|
Zinc Supplementation
Zinc deficiency is defined either as insufficient zinc to meet the needs of the body, or as a serum zinc level below the normal range. However, since a decrease in the serum concentration is only detectable after long-term or severe depletion, serum zinc is not a reliable biomarker for zinc status. Common symptoms include increased rates of diarrhea. Zinc deficiency affects the skin and gastrointestinal tract; brain and central nervous system, immune, skeletal, and reproductive systems. Zinc deficiency in humans is caused by reduced dietary intake, inadequate absorption, increased loss, or increased body system use. The most common cause is reduced dietary intake. In the U.S., the Recommended Dietary Allowance (RDA) is 8 mg/day for women and 11 mg/day for men."Zinc" , pp. 442–501 in ''Dietary Reference Intakes for Vitamin A, Vitamin K, Ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zinc
Zinc is a chemical element with the symbol Zn and atomic number 30. Zinc is a slightly brittle metal at room temperature and has a shiny-greyish appearance when oxidation is removed. It is the first element in group 12 (IIB) of the periodic table. In some respects, zinc is chemically similar to magnesium: both elements exhibit only one normal oxidation state (+2), and the Zn2+ and Mg2+ ions are of similar size.The elements are from different metal groups. See periodic table. Zinc is the 24th most abundant element in Earth's crust and has five stable isotopes. The most common zinc ore is sphalerite (zinc blende), a zinc sulfide mineral. The largest workable lodes are in Australia, Asia, and the United States. Zinc is refined by froth flotation of the ore, roasting, and final extraction using electricity ( electrowinning). Zinc is an essential trace element for humans, animals, plants and for microorganisms and is necessary for prenatal and postnatal development. It ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Night Blindness
Nyctalopia (; ), also called night-blindness, is a condition making it difficult or impossible to see in relatively low light. It is a symptom of several eye diseases. Night blindness may exist from birth, or be caused by injury or malnutrition (for example, vitamin A deficiency). It can be described as insufficient adaptation to darkness. The most common cause of nyctalopia is retinitis pigmentosa, a disorder in which the rod cells in the retina gradually lose their ability to respond to the light. Patients with this genetic condition have progressive nyctalopia and eventually, their daytime vision may also be affected. In X-linked congenital stationary night blindness, from birth the rods either do not work at all, or work very little, but the condition does not get worse. Another cause of night blindness is a deficiency of retinol, or vitamin A1, found in fish oils, liver and dairy products. The opposite problem, the inability to see in bright light, is known as '' hemeralop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Puberty
Puberty is the process of physical changes through which a child's body matures into an adult body capable of sexual reproduction. It is initiated by hormonal signals from the brain to the gonads: the ovaries in a girl, the testes in a boy. In response to the signals, the gonads produce hormones that stimulate libido and the growth, function, and transformation of the brain, bones, muscle, blood, skin, hair, breasts, and sex organs. Physical growth—height and weight—accelerates in the first half of puberty and is completed when an adult body has been developed. Before puberty, the external sex organs, known as primary sexual characteristics, are sex characteristics that distinguish boys and girls. Puberty leads to sexual dimorphism through the development of the secondary sex characteristics, which further distinguish the sexes. On average, girls begin puberty at ages 10–11 and complete puberty at ages 15–17; boys generally begin puberty at ages 11–12 and c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypogonadism
Hypogonadism means diminished functional activity of the gonads—the testes or the ovaries—that may result in diminished production of sex hormones. Low androgen (e.g., testosterone) levels are referred to as hypoandrogenism and low estrogen (e.g., estradiol) as hypoestrogenism. These are responsible for the observed signs and symptoms in both males and females. Hypogonadism, commonly referred to by the symptom "low testosterone" or "Low T", can also decrease other hormones secreted by the gonads including progesterone, DHEA, anti-Müllerian hormone, activin, and inhibin. Sperm development (spermatogenesis) and release of the egg from the ovaries (ovulation) may be impaired by hypogonadism, which, depending on the degree of severity, may result in partial or complete infertility. In January 2020, the American College of Physicians issued clinical guidelines for testosterone treatment in adult men with age-related low levels of testosterone. The guidelines are sup ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Birth Weight
Birth weight is the body weight of a baby at its birth. The average birth weight in babies of European descent is , with the normative range between . On average, babies of South Asian and Chinese descent weigh about . As far as low birth weight prevalence rates changing over time, there has been a slight decrease from 7.9% (1970) to 6.8% (1980), then a slight increase to 8.3% (2006), to the current levels of 8.2% (2016). The prevalence of low birth weights has trended slightly upward from 2012 to the present. There have been numerous studies that have attempted, with varying degrees of success, to show links between birth weight and later-life conditions, including diabetes, obesity, tobacco smoking, and intelligence. Low birth weight is associated with neonatal infection and infant mortality. Abnormalities *A low birth weight can be caused either by a preterm birth (low gestational age at birth) or of the infant being small for gestational age (slow prenatal growth rate), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zinc Finger
A zinc finger is a small protein structural motif that is characterized by the coordination of one or more zinc ions (Zn2+) in order to stabilize the fold. It was originally coined to describe the finger-like appearance of a hypothesized structure from the African clawed frog (''Xenopus laevis'') transcription factor IIIA. However, it has been found to encompass a wide variety of differing protein structures in eukaryotic cells. '' Xenopus laevis'' TFIIIA was originally demonstrated to contain zinc and require the metal for function in 1983, the first such reported zinc requirement for a gene regulatory protein followed soon thereafter by the Krüppel factor in ''Drosophila''. It often appears as a metal-binding domain in multi-domain proteins. Proteins that contain zinc fingers (zinc finger proteins) are classified into several different structural families. Unlike many other clearly defined supersecondary structures such as Greek keys or β hairpins, there are a number of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
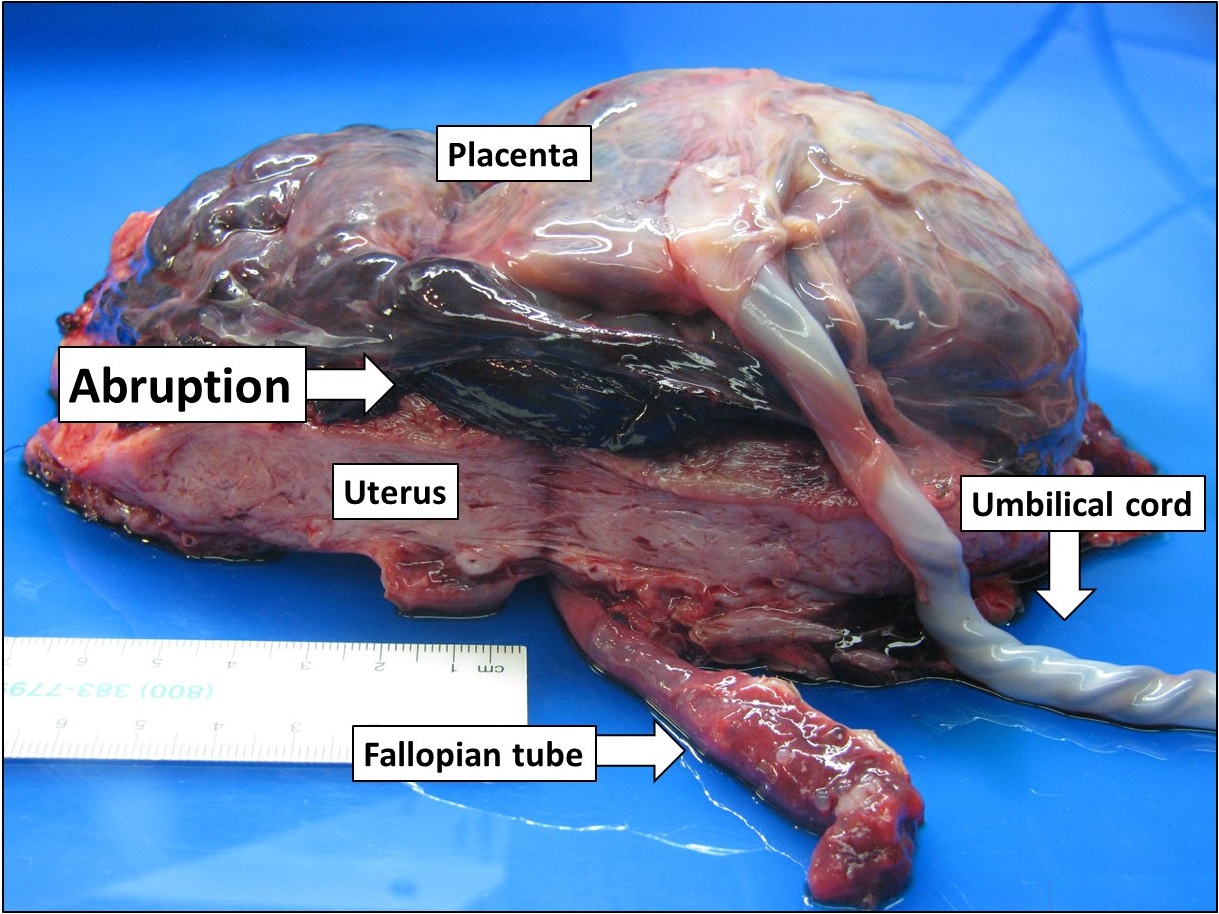
Placental Abruption
Placental abruption is when the placenta separates early from the uterus, in other words separates before childbirth. It occurs most commonly around 25 weeks of pregnancy. Symptoms may include vaginal bleeding, lower abdominal pain, and dangerously low blood pressure. Complications for the mother can include disseminated intravascular coagulopathy and kidney failure. Complications for the baby can include fetal distress, low birthweight, preterm delivery, and stillbirth. The cause of placental abruption is not entirely clear. Risk factors include smoking, pre-eclampsia, prior abruption (most important and predictive risk factor), trauma during pregnancy, cocaine use, and previous cesarean section. Diagnosis is based on symptoms and supported by ultrasound. It is classified as a complication of pregnancy. For small abruption, bed rest may be recommended, while for more significant abruptions or those that occur near term, delivery may be recommended. If everything is stab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dystocia
Obstructed labour, also known as labour dystocia, is the baby not exiting the pelvis because it is physically block during childbirth although the uterus contracts normally. Complications for the baby include not getting enough oxygen which may result in death. It increases the risk of the mother getting an infection, having uterine rupture, or having post-partum bleeding. Long-term complications for the mother include obstetrical fistula. Obstructed labour is said to result in prolonged labour, when the active phase of labour is longer than 12 hours. The main causes of obstructed labour include a large or abnormally positioned baby, a small pelvis, and problems with the birth canal. Abnormal positioning includes shoulder dystocia where the anterior shoulder does not pass easily below the pubic bone. Risk factors for a small pelvis include malnutrition and a lack of exposure to sunlight causing vitamin D deficiency. It is also more common in adolescence as the pelvis may ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anhedonia
Anhedonia is a diverse array of deficits in hedonic function, including reduced motivation or ability to experience pleasure. While earlier definitions emphasized the inability to experience pleasure, anhedonia is currently used by researchers to refer to reduced motivation, reduced anticipatory pleasure (wanting), reduced consummatory pleasure (liking), and deficits in reinforcement learning. In the ''Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition'' (DSM-5), anhedonia is a component of depressive disorders, substance-related disorders, psychotic disorders, and personality disorders, where it is defined by either a reduced ability to experience pleasure, or a diminished interest in engaging in pleasurable activities. While the ''International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems, Tenth Revision'' (ICD-10) does not explicitly mention anhedonia, the depressive symptom analogous to anhedonia as described in the DSM-5 is a loss of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hedonic Tone
Valence, or hedonic tone, is the affective quality referring to the intrinsic attractiveness/"good"-ness (positive valence) or averseness/"bad"-ness (negative valence) of an event, object, or situation. The term also characterizes and categorizes specific emotions. For example, emotions popularly referred to as "negative", such as anger and fear, have ''negative valence''. Joy has ''positive valence''. Positively valenced emotions are evoked by positively valenced events, objects, or situations. The term is also used to describe the hedonic tone of feelings, affect, certain behaviors (for example, approach and avoidance), goal attainment or nonattainment, and conformity with or violation of norms. Ambivalence can be viewed as conflict between positive and negative valence-carriers. Theorists taking a valence-based approach to studying affect, judgment, and choice posit that emotions with the same valence (e.g., anger and fear or pride and surprise) produce a similar influe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TNF-α
Tumor necrosis factor (TNF, cachexin, or cachectin; formerly known as tumor necrosis factor alpha or TNF-α) is an adipokine and a cytokine. TNF is a member of the TNF superfamily, which consists of various transmembrane proteins with a homologous TNF domain. As an adipokine, TNF promotes insulin resistance, and is associated with obesity-induced type 2 diabetes. As a cytokine, TNF is used by the immune system for cell signaling. If macrophages (certain white blood cells) detect an infection, they release TNF to alert other immune system cells as part of an inflammatory response. TNF signaling occurs through two receptors: TNFR1 and TNFR2. TNFR1 is constituitively expressed on most cell types, whereas TNFR2 is restricted primarily to endothelial, epithelial, and subsets of immune cells. TNFR1 signaling tends to be pro-inflammatory and apoptotic, whereas TNFR2 signaling is anti-inflammatory and promotes cell proliferation. Suppression of TNFR1 signaling has been importan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interleukin 6
Interleukin 6 (IL-6) is an interleukin that acts as both a pro-inflammatory cytokine and an anti-inflammatory myokine. In humans, it is encoded by the ''IL6'' gene. In addition, osteoblasts secrete IL-6 to stimulate osteoclast formation. Smooth muscle cells in the tunica media of many blood vessels also produce IL-6 as a pro-inflammatory cytokine. IL-6's role as an anti-inflammatory myokine is mediated through its inhibitory effects on TNF-alpha and IL-1 and its activation of IL-1ra and IL-10. There is some early evidence that IL-6 can be used as an inflammatory marker for severe COVID-19 infection with poor prognosis, in the context of the wider coronavirus pandemic. Function Immune system IL-6 is secreted by macrophages in response to specific microbial molecules, referred to as pathogen-associated molecular patterns ( PAMPs). These PAMPs bind to an important group of detection molecules of the innate immune system, called pattern recognition receptors (PRRs), inc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |