Frequency Mixer on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
In
 Mixers may also be classified by their
Mixers may also be classified by their
RF mixers & mixing tutorial
{{DEFAULTSORT:Frequency Mixer Electronic circuits Communication circuits Radio electronics Telecommunication theory
electronics
The field of electronics is a branch of physics and electrical engineering that deals with the emission, behaviour and effects of electrons using electronic devices. Electronics uses active devices to control electron flow by amplification ...
, a mixer, or frequency mixer, is an electrical circuit that creates new frequencies from two signals applied to it. In its most common application, two signals are applied to a mixer, and it produces new signals at the sum and difference of the original frequencies. Other frequency components may also be produced in a practical frequency mixer.
Mixers are widely used to shift signals from one frequency range to another, a process known as heterodyning, for convenience in transmission or further signal processing. For example, a key component of a superheterodyne receiver
A superheterodyne receiver, often shortened to superhet, is a type of radio receiver that uses frequency mixing to convert a received signal to a fixed intermediate frequency (IF) which can be more conveniently processed than the original carr ...
is a mixer used to move received signals to a common intermediate frequency. Frequency mixers are also used to modulate a carrier signal
In telecommunications, a carrier wave, carrier signal, or just carrier, is a waveform (usually sinusoidal) that is modulated (modified) with an information-bearing signal for the purpose of conveying information. This carrier wave usually has ...
in radio transmitters.
Types
The essential characteristic of a mixer is that it produces a component in its output which is the product of the two input signals. Both active and passive circuits can realize mixers. Passive mixers use one or more diodes and rely on their non-linear relation between voltage and current to provide the multiplying element. In a passive mixer, the desired output signal is always of lower power than the input signals. Active mixers use an amplifying device (such as atransistor
upright=1.4, gate (G), body (B), source (S) and drain (D) terminals. The gate is separated from the body by an insulating layer (pink).
A transistor is a semiconductor device used to Electronic amplifier, amplify or electronic switch, switch ...
or vacuum tube
A vacuum tube, electron tube, valve (British usage), or tube (North America), is a device that controls electric current flow in a high vacuum between electrodes to which an electric voltage, potential difference has been applied.
The type kn ...
) that may increase the strength of the product signal. Active mixers improve isolation between the ports, but may have higher noise and more power consumption. An active mixer can be less tolerant of overload.
Mixers may be built of discrete components, may be part of integrated circuits
An integrated circuit or monolithic integrated circuit (also referred to as an IC, a chip, or a microchip) is a set of electronic circuits on one small flat piece (or "chip") of semiconductor material, usually silicon. Transistor count, Large ...
, or can be delivered as hybrid modules.
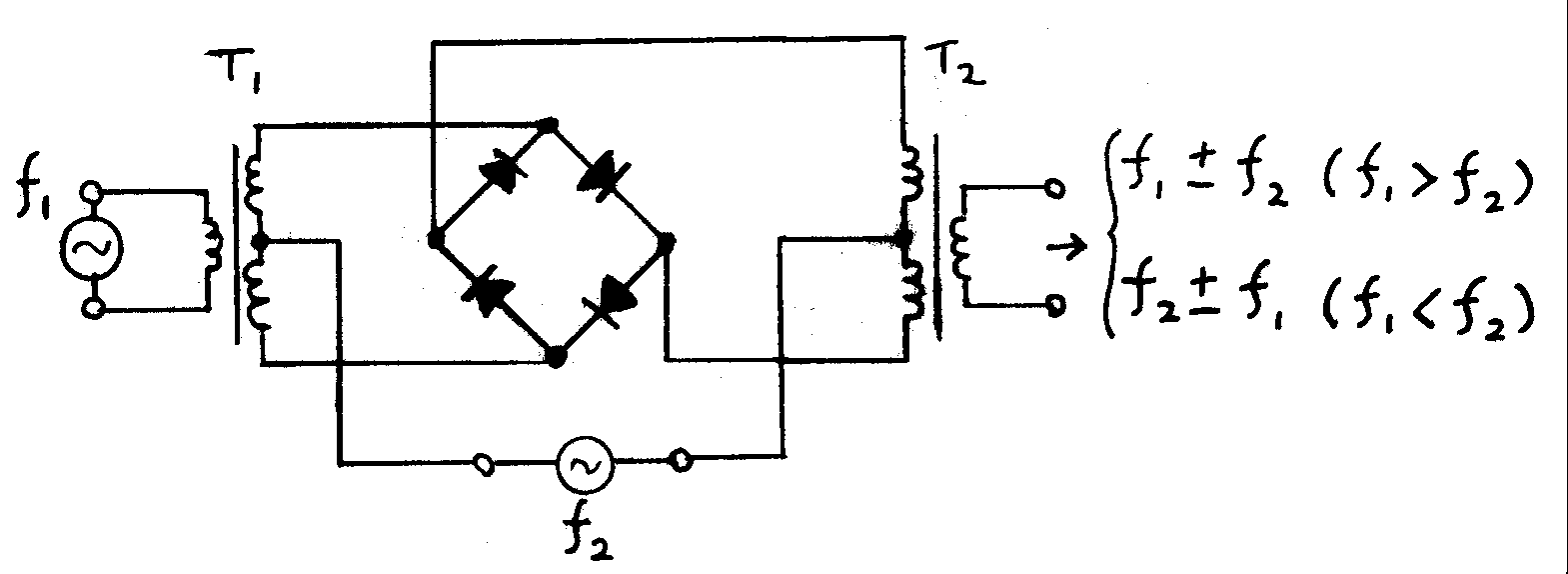
 Mixers may also be classified by their
Mixers may also be classified by their topology
In mathematics, topology (from the Greek words , and ) is concerned with the properties of a geometric object that are preserved under continuous deformations, such as stretching, twisting, crumpling, and bending; that is, without closing ho ...
:
*An ''unbalanced mixer,'' in addition to producing a product signal, allows both input signals to pass through and appear as components in the output.
*A ''single balanced mixer'' is arranged with one of its inputs applied to a balanced ( differential) circuit so that either the local oscillator (LO) or signal input (RF) is suppressed at the output, but not both.
*A ''double balanced mixer'' has both its inputs applied to differential circuits, so that neither of the input signals and only the product signal appears at the output. Double balanced mixers are more complex and require higher drive levels than unbalanced and single balanced designs.
Selection of a mixer type is a trade off for a particular application.
Mixer circuits are characterized by their properties such as conversion gain
Gain or GAIN may refer to:
Science and technology
* Gain (electronics), an electronics and signal processing term
* Antenna gain
* Gain (laser), the amplification involved in laser emission
* Gain (projection screens)
* Information gain in d ...
(or loss), noise figure and nonlinearity.
Nonlinear electronic components that are used as mixers include diodes and transistor
upright=1.4, gate (G), body (B), source (S) and drain (D) terminals. The gate is separated from the body by an insulating layer (pink).
A transistor is a semiconductor device used to Electronic amplifier, amplify or electronic switch, switch ...
s biased near cutoff. Linear, time-varying devices, such as analog multipliers, provide superior performance, as it is only in true multipliers that the output amplitude is proportional to the input amplitude, as required for linear conversion. Ferromagnetic-core inductors driven into saturation have also been used. In nonlinear optics
Nonlinear optics (NLO) is the branch of optics that describes the behaviour of light in ''nonlinear media'', that is, media in which the polarization density P responds non-linearly to the electric field E of the light. The non-linearity is typic ...
, crystals with nonlinear characteristics are used to mix two frequencies of laser light to create optical heterodynes.
Diode
A diode can be used to create a simple unbalanced mixer. This type of mixer produces the original frequencies as well as their sum and their difference. The important property of the diode is its non-linearity (or non- Ohmic behavior), which means its response (current) is not proportional to its input (voltage). The diode does not reproduce the frequencies of its driving voltage in the current through it, which allows the desired frequency manipulation. The current through an ideal diode as a function of the voltage across it is given by : where the important property of non-linearity results from being in 's exponent. The exponential can be expanded as : and can be approximated for small (that is, small voltages) by the first few terms of that series: : Suppose that the sum of the two input signals is applied to a diode, and that an output voltage is generated that is proportional to the current through the diode (perhaps by providing the voltage that is present across aresistor
A resistor is a passive two-terminal electrical component that implements electrical resistance as a circuit element. In electronic circuits, resistors are used to reduce current flow, adjust signal levels, to divide voltages, bias activ ...
in series with the diode). Then, disregarding the constants in the diode equation, the output voltage will have the form
:
The first term on the right is the original two signals, as expected, followed by the square of the sum, which can be rewritten as , where the multiplied signal is obvious. The ellipsis represents all the higher powers of the sum which we assume to be negligible for small signals.
Suppose that two input sinusoids of different frequencies are fed into the diode, such that and . The signal becomes:
:
Expanding the square term yields:
:
Ignoring all terms except for the term and utilizing the prosthaphaeresis
Prosthaphaeresis (from the Greek ''προσθαφαίρεσις'') was an algorithm used in the late 16th century and early 17th century for approximate multiplication and division using formulas from trigonometry. For the 25 years preceding th ...
(product to sum) identity,
:
yields,
:
demonstrating how new frequencies are created from the mixer.
Switching
Another form of mixer operates by switching, which is equivalent to multiplication of an input signal by a square wave. In a double-balanced mixer, the (smaller) input signal is alternately inverted or non inverted according to the phase of the local oscillator (LO). That is, the input signal is effectively multiplied by a square wave that alternates between +1 and -1 at the LO rate. In a single-balanced switching mixer, the input signal is alternately passed or blocked. The input signal is thus effectively multiplied by a square wave that alternates between 0 and +1. This results in frequency components of the input signal being present in the output together with the product, since the multiplying signal can be viewed as a square wave with a DC offset (i.e. a zero frequency component). The aim of a switching mixer is to achieve the linear operation by means of hard switching, driven by the local oscillator. In the frequency domain, the switching mixer operation leads to the usual sum and difference frequencies, but also to further terms e.g. ±3''f''LO, ±5''f''LO, etc. The advantage of a switching mixer is that it can achieve (with the same effort) a lower noise figure (NF) and larger conversion gain. This is because the switching diodes or transistors act either like a small resistor (switch closed) or large resistor (switch open), and in both cases only a minimal noise is added. From the circuit perspective, many multiplying mixers can be used as switching mixers, just by increasing the LO amplitude. So RF engineers simply talk about mixers, while they mean switching mixers. The mixer circuit can be used not only to shift the frequency of an input signal as in a receiver, but also as a product detector, modulator, phase detector or frequency multiplier.Paul Horowitz, Winfred Hill '' The Art of Electronics Second Edition'', Cambridge University Press 1989, pp. 885–887. For example, acommunications receiver
A communications receiver is a type of radio receiver used as a component of a radio communication link. This is in contrast to a ''broadcast receiver'' which is used to receive radio broadcasts. A communication receiver receives parts of the ...
might contain two mixer stages for conversion of the input signal to an intermediate frequency and another mixer employed as a detector for demodulation of the signal.
See also
* Frequency multiplier *Subharmonic mixer
The harmonic mixer and subharmonic mixer are a type of frequency mixer, which is a circuit that changes one signal frequency to another. The ordinary mixer has two input signals and one output signal. If the two input signals are sinewaves at freq ...
* Product detector
* Pentagrid converter
* Beam deflection tube
* Ring modulation
In electronics, ring modulation is a signal processing function, an implementation of frequency mixing, in which two signals are combined to yield an output signal. One signal, called the carrier, is typically a sine wave or another simple ...
* Gilbert cell
* Optical heterodyne detection
* Intermodulation
Intermodulation (IM) or intermodulation distortion (IMD) is the amplitude modulation of signals containing two or more different frequencies, caused by nonlinearities or time variance in a system. The intermodulation between frequency com ...
* Third-order intercept point
* Rusty bolt effect
The rusty bolt effect is a form of radio interference due to interactions of the radio waves with dirty connections or corroded parts.Lui, P.L., ''Passive intermodulation interference in communication systems,'' IEEE Electronics & Communication Eng ...
References
External links
RF mixers & mixing tutorial
{{DEFAULTSORT:Frequency Mixer Electronic circuits Communication circuits Radio electronics Telecommunication theory