|
XCP (protocol)
XCP (or) "Universal Measurement and Calibration Protocol" is a network protocol originating from ASAM for connecting calibration systems to electronic control units, ECUs. It enables read and write access to variables and memory contents of microcontroller systems at runtime. Entire datasets can be acquired or stimulated synchronous to events triggered by timers or operating conditions. In addition, XCP also supports programming of flash memory. ASAM states "The primary purpose of XCP is to adjust internal parameters and acquire the current values of internal variables of an ECU. The first letter X in XCP expresses the fact that the protocol is designed for a variety of bus systems." In 2003, the protocol was standardized as "ASAM MCD-1 XCP". XCP is a successor to CAN Calibration Protocol ( CCP) that was developed back in the mid-1990s. At that time, CAN was the dominant networking system in the automobile industry. Over time, other bus systems such as LIN, MOST and FlexRay ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Association For Standardisation Of Automation And Measuring Systems
Association for Standardization of Automation and Measuring Systems or ASAM is an incorporated association under German law. Its members are primarily international car manufacturers, suppliers and engineering service providers from the automotive industry. The association coordinates the development of technical standards, which are developed by working groups composed of experts from its member companies. ASAM pursues the vision that the tools of a development process chain can be freely interconnected and allow a seamless exchange of data. The standards define protocols, data models, file formats and application programming interfaces (APIs) for the use in the development and testing of automotive electronic control units. A large amount of popular tools in the areas of simulation, measurement, calibration and test automation are compliant to ASAM standards. Compliance shall guarantee interoperability of tools from different vendors, allow data exchange without the need for co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
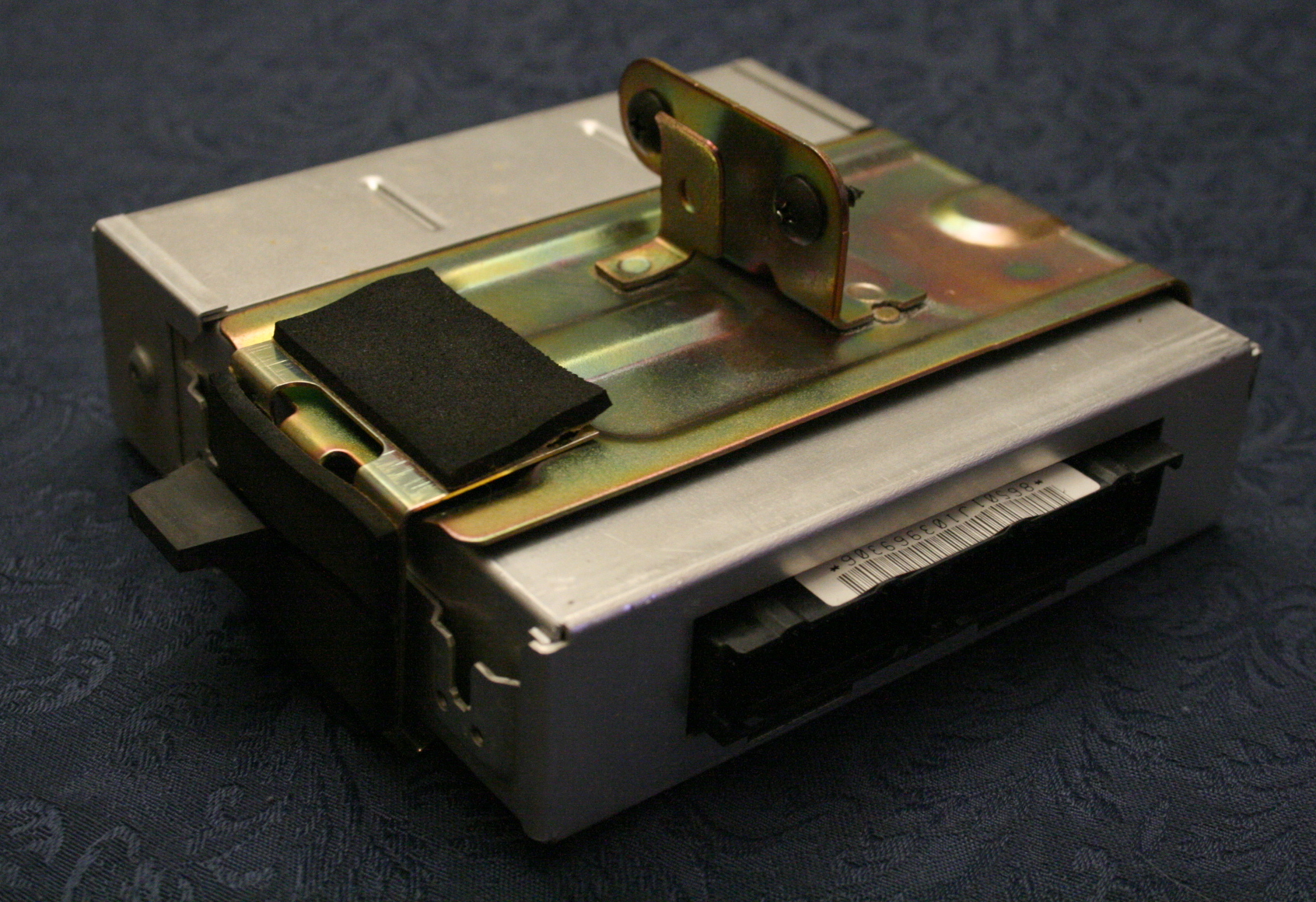
Electronic Control Unit
An electronic control unit (ECU), also known as an electronic control module (ECM), is an embedded system in automotive electronics that controls one or more of the electrical systems or subsystems in a car or other motor vehicle. Modern vehicles have many ECUs, and these can include some or all of the following: engine control module (ECM), powertrain control module (PCM), transmission control module (TCM), brake control module (BCM or EBCM), central control module (CCM), central timing module (CTM), general electronic module (GEM), body control module (BCM), and suspension control module (SCM). These ECUs together are sometimes referred to collectively as the car's computer though technically they are all separate computers, not a single one. Sometimes an assembly incorporates several individual control modules (a PCM often controls both the engine and the transmission). [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CAN Calibration Protocol
{{disambiguation ...
Can may refer to: Containers * Aluminum can * Drink can * Oil can * Steel and tin cans * Trash can * Petrol can * Metal can (other) Music * Can (band), West Germany, 1968 ** ''Can'' (album), 1979 * Can (South Korean band) Other * Can (name), Turkish and Circassian given name and surname * Can (verb) * Canning of food * River Can, Essex, UK * Canada * Tomato can (sports idiom) See also * CAN (other) * Cann (other) * Cans (other) * Kan (other) Kan or KAN may refer to: Places * Kan (river), a tributary of the Yenisey in Russia * Kan District of Iran * Kan, Kyrgyzstan, a village in Batken Region * Mallam Aminu Kano International Airport, Kano, Nigeria, IATA code * Kannapolis (Amtrak sta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CAN Bus
A Controller Area Network (CAN bus) is a robust vehicle bus standard designed to allow microcontrollers and devices to communicate with each other's applications without a host computer. It is a message-based protocol, designed originally for multiplex electrical wiring within automobiles to save on copper, but it can also be used in many other contexts. For each device, the data in a frame is transmitted serially but in such a way that if more than one device transmits at the same time, the highest priority device can continue while the others back off. Frames are received by all devices, including by the transmitting device. History Development of the CAN bus started in 1983 at Robert Bosch GmbH. The protocol was officially released in 1986 at the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE) conference in Detroit, Michigan. The first CAN controller chips were introduced by Intel in 1987, and shortly thereafter by Philips. Released in 1991, the Mercedes-Benz W140 was the first ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Local Interconnect Network
LIN (Local Interconnect Network) is a serial network protocol used for communication between components in vehicles. It is a single wire, serial network protocol that supports communications up to 19.2 Kbit/s at a bus length of 40 meters. The need for a cheap serial network arose as the technologies and the facilities implemented in the car grew, while the CAN bus was too expensive to implement for every component in the car. European car manufacturers started using different serial communication technologies, which led to compatibility problems. In the late 1990s, the LIN Consortium was founded by five automakers ( BMW, Volkswagen Group, Audi, Volvo Cars, Mercedes-Benz), with the technologies supplied (networking and hardware expertise) from Volcano Automotive Group and Motorola. The first fully implemented version of the new LIN specification (LIN version 1.3) was published in November 2002. In September 2003, version 2.0 was introduced to expand capabilities and make provisions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MOST Bus
MOST (Media Oriented Systems Transport) is a high-speed multimedia network technology optimized by the automotive industry. It can be used for applications inside or outside the car. The serial MOST bus uses a daisy-chain topology or ring topology and synchronous data communication to transport audio, video, voice and data signals via plastic optical fiber (POF) (MOST25, MOST150) or electrical conductor (MOST50, MOST150) physical layers. MOST technology was used in almost every car brand worldwide, including Audi, BMW, General Motors, Honda, Hyundai, Jaguar, Lancia, Land Rover, Mercedes-Benz, Porsche, Toyota, Volkswagen, SAAB, SKODA, SEAT and Volvo. SMSC and MOST are registered trademarks of Standard Microsystems Corporation (“SMSC”), now owned by Microchip Technology. This technology is obsolete and not in use anymore. Principles of communication The MOST specification defines the physical and the data link layer as well as all seven layers of the ISO/OSI-Model of da ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
JTAG
JTAG (named after the Joint Test Action Group which codified it) is an industry standard for verifying designs and testing printed circuit boards after manufacture. JTAG implements standards for on-chip instrumentation in electronic design automation (EDA) as a complementary tool to digital simulation. It specifies the use of a dedicated debug port implementing a serial communications interface for low-overhead access without requiring direct external access to the system address and data buses. The interface connects to an on-chip Test Access Port (TAP) that implements a stateful protocol to access a set of test registers that present chip logic levels and device capabilities of various parts. The Joint Test Action Group formed in 1985 to develop a method of verifying designs and testing printed circuit boards after manufacture. In 1990 the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers codified the results of the effort in IEEE Standard 1149.1-1990, entitled ''Standard Test ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CAN FD
CAN FD (Controller Area Network Flexible Data-Rate) is a data-communication protocol used for broadcasting sensor data and control information on 2 wire interconnections between different parts of electronic instrumentation and control system. This protocol is used in modern high performance vehicles. CAN FD is an extension to the original CAN bus protocol that was specified in ISO 11898-1. The basic idea to overclock part of the frame and to oversize the payload dates back to 1999. Developed in 2011 and released in 2012 by Bosch, CAN FD was developed to meet the need to increase the data transfer rate up to 5 times faster and with larger frame/message sizes for use in modern automotive Electronic Control Units (ECUs). As in the classic CAN, CAN FD protocol is designed to reliably transmit and receive sensor data, control commands and to detect data errors between electronic sensor devices, controllers and microcontrollers. Although CAN FD was primarily designed for use in high p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serial Peripheral Interface Bus
The Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) is a synchronous serial communication interface specification used for short-distance communication, primarily in embedded systems. The interface was developed by Motorola in the mid-1980s and has become a ''de facto'' standard. Typical applications include Secure Digital cards and liquid crystal displays. SPI devices communicate in full duplex mode using a master-slave architecture usually with a single master (though some Atmel and Silabs devices support changing roles on the fly depending on an external (SS) pin). The master (controller) device originates the frame for reading and writing. Multiple slave-devices may be supported through selection with individual chip select (CS), sometimes called slave select (SS) lines. Sometimes SPI is called a ''four-wire'' serial bus, contrasting with three-, two-, and one-wire serial buses. The SPI may be accurately described as a synchronous serial interface, but it is different from the S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serial Communication Interface
A universal asynchronous receiver-transmitter (UART ) is a computer hardware device for asynchronous serial communication in which the data format and transmission speeds are configurable. It sends data bits one by one, from the least significant to the most significant, framed by start and stop bits so that precise timing is handled by the communication channel. The electric signaling levels are handled by a driver circuit external to the UART. Two common signal levels are RS-232, a 12-volt system, and RS-485, a 5-volt system. Early teletypewriters used current loops. It was one of the earliest computer communication devices, used to attach teletypewriters for an operator console. It was also an early hardware system for the Internet. A UART is usually an individual (or part of an) integrated circuit (IC) used for serial communications over a computer or peripheral device serial port. One or more UART peripherals are commonly integrated in microcontroller chips. Specialis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TCP/IP
The Internet protocol suite, commonly known as TCP/IP, is a framework for organizing the set of communication protocols used in the Internet and similar computer networks according to functional criteria. The foundational protocols in the suite are the Transmission Control Protocol (TCP), the User Datagram Protocol (UDP), and the Internet Protocol (IP). In the development of this networking model, early versions of it were known as the Department of Defense (DoD) model because the research and development were funded by the United States Department of Defense through DARPA. The Internet protocol suite provides end-to-end data communication specifying how data should be packetized, addressed, transmitted, routed, and received. This functionality is organized into four abstraction layers, which classify all related protocols according to each protocol's scope of networking. An implementation of the layers for a particular application forms a protocol stack. From lowest to high ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |