|
Winneshiek Shale
The Winneshiek Shale (originally the Winneshiek Lagerstätte) is a Middle Ordovician (Darriwilian-age) geological formation in Iowa. The formation is restricted to the Decorah crater, an impact crater near Decorah, Iowa. Despite only being discovered in 2005, the Winneshiek Shale is already renowned for the exceptional preservation of its fossils. The shale preserves a unique ecosystem, the Winneshiek biota, which is among the most remarkable Ordovician lagerstätten in the United States. Fossils include the oldest known eurypterid, ''Pentecopterus'', as well as giant conodonts such as ''Iowagnathus'' and ''Archeognathus''. Geology The Winneshiek Shale is a thin and geologically homogeneous package of dark grey to greenish-brown sandy shale. Drill core data has estimated a maximum thickness of 38 meters, though in most areas its thickness is only about 18–27 meters. The shale is replete with pyrite and organic carbon. It lies solely within the Decorah Structure, a 5.6 km ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Formation (stratigraphy)
A geological formation, or simply formation, is a body of rock having a consistent set of physical characteristics (lithology) that distinguishes it from adjacent bodies of rock, and which occupies a particular position in the layers of rock exposed in a geographical region (the stratigraphic column). It is the fundamental unit of lithostratigraphy, the study of strata or rock layers. A formation must be large enough that it can be mapped at the surface or traced in the subsurface. Formations are otherwise not defined by the thickness (geology), thickness of their rock strata, which can vary widely. They are usually, but not universally, tabular in form. They may consist of a single lithology (rock type), or of alternating beds of two or more lithologies, or even a heterogeneous mixture of lithologies, so long as this distinguishes them from adjacent bodies of rock. The concept of a geologic formation goes back to the beginnings of modern scientific geology. The term was used by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
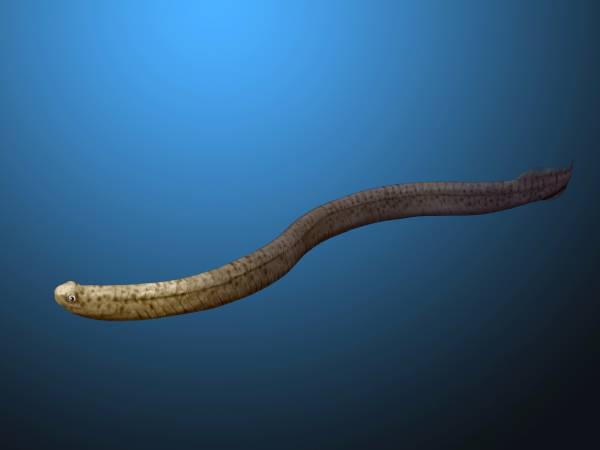
Conodonts
Conodonts (Greek ''kōnos'', "cone", + ''odont'', "tooth") are an extinct group of agnathan (jawless) vertebrates resembling eels, classified in the class Conodonta. For many years, they were known only from their tooth-like oral elements, which are usually found in isolation and are now called conodont elements. Knowledge about soft tissues remains limited. They existed in the world's oceans for over 300 million years, from the Cambrian to the beginning of the Jurassic. Conodont elements are widely used as index fossils, fossils used to define and identify geological periods. The animals are also called Conodontophora (conodont bearers) to avoid ambiguity. Discovery and understanding of conodonts The teeth-like fossils of the conodont were first discovered by Heinz Christian Pander and the results published in Saint Petersburg, Russia, in 1856. The name ''pander'' is commonly used in scientific names of conodonts. It was only in the early 1980s that the first fossil evidence of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apatite
Apatite is a group of phosphate minerals, usually hydroxyapatite, fluorapatite and chlorapatite, with high concentrations of OH−, F− and Cl− ions, respectively, in the crystal. The formula of the admixture of the three most common endmembers is written as Ca10( PO4)6(OH,F,Cl)2, and the crystal unit cell formulae of the individual minerals are written as Ca10(PO4)6(OH)2, Ca10(PO4)6F2 and Ca10(PO4)6Cl2. The mineral was named apatite by the German geologist Abraham Gottlob Werner in 1786, although the specific mineral he had described was reclassified as fluorapatite in 1860 by the German mineralogist Karl Friedrich August Rammelsberg. Apatite is often mistaken for other minerals. This tendency is reflected in the mineral's name, which is derived from the Greek word ἀπατάω (apatáō), which means ''to deceive''. Geology Apatite is very common as an accessory mineral in igneous and metamorphic rocks, where it is the most common phosphate mineral. However, occu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bromalite
Bromalites are the fossilized remains of material sourced from the digestive system of organisms. As such, they can be broadly considered to be trace fossils. The most well-known types of bromalites are fossilized faeces or coprolites A coprolite (also known as a coprolith) is fossilized feces. Coprolites are classified as trace fossils as opposed to body fossils, as they give evidence for the animal's behaviour (in this case, diet) rather than morphology. The name is d .... However, other types are recognised, including: regurgitalites (fossilized remains of vomit or other regurgitated objects such as owl pellets); cololites (intestinal contents); and gastrolites (stomach contents). Regurtitalites and coprolites are thus essentially known only after they have left the body of the producing organisms, whereas gastrolites and cololites are found in ''situ'' in their respective organs, but there are rare exceptions (see Seilacher, 2002). Whilst coprolites and regurgit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphatic Fossilization
Phosphatic fossilization has occurred in unusual circumstances to preserve some extremely high-resolution microfossils in which careful preparation can even reveal preserved cellular structures. Such microscopic fossils are only visible under the scanning electron microscope. Mechanism Large quantities of phosphate are required, either from seawater or from the tissues of the decaying organism. In some cases microbes control the phosphatization, and the remains of the microbes that fed on the preserved tissue form the fossil. In other, the tissue itself is the source of phosphate and its phosphatized remains form the fossil. In the intermediate case the phosphatized tissue retains the impressions of the phosphatizing microbes. Phosphatic preservation in Burgess Shale-type fossils Soft-tissue fossils, such as those found in the Burgess Shale, are rare. In some cases their internal organs are replicated in phosphate. The phosphate mainly comes from the tissue itself, and may late ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ceratiocaris
''Ceratiocaris'' is a genus of paleozoic phyllocarid crustaceans whose fossils are found in marine strata from the Upper Ordovician until the genus' extinction during the Silurian. They are typified by eight short thoracic segments, seven longer abdominal somites and an elongated pretelson somite. Their carapace is slightly oval shaped; they have many ridges parallel to the ventral margin and possess a horn at the anterior end. They are well known from the Silurian Eramosa formation of Ontario, Canada Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by tot .... The following species are included: *''Ceratiocaris bohemica'' Barrande, 1872 *''Ceratiocaris harpago'' Poschmann, Bergmann & Kühl, 2018 *''Ceratiocaris macroura'' Collette & Rudkin, 2010 *''Ceratiocaris monroei'' Salter ''in'' M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biomineralization
Biomineralization, also written biomineralisation, is the process by which living organisms produce minerals, often to harden or stiffen existing tissues. Such tissues are called mineralized tissues. It is an extremely widespread phenomenon; all six taxonomic kingdoms contain members that are able to form minerals, and over 60 different minerals have been identified in organisms. Examples include silicates in algae and diatoms, carbonates in invertebrates, and calcium phosphates and carbonates in vertebrates. These minerals often form structural features such as sea shells and the bone in mammals and birds. Organisms have been producing mineralized skeletons for the past 550 million years. Calcium carbonates and calcium phosphates are usually crystalline, but silica organisms (sponges, diatoms...) are always non crystalline minerals. Other examples include copper, iron and gold deposits involving bacteria. Biologically formed minerals often have special uses such as magnetic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Upper Iowa River
The Upper Iowa River is a U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map, accessed May 13, 2011 tributary of the Mississippi River in the upper Midwest of the United States. Its headwaters rise in southeastern Minnesota, in Mower County, Minnesota, Mower County (Le Roy Township, Minnesota, Le Roy and Lodi Township, Minnesota, Lodi civil township, townships) near the border with Iowa. It then flows through the Iowa County (United States), counties of Howard County, Iowa, Howard, Winneshiek County, Iowa, Winneshiek, and Allamakee County, Iowa, Allamakee, and finally into the Upper Mississippi River near New Albin, Iowa. Along its course, it passes through the Iowa city, cities of Chester, Iowa, Chester, Lime Springs, Florenceville, Iowa, Florenceville, Kendallville, Iowa, Kendallville, Bluffton, and Decorah, Iowa, Decorah. Its watershed comprises nearly . The Upper Iowa and its tributaries are part of the Driftless Area of Iowa, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unconformity
An unconformity is a buried erosional or non-depositional surface separating two rock masses or strata of different ages, indicating that sediment deposition was not continuous. In general, the older layer was exposed to erosion for an interval of time before deposition of the younger layer, but the term is used to describe any break in the sedimentary geologic record. The significance of angular unconformity (see below) was shown by James Hutton, who found examples of Hutton's Unconformity at Jedburgh in 1787 and at Siccar Point in 1788. The rocks above an unconformity are younger than the rocks beneath (unless the sequence has been overturned). An unconformity represents time during which no sediments were preserved in a region or were subsequently eroded before the next deposition. The local record for that time interval is missing and geologists must use other clues to discover that part of the geologic history of that area. The interval of geologic time not represented is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shakopee Formation
The Knox Supergroup, also known as the Knox Group and the Knox Formation, is a widespread Group (geology), geologic group in the Southeastern United States. The age is from the Cambrian, Late Cambrian to the Ordovician, Early Ordovician. Predominantly, it is composed of Carbonate rock, carbonates, chiefly Dolomite (rock), dolomite, with some limestone. There are also cherty inclusions as well as thin beds of sandstone. Stratigraphy The Knox lies beneath a unconformity known as the Knox Unconformity. There is well-developed Karst, karst topography at the top of the Knox Supergroup. This demonstrates a prolonged period of erosion. This has modern economic impact because of forming reservoirs for hydrocarbons as well as some mineral deposits. Everton Formation The Everton Formation is a Formation (geology), geologic formation in northern Arkansas through Missouri, Illinois and Indiana that dates to the middle Ordovician Geological period, Period. It was named by Ulrich (1907) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbon
Carbon () is a chemical element with the symbol C and atomic number 6. It is nonmetallic and tetravalent In chemistry, the valence (US spelling) or valency (British spelling) of an element is the measure of its combining capacity with other atoms when it forms chemical compounds or molecules. Description The combining capacity, or affinity of an ...—its atom making four electrons available to form covalent bond, covalent chemical bonds. It belongs to group 14 of the periodic table. Carbon makes up only about 0.025 percent of Earth's crust. Three Isotopes of carbon, isotopes occur naturally, Carbon-12, C and Carbon-13, C being stable, while Carbon-14, C is a radionuclide, decaying with a half-life of about 5,730 years. Carbon is one of the Timeline of chemical element discoveries#Ancient discoveries, few elements known since antiquity. Carbon is the 15th Abundance of elements in Earth's crust, most abundant element in the Earth's crust, and the Abundance of the c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyrite
The mineral pyrite (), or iron pyrite, also known as fool's gold, is an iron sulfide with the chemical formula Iron, FeSulfur, S2 (iron (II) disulfide). Pyrite is the most abundant sulfide mineral. Pyrite's metallic Luster (mineralogy), luster and pale brass-yellow hue give it a superficial resemblance to gold, hence the well-known nickname of ''fool's gold''. The color has also led to the nicknames ''brass'', ''brazzle'', and ''Brazil'', primarily used to refer to pyrite found in coal. The name ''pyrite'' is derived from the Greek language, Greek (), 'stone or mineral which strikes fire', in turn from (), 'fire'. In ancient Roman times, this name was applied to several types of stone that would create sparks when struck against steel; Pliny the Elder described one of them as being brassy, almost certainly a reference to what we now call pyrite. By Georgius Agricola's time, , the term had become a generic term for all of the pyrite group, sulfide minerals. Pyrite is usua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |