|
X-parameters
X-parameters are a generalization of S-parameters and are used for characterizing the amplitudes and relative phase of harmonics generated by nonlinear components under large input power levels. X-parameters are also referred to as the parameters of the Poly-Harmonic Distortion (PHD) nonlinear behavioral model. Description X-parameters represent a new category of nonlinear network parameters for high-frequency design (Nonlinear vector network analyzers are sometimes called large signal network analyzers.) X-parameters are applicable to both large-signal and small-signal conditions, for linear and nonlinear components. They are an extension of S-parameters meaning that, in the limit of a small signal, X-parameters reduce to S-parameters. They help overcome a key challenge in RF engineering, namely that nonlinear impedance differences, harmonic mixing, and nonlinear reflection effects occur when components are cascaded under large signal operating conditions. This means that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scattering Parameters
Scattering parameters or S-parameters (the elements of a scattering matrix or S-matrix) describe the electrical behavior of linear electrical networks when undergoing various steady state stimuli by electrical signals. The parameters are useful for several branches of electrical engineering, including electronics, communication systems design, and especially for microwave engineering. The S-parameters are members of a family of similar parameters, other examples being: Y-parameters, Z-parameters, H-parameters, T-parameters or ABCD-parameters. They differ from these, in the sense that ''S-parameters'' do not use open or short circuit conditions to characterize a linear electrical network; instead, matched loads are used. These terminations are much easier to use at high signal frequencies than open-circuit and short-circuit terminations. Contrary to popular belief, the quantities are not measured in terms of power (except in now-obsolete six-port network analyzers). Modern ve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrical Parameters
Electricity is the set of physical phenomena associated with the presence and motion of matter that has a property of electric charge. Electricity is related to magnetism, both being part of the phenomenon of electromagnetism, as described by Maxwell's equations. Various common phenomena are related to electricity, including lightning, static electricity, electric heating, electric discharges and many others. The presence of an electric charge, which can be either positive or negative, produces an electric field. The movement of electric charges is an electric current and produces a magnetic field. When a charge is placed in a location with a non-zero electric field, a force will act on it. The magnitude of this force is given by Coulomb's law. If the charge moves, the electric field would be doing work on the electric charge. Thus we can speak of electric potential at a certain point in space, which is equal to the work done by an external agent in carrying a unit of posi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
David Vye
David (; , "beloved one") (traditional spelling), , ''Dāwūd''; grc-koi, Δαυΐδ, Dauíd; la, Davidus, David; gez , ዳዊት, ''Dawit''; xcl, Դաւիթ, ''Dawitʿ''; cu, Давíдъ, ''Davidŭ''; possibly meaning "beloved one". was, according to the Hebrew Bible, the third king of the United Kingdom of Israel. In the Books of Samuel, he is described as a young shepherd and harpist who gains fame by slaying Goliath, a champion of the Philistines, in southern Canaan. David becomes a favourite of Saul, the first king of Israel; he also forges a notably close friendship with Jonathan, a son of Saul. However, under the paranoia that David is seeking to usurp the throne, Saul attempts to kill David, forcing the latter to go into hiding and effectively operate as a fugitive for several years. After Saul and Jonathan are both killed in battle against the Philistines, a 30-year-old David is anointed king over all of Israel and Judah. Following his rise to power, David ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Two-port Network
A two-port network (a kind of four-terminal network or quadripole) is an electrical network (circuit) or device with two ''pairs'' of terminals to connect to external circuits. Two terminals constitute a port if the currents applied to them satisfy the essential requirement known as the port condition: the electric current entering one terminal must equal the current emerging from the other terminal on the same port.Gray, §3.2, p. 172Jaeger, §10.5 §13.5 §13.8 The ports constitute interfaces where the network connects to other networks, the points where signals are applied or outputs are taken. In a two-port network, often port 1 is considered the input port and port 2 is considered the output port. It's used in mathematical circuit analysis. Application The two-port network model is used in mathematical circuit analysis techniques to isolate portions of larger circuits. A two-port network is regarded as a "black box" with its properties specified by a matrix of nu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Advanced Design System
Advanced Design System (ADS) is an electronic design automation software system produced by PathWave Design, a division of Keysight Technologies. It provides an integrated design environment to designers of RF electronic products such as mobile phones, pagers, wireless networks, satellite communications, radar systems, and high-speed data links. Keysight ADS supports every step of the design process—schematic capture, layout, design rule checking, frequency-domain and time-domain circuit simulation, and electromagnetic field simulation—allowing the engineer to fully characterize and optimize an RF design without changing tools. Keysight has donated copies of the ADS software to the electrical engineering departments at many universities. See also * Momentum (electromagnetic simulator) - 3D Planar EM simulator element of ADS platform * FEM Element - Arbitrary 3D geometry EM simulator element of ADS platform Notes The deprecated Tektronix ADS is another, unrelate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Keysight Technologies
Keysight Technologies, or Keysight, is an American company that manufactures electronics test and measurement equipment and software. The name is a blend of ''key'' and ''insight''. The company was formed as a spin-off of Agilent Technologies, which inherited and rebranded the test and measurement product lines developed and produced from the late 1960's to the turn of the millenium by Hewlett-Packard's Test & Measurement division. Products Keysight's products include hardware and software for benchtop, modular, and field instruments. Instruments include oscilloscopes, multimeters, logic analyzers, signal generators, spectrum analyzers, vector network analyzers, atomic force microscopes (AFM), automated optical inspection, automated X-ray inspection ( 5DX), in-circuit testers, power supplies, tunable lasers, optical power meters, wavelength-meters, electro-optic converters, optical modulation analyzers and handheld tools. In addition, it produces electronic design automat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Resistor
A resistor is a passive two-terminal electrical component that implements electrical resistance as a circuit element. In electronic circuits, resistors are used to reduce current flow, adjust signal levels, to divide voltages, bias active elements, and terminate transmission lines, among other uses. High-power resistors that can dissipate many watts of electrical power as heat may be used as part of motor controls, in power distribution systems, or as test loads for generators. Fixed resistors have resistances that only change slightly with temperature, time or operating voltage. Variable resistors can be used to adjust circuit elements (such as a volume control or a lamp dimmer), or as sensing devices for heat, light, humidity, force, or chemical activity. Resistors are common elements of electrical networks and electronic circuits and are ubiquitous in electronic equipment. Practical resistors as discrete components can be composed of various compounds and forms. R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
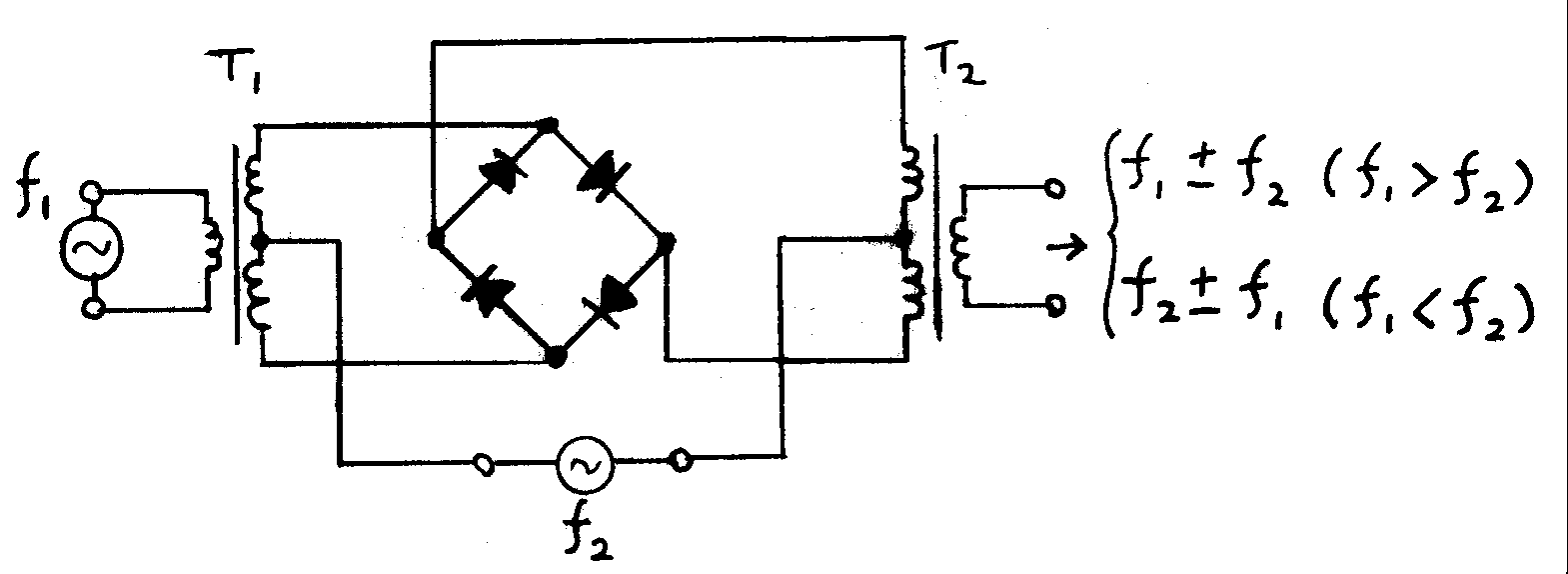
Frequency Mixer
In electronics, a mixer, or frequency mixer, is an electrical circuit that creates new frequencies from two signals applied to it. In its most common application, two signals are applied to a mixer, and it produces new signals at the sum and difference of the original frequencies. Other frequency components may also be produced in a practical frequency mixer. Mixers are widely used to shift signals from one frequency range to another, a process known as heterodyning, for convenience in transmission or further signal processing. For example, a key component of a superheterodyne receiver is a mixer used to move received signals to a common intermediate frequency. Frequency mixers are also used to modulate a carrier signal in radio transmitters. Types The essential characteristic of a mixer is that it produces a component in its output which is the product of the two input signals. Both active and passive circuits can realize mixers. Passive mixers use one or more diodes an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Direct Current
Direct current (DC) is one-directional flow of electric charge. An electrochemical cell is a prime example of DC power. Direct current may flow through a conductor such as a wire, but can also flow through semiconductors, insulators, or even through a vacuum as in electron or ion beams. The electric current flows in a constant direction, distinguishing it from alternating current (AC). A term formerly used for this type of current was galvanic current. The abbreviations ''AC'' and ''DC'' are often used to mean simply ''alternating'' and ''direct'', as when they modify '' current'' or '' voltage''. Direct current may be converted from an alternating current supply by use of a rectifier, which contains electronic elements (usually) or electromechanical elements (historically) that allow current to flow only in one direction. Direct current may be converted into alternating current via an inverter. Direct current has many uses, from the charging of batteries to large po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrical Impedance
In electrical engineering, impedance is the opposition to alternating current presented by the combined effect of resistance and reactance in a circuit. Quantitatively, the impedance of a two-terminal circuit element is the ratio of the complex representation of the sinusoidal voltage between its terminals, to the complex representation of the current flowing through it. In general, it depends upon the frequency of the sinusoidal voltage. Impedance extends the concept of resistance to alternating current (AC) circuits, and possesses both magnitude and phase, unlike resistance, which has only magnitude. Impedance can be represented as a complex number, with the same units as resistance, for which the SI unit is the ohm (). Its symbol is usually , and it may be represented by writing its magnitude and phase in the polar form . However, Cartesian complex number representation is often more powerful for circuit analysis purposes. The notion of impedance is useful for pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RF Engineering
Radio-frequency (RF) engineering is a subset of electronic engineering involving the application of transmission line, waveguide, antenna and electromagnetic field principles to the design and application of devices that produce or use signals within the radio band, the frequency range of about 20 kHz up to 300 GHz. It is incorporated into almost everything that transmits or receives a radio wave, which includes, but is not limited to, mobile phones, radios, WiFi, and two-way radios. RF engineering is a highly specialized field that typically includes the following areas of expertise: # Design of antenna systems to provide radiative coverage of a specified geographical area by an electromagnetic field or to provide specified sensitivity to an electromagnetic field impinging on the antenna. # Design of coupling and transmission line structures to transport RF energy without radiation. # Application of circuit elements and transmission line structures in the design of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |