|
Zi Chan
Gongsun Qiao (), died 522 BC, was better known by his courtesy name Zichan () (Wade-Giles, WG: Tzu Ch'an). From 544 BC until his death, he served as the chief minister of the Zheng (state), State of Zheng. His ancestral surname was Ji (姬), and clan name Guo (國). As politician of a small but venerable state in central China during the Spring and Autumn period (Chunqiu), he faced not only aggressive larger states, but also the confusion caused by a governing tradition in crisis. Under him the Zheng state managed to grow and prosper. Zichan was responsible for many of its strengthening reforms and his statecraft was often viewed with respect. Career profile A grandson of Duke Mu of Zheng, Zichan served as prime minister of Zheng from 544 BC until his death. Under Zichan, the Zheng state managed to grow and prosper. It expanded its territory. This was a difficult task for a small state surrounded by several large states, accomplished toward the end of the Spring and Autumn period. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
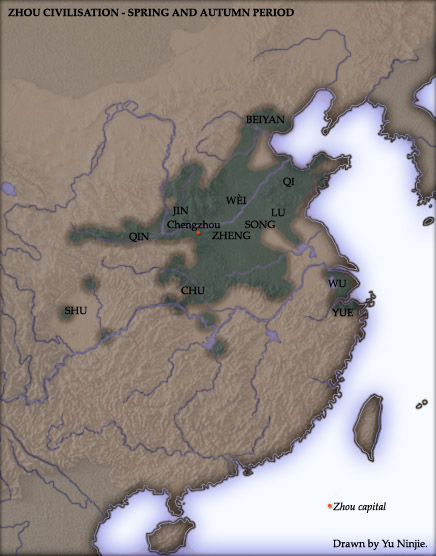
Eastern Zhou
The Eastern Zhou (; zh, c=, p=Dōngzhōu, w=Tung1-chou1, t= ; 771–256 BC) was a royal dynasty of China and the second half of the Zhou dynasty. It was divided into two periods: the Spring and Autumn and the Warring States. History In 770 BCE, the capital of the Zhou Kingdom was moved from Haojing (Chang'an County in Xi'an City) to Luoyi (known today as Luoyang, Henan Province). This brought about the beginning of the Eastern Zhou dynasty (as opposed to Western Zhou dynasty), so named due to Luoyi being situated to the east of Haojing. Over 25 kings reigned over the Eastern Zhou Dynasty, lasting 515 years in all. With the death of King You of Zhou, the last king of the Western Zhou Dynasty, ascended Crown Prince Yijiu was proclaimed the new king by the nobles from the states of Zheng, Lü, Qin and the Marquess of Shen. He was King Ping of Zhou. In the second year of his reign, he moved the capital east to Luoyi as Quanrong invaded Haojing, indicating the end of the W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hegemony
Hegemony (, , ) is the political, economic, and military predominance of one state over other states. In Ancient Greece (8th BC – AD 6th ), hegemony denoted the politico-military dominance of the ''hegemon'' city-state over other city-states. In the 19th century, ''hegemony'' denoted the "social or cultural predominance or ascendancy; predominance by one group within a society or milieu" and "a group or regime which exerts undue influence within a society". In cultural imperialism, the leader state dictates the internal politics and the societal character of the subordinate states that constitute the hegemonic sphere of influence, either by an internal, sponsored government or by an external, installed government. The term ''hegemonism'' denoted the geopolitical and the cultural predominance of one country over other countries, e.g. the hegemony of the Great Powers established with European colonialism in Africa, Asia, and Latin America. In Marxist philosophy, Antonio Gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Western Zhou
The Western Zhou ( zh, c=, p=Xīzhōu; c. 1045 BC – 771 BC) was a royal dynasty of China and the first half of the Zhou dynasty. It began when King Wu of Zhou overthrew the Shang dynasty at the Battle of Muye and ended when the Quanrong nomads sacked its capital Haojing and killed King You of Zhou in 771 BC. The Western Zhou early state was successful for about seventy-five years and then slowly lost power. The former Shang lands were divided into hereditary fiefs which became increasingly independent of the king. In 771 BC, the Zhou were driven out of the Wei River valley; afterwards real power was in the hands of the king's nominal vassals. Civil war Few records survive from this early period and accounts from the Western Zhou period cover little beyond a list of kings with uncertain dates. King Wu died two or three years after the conquest. Because his son, King Cheng of Zhou was young, his brother, the Duke of Zhou Ji Dan assisted the young and inexperienced king ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shi (class)
The four occupations () or "four categories of the people" ()Hansson, pp. 20-21Brook, 72. was an occupation classification used in ancient China by either Confucian or Legalist scholars as far back as the late Zhou dynasty and is considered a central part of the fengjian social structure (c. 1046–256 BC).Fairbank, 108. These were the ''shi'' (gentry scholars), the ''nong'' (peasant farmers), the ''gong'' (artisans and craftsmen), and the ''shang'' (merchants and traders). The four occupations were not always arranged in this order. The four categories were not socioeconomic classes; wealth and standing did not correspond to these categories, nor were they hereditary. The system did not factor in all social groups present in premodern Chinese society, and its broad categories were more an idealization than a practical reality. The commercialization of Chinese society in the Song and Ming periods further blurred the lines between these four occupations. The definition of the iden ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Divination
Divination (from Latin ''divinare'', 'to foresee, to foretell, to predict, to prophesy') is the attempt to gain insight into a question or situation by way of an occultic, standardized process or ritual. Used in various forms throughout history, diviners ascertain their interpretations of how a querent should proceed by reading signs, events, or omens, or through alleged contact or interaction with a supernatural agency. Divination can be seen as a systematic method with which to organize what appears to be disjointed, random facets of existence such that they provide insight into a problem at hand. If a distinction is to be made between divination and fortune-telling, divination has a more formal or ritualistic element and often contains a more social character, usually in a religious context, as seen in traditional African medicine. Fortune-telling, on the other hand, is a more everyday practice for personal purposes. Particular divination methods vary by culture and reli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinese Philosophy
Chinese philosophy originates in the Spring and Autumn period () and Warring States period (), during a period known as the " Hundred Schools of Thought", which was characterized by significant intellectual and cultural developments. Although much of Chinese philosophy begun in the Warring States period, elements of Chinese philosophy have existed for several thousand years. Some can be found in the '' I Ching'' (the ''Book of Changes''), an ancient compendium of divination, which dates back to at least 672 BCE. It was during the Warring States era that what Sima Tan termed the major philosophical schools of China—Confucianism, Legalism, and Taoism—arose, along with philosophies that later fell into obscurity, like Agriculturalism, Mohism, Chinese Naturalism, and the Logicians. Even in modern society, Confucianism is still the creed of etiquette for Chinese society. Chinese philosophy as a philosophy The debate over whether the ''thought'' of ancient ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sovereignty
Sovereignty is the defining authority within individual consciousness, social construct, or territory. Sovereignty entails hierarchy within the state, as well as external autonomy for states. In any state, sovereignty is assigned to the person, body, or institution that has the ultimate authority over other people in order to establish a law or change an existing law. In political theory, sovereignty is a substantive term designating supreme legitimate authority over some polity. In international law, sovereignty is the exercise of power by a state. '' De jure'' sovereignty refers to the legal right to do so; '' de facto'' sovereignty refers to the factual ability to do so. This can become an issue of special concern upon the failure of the usual expectation that ''de jure'' and ''de facto'' sovereignty exist at the place and time of concern, and reside within the same organization. Etymology The term arises from the unattested Vulgar Latin's ''*superanus'', (itself derived ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jin (Chinese State)
Jin (, Old Chinese: ''*''), originally known as Tang (唐), was a major state during the middle part of the Zhou dynasty, based near the centre of what was then China, on the lands attributed to the legendary Xia dynasty: the southern part of modern Shanxi. Although it grew in power during the Spring and Autumn period, its aristocratic structure saw it break apart when the duke lost power to his nobles. In 403BC, Jin was split into three successor states: Han, Zhao and Wei. The Partition of Jin marks the end of the Spring and Autumn Period and the beginning of the Warring States period. Geography Jin was located in the lower Fen River drainage basin on the Shanxi plateau. To the north were the Xirong and Beidi peoples. To the west were the Lüliang Mountains and then the Loess Plateau of northern Shaanxi. To the southwest the Fen River turns west to join the south-flowing part of the Yellow River which soon leads to the Guanzhong, an area of the Wei River Valley tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sophists
A sophist ( el, σοφιστής, sophistes) was a teacher in ancient Greece in the fifth and fourth centuries BC. Sophists specialized in one or more subject areas, such as philosophy, rhetoric, music, athletics, and mathematics. They taught ''arete'' – "virtue" or "excellence" – predominantly to young statesmen and nobility. In the present day, however, a sophist refers to someone who deliberately argues using fallacious arguments or reasoning, in order to mislead; see the section below. Etymology The Greek word el, σοφός, sophos, a wise man, label=none is related to the noun el, σοφία, sophia, wisdom, label=none. Since the times of Homer it commonly referred to an expert in his profession or craft. Charioteers, sculptors, or military experts could be referred to as in their occupations. The word has gradually come to connote general wisdom and especially wisdom in human affairs such as politics, ethics, and household management. This was the meaning a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xunzi (book)
The ''Xunzi'' () is an ancient Chinese collection of philosophical writings attributed to and named after Xun Kuang, a 3rd-century BCE philosopher usually associated with the Confucian tradition. The ''Xunzi'' is perhaps most famous for the emphasis it places on education and propriety, as well as its striking assertion that "human nature is detestable". The text is furthermore an important source of early theories of ritual, cosmology, and governance. The ideas within the ''Xunzi'' are thought to have exerted a strong influence on Legalist thinkers, such as Han Fei, and laid the groundwork for much of Han Dynasty political ideology. The text criticizes a wide range of other prominent early Chinese thinkers, including Laozi, Zhuangzi, Mozi, and Mencius. Some ''Xunzi'' chapters are especially significant. The "Discussion of Heaven ( ''Tiān lùn'')" rejects the notion that heaven has a moral will. Instead, Xunzi asserts that heaven operates according to constant principles; thus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lüshi Chunqiu
The ''Lüshi Chunqiu'', also known in English as ''Master Lü's Spring and Autumn Annals'', is an encyclopedic Chinese classic text compiled around 239 BC under the patronage of the Qin Dynasty Chancellor Lü Buwei. In the evaluation of Michael Carson and Michael Loewe, "The ''Lü shih ch'un ch'iu'' is unique among early works in that it is well organized and comprehensive, containing extensive passages on such subjects as music and agriculture, which are unknown elsewhere. It is also one of the longest of the early texts, extending to something over 100,000 words. Background The ''Shiji'' (chap. 85, p. 2510) biography of Lü Buwei has the earliest information about the ''Lüshi Chunqiu''. Lü was a successful merchant from Handan who befriended King Zhuangxiang of Qin. The king's son Zheng, who the ''Shiji'' suggests was actually Lü's son, eventually became the first emperor Qin Shi Huang in 221 BC. When Zhuangxiang died in 247 BC, Lü Buwei was made regent for the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |