Birth Weight on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Birth weight is the
Birth weight is the
 Children born with an abnormally low birth weight can have significant problems within the first few years of life. They may have trouble gaining weight, obtaining adequate nutrition, and devleoping a strong immune system. They also have higher risks for mortality, behavior problems, and mental deficiencies. Low birth weight babies are more likely to develop the following conditions compared to normal birth weight babies:
* Breathing problems (
Children born with an abnormally low birth weight can have significant problems within the first few years of life. They may have trouble gaining weight, obtaining adequate nutrition, and devleoping a strong immune system. They also have higher risks for mortality, behavior problems, and mental deficiencies. Low birth weight babies are more likely to develop the following conditions compared to normal birth weight babies:
* Breathing problems (
 Birth weight is the
Birth weight is the body weight
Human body weight is a person's mass or weight.
Strictly speaking, body weight is the measurement of weight without items located on the person. Practically though, body weight may be measured with clothes on, but without shoes or heavy accessor ...
of a baby
An infant or baby is the very young offspring of human beings. ''Infant'' (from the Latin word ''infans'', meaning 'unable to speak' or 'speechless') is a formal or specialised synonym for the common term ''baby''. The terms may also be used to ...
at its birth
Birth is the act or process of bearing or bringing forth offspring, also referred to in technical contexts as parturition. In mammals, the process is initiated by hormones which cause the muscular walls of the uterus to contract, expelling the f ...
. The average birth weight in babies of European descent is , with the normative range between . On average, babies of South Asian and Chinese descent weigh about . As far as low birth weight prevalence rates changing over time, there has been a slight decrease from 7.9% (1970) to 6.8% (1980), then a slight increase to 8.3% (2006), to the current levels of 8.2% (2016). The prevalence of low birth weights has trended slightly upward from 2012 to the present.
There have been numerous studies that have attempted, with varying degrees of success, to show links between birth weight and later-life conditions, including diabetes
Diabetes, also known as diabetes mellitus, is a group of metabolic disorders characterized by a high blood sugar level ( hyperglycemia) over a prolonged period of time. Symptoms often include frequent urination, increased thirst and increased ap ...
, obesity
Obesity is a medical condition, sometimes considered a disease, in which excess body fat has accumulated to such an extent that it may negatively affect health. People are classified as obese when their body mass index (BMI)—a person's we ...
, tobacco smoking
Tobacco smoking is the practice of burning tobacco and ingesting the resulting smoke. The smoke may be inhaled, as is done with cigarettes, or simply released from the mouth, as is generally done with pipes and cigars. The practice is believed ...
, and intelligence
Intelligence has been defined in many ways: the capacity for abstraction, logic, understanding, self-awareness, learning, emotional knowledge, reasoning, planning, creativity, critical thinking, and problem-solving. More generally, it can b ...
. Low birth weight is associated with neonatal infection
Neonatal infections are infections of the neonate (newborn) acquired during prenatal development or in the first four weeks of life (neonatal period). Neonatal infections may be contracted by mother to child transmission, in the birth canal dur ...
and infant mortality
Infant mortality is the death of young children under the age of 1. This death toll is measured by the infant mortality rate (IMR), which is the probability of deaths of children under one year of age per 1000 live births. The under-five morta ...
.
Abnormalities
*Alow birth weight
Low birth weight (LBW) is defined by the World Health Organization as a birth weight of an
infant of or less, regardless of gestational age. Infants born with LBW have added health risks which require close management, often in a neonatal inten ...
can be caused either by a preterm birth
Preterm birth, also known as premature birth, is the birth of a baby at fewer than 37 weeks gestational age, as opposed to full-term delivery at approximately 40 weeks. Extreme preterm is less than 28 weeks, very early preterm birth is between 2 ...
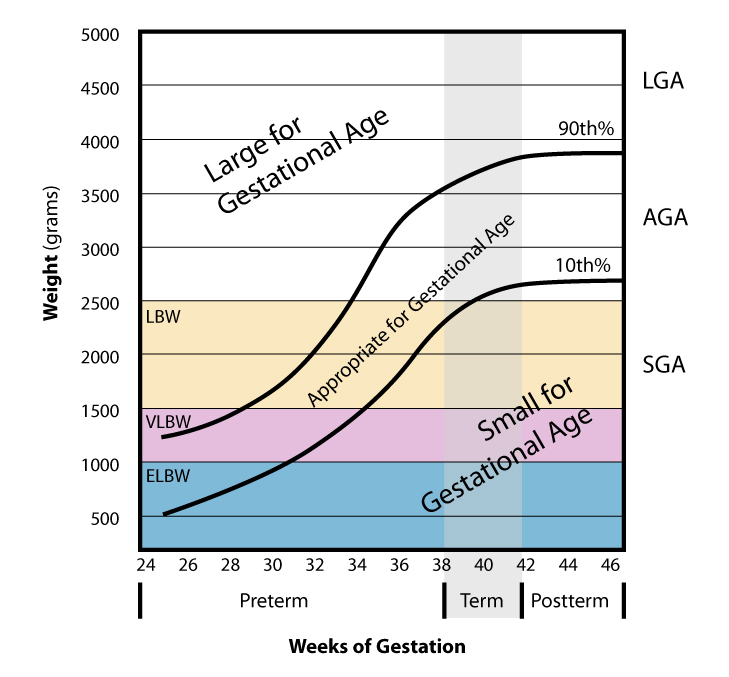
(low gestational age at birth) or of the infant being small for gestational age
Small for gestational age (SGA) newborns are those who are smaller in size than normal for the gestational age, most commonly defined as a weight below the 10th percentile for the gestational age.
Causes
Being small for gestational age is broadly ...
(slow prenatal growth rate), or a combination of both. Potential causes of low birth weight can also be cause by health issues in the person giving birth, genetic factors, or problems in the placenta
The placenta is a temporary embryonic and later fetal organ that begins developing from the blastocyst shortly after implantation. It plays critical roles in facilitating nutrient, gas and waste exchange between the physically separate mater ...
.
*A very large birth weight is usually caused by the infant having been large for gestational age
Large for gestational age (LGA) is a term used to describe infants that are born with an abnormally high weight, specifically in the 90th percentile or above, compared to other babies of the same developmental age. Macrosomia is a similar term tha ...
. Infants that are large for gestational age have been associated with significantly higher rates of neonatal morbidity.
Determinants

Genetics
There are two genetic loci that have been strongly linked to birth weight,ADCY5
Adenylyl cyclase type 5 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''ADCY5'' gene.
Interactions
ADCY5 has been shown to interact with RGS2
Regulator of G-protein signaling 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''RGS2'' gene. It i ...
and CCNL1
Cyclin-L1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''CCNL1'' gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "...Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or '' ...
, as well four that show some evidence ( CDKAL1, HHEX-IDE, GCK, and TCF7L2
Transcription factor 7-like 2 (T-cell specific, HMG-box), also known as TCF7L2 or TCF4, is a protein acting as a transcription factor that, in humans, is encoded by the ''TCF7L2'' gene. The TCF7L2 gene is located on chromosome 10q25.2–q25.3, con ...
). The heritability
Heritability is a statistic used in the fields of breeding and genetics that estimates the degree of ''variation'' in a phenotypic trait in a population that is due to genetic variation between individuals in that population. The concept of h ...
of birth weight ranges from 25 to 40%. There is a complex relationship between a baby's genes and the maternal environment that the child is developing in. Foetal
A fetus or foetus (; plural fetuses, feti, foetuses, or foeti) is the unborn offspring that develops from an animal embryo. Following embryonic development the fetal stage of development takes place. In human prenatal development, fetal develo ...
genes influence how the fetus grows in utero, and the maternal genes influence how the environment affects the growing fetus.
Maternal health
Thehealth
Health, according to the World Health Organization, is "a state of complete physical, mental and social well-being and not merely the absence of disease and infirmity".World Health Organization. (2006)''Constitution of the World Health Organiza ...
of the mother during the pregnancy can affect birth weight. A pre-existing disease or acquired disease in pregnancy is sometimes associated with decreased birth weight. For example, celiac disease
Coeliac disease (British English) or celiac disease (American English) is a long-term autoimmune disorder, primarily affecting the small intestine, where individuals develop intolerance to gluten, present in foods such as wheat, rye and barle ...
confers an odds ratio
An odds ratio (OR) is a statistic that quantifies the strength of the association between two events, A and B. The odds ratio is defined as the ratio of the odds of A in the presence of B and the odds of A in the absence of B, or equivalently (due ...
of low birth weight of approximately 1.8. Certain medications (e.g. for high blood pressure or epilepsy) can put a mother at a higher risk for delivering a low birth weight baby. Women younger than 15 or older than 35 are at a higher risk to have a low-birth weight baby. Multiple births, where a mother has more than one child at one time, can also be a determinant in birth weight as each baby is likely to be outside the AGA (appropriate for gestational age). Multiple births put children at a higher rate to have low birth weight (56.6%) compared to children born in a single birth ( 6.2%). Low birth weight can also vary by maternal age. In 2008 the rate of low birth weight was the highest in babies born to women younger than 15 years old (12.4%). Women aged 40–54 had a rate of low birth weight at 11.8 percent. The lowest rates of low birth weight happened among babies whose mothers were between the ages of 25–29 years (4.4%) and 30–34 years (7.6%).
Stress
Stressful events have been demonstrated to produce significant effects on birth weight. Those mothers who have stressful events duringpregnancy
Pregnancy is the time during which one or more offspring develops ( gestates) inside a woman's uterus (womb). A multiple pregnancy involves more than one offspring, such as with twins.
Pregnancy usually occurs by sexual intercourse, but ca ...
, especially during the first and second trimester, are at higher risk to deliver low-birth weight babies. Researchers furthered this study and found that maternal stressful events that occur prior to conception have a negative impact on birth weight as well, and can result in a higher risk for preterm and lower birth weight babies. Women who experienced abuse (physical, sexual, or emotional) during pregnancy are also at increased risk of delivering a low-birth weight baby. For example, in a study completed by Witt et al., those women who experienced a stressful event (i.e. death of close family member, infertility issues, separation from partner) prior to conception had 38% more of a chance to have a very low birth weight baby compared to those who had not experienced a stressful life event. The theory is that stress can impact a baby based on two different mechanisms: neuroendocrine pathway or immune/inflammatory pathway. Stress causes the body to produce stress hormones called glucocorticoid
Glucocorticoids (or, less commonly, glucocorticosteroids) are a class of corticosteroids, which are a class of steroid hormones. Glucocorticoids are corticosteroids that bind to the glucocorticoid receptor that is present in almost every verteb ...
s that can suppress the immune system., as well as raises levels of placental corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH) which can lead to preterm
Preterm birth, also known as premature birth, is the birth of a baby at fewer than 37 weeks gestational age, as opposed to full-term delivery at approximately 40 weeks. Extreme preterm is less than 28 weeks, very early preterm birth is between ...
labor. These findings can pose evidence for future prevention efforts for low birth weight babies. One way to decrease rates of low birth weight and premature delivery is to focus on the health of women prior to conception through reproductive education, screening and counseling regarding mental health issues and stress, and access to primary care.
Racial stress
Non-Hispanic Blacks have the highest infant mortality rate in the United States (11.4 deaths per 1,000 live births compared to the national average of 5.9 deaths per 1,000 live births). Subsequently, there has been growing research supporting the idea ofracial discrimination
Racial discrimination is any discrimination against any individual on the basis of their skin color, race or ethnic origin.Individuals can discriminate by refusing to do business with, socialize with, or share resources with people of a certain g ...
as a risk factor for low birth weight. In one study by Collins et al., evidence suggested that African American mothers who experienced high levels of racial discrimination were at significantly higher risk of delivering a very low-birth weight baby compared to African American mothers who had not experienced racial discrimination. Black infants (13.2%) are more likely to have low birth weight compared to Asian and Pacific Islander (8.1%), American Indian and Alaska Native (7.6%), Non-Hispanic White (7.0%), and Hispanic Infants (7.1%).
Environmental factors
Environmental factors, including exposure of the mother tosecondhand smoke
Passive smoking is the inhalation of tobacco smoke, called secondhand smoke (SHS), or environmental tobacco smoke (ETS), by persons other than the intended "active" smoker. It occurs when tobacco smoke enters an environment, causing its inhalat ...
can be a factor in determining the birth weight of child. In 2014, 13% of children exposed to smoke were born with low birth weight compared with 7.5% of those children born to nonsmokers. Children born to mothers who smoked or were exposed to secondhand smoke are more likely to develop health problems earlier in life such as neurodevelopmental delays. When mothers actively smoke during pregnancy, their child is at a higher risk of being born with a low birth weight. Smoking can also be a stress management tool used by expecting mothers. There is some support for lower socioeconomic status of the parents being a determinant of low birth weight, but there is conflicting evidence, as socioeconomic status is tied to many other factors.
Neonatal care
Most babies admitted to theNICU
A neonatal intensive care unit (NICU), also known as an intensive care nursery (ICN), is an intensive care unit (ICU) specializing in the care of ill or premature newborn infants. Neonatal refers to the first 28 days of life. Neonatal care, as kn ...
are born before 37 weeks of pregnancy or have low birth weight which is less than . They could also have a medical condition that requires special care. In the United States nearly half a million babies are born preterm. Because of this, many of these babies also have low birth weights. There are four levels of care in the neonatal care units: Intensive Care
Intensive care medicine, also called critical care medicine, is a medical specialty that deals with seriously or critically ill patients who have, are at risk of, or are recovering from conditions that may be life-threatening. It includes pro ...
, High Dependency Care, Low Dependency, and Transitional Care:
* Intensive Care: For babies with serious problems. This includes babies born three months early and have extremely low birth weight.
* High Dependency Care: For babies with less serious problem, but who still may not to be looked after or babies that are recovering from a critical illness.
* Low Dependency Care: For babies that do not need a continuous supervision.
* Transitional Care: For babies that still need medical treatment, but are well enough to be called for at their mother's bedside.
Influence on early life
 Children born with an abnormally low birth weight can have significant problems within the first few years of life. They may have trouble gaining weight, obtaining adequate nutrition, and devleoping a strong immune system. They also have higher risks for mortality, behavior problems, and mental deficiencies. Low birth weight babies are more likely to develop the following conditions compared to normal birth weight babies:
* Breathing problems (
Children born with an abnormally low birth weight can have significant problems within the first few years of life. They may have trouble gaining weight, obtaining adequate nutrition, and devleoping a strong immune system. They also have higher risks for mortality, behavior problems, and mental deficiencies. Low birth weight babies are more likely to develop the following conditions compared to normal birth weight babies:
* Breathing problems (infant respiratory distress syndrome
Infantile respiratory distress syndrome (IRDS), also called respiratory distress syndrome of newborn, or increasingly surfactant deficiency disorder (SDD), and previously called hyaline membrane disease (HMD), is a syndrome in premature infants ...
)
* Bleeding in the brain (intraventricular hemorrhage
Intraventricular hemorrhage (IVH), also known as intraventricular bleeding, is a bleeding into the brain's ventricular system, where the cerebrospinal fluid is produced and circulates through towards the subarachnoid space. It can result from phys ...
)
* Patent ductus arteriosus
''Patent ductus arteriosus'' (PDA) is a medical condition in which the ''ductus arteriosus'' fails to close after birth: this allows a portion of oxygenated blood from the left heart to flow back to the lungs by flowing from the aorta, which has ...
(PDA)
* Necrotizing enterocolitis
Necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC) is a devastating intestinal disease that affects premature or very low birth weight infants.Gephart S.M., Quinn M. A call to action to fight for equity and end necrotizing enterocolitis disparities. ''Adv. Neonata ...
* Retinopathy of prematurity
Retinopathy of prematurity (ROP), also called retrolental fibroplasia (RLF) and Terry syndrome, is a disease of the eye affecting prematurely born babies generally having received neonatal intensive care, in which oxygen therapy is used due to ...
* Jaundice
Jaundice, also known as icterus, is a yellowish or greenish pigmentation of the skin and sclera due to high bilirubin levels. Jaundice in adults is typically a sign indicating the presence of underlying diseases involving abnormal heme meta ...
* Infections
That said, the effects of low birth weight on a child's first few years of life are often intertwined with other maternal, environmental, and genetic factors and most effects of low birth weight are only slightly negatively significant on a child's life when these factors are controlled for. When these factors are taken into account, the only significant effect low birth weight has on a child's development is early physical growth and the likelihood of being underweight, compared to those with a normal birth rate.
Influence on adult life
Studies have investigated how a person's birth weight can influence their future life, including potential links withobesity
Obesity is a medical condition, sometimes considered a disease, in which excess body fat has accumulated to such an extent that it may negatively affect health. People are classified as obese when their body mass index (BMI)—a person's we ...
, diabetes
Diabetes, also known as diabetes mellitus, is a group of metabolic disorders characterized by a high blood sugar level ( hyperglycemia) over a prolonged period of time. Symptoms often include frequent urination, increased thirst and increased ap ...
and intelligence
Intelligence has been defined in many ways: the capacity for abstraction, logic, understanding, self-awareness, learning, emotional knowledge, reasoning, planning, creativity, critical thinking, and problem-solving. More generally, it can b ...
.
A baby born small or large for gestational age (either of the two extremes) is thought to have an increased risk of developing obesity
Obesity is a medical condition, sometimes considered a disease, in which excess body fat has accumulated to such an extent that it may negatively affect health. People are classified as obese when their body mass index (BMI)—a person's we ...
, but it was also shown that this relationship is fully explained by maternal weight.
Growth hormone (GH) therapy at a certain dose induced catch-up of lean body mass (LBM). However percentage body fat decreased in the GH-treated subjects. Bone mineral density SDS measured by DEXA
Dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA, or DEXA) is a means of measuring bone mineral density (BMD) using spectral imaging. Two X-ray beams, with different energy levels, are aimed at the patient's bones. When soft tissue absorption is subtracted ...
increased significantly in the GH-treated group compared to the untreated subjects, though there is much debate over whether or not SGA (small for gestational age) is significantly adverse to children to warrant inducing catch-up.
Babies that have a low birth weight are thought to have an increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes
Diabetes, also known as diabetes mellitus, is a group of metabolic disorders characterized by a high blood sugar level ( hyperglycemia) over a prolonged period of time. Symptoms often include frequent urination, increased thirst and increased ap ...
in later life. Low birth weight is linked with increase rates of obesity, insulin resistance, and type 2 diabetes and it is shown that children with the low birth weights have increased leptin levels after they catch up growth during childhood. Adiponectin
Adiponectin (also referred to as GBP-28, apM1, AdipoQ and Acrp30) is a protein hormone and adipokine, which is involved in regulating glucose levels as well as fatty acid breakdown. In humans it is encoded by the ''ADIPOQ'' gene and it is produ ...
levels are positively related with birth weight and BMI in babies with an increase of risk of type 2 diabetes. The leptin and adiponection mechanisms are still being studied when involving low birth weight.
Around the world
There is much variation regarding birth weight within continents, countries, and cities. Even though over 20 million babies are born each year with low birth weight, it is hard to know the exact number, as more than half of babies born in the world are not weighed at birth. The baby's weight is an indicator of the mother and baby's health. In 2013, 22 million newborns had low birth weight, around 16 percent of all babies globally. Data on low birth weight is adjusted to account for under reporting. South Asia has the highest rate of babies not weighed at birth with 66 percent, but also have the highest low birth weight, at 28 percent worldwide. West and Central Africa and least developed countries are next, with 14 percent low birth weight worldwide. More than 96.5% of low birth weight babies are born in developing countries around the world. Because low birth weight babies can require more extensive care, it places a financial burden on communities.Prevention
TheWorld Health Organization
The World Health Organization (WHO) is a specialized agency of the United Nations responsible for international public health. The WHO Constitution states its main objective as "the attainment by all peoples of the highest possible level of h ...
