|
Yamaha YM2149
The AY-3-8910 is a 3-voice programmable sound generator (PSG) designed by General Instrument in 1978, initially for use with their 16-bit CP1610 or one of the PIC1650 series of 8-bit microcomputers. The AY-3-8910 and its variants were used in many arcade games—Konami's ''Gyruss'' contains five—and pinball machines as well as being the sound chip in the Intellivision and Vectrex video game consoles, and the Amstrad CPC, Oric-1, Colour Genie, Elektor TV Games Computer, MSX, and later ZX Spectrum home computers. It was also used in the Mockingboard and Cricket sound cards for the Apple II and the Speech/Sound Cartridge for the TRS-80 Color Computer. After General Instrument's spinoff of Microchip Technology in 1987, the chip was sold for a few years under the Microchip brand. It was also manufactured under license by Yamaha (with a selectable clock divider pin and a double-resolution and double-rate volume envelope table) as the YM2149F; the Atari ST uses this versi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
AY-3-8910
The AY-3-8910 is a 3-voice programmable sound generator (PSG) designed by General Instrument in 1978, initially for use with their 16-bit General Instrument CP1600, CP1610 or one of the PIC1650 series of 8-bit microcomputers. The AY-3-8910 and its variants were used in many arcade games—Konami's ''Gyruss'' contains five—and pinball machines as well as being the sound chip in the Intellivision and Vectrex video game consoles, and the Amstrad CPC, Oric-1, Colour Genie, Elektor TV Games Computer, MSX, and later ZX Spectrum home computers. It was also used in the Mockingboard and Cricket sound cards for the Apple II and the Speech/Sound Cartridge for the TRS-80 Color Computer. After General Instrument's spinoff of Microchip Technology in 1987, the chip was sold for a few years under the Microchip brand. It was also manufactured under license by Yamaha Corporation, Yamaha (with a selectable clock divider pin and a double-resolution and double-rate volume envelope table) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apple II
The Apple II (stylized as ) is an 8-bit home computer and one of the world's first highly successful mass-produced microcomputer products. It was designed primarily by Steve Wozniak; Jerry Manock developed the design of Apple II's foam-molded plastic case, Rod Holt developed the switching power supply, while Steve Jobs's role in the design of the computer was limited to overseeing Jerry Manock's work on the plastic case. It was introduced by Jobs and Wozniak at the 1977 West Coast Computer Faire, and marks Apple's first launch of a personal computer aimed at a consumer market—branded toward American households rather than businessmen or computer hobbyists. ''Byte'' magazine referred to the Apple II, Commodore PET 2001, and TRS-80 as the "1977 Trinity". As the Apple II had the defining feature of being able to display color graphics, the Apple logo was redesigned to have a spectrum of colors. The Apple II is the first model in the Apple II series, followed by Apple ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MOS Technology 6522
The 6522 Versatile Interface Adapter (VIA) is an integrated circuit that was designed and manufactured by MOS Technology as an I/O port controller for the MOS Technology 6502, 6502 family of microprocessors. It provides two bidirectional 8-bit parallel I/O ports, two 16-bit timers (one of which can also operate as an event counter), and an 8-bit shift register for serial communications or data conversion between serial and parallel forms. The direction of each bit of the two I/O ports can be individually programmed. In addition to being manufactured by MOS Technology, the 6522 was second sourced by other companies including Rockwell International, Rockwell and Synertek. The 6522 was widely used in computers of the 1980s, particularly Commodore International, Commodore's machines, and was also a central part of the designs of the Apple III, Oric#Oric-1, Oric-1 and Oric#Oric Atmos, Oric Atmos, BBC Micro, Sirius Systems Technology, Victor 9000/Sirius 1 and Macintosh, Apple Macintosh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glue Logic
In electronics, glue logic is the custom logic circuitry used to interface a number of off-the-shelf integrated circuits. This is often achieved using common, inexpensive 7400- or 4000-series components. In more complex cases, a programmable logic device like a CPLD or FPGA might be used. The falling price of programmable logic devices, combined with their reduced size and power consumption compared to discrete components, is making them common even for simple systems. In addition, programmable logic can be used to hide the exact function of a circuit, in order to prevent a product from being cloned or counterfeited. The software equivalent of glue logic is called glue code. Usage Typical functions of glue logic may include: * Simple logic functions. * Address decoding circuitry used with older processors like the MOS Technology 6502 or Zilog Z80 to divide up the processor's address space into RAM, ROM and I/O. Newer versions of these processors, such as the WDC 65816 or the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hardware Register
In digital electronics, especially computing, hardware registers are circuits typically composed of flip flops, often with many characteristics similar to memory, such as: * The ability to read or write multiple bits at a time, and * Using an address to select a particular register in a manner similar to a memory address. Their distinguishing characteristic, however, is that they also have special hardware-related functions beyond those of ordinary memory. So, depending on the point of view, hardware registers are like memory with additional hardware-related functions; or, memory circuits are like hardware registers that just store data. Hardware registers are used in the interface between software and peripherals. Software writes them to send information to the device, and reads them to get information from the device. Some hardware devices also include registers that are not visible to software, for their internal use. Depending on their complexity, modern hardware devices c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
8-bit
In computer architecture, 8-bit Integer (computer science), integers or other Data (computing), data units are those that are 8 bits wide (1 octet (computing), octet). Also, 8-bit central processing unit (CPU) and arithmetic logic unit (ALU) architectures are those that are based on processor register, registers or Bus (computing), data buses of that size. Memory addresses (and thus address buses) for 8-bit CPUs are generally larger than 8-bit, usually 16-bit. 8-bit microcomputers are microcomputers that use 8-bit microprocessors. The term '8-bit' is also applied to the character sets that could be used on computers with 8-bit bytes, the best known being various forms of extended ASCII, including the ISO/IEC 8859 series of national character sets especially ISO/IEC 8859-1, Latin 1 for English and Western European languages. The IBM System/360 introduced byte-addressable memory with 8-bit bytes, as opposed to bit-addressable or decimal digit-addressable or word-addressable memory ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
State Machine
A finite-state machine (FSM) or finite-state automaton (FSA, plural: ''automata''), finite automaton, or simply a state machine, is a mathematical model of computation. It is an abstract machine that can be in exactly one of a finite number of '' states'' at any given time. The FSM can change from one state to another in response to some inputs; the change from one state to another is called a ''transition''. An FSM is defined by a list of its states, its initial state, and the inputs that trigger each transition. Finite-state machines are of two types— deterministic finite-state machines and non-deterministic finite-state machines. A deterministic finite-state machine can be constructed equivalent to any non-deterministic one. The behavior of state machines can be observed in many devices in modern society that perform a predetermined sequence of actions depending on a sequence of events with which they are presented. Simple examples are vending machines, which dispense p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
FPGA
A field-programmable gate array (FPGA) is an integrated circuit designed to be configured by a customer or a designer after manufacturinghence the term '' field-programmable''. The FPGA configuration is generally specified using a hardware description language (HDL), similar to that used for an application-specific integrated circuit (ASIC). Circuit diagrams were previously used to specify the configuration, but this is increasingly rare due to the advent of electronic design automation tools. FPGAs contain an array of programmable logic blocks, and a hierarchy of reconfigurable interconnects allowing blocks to be wired together. Logic blocks can be configured to perform complex combinational functions, or act as simple logic gates like AND and XOR. In most FPGAs, logic blocks also include memory elements, which may be simple flip-flops or more complete blocks of memory. Many FPGAs can be reprogrammed to implement different logic functions, allowing flexible reconfigurabl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
VHDL
The VHSIC Hardware Description Language (VHDL) is a hardware description language (HDL) that can model the behavior and structure of digital systems at multiple levels of abstraction, ranging from the system level down to that of logic gates, for design entry, documentation, and verification purposes. Since 1987, VHDL has been standardized by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) as IEEE Std 1076; the latest version of which is IEEE Std 1076-2019. To model analog and mixed-signal systems, an IEEE-standardized HDL based on VHDL called VHDL-AMS (officially IEEE 1076.1) has been developed. VHDL is named after the United States Department of Defense program that created it, the Very High-Speed Integrated Circuits Program (VHSIC). In the early 1980s, the VHSIC Program sought a new HDL for use in the design of the integrated circuits it aimed to develop. The product of this effort was VHDL Version 7.2, released in 1985. The effo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Texas Instruments SN76489
The SN76489 Digital Complex Sound Generator (DCSG) is a TTL-compatible programmable sound generator chip from Texas Instruments. Its main application was the generation of music and sound effects in game consoles, arcade games and home computers (such as the TI-99/4A, BBC Micro, ColecoVision, IBM PCjr, Tomy Tutor, and Tandy 1000), competing with the similar General Instrument AY-3-8910. It contains: * 3 square wave tone generators. ** A wide range of frequencies. ** 16 different volume levels. * 1 noise generator. ** 2 types (white noise and periodic). ** 3 different frequencies. ** 16 different volume levels. Overview The SN76489 was originally designed to be used in the TI-99/4 computer, where it was first called the TMS9919 and later SN94624, and had a 500 kHz max clock input rate. Later, when it was sold outside of TI, it was renamed the SN76489, and a divide-by-8 was added to its clock input, increasing the max clock input rate to , to facilitate sharing a crystal fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atari ST
The Atari ST is a line of personal computers from Atari Corporation and the successor to the Atari 8-bit family. The initial model, the Atari 520ST, had limited release in April–June 1985 and was widely available in July. It was the first personal computer with a bitmapped color GUI, using a version of Digital Research's GEM (desktop environment), GEM from February 1985. The Atari 1040ST, released in 1986 with 1 MB of RAM, was the first home computer with a cost-per-kilobyte of less than US$1. "ST" officially stands for "Sixteen/Thirty-two", referring to the Motorola 68000's 16-bit computing, 16-bit external bus and 32-bit computing, 32-bit internals. The system was designed by a small team led by Shiraz Shivji. Alongside the Macintosh, Amiga, Apple IIGS, and Acorn Archimedes, the ST is part of a mid-1980s generation of computers with 16- or 32-bit processors, 256 Kilobyte, KB or more of RAM, and computer mouse, mouse-controlled graphical user interfaces. The ST was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
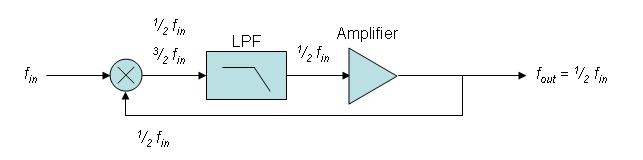
Clock Divider
A frequency divider, also called a clock divider or scaler or prescaler, is a circuit that takes an input signal of a frequency, f_, and generates an output signal of a frequency: : f_ = \frac where n is an integer. Phase-locked loop frequency synthesizers make use of frequency dividers to generate a frequency that is a multiple of a reference frequency. Frequency dividers can be implemented for both analog and digital applications. Analog Analog frequency dividers are less common and used only at very high frequencies. Digital dividers implemented in modern IC technologies can work up to tens of GHz. Regenerative A regenerative frequency divider, also known as a Miller frequency divider, mixes the input signal with the feedback signal from the mixer. The feedback signal is f_/2. This produces sum and difference frequencies f_/2, 3f_/2 at the output of the mixer. A low pass filter removes the higher frequency and the f_/2 frequency is amplified and fed back into mixer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |