|
Wang Yingkai
Wang Yingkai (; 1861–1908), whose courtesy name was Shaochen (), was a Chinese general in the Beiyang Army and first rank official of the late Qing dynasty, who served as the vice president of the Ministry of War and vice-commander-in-chief of the Plain White Banner. Wang graduated from the Tianjin Military Academy (), also known as Beiyang Wubei Xuetang (), and fought with distinction in the First Sino-Japanese War. After China lost the war, he joined the Beiyang Army established by Yuan Shikai and became one of leading commanders of the army. However, during subsequent political struggles he sided with the court party against Yuan. Sun Chuanfang, who later became one of the most important warlords in the early Republican years, was his brother-in-law and protégée. Wang Yingkai died in Beijing in 1908. Early life and career Wang Yingkai was born into a wealthy farming family in Niuzhuang, Fengtian Province (now Yingkou, Liaoning), with his ancestral home in Shandong. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yingkou
Yingkou () is a coastal prefecture-level city of central southern Liaoning province, People's Republic of China, on the northeastern shore of Liaodong Bay. It is the third-smallest city in Liaoning with a total area of , and the ninth most populous with a population of 2,328,582 as of the 2020 census, of whom 1,228,198 lived in the built-up (or metro) area made of three urban districts ( Zhanqian, Xishi and Laobian) and one county-level city ( Dashiqiao). It borders the sub-provincial city of Dalian to the south, the prefectural cities of Anshan to the north and east and Panjin to the northwest, and also shares maritime boundaries with Jinzhou and Huludao across the Liaodong Bay to its west. Located on the east bank of the Daliao River mouth, Yingkou is an important port city, with the Port of Yingkou being the second-largest container port in the Bohai Sea (after the Port of Tianjin) and Northeast China (after the Port of Dalian), the tenth-largest nationwide, and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shandong
Shandong ( , ; ; Chinese postal romanization, alternately romanized as Shantung) is a coastal Provinces of China, province of the China, People's Republic of China and is part of the East China region. Shandong has played a major role in History of China, Chinese history since the beginning of Chinese civilization along the lower reaches of the Yellow River. It has served as a pivotal cultural and religious center for Taoism, Chinese Buddhism and Confucianism. Shandong's Mount Tai is the most revered mountain of Taoism and a site with one of the longest histories of continuous religious worship in the world. The Buddhist temples in the mountains to the south of the provincial capital of Jinan were once among the foremost Buddhist sites in China. The city of Qufu is the birthplace of Confucius and was later established as the center of Confucianism. Confucianism developed from what was later called the Hundred Schools of Thought from the teachings of the Chinese philosopher Con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Huai Army
The Huai Army (), named for the Huai River, was a military force allied with the Qing dynasty raised to contain the Taiping Rebellion in 1862. It was also called the Anhui Army because it was based in Anhui province. It helped to restore the stability of the Qing dynasty. Unlike the traditional Green Standard Army or Eight Banners forces of the Qing, the Huai Army was largely a militia army, based on personal rather than institutional loyalties. It was armed with a mixture of traditional and modern weapons. Li Hongzhang, a commander in the Xiang Army, created the Huai Army in October 1861. It succeeded Zeng Guofan’s Xiang Army. The Huai Army itself was succeeded by the New Army and the Beiyang Army, which were created in the late 19th century. Founding Before recovering Anqing in late 1861, Zeng Guofan ordered his student Li Hongzhang to bring some of the Xiang Army back to Anhui, Li's homeland, for military service and to organize an independent force under Li Hongzhang's comm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jinan
Jinan (), Postal Map Romanization, alternately romanization of Chinese, romanized as Tsinan, is the Capital (political), capital of Shandong province in East China, Eastern China. With a population of 9.2 million, it is the second-largest city in Shandong. The area of present-day Jinan has played an important role in the history of the region from the earliest beginnings of civilization and has evolved into a major national administrative, economic, and transportation hub. The city has held Sub-provincial city, sub-provincial administrative status since 1994. Jinan is often called the "City of Springs" for its famous 72 Artesian aquifer, artesian springs. Jinan is one of the top List of cities by scientific output, 40 cities in the world for scientific research as tracked by the Nature Index according to the Nature Index 2022 Science Cities. The city is home to List of universities and colleges in Shandong, several major universities, including Shandong University, Shangdong, Sha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zhili
Zhili, alternately romanized as Chihli, was a northern administrative region of China since the 14th-century that lasted through the Ming dynasty and Qing dynasty until 1911, when the region was dissolved, converted to a province, and renamed Hebei in 1928. History The name ''Zhili'' means "directly ruled" and indicates regions directly ruled by the imperial government of China. Zhili province was first constituted during the Ming dynasty when the capital of China was located at Nanjing along the Yangtze River. In 1403, the Ming Yongle Emperor relocated the capital to Beiping, which was subsequently renamed Beijing.Susan Naquin, ''Peking: Temples and City Life, 1400-1900'', p xxxiii The region known as North Zhili was composed of parts of the modern provinces of Hebei, Henan, Shandong, including the provincial-level municipalities of Beijing and Tianjin. There was another region located around the "reserve capital" Nanjing known as South Zhili that included parts of what ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shanhaiguan District
Shanhaiguan District (), formerly Shan-hai-kwan or Shan-hai-kuan, is a district of the city of Qinhuangdao, Hebei Province, China, named after the pass of the Great Wall within the district, Shanhai Pass. It is located east of the city centre. Administrative divisions There are five subdistricts, three towns, and one township, Bohai Township (), in the district. Subdistricts * Nanguan Subdistrict () * Dongjie Subdistrict () *[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Song Qing (Qing Dynasty)
Song Qing () (1820–1902), courtesy name Zhusan, was a Chinese general who served the Imperial government during the First Sino-Japanese War and in the Boxer Rebellion. Song was a native of what is now Penglai City, Shandong Province. Passing his imperial examinations for bureaucratic positions, he was assigned as a magistrate to what is now Bozhou in Anhui Province. During the Nien Rebellion, he led a local army against the rebels in southern Henan Province and northern Anhui Province. In 1862, he was promoted to general, and awarded the title of Baturu. He later joined his forces to that of the Huai Army, and assisted Sengge Rinchen in the suppression of the Taiping rebellion, and subsequently (in 1869) fought in the Dungan revolt (1862–1877), Dungan revolt under the command of Zuo Zongtang. From 1880, Song worked under Li Hongzhang towards overseeing the defence of Manchuria against the Russian Empire, and from 1882 had been stationed in strategic port of Lushunkou, home of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haicheng, Liaoning
Haicheng () is a county-level city in central Liaoning Province, People's Republic of China, located about southwest of the provincial capital Shenyang. It is under the administration of Anshan City, the seat of which lies to the northeast. Haicheng has an area of and as of the 2020 census, a decreasing population of 1,067,905 inhabitants (1,232,739 in 2020). The infamous warlord General Zhang Zuolin was born in Haicheng. Haicheng earthquake of 1975 On 4 February 1975, an earthquake measuring 7.3 on the Richter Scale hit the city of Haicheng, which at the time had approximately 1 million residents. However, seismologists sent out warnings about this earthquake a day earlier and ordered evacuations. Because of this correct prediction, many lives were saved. This was the first successful earthquake prediction in history. Further aiding the prediction, cats and other animals are also said to have acted strangely in the days leading up to the earthquake. There are some ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Korean Peninsula
Korea ( ko, 한국, or , ) is a peninsular region in East Asia. Since 1945, it has been divided at or near the 38th parallel, with North Korea (Democratic People's Republic of Korea) comprising its northern half and South Korea (Republic of Korea) comprising its southern half. Korea consists of the Korean Peninsula, Jeju Island, and several minor islands near the peninsula. The peninsula is bordered by China to the northwest and Russia to the northeast. It is separated from Japan to the east by the Korea Strait and the Sea of Japan (East Sea). During the first half of the 1st millennium, Korea was divided between three states, Goguryeo, Baekje, and Silla, together known as the Three Kingdoms of Korea. In the second half of the 1st millennium, Silla defeated and conquered Baekje and Goguryeo, leading to the "Unified Silla" period. Meanwhile, Balhae formed in the north, superseding former Goguryeo. Unified Silla eventually collapsed into three separate states due to civi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyongyang
Pyongyang (, , ) is the capital and largest city of North Korea, where it is known as the "Capital of the Revolution". Pyongyang is located on the Taedong River about upstream from its mouth on the Yellow Sea. According to the 2008 population census, it has a population of 3,255,288. Pyongyang is a directly administered city () with equal status to North Korean provinces. Pyongyang is one of the oldest cities in Korea. It was the capital of two ancient Korean kingdoms, Gojoseon and Goguryeo, and served as the secondary capital of Goryeo. Much of the city was destroyed during the First Sino-Japanese War, but it was revived under Japanese rule and became an industrial center. Following the establishment of North Korea in 1948, Pyongyang became its ''de facto'' capital. The city was again devastated during the Korean War, but was quickly rebuilt after the war with Soviet assistance. Pyongyang is the political, industrial and transport center of North Korea. It is home ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
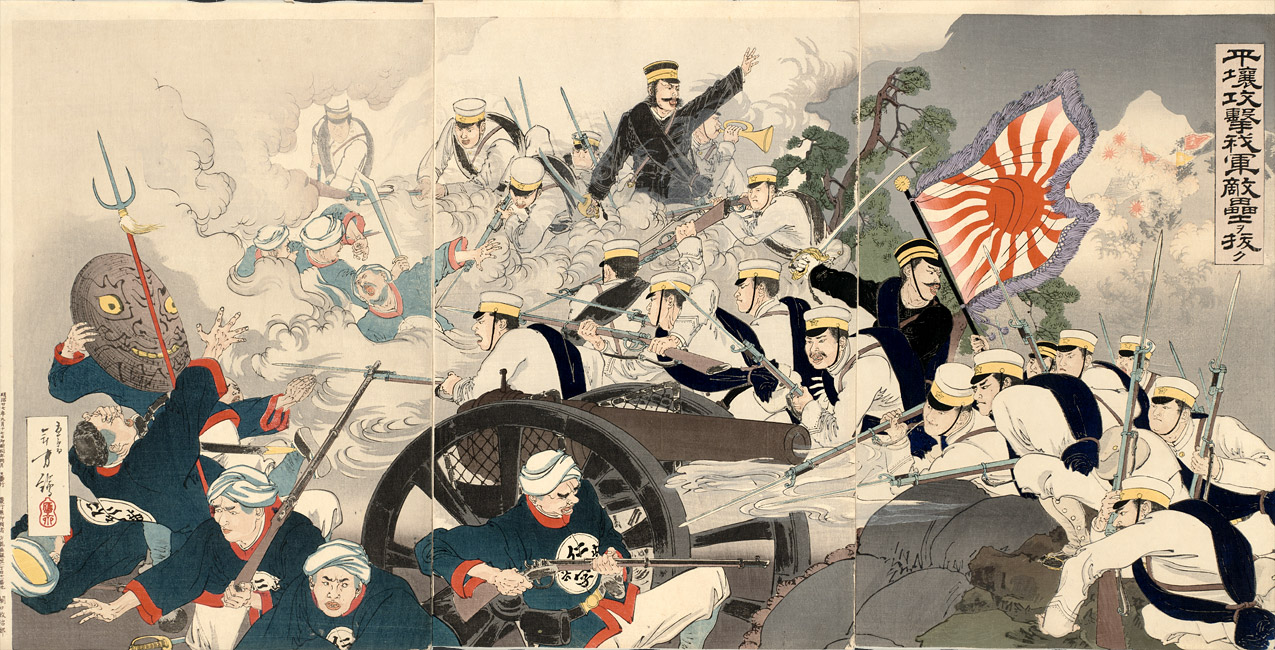
Battle Of Pyongyang (1894)
The Battle of Pyongyang ( ja, 平壌作戦; zh, 平壤之戰) was the second major land battle of the First Sino-Japanese War. It took place on 15 September 1894 in Pyongyang, Korea between the forces of Meiji Japan and Qing China. It is sometimes referred to archaically in Western sources as the "Battle of Ping-yang". Between 13,000 and 15,000 Chinese troops of the Beiyang Army under overall command of General Ye Zhichao had arrived in Pyongyang on 4 August 1894, and had made extensive repairs to its ancient city walls, feeling itself secure in its superior numbers and in the strength of the defenses. Prince Yamagata Aritomo's First Army of the Imperial Japanese Army converged on Pyongyang from several directions on 15 September 1894, and in the morning made a direct attack on the north and southeast corners of the walled city under very little cover. The Chinese defense was strong, but was eventually outmaneuvered by an unexpected flanking attack by the Japanese fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imperial Japanese Army
The was the official ground-based armed force of the Empire of Japan from 1868 to 1945. It was controlled by the Imperial Japanese Army General Staff Office and the Ministry of the Army, both of which were nominally subordinate to the Emperor of Japan as supreme commander of the army and the Imperial Japanese Navy. Later an Inspectorate General of Aviation became the third agency with oversight of the army. During wartime or national emergencies, the nominal command functions of the emperor would be centralized in an Imperial General Headquarters (IGHQ), an ad hoc body consisting of the chief and vice chief of the Army General Staff, the Minister of the Army, the chief and vice chief of the Naval General Staff, the Inspector General of Aviation, and the Inspector General of Military Training. History Origins (1868–1871) In the mid-19th century, Japan had no unified national army and the country was made up of feudal domains (''han'') with the Tokugawa shogunate (''bakufu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |