|
Wood Street Congregational Church
Wood Street Congregational Church was a congregational chapel which formerly stood on Wood Street, Cardiff. It was once the largest congregational chapel in South Wales. It was demolished in the 1970s. Early history The building which became the church was built in 1858, initially as a temperance hall. It was built as part of Temperance Town, a grid of small streets which formerly occupied much of the area to the north of Cardiff Central railway station. Within a year of opening, the building became a music hall and a circus. The acrobat Charles Blondin performed there in the early 1860s. In the later years of the decade, the building came to the attention of minister William Watkiss (1827-1892), who believed that it would be an ideal venue to fill with crowds of unchurched working people. Purchase and scandal Watkiss was assisted in his endeavours by a Mr Ashton, a prominent member of his existing congregation. Under Ashton's expectations, the building was purchased, the loc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Congregational
Congregational churches (also Congregationalist churches or Congregationalism) are Protestant churches in the Calvinist tradition practising congregationalist church governance, in which each congregation independently and autonomously runs its own affairs. Congregationalism, as defined by the Pew Research Center, is estimated to represent 0.5 percent of the worldwide Protestant population; though their organizational customs and other ideas influenced significant parts of Protestantism, as well as other Christian congregations. The report defines it very narrowly, encompassing mainly denominations in the United States and the United Kingdom, which can trace their history back to nonconforming Protestants, Puritans, Separatists, Independents, English religious groups coming out of the English Civil War, and other English Dissenters not satisfied with the degree to which the Church of England had been reformed. Congregationalist tradition has a presence in the United States ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cardiff
Cardiff (; cy, Caerdydd ) is the capital and largest city of Wales. It forms a principal area, officially known as the City and County of Cardiff ( cy, Dinas a Sir Caerdydd, links=no), and the city is the eleventh-largest in the United Kingdom. Located in the south-east of Wales and in the Cardiff Capital Region, Cardiff is the county town of the historic county of Glamorgan and in 1974–1996 of South Glamorgan. It belongs to the Eurocities network of the largest European cities. A small town until the early 19th century, its prominence as a port for coal when mining began in the region helped its expansion. In 1905, it was ranked as a city and in 1955 proclaimed capital of Wales. Cardiff Built-up Area covers a larger area outside the county boundary, including the towns of Dinas Powys and Penarth. Cardiff is the main commercial centre of Wales as well as the base for the Senedd. At the 2021 census, the unitary authority area population was put at 362,400. The popula ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South Wales
South Wales ( cy, De Cymru) is a loosely defined region of Wales bordered by England to the east and mid Wales to the north. Generally considered to include the historic counties of Glamorgan and Monmouthshire, south Wales extends westwards to include Carmarthenshire and Pembrokeshire. In the western extent, from Swansea westwards, local people would probably recognise that they lived in both south Wales and west Wales. The Brecon Beacons National Park covers about a third of south Wales, containing Pen y Fan, the highest British mountain south of Cadair Idris in Snowdonia. A point of some discussion is whether the first element of the name should be capitalised: 'south Wales' or 'South Wales'. As the name is a geographical expression rather than a specific area with well-defined borders, style guides such as those of the BBC and ''The Guardian'' use the form 'south Wales'. In a more authoritative style guide, the Welsh Government, in their international gateway website, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Temperance Movement
The temperance movement is a social movement promoting temperance or complete abstinence from consumption of alcoholic beverages. Participants in the movement typically criticize alcohol intoxication or promote teetotalism, and its leaders emphasize alcohol's negative effects on people's health, personalities and family lives. Typically the movement promotes alcohol education and it also demands the passage of new laws against the sale of alcohol, either regulations on the availability of alcohol, or the complete prohibition of it. During the 19th and early 20th centuries, the temperance movement became prominent in many countries, particularly in English-speaking, Scandinavian, and majority Protestant ones, and it eventually led to national prohibitions in Canada (1918 to 1920), Norway (spirits only from 1919 to 1926), Finland (1919 to 1932), and the United States (1920 to 1933), as well as provincial prohibition in India (1948 to present). A number of temperance organiza ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
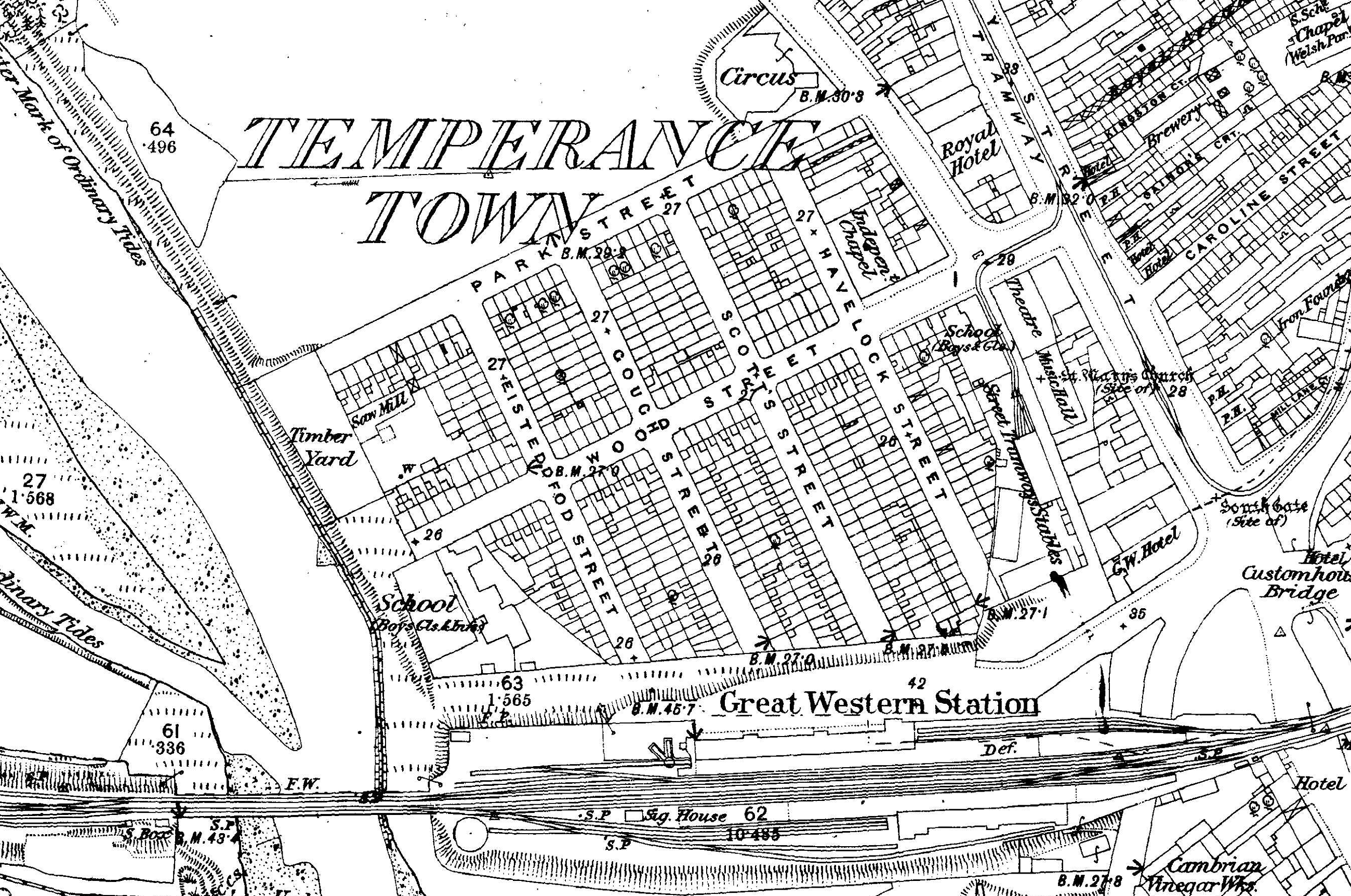
Temperance Town, Cardiff
Temperance Town, Cardiff, was the unofficial name for a working-class inner-city suburb established in the late 1850s and demolished in the 1930s to make way for Cardiff Bus Station. History Temperance Town was built on reclaimed land next to the River Taff. The land was owned by Colonel Edward Wood, a teetotaller, who imposed a condition on the developer that the sale of alcohol would not be allowed - hence the district's name. Development took place in the late 1850s and the early 1860s. Schools were opened in January 1879 and a church, St Dyfrig's, was built in 1888. The main street, Wood Street, was filled with shops and other businesses. The large Temperance Hall was eventually converted into the Wood Street Congregational Church. In the early 20th century Cardiff's prosperity had been reduced by the decline in coal exports. Poverty and overcrowding in Temperance Town increased, and conditions deteriorated. In 1930 the Great Western Railway built a new station on the edge o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cardiff Central Railway Station
, symbol_location = gb , symbol = rail , image = Cardiff Central station (26526139271).jpg , caption = 1930s frontage of Cardiff Central station (northern entrance) , borough = Cardiff, City and County of Cardiff , country = Wales , coordinates = , grid_name = Grid reference , grid_position = , owned = Network Rail , manager = Transport for Wales Rail , platforms = 8 , code = CDF , classification = DfT category A , years = 19 June 1850 , events = Opened as ''Cardiff'' , years1 = 1896 , events1 = Enlarged , years2 = 1924 , events2 = Renamed ''Cardiff General'' , years3 = 1931–34 , events3 = Rebuilt , years4 = 1940 , events4 = Merged with Cardiff Riverside station , years5 = 1964 , events5 = Riverside platforms closed , years6 = 1973 , events6 = Renamed ''Cardiff Central'' , years7 = 2015-17 , events7 = Enlarged , mpassengers = , footnotes = Passenger statistics from the Office of Rail and Road , mapframe=yes , mapframe-zoom = 13 Cardiff Cen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Music Hall
Music hall is a type of British theatrical entertainment that was popular from the early Victorian era, beginning around 1850. It faded away after 1918 as the halls rebranded their entertainment as variety. Perceptions of a distinction in Britain between bold and scandalous ''Music Hall'' and subsequent, more respectable ''Variety'' differ. Music hall involved a mixture of popular songs, comedy, speciality acts, and variety entertainment. The term is derived from a type of theatre or venue in which such entertainment took place. In North America vaudeville was in some ways analogous to British music hall, featuring rousing songs and comic acts. Originating in saloon bars within public houses during the 1830s, music hall entertainment became increasingly popular with audiences. So much so, that during the 1850s some public houses were demolished, and specialised music hall theatres developed in their place. These theatres were designed chiefly so that people could consume food ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Circus
A circus is a company of performers who put on diverse entertainment shows that may include clowns, acrobats, trained animals, trapeze acts, musicians, dancers, hoopers, tightrope walkers, jugglers, magicians, ventriloquists, and unicyclists as well as other object manipulation and stunt-oriented artists. The term ''circus'' also describes the performance which has followed various formats through its 250-year modern history. Although not the inventor of the medium, Philip Astley is credited as the father of the modern circus. In 1768, Astley, a skilled equestrian, began performing exhibitions of trick horse riding in an open field called Ha'Penny Hatch on the south side of the Thames River, England. In 1770, he hired acrobats, tightrope walkers, jugglers and a clown to fill in the pauses between the equestrian demonstrations and thus chanced on the format which was later named a "circus". Performances developed significantly over the next fifty years, with large-scale theat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Blondin
Charles Blondin (born Jean François Gravelet, 28 February 182422 February 1897) was a French tightrope walker and acrobat. He toured the United States and was known for crossing the Niagara Gorge on a tightrope. During an event in Dublin in 1860, the rope on which he was walking broke and two workers were killed, although Blondin was not injured. He married three times and had eight children. His name became synonymous with tightrope walking. Early life Blondin was born on 28 February 1824 in Hesdin, Pas-de-Calais, France.''Irish Times'', Dublin, 25 May 1861 His birth name was Jean-François Gravelet, though he was known by many other names and nicknames: Charles Blondin, Jean-François Blondin, Chevalier Blondin, and The Great Blondin. At the age of five, he was sent to the École de Gymnase in Lyon and, after six months of training as an acrobat, made his first public appearance as "The Boy Wonder". His superior skill and grace, as well as the originality of the settings ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theatre Royal (1826), Cardiff
Theatre Royal may refer to: Theatres ; United Kingdom: *Theatre Royal, Aldershot, Aldershot, built in 1891 and demolished in 1959 *Theatre Royal, Aston, Birmingham, later Alpha Television * Theatre Royal, Barnwell, Cambridge * Theatre Royal, Bath, Somerset * Theatre Royal, Birmingham (1774–1956; so named from 1807) *Theatre Royal, Brighton *Theatre Royal, Bristol * Theatre Royal, Bury St Edmunds *Theatre Royal, Cardiff, later known as Prince of Wales Theatre, Cardiff *Theatre Royal, Covent Garden, London later Royal Opera House Covent Garden *Theatre Royal, Drury Lane, London *Theatre Royal, Dumfries *Theatre Royal, Edinburgh *Theatre Royal, Exeter *Theatre Royal, Glasgow * Theatre Royal, Gravesend *Theatre Royal, Hanley, Stoke-on-Trent (opened 1852, rebuilt 1871, 1887, 1894, 1951, closed 2000) * Theatre Royal, Haymarket, London * Theatre Royal, Hyde, Hyde, Greater Manchester (opened 1902, closed 1992) *Theatre Royal, Lincoln, England *Theatre Royal, Lichfield, former theatre on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Congregational Church
Congregational churches (also Congregationalist churches or Congregationalism) are Protestant churches in the Calvinist tradition practising congregationalist church governance, in which each congregation independently and autonomously runs its own affairs. Congregationalism, as defined by the Pew Research Center, is estimated to represent 0.5 percent of the worldwide Protestant population; though their organizational customs and other ideas influenced significant parts of Protestantism, as well as other Christian congregations. The report defines it very narrowly, encompassing mainly denominations in the United States and the United Kingdom, which can trace their history back to nonconforming Protestants, Puritans, Separatists, Independents, English religious groups coming out of the English Civil War, and other English Dissenters not satisfied with the degree to which the Church of England had been reformed. Congregationalist tradition has a presence in the United States ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lionel B , a defense in the game of bridge
{{disambiguation ...
__TOC__ Lionel may refer to: Name *Lionel (given name) Places *Lionel, Lewis, a village in the Outer Hebrides of Scotland *Lionel Town, Jamaica, a settlement Brands and enterprises *Lionel, LLC, an American designer and importer of toy trains and model railroads, which owns the trademarks and most of the product rights associated with Lionel Corp., but is not directly related *Lionel Corporation, an American manufacturer and retailer of toy trains and model railroads Other uses *Lionel (bridge) Lionel is a contract bridge bidding convention used in defense against an opposing 1NT openings. Using Lionel, over a 1NT opening of the opponents: :* a double is conventional and denotes spades and a lower suit (4-4 or longer), :* a 2/2 overcall de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)