|
Zamenhof
L. L. Zamenhof (15 December 185914 April 1917) was an ophthalmologist who lived for most of his life in Warsaw. He is best known as the creator of Esperanto, the most widely used constructed international auxiliary language. Zamenhof first developed the Esperanto language in 1873 while still in school. He grew up fascinated by the idea of a world without war and believed that this could happen with the help of a new international auxiliary language. The language would be a tool to gather people together through neutral, fair, equitable communication. He successfully formed a community that continues today despite the World Wars of the 20th century, attempts to reform the language, and more modern IALs (the only other language like it at the time was Volapük). Additionally, Esperanto has developed like other languages: through the interaction and creativity of its users. In light of his achievements, and his support of intercultural dialogue, UNESCO selected Zamenhof as one ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
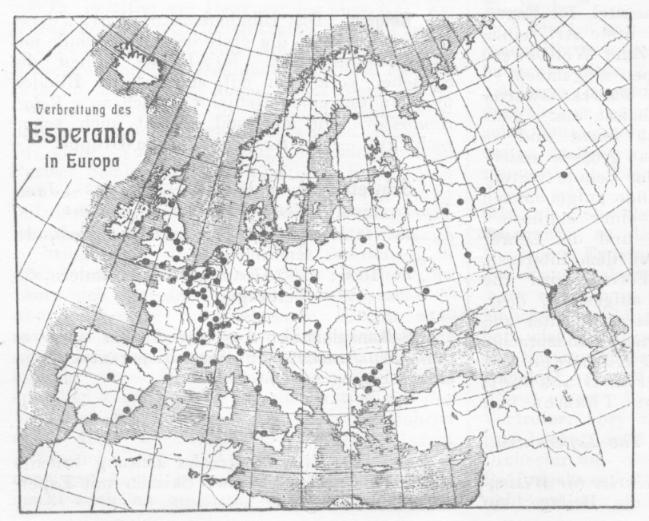
Esperanto
Esperanto ( or ) is the world's most widely spoken constructed international auxiliary language. Created by the Warsaw-based ophthalmologist L. L. Zamenhof in 1887, it was intended to be a universal second language for international communication, or "the international language" (). Zamenhof first described the language in '' Dr. Esperanto's International Language'' (), which he published under the pseudonym . Early adopters of the language liked the name ''Esperanto'' and soon used it to describe his language. The word translates into English as "one who hopes". Within the range of constructed languages, Esperanto occupies a middle ground between "naturalistic" (imitating existing natural languages) and ''a'priori'' (where features are not based on existing languages). Esperanto's vocabulary, syntax and semantics derive predominantly from languages of the Indo-European group. The vocabulary derives primarily from Romance languages, with substantial contributions from Ge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lidia Zamenhof
Lidia Zamenhof ( eo, Lidja Zamenhofo; 29 January 1904–1942) was a Polish writer, publisher, translator and the youngest daughter of Klara (Silbernik) and L. L. Zamenhof, the creator of Esperanto. She was an active promoter of Esperanto as well as of Homaranismo, a form of religious humanism first defined by her father. Around 1925 she became a member of the Baháʼí Faith. In late 1937 she went to the United States to teach that religion as well as Esperanto. In December 1938 she returned to Poland, where she continued to teach and translated many Baháʼí writings. ֿShe was murdered at the Treblinka extermination camp during the Holocaust. Life Lidia Zamenhof learned Esperanto as a nine-year-old girl. By the age of fourteen she translated from Polish literature; her first publications appeared several years thereafter. Having completed her university studies in law in 1925, she dedicated herself totally to working for Esperanto. In the same year during the 17th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unua Libro
''Dr. Esperanto's International Language'' (russian: wikt:международный#Russian, Международный wikt:язык#Russian, язык), commonly referred to as ' (''First Book''), is an 1887 book by Polish ophthalmologist L. L. Zamenhof, in which he first introduced and described the constructed language Esperanto. First published in Russian on , the publication of ''Unua Libro'' marks the formal beginning of the Esperanto movement. Writing under the pseudonym "Dr. Esperanto", Zamenhof originally referred to the language as the ''international language''; the use of ''Esperanto'' did not arise until 1889 when people began to use his pseudonym as the name of the language itself. Zamenhof reproduced a significant portion of the content of ''Unua Libro'' in the 1905 ''Fundamento de Esperanto'', which he established as the sole obligatory authority over Esperanto in the Declaration of Boulogne, ratified by the first World Esperanto Congress later that year. Histor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Klara Zamenhof
Klara Zamenhof (; 6 October 18636 December 1924) was a Polish Esperantist. She was married to L. L. Zamenhof, the inventor of the Esperanto language. Biography She was born on 6 October 1863 in Kaunas, Lithuania, then part of the Russian Empire as Kovno. She was the oldest daughter of Alexander Sender Silbernik and Golda Silbernik, wealthy Jewish merchants from Kovno. Contributions to Esperanto After her husband's premature death on 14 April 1917, she took over the promotion of Esperanto. She continued the development of the community centred around the language and supported her daughter Lidia, who trained as an Esperanto teacher in Europe and the US. Personal life She married Ludwik Lejzer Zamenhof in 1887, and raised three children: Adam, Lidia, and Zofia. All three were murdered in the Holocaust. She died in Warsaw on 6 December 1924, and is buried in the Jewish Cemetery A Jewish cemetery ( he, בית עלמין ''beit almin'' or ''beit kvarot'') is a cemetery ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dua Libro
''Dua Libro de l' Lingvo Internacia'' (''Second Book of the International Language''), usually referred to simply as ''Dua Libro'', is an 1888 book by L. L. Zamenhof. It is the second book in which Zamenhof wrote about the constructed language Esperanto, following ''Unua Libro'' in 1887, and the first book to be written entirely in the language. ''Dua Libro'' consists primarily of translations, which Zamenhof provided as reading material for those who expressed interest in the language after the publication of ''Unua Libro'' the previous year. It also usually includes ''Aldono al la Dua Libro'' (''Supplement to the Second Book''), which was originally published separately. In ''Aldono'', Zamenhof solidified Esperanto into its final form. History Zamenhof originally intended to publish ''Dua Libro'' in five or six volumes throughout 1888, with one volume appearing approximately every two months. Zamenhof's intention with the publications was to provide reading material in Esperan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zofia Zamenhof
Zofia Zamenhof (December 13, 1889 – September 12, 1942) was a Polish pediatrician and the daughter of Klara (Silbernik) and L. L. Zamenhof, the inventor of Esperanto. From 1907 to 1913 she completed her medical studies at the University of Lausanne and she passed a state examination in Saint Petersburg in 1914. She then continued to specialize in internal and pediatric diseases. She worked at a hospital in Lebedin, and from 1922 in a hospital in Warsaw. During World War II, she moved to the Warsaw Ghetto. Despite the presence of the Nazis, she continued her medical practice until she was arrested and transported to a death camp. In 1942 she was taken from the Umschlagplatz in Warsaw's ghetto to the extermination camp in Treblinka, where she was murdered, most likely in a gas chamber. Her symbolic tomb (commemorative plaque near the tomb of Klara Zamenhof) is located on the Jewish Cemetery, Warsaw The Warsaw Jewish Cemetery is one of the largest Jewish cemeteries in Europe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adam Zamenhof
Adam Zamenhof (1888 – 29 January 1940) was a Polish physician known for his work on ophthalmology and the son of L. L. Zamenhof, the inventor of Esperanto. Before the Holocaust, Zamenhof had invented a device to check blind spots in the field of vision. During World War II, 6 September 1939, he was head of the Starozakonnych Hospital in Warsaw, and its director. On 1 October 1939 Zamenhof was arrested and sent to the camp in Palmiry, where he was murdered by the Nazis. Adam and his wife Wanda were the parents of Louis-Christophe Zaleski-Zamenhof Louis-Christophe Zaleski-Zamenhof (born Ludwik Zamenhof; 23 January 1925 – 9 October 2019) was a Polish-born French civil and marine engineer, specializing in the design of structural steel and concrete construction. He was a grandson of the Po .... References 1888 births 1940 deaths Polish ophthalmologists Jewish physicians Polish people executed by Nazi Germany Esperanto speaking Jews Polish Jews who died in the Holoc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fundamento De Esperanto
''Fundamento de Esperanto'' (English: ''Foundation of Esperanto'') is a 1905 book by L. L. Zamenhof, in which the author explains the basic grammar rules and vocabulary that constitute the basis of the constructed language Esperanto. On August 9, 1905, it was made the only obligatory authority over the language by the Declaration of Boulogne at the first World Esperanto Congress. Much of the content of the book is a reproduction of content from Zamenhof's earlier works, particularly ''Unua Libro''. Content ''Fundamento de Esperanto'' consists of four parts: a foreword, a grammar section, a collection of exercises, and a dictionary. With the exception of the foreword, almost everything in the ''Fundamento'' comes directly from Zamenhof's earlier works, primarily ''Unua Libro''. Esperanto, however, underwent a minor change in 1888 in '' Aldono al la Dua Libro'', in which Zamenhof changed the ending of the temporal correlatives (''when'', ''then'', ''always'', ''sometimes'', ''nev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Białystok
Białystok is the largest city in northeastern Poland and the capital of the Podlaskie Voivodeship. It is the tenth-largest city in Poland, second in terms of population density, and thirteenth in area. Białystok is located in the Białystok Uplands of the Podlachian Plain on the banks of the Biała River, by road northeast of Warsaw. It has historically attracted migrants from elsewhere in Poland and beyond, particularly from Central and Eastern Europe. This is facilitated by the nearby border with Belarus also being the eastern border of the European Union, as well as the Schengen Area. The city and its adjacent municipalities constitute Metropolitan Białystok. The city has a warm summer continental climate, characterized by warm summers and long frosty winters. Forests are an important part of Białystok's character and occupy around (18% of the administrative area of the city) which places it as the fifth-most forested city in Poland. The first settlers arrived in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jewish Cemetery, Warsaw
The Warsaw Jewish Cemetery is one of the largest Jewish cemeteries in Europe and in the world. Located on Warsaw's Okopowa Street and abutting the Christian Powązki Cemetery, the Jewish necropolis was established in 1806 and occupies 33 hectares (83 acres) of land. The cemetery contains over 250,000 marked graves, as well as mass graves of victims of the Warsaw Ghetto. Although the cemetery was closed down during World War II, after the war it was reopened and a small portion of it remains active, serving Warsaw's existing Jewish population. As the necropolis was established to replace many smaller cemeteries closer to the city centre, it was designed to serve all Jewish communities of Warsaw, regardless of their affiliation. Hence, it is subdivided into several districts dubbed quarters (''kwatery''), historically reserved for various groups. Among them are three Orthodox (for men, women and one for holy scriptures), Reform Judaism, children, military and Warsaw Ghetto Uprising ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Auxiliary Language
An international auxiliary language (sometimes acronymized as IAL or contracted as auxlang) is a language meant for communication between people from all different nations, who do not share a common first language. An auxiliary language is primarily a foreign language and often a constructed language. The concept is related to but separate from the idea of a '' lingua franca'' (or dominant language) that people must use to communicate. The term "auxiliary" implies that it is intended to be an additional language for communication between the people of the world, rather than to replace their native languages. Often, the term is used specifically to refer to planned or constructed languages proposed to ease international communication, such as Esperanto, Ido and Interlingua. It usually takes words from widely spoken languages. However, it can also refer to the concept of such a language being determined by international consensus, including even a standardized natural language (e.g., ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ophthalmologist
Ophthalmology ( ) is a surgery, surgical subspecialty within medicine that deals with the diagnosis and treatment of eye disorders. An ophthalmologist is a physician who undergoes subspecialty training in medical and surgical eye care. Following a medical degree, a doctor specialising in ophthalmology must pursue additional postgraduate residency (medicine), residency training specific to that field. This may include a one-year integrated internship that involves more general medical training in other fields such as internal medicine or general surgery. Following residency, additional specialty training (or fellowship) may be sought in a particular aspect of eye pathology. Ophthalmologists prescribe medications to treat eye diseases, implement laser therapy, and perform surgery when needed. Ophthalmologists provide both primary and specialty eye care - medical and surgical. Most ophthalmologists participate in academic research on eye diseases at some point in their training an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |