|
Advanced Design System
Advanced Design System (ADS) is an electronic design automation software system produced by PathWave Design, a division of Keysight Technologies. It provides an integrated design environment to designers of RF electronic products such as mobile phones, pagers, wireless networks, satellite communications, radar systems, and high-speed data links. Keysight ADS supports every step of the design process—schematic capture, layout, design rule checking, frequency-domain and time-domain circuit simulation, and electromagnetic field simulation—allowing the engineer to fully characterize and optimize an RF design without changing tools. Keysight has donated copies of the ADS software to the electrical engineering departments at many universities. See also * Momentum (electromagnetic simulator) - 3D Planar EM simulator element of ADS platform * FEM Element - Arbitrary 3D geometry EM simulator element of ADS platform Notes The deprecated Tektronix ADS is another, unrelate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PathWave Design
PathWave Design is a division of Keysight Technologies that was formerly called EEsof ( ; electronic engineering software). It is a provider of electronic design automation (EDA) software that helps engineers design products such as cellular phones, wireless networks, radar, satellite communications systems, and high-speed digital wireline infrastructure. Applications include electronic system level (ESL), high-speed digital, RF-Mixed signal, device modeling, RF and Microwave design for commercial wireless, aerospace, and defense markets. History EEsof was founded in 1983 by an entrepreneur, Charles J. ("Chuck") Abronson, and a former Compact Software employee, Bill Childs. EEsof's first products included high-frequency circuit simulators such as Touchstone and Libra. Although the Touchstone simulator itself is obsolete, its eponymous file format lives on. EEsof was acquired by Hewlett-Packard in 1993 and later spun out first as part of Agilent Technologies in 1999 and then as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Design Rule Checking
In electronic design automation, a design rule is a geometric constraint imposed on circuit board, semiconductor device, and integrated circuit (IC) designers to ensure their designs function properly, reliably, and can be produced with acceptable yield. Design rules for production are developed by process engineers based on the capability of their processes to realize design intent. Electronic design automation is used extensively to ensure that designers do not violate design rules; a process called design rule checking (DRC). DRC is a major step during physical verification signoff on the design, which also involves LVS ( layout versus schematic) checks, XOR checks, ERC (electrical rule check), and antenna checks. The importance of design rules and DRC is greatest for ICs, which have micro- or nano-scale geometries; for advanced processes, some fabs also insist upon the use of more restricted rules to improve yield. Design rules Design rules are a series of parameters prov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electronic Design Automation Software
Electronic may refer to: *Electronics, the science of how to control electric energy in semiconductor * ''Electronics'' (magazine), a defunct American trade journal *Electronic storage, the storage of data using an electronic device *Electronic commerce or e-commerce, the trading in products or services using computer networks, such as the Internet * Electronic publishing or e-publishing, the digital publication of books and magazines using computer networks, such as the Internet *Electronic engineering, an electrical engineering discipline Entertainment *Electronic (band), an English alternative dance band ** ''Electronic'' (album), the self-titled debut album by British band Electronic *Electronic music, a music genre * Electronic musical instrument *Electronic game, a game that employs electronics See also *Electronica, an electronic music genre *Consumer electronics Consumer electronics or home electronics are Electronics, electronic (Analogue electronics, analog or digi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
FEM Element
FEM Element is a commercial finite element method solver for electromagnetic structures from EEsof. FEM Element can perform electromagnetic simulation of arbitrarily-shaped, passive three-dimensional structures. It is aimed at providing 3D EM simulation to designers working on RF circuits, MMICs, PC boards, modules, and signal integrity applications. It provides a full 3D electromagnetic field solver, a solid modeling GUI, and fully automated meshing and convergence capabilities for modeling arbitrary 3D shapes such as connectors, machined parts, components, bond wires, antennas, and packages. FEM Element is available with integration into Keysight EEsof's Advanced Design System (ADS) and EMPro platforms. It was originally called Electromagnetic Design System (EMDS). See also * Computational electromagnetics Computational electromagnetics (CEM), computational electrodynamics or electromagnetic modeling is the process of modeling the interaction of electromagnetic fields with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Momentum (electromagnetic Simulator)
Momentum is 3-D planar EM simulation software for electronics and antenna analysis, a partial differential equation solver of Maxwell's equations based on the method of moments. It is a 3-D planar electromagnetic (EM) simulator used for passive circuit analysis. It combines full-wave and quasi-static EM solvers to provide insight into EM behavior of MMIC, RFIC, RF Board, Signal Integrity, and antenna designs. The Momentum simulation engine is integrated into Keysight ADS anKeysight Genesys It was originally developed by a Belgian company, Alphabit, a spinoff from the Electromagnetics Group of Ghent University and IMEC. Early contributors to the technology include Niels Faché, Jan Van Hese, Frank Libbrecht, Jeannick Sercu, Luc Vandormael, Mieke Herreman, Peter Kok, Tom Dhaene and Krist Blomme. The company was acquired by Hewlett-Packard, later it became part of Agilent Technologies and since November 2014 it is part of Keysight Technologies EEsof PathWave Design is a divis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University
A university () is an institution of higher (or tertiary) education and research which awards academic degrees in several academic disciplines. ''University'' is derived from the Latin phrase ''universitas magistrorum et scholarium'', which roughly means "community of teachers and scholars". Universities typically offer both undergraduate and postgraduate programs. The first universities in Europe were established by Catholic Church monks. The University of Bologna (), Italy, which was founded in 1088, is the first university in the sense of: *being a high degree-awarding institute. *using the word ''universitas'' (which was coined at its foundation). *having independence from the ecclesiastic schools and issuing secular as well as non-secular degrees (with teaching conducted by both clergy and non-clergy): grammar, rhetoric, logic, theology, canon law, notarial law.Hunt Janin: "The university in medieval life, 1179–1499", McFarland, 2008, , p. 55f.de Ridder-Symoens, H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrical Engineering
Electrical engineering is an engineering discipline concerned with the study, design, and application of equipment, devices, and systems which use electricity, electronics, and electromagnetism. It emerged as an identifiable occupation in the latter half of the 19th century after commercialization of the electric telegraph, the telephone, and electrical power generation, distribution, and use. Electrical engineering is now divided into a wide range of different fields, including computer engineering, systems engineering, power engineering, telecommunications, radio-frequency engineering, signal processing, instrumentation, photovoltaic cells, electronics, and optics and photonics. Many of these disciplines overlap with other engineering branches, spanning a huge number of specializations including hardware engineering, power electronics, electromagnetics and waves, microwave engineering, nanotechnology, electrochemistry, renewable energies, mechatronics/control, and electrical m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electromagnetic Field
An electromagnetic field (also EM field or EMF) is a classical (i.e. non-quantum) field produced by (stationary or moving) electric charges. It is the field described by classical electrodynamics (a classical field theory) and is the classical counterpart to the quantized electromagnetic field tensor in quantum electrodynamics (a quantum field theory). The electromagnetic field propagates at the speed of light (in fact, this field can be identified ''as'' light) and interacts with charges and currents. Its quantum counterpart is one of the four fundamental forces of nature (the others are gravitation, weak interaction and strong interaction.) The field can be viewed as the combination of an electric field and a magnetic field. The electric field is produced by stationary charges, and the magnetic field by moving charges (currents); these two are often described as the sources of the field. The way in which charges and currents interact with the electromagnetic field is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Simulation
A simulation is the imitation of the operation of a real-world process or system over time. Simulations require the use of models; the model represents the key characteristics or behaviors of the selected system or process, whereas the simulation represents the evolution of the model over time. Often, computers are used to execute the simulation. Simulation is used in many contexts, such as simulation of technology for performance tuning or optimizing, safety engineering, testing, training, education, and video games. Simulation is also used with scientific modelling of natural systems or human systems to gain insight into their functioning, as in economics. Simulation can be used to show the eventual real effects of alternative conditions and courses of action. Simulation is also used when the real system cannot be engaged, because it may not be accessible, or it may be dangerous or unacceptable to engage, or it is being designed but not yet built, or it may simply ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Time Domain
Time domain refers to the analysis of mathematical functions, physical signals or time series of economic or environmental data, with respect to time. In the time domain, the signal or function's value is known for all real numbers, for the case of continuous time, or at various separate instants in the case of discrete time. An oscilloscope is a tool commonly used to visualize real-world signals in the time domain. A time-domain graph shows how a signal changes with time, whereas a frequency-domain graph shows how much of the signal lies within each given frequency band over a range of frequencies. Though most precisely referring to time in physics, the term ''time domain'' may occasionally informally refer to position in space when dealing with spatial frequencies, as a substitute for the more precise term ''spatial domain''. Origin of term The use of the contrasting terms ''time domain'' and '' frequency domain'' developed in U.S. communication engineering in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frequency Domain
In physics, electronics, control systems engineering, and statistics, the frequency domain refers to the analysis of mathematical functions or signals with respect to frequency, rather than time. Put simply, a time-domain graph shows how a signal changes over time, whereas a frequency-domain graph shows how much of the signal lies within each given frequency band over a range of frequencies. A frequency-domain representation can also include information on the phase shift that must be applied to each sinusoid in order to be able to recombine the frequency components to recover the original time signal. A given function or signal can be converted between the time and frequency domains with a pair of mathematical operators called transforms. An example is the Fourier transform, which converts a time function into a complex valued sum or integral of sine waves of different frequencies, with amplitudes and phases, each of which represents a frequency component. The "spec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
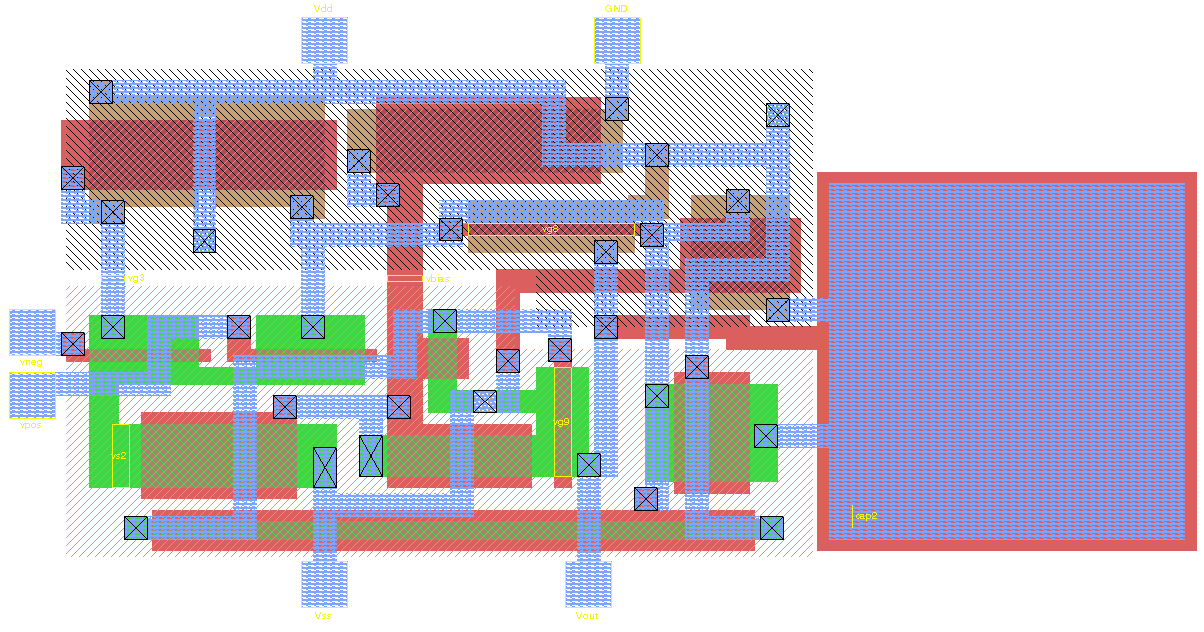
Integrated Circuit Layout
Integrated circuit layout, also known IC layout, IC mask layout, or mask design, is the representation of an integrated circuit in terms of planar geometric shapes which correspond to the patterns of metal, oxide, or semiconductor layers that make up the components of the integrated circuit. Originally the overall process was called tapeout as historically early ICs used graphical black crepe tape on mylar media for photo imaging (erroneously believed to reference magnetic data—the photo process greatly predated magnetic media). When using a standard process—where the interaction of the many chemical, thermal, and photographic variables is known and carefully controlled—the behaviour of the final integrated circuit depends largely on the positions and interconnections of the geometric shapes. Using a computer-aided layout tool, the layout engineer—or layout technician—places and connects all of the components that make up the chip such that they meet certain criteria ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.gif)