(WHO) recently announced an initiative to have a thirty percent reduction in low birth weight worldwide. This is public health priority, as birth weight can have short and long term effects. WHO estimates that worldwide, 15-20 % of all births each year are considered low birth weight, which is about 20 million births.
The start of prenatal care is very important to help prevent low birth weight and early medical problems. Going to regular doctor's visits is very important for the health of the mother and the baby. At the visits the OB/GYN will be checking maternal nutrition and weight gain because that is linked with the baby's weight gain. The mother having a healthy diet is essential for the baby. Maintaining good nutrition by taking folic acid
Folate, also known as vitamin B9 and folacin, is one of the B vitamins. Manufactured folic acid, which is converted into folate by the body, is used as a dietary supplement and in food fortification as it is more stable during processing and ...
, which can be found in fruits and vegetables, is linked to the prevention of premature births and low birth weight. Alcohol, cigarettes, and drugs should also be avoided during pregnancy because they can also lead to poor growth and other complications. By seeing the doctor they are also able to monitor pre-existing medical illnesses to make sure they are under control during pregnancy. Mothers with high blood pressure
Hypertension (HTN or HT), also known as high blood pressure (HBP), is a long-term medical condition in which the blood pressure in the arteries is persistently elevated. High blood pressure usually does not cause symptoms. Long-term high bl ...
and type 2 diabetes
Type 2 diabetes, formerly known as adult-onset diabetes, is a form of diabetes mellitus that is characterized by high blood sugar, insulin resistance, and relative lack of insulin. Common symptoms include increased thirst, frequent urinatio ...
are more likely to have infants with low birth weights. One essential action to increase normal birth weights is to have affordable, accessible, and culturally sensitive
Cultural sensitivity, also referred to as cross-cultural sensitivity or cultural awareness, is the knowledge, awareness, and acceptance of other cultures and others' cultural identities. It is related to cultural competence (the skills needed fo ...
prenatal care worldwide. This is essential not just for treating low birth weight, but also preventing it. Other prevention efforts include: smoking cessation
Smoking cessation, usually called quitting smoking or stopping smoking, is the process of discontinuing tobacco smoking. Tobacco smoke contains nicotine, which is addictive and can cause dependence. As a result, nicotine withdrawal often m ...
programs, food-distribution systems, stress reduction and social service supports.
See also
*Infant mortality
Infant mortality is the death of young children under the age of 1. This death toll is measured by the infant mortality rate (IMR), which is the probability of deaths of children under one year of age per 1000 live births. The under-five morta ...
*Low birth-weight paradox {{Short description, Statistical quirk of babies' birth weights
The low birth-weight paradox is an apparently paradoxical observation relating to the birth weights and mortality rate of children born to tobacco smoking mothers. Low birth-weight chi ...
*MOMO syndrome
MOMO syndrome is an extremely rare genetic disorder which belongs to the overgrowth syndromes and has been diagnosed in only seven cases around the world, and occurs in 1 in 100 million births. The name is an acronym of the four primary aspects o ...
*Prenatal nutrition
Prenatal nutrition addresses nutrient recommendations before and during pregnancy. Nutrition and weight management before and during pregnancy has a profound effect on the development of infants. This is a rather critical time for healthy develo ...
*Thrifty phenotype
Thrifty phenotype refers to the correlation between low birth weight of neonates and the increased risk of developing metabolic syndromes later in life, including type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular diseases. Although early life undernutrition is th ...
References
Further reading
* *External links
* * {{DEFAULTSORT:Birth weight Obstetrics Neonatology Human body weight Midwifery