this reason, parrot rescue groups estimate that most parrots are surrendered and rehomed through at least five homes before reaching their permanent destinations or before dying prematurely from unintentional or intentional neglect and abuse. The parrots' ability to mimic human words and their bright colours and beauty prompt impulse buying from unsuspecting consumers. The domesticated budgerigar, a small parrot, is the most popular of all pet bird species. In 1992, the newspaper ''USA Today
''USA Today'' (stylized in all uppercase) is an American daily middle-market newspaper and news broadcasting company. Founded by Al Neuharth on September 15, 1982, the newspaper operates from Gannett's corporate headquarters in Tysons, Virgini ...
'' published that 11 million pet birds were in the United States alone, many of them parrots. Europeans kept birds matching the description of the rose-ringed parakeet
The rose-ringed parakeet (''Psittacula krameri''), also known as the ring-necked parakeet (more commonly known as the Indian ringneck parrot), is a medium-sized parrot in the genus Psittacula, of the family Psittacidae. It has disjunct native ra ...
(or called the ring-necked parrot), documented particularly in a first-century account by Pliny the Elder
Gaius Plinius Secundus (AD 23/2479), called Pliny the Elder (), was a Roman author, naturalist and natural philosopher, and naval and army commander of the early Roman Empire, and a friend of the emperor Vespasian. He wrote the encyclopedic ' ...
. As they have been prized for thousands of years for their beauty and ability to talk, they have also often been misunderstood. For example, author Wolfgang de Grahl says in his 1987 book ''The Grey Parrot'' that some importers had parrots drink only coffee while they were shipped by boat, believing that pure water was detrimental and that their actions would increase survival rates during shipping. Nowadays, it is commonly accepted that the caffeine in coffee is toxic to birds.
Pet parrots may be kept in a cage or aviary
An aviary is a large enclosure for confining birds, although bats may also be considered for display. Unlike birdcages, aviaries allow birds a larger living space where they can fly; hence, aviaries are also sometimes known as flight cages. Avi ...
; though generally, tame parrots should be allowed out regularly on a stand or gym. Depending on locality, parrots may be either wild-caught or be captive-bred, though in most areas without native parrots, pet parrots are captive-bred. Parrot species that are commonly kept as pets include conures
Conures are a diverse, loosely defined group of small to medium-sized parrots. They belong to several genera within a long-tailed group of the New World parrot subfamily Arinae. The term "conure" is used primarily in bird keeping, though it has ...
, macaw
Macaws are a group of New World parrots that are long-tailed and often colorful. They are popular in aviculture or as companion parrots, although there are conservation concerns about several species in the wild.
Biology
Of the many differ ...
s, amazon parrots, cockatoos, greys, lovebirds
Lovebird is the common name for the genus ''Agapornis'', a small group of parrots in the Old World parrot family Psittaculidae. Of the nine species in the genus, all are native to the African continent, with the grey-headed lovebird being native ...
, cockatiel
The cockatiel (; ''Nymphicus hollandicus''), also known as weiro (also spelt weero), or quarrion, is a medium-sized parrot that is a member of its own branch of the cockatoo family endemic to Australia. They are prized as household pets and c ...
s, budgerigar
The budgerigar ( ; ''Melopsittacus undulatus''), also known as the common parakeet or shell parakeet, is a small, long-tailed, seed-eating parrot usually nicknamed the budgie ( ), or in American English, the parakeet. Budgies are the only spe ...
s, caiques
Caique ( or ) refers to a group of four species of parrots in the genus ''Pionites'' endemic to the Amazon Basin in South America. Name
The term "caique" is primarily used in aviculture, with ornithologists typically referring to them as th ...
, parakeets, and '' Eclectus'', ''Pionus
''Pionus'' is a genus of medium-sized parrots native to Mexico, and Central and South America. Characteristic of the genus are the chunky body, bare eye ring (which can vary in color), and short square tail. They are superficially similar to ...
'', and '' Poicephalus'' species. Temperaments and personalities vary even within a species, just as with dog breeds. Grey parrots are thought to be excellent talkers, but not all grey parrots want to talk, though they have the capability to do so. Noise level, talking ability, cuddliness with people, and care needs can sometimes depend on how the bird is cared for and the attention he/she regularly receives.
 Parrots invariably require an enormous amount of attention, care, and intellectual stimulation to thrive, akin to that required by a three-year-old child, which many people find themselves unable to provide in the long term. Parrots that are bred for pets may be hand fed or otherwise accustomed to interacting with people from a young age to help ensure they become tame and trusting. However, even when hand fed, parrots revert to biting and aggression during hormonal surges and if mishandled or neglected. Parrots are not low-maintenance pets; they require feeding, grooming, veterinary care, training, environmental enrichment through the provision of toys, exercise, and social interaction (with other parrots or humans) for good health.
Some large parrot species, including large cockatoos, amazons, and macaws, have very long lifespans, with 80 years being reported, and record ages of over 100. Small parrots, such as lovebirds, hanging parrots, and budgies, have shorter lifespans up to 15–20 years. Some parrot species can be quite loud, and many of the larger parrots can be destructive and require a very large cage, and a regular supply of new toys, branches, or other items to chew up. The intelligence of parrots means they are quick to learn tricks and other behaviours—both good and bad—that get them what they want, such as attention or treats.
The popularity, longevity, and intelligence of many of the larger kinds of pet parrots and their wild traits such as screaming, has led to many birds needing to be rehomed during the course of their long lifespans. A common problem is that large parrots that are cuddly and gentle as juveniles mature into intelligent, complex, often demanding adults who can outlive their owners, and can also become aggressive or even dangerous. Due to an increasing number of homeless parrots, they are being euthanised like dogs and cats, and parrot adoption centres and sanctuaries are becoming more common. Parrots do not often do well in captivity, causing some parrots to go insane and develop repetitive behaviours, such as swaying and screaming, or they become riddled with intense fear. Feather destruction and self-mutilation, although not commonly seen in the wild, occur frequently in captivity.
Parrots invariably require an enormous amount of attention, care, and intellectual stimulation to thrive, akin to that required by a three-year-old child, which many people find themselves unable to provide in the long term. Parrots that are bred for pets may be hand fed or otherwise accustomed to interacting with people from a young age to help ensure they become tame and trusting. However, even when hand fed, parrots revert to biting and aggression during hormonal surges and if mishandled or neglected. Parrots are not low-maintenance pets; they require feeding, grooming, veterinary care, training, environmental enrichment through the provision of toys, exercise, and social interaction (with other parrots or humans) for good health.
Some large parrot species, including large cockatoos, amazons, and macaws, have very long lifespans, with 80 years being reported, and record ages of over 100. Small parrots, such as lovebirds, hanging parrots, and budgies, have shorter lifespans up to 15–20 years. Some parrot species can be quite loud, and many of the larger parrots can be destructive and require a very large cage, and a regular supply of new toys, branches, or other items to chew up. The intelligence of parrots means they are quick to learn tricks and other behaviours—both good and bad—that get them what they want, such as attention or treats.
The popularity, longevity, and intelligence of many of the larger kinds of pet parrots and their wild traits such as screaming, has led to many birds needing to be rehomed during the course of their long lifespans. A common problem is that large parrots that are cuddly and gentle as juveniles mature into intelligent, complex, often demanding adults who can outlive their owners, and can also become aggressive or even dangerous. Due to an increasing number of homeless parrots, they are being euthanised like dogs and cats, and parrot adoption centres and sanctuaries are becoming more common. Parrots do not often do well in captivity, causing some parrots to go insane and develop repetitive behaviours, such as swaying and screaming, or they become riddled with intense fear. Feather destruction and self-mutilation, although not commonly seen in the wild, occur frequently in captivity.
Trade
Tony Silva
Tony Silva, also known as Antonio H. Silva (born 1960) is an American aviculturist and ornithologist, and the author of books and articles about parrots. From 1989 to 1992, he was curator of birds at Loro Parque, the largest parrot park in the ...
case of 1996, in which a parrot expert and former director at Tenerife
Tenerife (; ; formerly spelled ''Teneriffe'') is the largest and most populous island of the Canary Islands. It is home to 43% of the total population of the Archipelago, archipelago. With a land area of and a population of 978,100 inhabitant ...
's Loro Parque
Loro Parque (Spanish for "parrot park") or 'Loro Park' is a 135,000 m² (13.5 ha) zoo on the outskirts of Puerto de la Cruz on Tenerife, Spain where it houses an extensive and diverse reserve of animal and plant species. The park was conceived a ...
(Europe's largest parrot park) was jailed in the United States for 82 months and fined $100,000 for smuggling hyacinth macaws (such birds command a very high price.)
Different nations have different methods of handling internal and international trade. Australia has banned the export of its native birds since 1960. In July 2007, following years of campaigning by NGOs
A non-governmental organization (NGO) or non-governmental organisation (see spelling differences) is an organization that generally is formed independent from government. They are typically nonprofit entities, and many of them are active in ...
and outbreaks of avian flu, the European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational union, supranational political union, political and economic union of Member state of the European Union, member states that are located primarily in Europe, Europe. The union has a total area of ...
(EU) halted the importation of all wild birds with a permanent ban on their import. Prior to an earlier temporary ban started in late October 2005, the EU was importing about two million live birds a year, about 90% of the international market: hundreds of thousands of these were parrots. No national laws protect feral parrot populations in the U.S.
Mexico has a licensing system for capturing and selling native birds. According to a 2007 report, 65,000 to 78,500 parrots are captured annually, but the mortality rate before reaching a buyer is over 75%, meaning around 50,000 to 60,000 will die.
Culture
 Parrots have featured in human writings, story, art, humor, religion, and music for thousands of years, such as
Parrots have featured in human writings, story, art, humor, religion, and music for thousands of years, such as Aesop's fable
Aesop's Fables, or the Aesopica, is a collection of fables credited to Aesop, a slave and storyteller believed to have lived in ancient Greece between 620 and 564 BCE. Of diverse origins, the stories associated with his name have descended to m ...
"The parrot and the cat" the ''Masnavi
The ''Masnavi'', or ''Masnavi-ye-Ma'navi'' ( fa, مثنوی معنوی), also written ''Mathnawi'', or ''Mathnavi'', is an extensive poem written in Persian by Jalal al-Din Muhammad Balkhi, also known as Rumi. The ''Masnavi'' is one of the mos ...
'' by Rumi
Jalāl al-Dīn Muḥammad Rūmī ( fa, جلالالدین محمد رومی), also known as Jalāl al-Dīn Muḥammad Balkhī (), Mevlânâ/Mawlānā ( fa, مولانا, lit= our master) and Mevlevî/Mawlawī ( fa, مولوی, lit= my ma ...
of Persia
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmeni ...
in 1250 "The Merchant and the Parrot". Recent books about parrots in human culture include ''Parrot Culture''.
In ancient times and current, parrot feathers
Feathers are epidermal growths that form a distinctive outer covering, or plumage, on both avian (bird) and some non-avian dinosaurs and other archosaurs. They are the most complex integumentary structures found in vertebrates and a premier ...
have been used in ceremonies and for decoration. They also have a long history as pets, stretching back thousands of years, and were often kept as a symbol of royalty or wealth. In Polynesian legend as current in the Marquesas Islands
The Marquesas Islands (; french: Îles Marquises or ' or '; Marquesan: ' (North Marquesan) and ' ( South Marquesan), both meaning "the land of men") are a group of volcanic islands in French Polynesia, an overseas collectivity of France in ...
, the hero Laka
In Hawaiian mythology, Laka is the name of two different popular heroes from Polynesian mythology. (In other parts of Polynesia they are known as Rātā, Rata, Lata, Ata, or Lasa).
In one Hawaiian legend, Laka is the son of the '' Ali'i nui'' ...
/Aka
Aka, AKA or a.k.a. may refer to:
* "Also known as", used to introduce an alternative name
Languages
* Aka language (Sudan)
* Aka language, in the Central African Republic
* Hruso language, in India, also referred to as Aka
* a prefix in the n ...
is mentioned as having undertaken a long and dangerous voyage to Aotona in what are now the Cook Islands
)
, image_map = Cook Islands on the globe (small islands magnified) (Polynesia centered).svg
, capital = Avarua
, coordinates =
, largest_city = Avarua
, official_languages =
, lan ...
, to obtain the highly prized feathers of a red parrot as gifts for his son and daughter. On the voyage, 100 of his 140 rowers died of hunger on their way, but the survivors reached Aotona and captured enough parrots to fill 140 bags with their feathers. Parrots have also been considered sacred. The Moche people of ancient Peru
, image_flag = Flag of Peru.svg
, image_coat = Escudo nacional del Perú.svg
, other_symbol = Great Seal of the State
, other_symbol_type = National seal
, national_motto = "Firm and Happy f ...
worshipped birds and often depicted parrots in their art. Parrots are popular in Buddhist
Buddhism ( , ), also known as Buddha Dharma and Dharmavinaya (), is an Indian religion or philosophical tradition based on teachings attributed to the Buddha. It originated in northern India as a -movement in the 5th century BCE, and ...
scripture and many writings about them exist. For example, Amitābha
Amitābha ( sa, अमिताभ, IPA: ), also known as Amitāyus, is the primary Buddha of Pure Land Buddhism. In Vajrayana Buddhism, he is known for his longevity, discernment, pure perception, purification of aggregates, and deep awaren ...
once changed himself into a parrot to aid in converting people. Another old story tells how after a forest caught fire, the parrot was so concerned, it carried water to try to put out the flames. The ruler of heaven was so moved upon seeing the parrot's act, he sent rain to put out the fire. In Chinese Buddhist
Chinese Buddhism or Han Buddhism ( zh, s=汉传佛教, t=漢傳佛教, p=Hànchuán Fójiào) is a Chinese form of Mahayana Buddhism which has shaped Chinese culture in a wide variety of areas including art, politics, literature, philosophy, ...
iconography, a parrot is sometimes depicted hovering on the upper right side Guan Yin
Guanyin () is a Bodhisattva associated with compassion. She is the East Asian representation of Avalokiteśvara ( sa, अवलोकितेश्वर) and has been adopted by other Eastern religions, including Chinese folk religion. She w ...
clasping a pearl or prayer beads in its beak.
Parrots are used as symbols of nations and nationalism. A parrot is found on the flag of Dominica
The flag of Dominica was adopted on 3 November 1978, with some small changes having been made in 1981, 1988, and 1990. The original flag was designed by playwright Alwin Bully in early 1978 as the country prepared for independence.
It is one o ...
and two parrots on their coat of arms
A coat of arms is a heraldic visual design on an escutcheon (i.e., shield), surcoat, or tabard (the latter two being outer garments). The coat of arms on an escutcheon forms the central element of the full heraldic achievement, which in its ...
. The St. Vincent parrot is the national bird of St. Vincent and the Grenadines, a Caribbean nation.
Sayings about parrots colour the modern English language. The verb "parrot" in the dictionary means "to repeat by rote". Also clichés such as the British expression "sick as a parrot" are given; although this refers to extreme disappointment rather than illness, it may originate from the disease of psittacosis
Psittacosis—also known as parrot fever, and ornithosis—is a zoonotic infectious disease in humans caused by a bacterium called '' Chlamydia psittaci'' and contracted from infected parrots, such as macaws, cockatiels, and budgerigars, and f ...
, which can be passed to humans. The first occurrence of a related expression is in Aphra Behn
Aphra Behn (; bapt. 14 December 1640 – 16 April 1689) was an English playwright, poet, prose writer and translator from the Restoration era. As one of the first English women to earn her living by her writing, she broke cultural barrie ...
's 1681 play ''The False Count''. Fans of Jimmy Buffett
James William Buffett (born December 25, 1946) is an American singer-songwriter, musician, author, and businessman. He is best known for his music, which often portrays an "island escapism" lifestyle. Together with his Coral Reefer Band, Buffe ...
are known as parrotheads. Parrots feature in many media. Magazines are devoted to parrots as pets, and to the conservation of parrots. Fictional media include Monty Python
Monty Python (also collectively known as the Pythons) were a British comedy troupe who created the sketch comedy television show ''Monty Python's Flying Circus'', which first aired on the BBC in 1969. Forty-five episodes were made over fou ...
's " Dead Parrot sketch", ''Home Alone 3
''Home Alone 3'' is a 1997 American family comedy film directed by Raja Gosnell in his directorial debut, produced by John Hughes, and starring Alex D. Linz and Haviland Morris. The film tells the story of an 8-year-old boy who defends his ho ...
'' and ''Rio
Rio or Río is the Portuguese, Spanish, Italian, and Maltese word for "river". When spoken on its own, the word often means Rio de Janeiro, a major city in Brazil.
Rio or Río may also refer to:
Geography Brazil
* Rio de Janeiro
* Rio do Sul, a ...
''; and documentaries include ''The Wild Parrots of Telegraph Hill
''The Wild Parrots of Telegraph Hill'' is a 2003 documentary film directed, produced, and edited by Judy Irving. It chronicles the relationship between Mark Bittner, an unemployed musician who lives rent-free in a cabin in the Telegraph Hill-ne ...
''.
Feral populations
 Escaped parrots of several species have become established in the wild outside their natural ranges and in some cases outside the natural range of parrots. Among the earliest instances were pet red shining-parrots from Fiji, which established a population on the islands of southern
Escaped parrots of several species have become established in the wild outside their natural ranges and in some cases outside the natural range of parrots. Among the earliest instances were pet red shining-parrots from Fiji, which established a population on the islands of southern Tonga
Tonga (, ; ), officially the Kingdom of Tonga ( to, Puleʻanga Fakatuʻi ʻo Tonga), is a Polynesian country and archipelago. The country has 171 islands – of which 45 are inhabited. Its total surface area is about , scattered over in ...
. These introductions were prehistoric and red-shining parrots were recorded in Tonga by Captain Cook
James Cook (7 November 1728 Old Style date: 27 October – 14 February 1779) was a British explorer, navigator, cartographer, and captain in the British Royal Navy, famous for his three voyages between 1768 and 1779 in the Pacific Ocean and ...
in the 1770s. Escapees first began breeding in cities in California
California is a state in the Western United States, located along the Pacific Coast. With nearly 39.2million residents across a total area of approximately , it is the most populous U.S. state and the 3rd largest by area. It is also the m ...
, Texas
Texas (, ; Spanish: ''Texas'', ''Tejas'') is a state in the South Central region of the United States. At 268,596 square miles (695,662 km2), and with more than 29.1 million residents in 2020, it is the second-largest U.S. state by ...
, and Florida
Florida is a state located in the Southeastern region of the United States. Florida is bordered to the west by the Gulf of Mexico, to the northwest by Alabama, to the north by Georgia, to the east by the Bahamas and Atlantic Ocean, and ...
in the 1950s (with unproven earlier claims dating back to the 1920s in Texas and Florida). They have proved surprisingly hardy in adapting to conditions in Europe and North America. They sometimes even multiply to the point of becoming a nuisance or pest, and a threat to local ecosystems, and control measures have been used on some feral populations.
Feral parrot flocks can be formed after mass escapes of newly imported, wild-caught parrots from airports or quarantine facilities. Large groups of escapees have the protection of a flock and possess the skills to survive and breed in the wild. Some feral parakeets may have descended from escaped zoo birds. Escaped or released pets rarely contribute to establishing feral populations, as they usually result in only a few escapees, and most captive-born birds do not possess the necessary survival skills to find food or avoid predators and often do not survive long without human caretakers. However, in areas where there are existing feral parrot populations, escaped pets may sometimes successfully join these flocks. The most common years that feral parrots were released to non-native environments was from the 1890s to the 1940s, during the wild-caught parrot era. In the "parrot fever
Psittacosis—also known as parrot fever, and ornithosis—is a zoonotic infectious disease in humans caused by a bacterium called ''Chlamydia psittaci'' and contracted from infected parrots, such as macaws, cockatiels, and budgerigars, and f ...
" panic of 1930, a city health commissioner urged everyone who owned a parrot to put them down, but some owners abandoned their parrots on the streets.
Threats and conservation
 The principal threats of parrots are habitat loss and degradation, hunting, and, for certain species, the wild-bird trade. Parrots are persecuted because, in some areas, they are (or have been) hunted for food and feathers, and as
The principal threats of parrots are habitat loss and degradation, hunting, and, for certain species, the wild-bird trade. Parrots are persecuted because, in some areas, they are (or have been) hunted for food and feathers, and as agricultural pests
A pest is any animal or plant harmful to humans or human concerns. The term is particularly used for creatures that damage crops, livestock, and forestry or cause a nuisance to people, especially in their homes. Humans have modified the environ ...
. For a time, Argentina offered a bounty on monk parakeets for that reason, resulting in hundreds of thousands of birds being killed, though apparently this did not greatly affect the overall population.
Parrots, being cavity nesters, are vulnerable to the loss of nesting sites and to competition with introduced species for those sites. The loss of old trees is a particular problem in some areas, particularly in Australia, where suitable nesting trees must be centuries old. Many parrots occur only on islands and are vulnerable to introduced species such as rats and feral cat
A feral cat or a stray cat is an unowned domestic cat (''Felis catus'') that lives outdoors and avoids human contact: it does not allow itself to be handled or touched, and usually remains hidden from humans. Feral cats may breed over dozens ...
, as they lack the appropriate antipredator behaviours needed to deal with predators. Island species, such as the Puerto Rican amazon
The Puerto Rican amazon (''Amazona vittata''), also known as the Puerto Rican parrot (Puerto Rican Spanish: ''cotorra puertorriqueña'') or ''iguaca'', is the only extant parrot endemic to the archipelago of Puerto Rico, and belongs to the Neo ...
, which have small populations in restricted habitats, are also vulnerable to natural events, such as hurricanes. Due to deforestation, the Puerto Rican amazon is one of the world's rarest birds despite conservation efforts.
 One of the largest parrot conservation groups is the World Parrot Trust, an international organisation. The group gives assistance to worthwhile projects, as well as producing a magazine (''PsittaScene'') and raising funds through donations and memberships, often from pet parrot owners. On a smaller scale, local parrot clubs raise money to donate to a conservation cause. Zoo and wildlife centres usually provide public education, to change habits that cause damage to wild populations. Conservation measures to conserve the habitats of some of the high-profile charismatic parrot species has also protected many of the less charismatic species living in the ecosystem. A popular attraction that many zoos employ is a feeding station for lories and lorikeets, where visitors feed them with cups of liquid food. This is usually done in association with educational signs and lectures.
One of the largest parrot conservation groups is the World Parrot Trust, an international organisation. The group gives assistance to worthwhile projects, as well as producing a magazine (''PsittaScene'') and raising funds through donations and memberships, often from pet parrot owners. On a smaller scale, local parrot clubs raise money to donate to a conservation cause. Zoo and wildlife centres usually provide public education, to change habits that cause damage to wild populations. Conservation measures to conserve the habitats of some of the high-profile charismatic parrot species has also protected many of the less charismatic species living in the ecosystem. A popular attraction that many zoos employ is a feeding station for lories and lorikeets, where visitors feed them with cups of liquid food. This is usually done in association with educational signs and lectures. Birdwatching
Birdwatching, or birding, is the observing of birds, either as a recreational activity or as a form of citizen science. A birdwatcher may observe by using their naked eye, by using a visual enhancement device like binoculars or a telescope, by ...
-based ecotourism
Ecotourism is a form of tourism involving responsible travel (using sustainable transport) to natural areas, conserving the environment, and improving the well-being of the local people. Its purpose may be to educate the traveler, to provide fund ...
can be beneficial to economies.
Several projects aimed specifically at parrot conservation have met with success. Translocation of vulnerable kakapo, followed by intensive management and supplementary feeding, has increased the population from 50 individuals to 123 in 2010. In New Caledonia, the Ouvea parakeet
The Ouvea parakeet (''Eunymphicus uvaeensis'') or Uvea parakeet, is a species of parrot in the genus ''Eunymphicus'', in the family Psittaculidae. It is endemic to the island of Uvea in the Loyalty Islands, New Caledonia. The species was once c ...
was threatened by trapping for the pet trade and loss of habitat. Community-based conservation, which eliminated the threat of poaching, has allowed the population to increase from around 600 birds in 1993 to over 2000 birds in 2009.
As of 2009, the IUCN recognises 19 species of parrot as extinct since 1500 (the date used to denote modern extinctions). This does not include species like the New Caledonian lorikeet
The New Caledonian lorikeet (''Vini diadema'') is a potentially extinct lorikeet endemic to the Melanesian island of New Caledonia.
Taxonomy
The New Caledonian lorikeet was formerly assigned to the genus ''Charmosyna''. It was moved to the ...
, which has not been officially seen for 100 years, yet is still listed as critically endangered.
Trade, export, and import of all wild-caught parrots is regulated and only permitted under special licensed circumstances in countries party to the Convention on the International Trade in Endangered Species (CITES) which came into force in 1975 to regulate the international trade of all endangered, wild-caught animal and plant species. In 1975, 24 parrot species were included on Appendix I, thus prohibiting commercial international trade in these birds. Since that initial listing, continuing threats from international trade led it to add an additional 32 parrot varieties to Appendix I. All other parrot species, aside from the rosy-faced lovebird
The rosy-faced lovebird (''Agapornis roseicollis''), also known as the rosy-collared or peach-faced lovebird, is a species of lovebird native to arid regions in southwestern Africa such as the Namib Desert. Loud and constant chirpers, these b ...
, budgerigar
The budgerigar ( ; ''Melopsittacus undulatus''), also known as the common parakeet or shell parakeet, is a small, long-tailed, seed-eating parrot usually nicknamed the budgie ( ), or in American English, the parakeet. Budgies are the only spe ...
, cockatiel
The cockatiel (; ''Nymphicus hollandicus''), also known as weiro (also spelt weero), or quarrion, is a medium-sized parrot that is a member of its own branch of the cockatoo family endemic to Australia. They are prized as household pets and c ...
and rose-ringed parakeet
The rose-ringed parakeet (''Psittacula krameri''), also known as the ring-necked parakeet (more commonly known as the Indian ringneck parrot), is a medium-sized parrot in the genus Psittacula, of the family Psittacidae. It has disjunct native ra ...
(which are not included in the appendices) are protected on Appendix II of CITES. In addition, individual countries may have laws to regulate trade in certain species; for example, the EU has banned parrot trade, whereas Mexico has a licensing system for capturing parrots.
World Parrot Day
Every year on 31 May, World Parrot Day is celebrated.See also
*List of parrots
Parrots, also known as psittacines (), are the 402 species of birds that make up the order Psittaciformes, found in most tropical and subtropical regions, of which 387 are extant. The order is subdivided into three superfamilies: the Psittacoide ...
* Parrots of New Zealand
* Parrots of New Guinea
References
Cited sources
*External links
*Parrot videos
on the Internet Bird Collection {{authority control Articles containing video clips Extant Ypresian first appearances