|
Wuhan Government
The Wuhan Nationalist government (), also known as the Wuhan government, Wuhan regime, or Hankow government, was a government dominated by the left-wing of the Nationalist or Kuomintang (KMT) Party of China that was based in Wuhan from 5 December 1926 to 21 September 1927, led first by Eugene Chen, and later by Wang Jingwei. Following the capture of Wuhan during the Northern Expedition, the Nationalist government based in Guangzhou moved there in December 1926. In April 1927, after National Revolutionary Army (NRA) commander-in-chief Chiang Kai-shek purged communists and leftists in the "Shanghai massacre", the Wuhan government split from Chiang in what is known as the "Nanjing–Wuhan split" (). Chiang subsequently formed his own government in Nanjing. While Chiang continued the Northern Expedition on his own, increasing tensions between communists and the KMT in the Wuhan government resulted in a new purge of communists from that government, and an eventual reconciliation with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blue Sky With A White Sun
The Blue Sky with a White Sun () serves as the design for the party flag and emblem of the Kuomintang, the canton of the flag of the Republic of China, the national emblem of the Republic of China, and as the naval jack of the ROC Navy. In the "Blue Sky with a White Sun" symbol, the twelve rays of the white Sun representing the twelve months and the twelve traditional Chinese hours (), each of which corresponds to two modern hours and symbolizes the spirit of progress. Official description The national emblem of the Republic of China is officially described in the ''National Emblem and National Flag of the Republic of China Act'': History of the Blue Sky White Sun design The "Blue Sky with a White Sun" flag was originally designed by Lu Hao-tung, a martyr of the Republican revolution. He presented his design to represent the revolutionary army at the inauguration of the Society for Regenerating China, an anti-Qing society in Hong Kong, on February 21, 1895. During the W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joseph Stalin
Joseph Vissarionovich Stalin (born Ioseb Besarionis dze Jughashvili; – 5 March 1953) was a Georgian revolutionary and Soviet political leader who led the Soviet Union from 1924 until his death in 1953. He held power as General Secretary of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union (1922–1952) and Chairman of the Council of Ministers of the Soviet Union (1941–1953). Initially governing the country as part of a collective leadership, he consolidated power to become a dictator by the 1930s. Ideologically adhering to the Leninist interpretation of Marxism, he formalised these ideas as Marxism–Leninism, while his own policies are called Stalinism. Born to a poor family in Gori in the Russian Empire (now Georgia), Stalin attended the Tbilisi Spiritual Seminary before joining the Marxist Russian Social Democratic Labour Party. He edited the party's newspaper, ''Pravda'', and raised funds for Vladimir Lenin's Bolshevik faction via robberies, kidnappings and protection ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mao Zedong
Mao Zedong pronounced ; also romanised traditionally as Mao Tse-tung. (26 December 1893 – 9 September 1976), also known as Chairman Mao, was a Chinese communist revolutionary who was the founder of the People's Republic of China (PRC), which he led as the chairman of the Chinese Communist Party from the establishment of the PRC in 1949 until his death in 1976. Ideologically a Marxist–Leninist, his theories, military strategies, and political policies are collectively known as Maoism. Mao was the son of a prosperous peasant in Shaoshan, Hunan. He supported Chinese nationalism and had an anti-imperialist outlook early in his life, and was particularly influenced by the events of the Xinhai Revolution of 1911 and May Fourth Movement of 1919. He later adopted Marxism–Leninism while working at Peking University as a librarian and became a founding member of the Chinese Communist Party (CCP), leading the Autumn Harvest Uprising in 1927. During the Chinese Civil War ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hubei
Hubei (; ; alternately Hupeh) is a landlocked province of the People's Republic of China, and is part of the Central China region. The name of the province means "north of the lake", referring to its position north of Dongting Lake. The provincial capital, Wuhan, serves as a major transportation hub and the political, cultural, and economic hub of central China. Hubei's name is officially abbreviated to "" (), an ancient name associated with the eastern part of the province since the State of E of the Western Zhou dynasty of –771 BCE; a popular name for Hubei is "" () (suggested by that of the powerful State of Chu, which existed in the area during the Eastern Zhou dynasty of 770 – 256 BCE). Hubei borders the provinces of Henan to the north, Anhui to the east, Jiangxi to the southeast, Hunan to the south, Chongqing to the west, and Shaanxi to the northwest. The high-profile Three Gorges Dam is located at Yichang, in the west of the province. Hubei is the 7th-largest p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hunan
Hunan (, ; ) is a landlocked province of the People's Republic of China, part of the South Central China region. Located in the middle reaches of the Yangtze watershed, it borders the province-level divisions of Hubei to the north, Jiangxi to the east, Guangdong and Guangxi to the south, Guizhou to the west and Chongqing to the northwest. Its capital and largest city is Changsha, which also abuts the Xiang River. Hengyang, Zhuzhou, and Yueyang are among its most populous urban cities. With a population of just over 66 million residing in an area of approximately , it is China's 7th most populous province, the fourth most populous among landlocked provinces, the second most populous in South Central China after Guangdong and the most populous province in Central China. It is the largest province in South-Central China and the fourth largest among landlocked provinces and the 10th most extensive province by area. Hunan's nominal GDP was US$ 724 billion (CNY 4.6 trillion) a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xu Qian
Xu Qian or George Hsu (; June 15, 1871 – September 26, 1940) was a Chinese politician and jurist. He made important contribution to the judicial system of modern China. Originated from She County of Anhui province and born in Nanchang of Jiangxi province, Xu Qian passed the highest level of Imperial Examination in 1903 and obtained Jinshi title. He was sent abroad to inspect European and American legal affairs, and participated in the judicial reforms of the late Qing Dynasty. Under the Republic of China, he served as the chief legal officer and director of the school committee of National Wuchang Sun Yat-Sen University (now Wuhan University). He was active in the politics of both the Beiyang government and the Nationalist government for many years. Xu Qian contributed a lot to the establishment and improvement of China's modern judicial system. Early life and education Xu Qian was born in the city of Nanchang, Jiangxi, on June 15, 1871. He lost his father at the age of fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sun Fo
Sun Fo or Sun Ke (; 21 October 1891 – 13 September 1973), courtesy name Zhesheng (), was a high-ranking official in the government of the Republic of China. He was the son of Sun Yat-sen, the founder of the Republic of China, and his first wife Lu Muzhen. Biography Sun was born in HeungShan (now Zhongshan), Guangdong, China. He travelled abroad to study, graduated in 1911 from Saint Louis College (now Saint Louis School, K-12, Honolulu, Hawaii), earned a Bachelor of Arts from the University of California, Berkeley in 1916 and a Master of Science from Columbia University in 1917. He also received an honorary LL.D. from Columbia. He married Chen Suk-ying and had two sons (Sun Tse-ping and Sun Tse-kiong) and two daughters (Sun Sui-ying and Sun Sui-hwa). He had two more daughters; Sun Sui-fong with Yan Ai-juang, and Sun Sui-fen with Lan Ni. Most of his children, including daughters, went on to have successful careers in public. After returning to China, Sun was appoint ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nanchang
Nanchang (, ; ) is the capital of Jiangxi Province, People's Republic of China. Located in the north-central part of the province and in the hinterland of Poyang Lake Plain, it is bounded on the west by the Jiuling Mountains, and on the east by Poyang Lake. Because of its strategic location connecting the prosperous East and South China, it has become a major railway hub in Southern China in recent decades. As the Nanchang Uprising in 1927 is distinctively recognized by the ruling Communist Party as "firing the first gunshot against the evil Nationalists", the current government has therefore named the city since 1949 "the City of Heroes", "the place where the People's Liberation Army was born", and the most widely known "place where the military banner of the People's Liberation Army was first raised". Nanchang is also a major city, appearing among the top 150 cities in the world by scientific research outputs, as tracked by the Nature Index and home to Nanchang Universit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trade Union
A trade union (labor union in American English), often simply referred to as a union, is an organization of workers intent on "maintaining or improving the conditions of their employment", ch. I such as attaining better wages and benefits (such as holiday, health care, and retirement), improving working conditions, improving safety standards, establishing complaint procedures, developing rules governing status of employees (rules governing promotions, just-cause conditions for termination) and protecting the integrity of their trade through the increased bargaining power wielded by solidarity among workers. Trade unions typically fund their head office and legal team functions through regularly imposed fees called ''union dues''. The delegate staff of the trade union representation in the workforce are usually made up of workplace volunteers who are often appointed by members in democratic elections. The trade union, through an elected leadership and bargaining committee, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
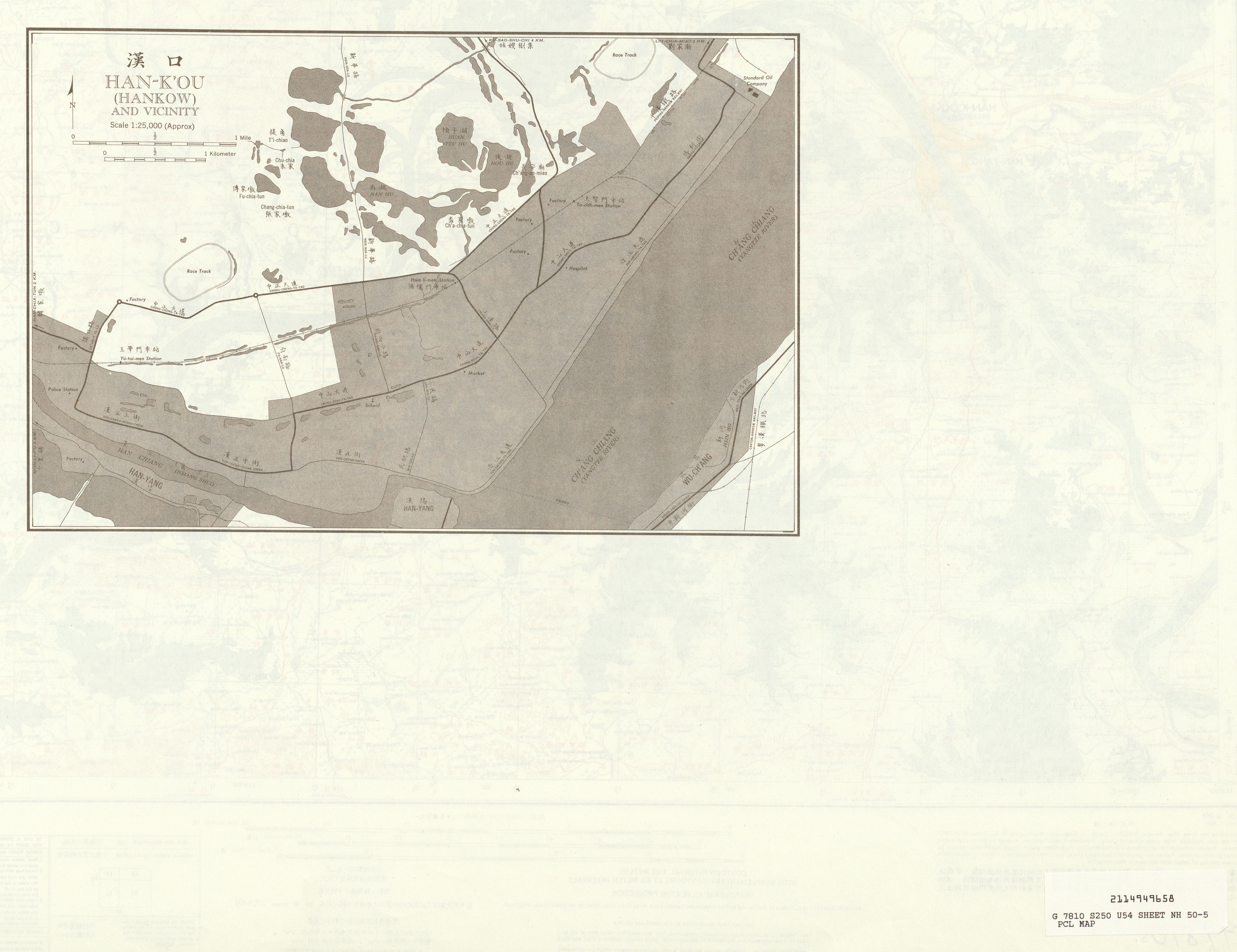
Hanyang District
Hanyang District () forms part of the urban core of and is one of 13 urban districts of the prefecture-level city of Wuhan, the capital of Hubei Province, China. Currently, it is a district and stands between the Han River (right/southern bank) and the Yangtze River (left/northwestern bank), where the former drains into the latter. It is connected by bridges with its former sister cities, Hankou and Wuchang. Presently, on the left bank of the Yangtze, it borders the districts of Qiaokou to the north across the Han River, Jianghan to the northeast, Caidian to the southwest, and Dongxihu to the northwest; on the opposite bank it borders Wuchang and Hongshan. Guiyuan Temple is located in Hanyang. The name "Hanyang" means "the Yang side of Han River", referring to the town's historic location on the north ("yang") bank of the Han River mouth. However, the lower Han River changed course to the north side of the town during Ming dynasty's Chenghua-era. The town, now on the south ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hankou
Hankou, alternately romanized as Hankow (), was one of the three towns (the other two were Wuchang and Hanyang) merged to become modern-day Wuhan city, the capital of the Hubei province, China. It stands north of the Han and Yangtze Rivers where the Han flows into the Yangtze. Hankou is connected by bridges to its triplet sister towns Hanyang (between Han and Yangtze) and Wuchang (on the south side of the Yangtze). Hankou is the main port of Hubei province and the single largest port in the middle reaches of Yangtze. History The city's name literally means "Mouth of the Han", from its position at the confluence of the Han with the Yangtze River. The name appears in a Tang Dynasty poem by Liu Changqing. Other historical names for the city include Xiakou (), Miankou (), and Lukou (). Hankou, from the Ming to late Qing, was under the administration of the local government in Hanyang, although it was already one of the four major national markets ( :zh:四大名镇) in Ming dyna ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wuchang
Wuchang forms part of the urban core of and is one of 13 urban districts of the prefecture-level city of Wuhan, the capital of Hubei Province, China. It is the oldest of the three cities that merged into modern-day Wuhan, and stood on the right (southeastern) bank of the Yangtze River, opposite the mouth of the Han River. The two other cities, Hanyang and Hankou, were on the left (northwestern) bank, separated from each other by the Han River. The name "Wuchang" remains in common use for the part of urban Wuhan south of the Yangtze River. Administratively, however, it is split between several districts of the City of Wuhan. The historic center of Wuchang lies within the modern Wuchang District, which has an area of and a population of 1,003,400. Other parts of what is colloquially known as Wuchang are within Hongshan District (south and south-east) and Qingshan District (north-east). Presently, on the right bank of the Yangtze, it borders the districts of Qingshan (for a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)