|
William Moorcroft (explorer)
William Moorcroft (176727 August 1825) was an English veterinarian and explorer employed by the East India Company. Moorcroft travelled extensively throughout the Himalayas, Tibet and Central Asia, eventually reaching Bukhara, in present-day Uzbekistan. Early life and education Moorcroft was born in Ormskirk, Lancashire, the illegitimate son of Ann Moorcroft, daughter of a local farmer. He was baptised in 1767 in St Peter & St Paul, the Parish Church of Ormskirk, where there is a commemorative plaque to his life. His family had sufficient means to secure an apprenticeship with a surgeon in Liverpool but during this time an unknown disease decimated cattle herds in Lancashire and young William was recruited to treat stricken animals. His proficiency so impressed the county landowners they offered to underwrite his education if he would abandon surgery to attend a veterinarian college in Lyon, France. He arrived in France in the revolutionary year of 1789 and became the first Eng ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Moorcroft's Plaque In Shalimar Gardens, Lahore
William is a masculine given name of Norman French origin.Hanks, Hardcastle and Hodges, ''Oxford Dictionary of First Names'', Oxford University Press, 2nd edition, , p. 276. It became very popular in the English language after the Norman conquest of England in 1066,All Things William"Meaning & Origin of the Name"/ref> and remained so throughout the Middle Ages and into the modern era. It is sometimes abbreviated "Wm." Shortened familiar versions in English include Will, Wills, Willy, Willie, Liam, Bill, and Billy. A common Irish form is Liam. Scottish diminutives include Wull, Willie or Wullie (as in Oor Wullie or the play ''Douglas''). Female forms are Willa, Willemina, Wilma and Wilhelmina. Etymology William is related to the German given name ''Wilhelm''. Both ultimately descend from Proto-Germanic ''*Wiljahelmaz'', with a direct cognate also in the Old Norse name ''Vilhjalmr'' and a West Germanic borrowing into Medieval Latin ''Willelmus''. The Proto-Germanic name is a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mir Izzat-Allah
''Mir'' (russian: Мир, ; ) was a space station that operated in low Earth orbit from 1986 to 2001, operated by the Soviet Union and later by Russia. ''Mir'' was the first modular space station and was assembled in orbit from 1986 to 1996. It had a greater mass than any previous spacecraft. At the time it was the largest artificial satellite in orbit, succeeded by the International Space Station (ISS) after ''Mir'''s orbital decay, orbit decayed. The station served as a microgravity research laboratory in which crews conducted experiments in biology, human biology, physics, astronomy, meteorology, and spacecraft systems with a goal of developing technologies required for permanent occupation of Outer space, space. ''Mir'' was the first continuously inhabited long-term research station in orbit and held the record for the longest continuous human presence in space at 3,644 days, until it was surpassed by the ISS on 23 October 2010. It holds the record for the longes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gorkha Kingdom
Gorkha Kingdom ( ne, गोरखा राज्य) was a member of the Chaubisi rajya, a confederation of 24 states on the Indian subcontinent ruled by Khas people. In 1743 CE, the kingdom began a campaign of military expansion, annexing several neighbors to become present-day Nepal. The Gorkha Kingdom extended to the Marshyangdi River in the west, forming its border with the Kingdom of Lamjung. To the east, the kingdom extended to the Trishuli River The Trishuli River ( ne, त्रिशूली नदी) is one of the major tributaries of the Narayani River basin in central Nepal. It originates in Tibet as a stream and enters Nepal at Gyirong Town. Etymology The Trishuli is named after ..., forming its border with the Nepal Mandala. The Gorkha Kingdom was established in 1559 CE by Prince Dravya Shah, second son of King Yasho Brahma Shah of Kingdom of Lamjung, Lamjung. The prince replaced the Khadka chiefs who previously ruled the region. Origin According to legen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sutlej
The Sutlej or Satluj River () is the longest of the five rivers that flow through the historic crossroads region of Punjab in northern India and Pakistan. The Sutlej River is also known as ''Satadru''. It is the easternmost tributary of the Indus River. The Bhakra Dam is built around the river Sutlej to provide irrigation and other facilities to the states of Punjab, Rajasthan and Haryana. The waters of the Sutlej are allocated to India under the Indus Waters Treaty between India and Pakistan, and are mostly diverted to irrigation canals in India like the Sirhind Canal, Bhakra Main Line and the Rajasthan canal. The mean annual flow is 14 million acre feet (MAF) upstream of Ropar barrage, downstream of the Bhakra dam. It has several major hydroelectric points, including the 1,325 MW Bhakra Dam, the 1,000 MW Karcham Wangtoo Hydroelectric Plant, and the 1,500 MW Nathpa Jhakri Dam. The drainage basin in India includes the states and union territories of Himachal Pra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indus
The Indus ( ) is a transboundary river of Asia and a trans-Himalayan river of South and Central Asia. The river rises in mountain springs northeast of Mount Kailash in Western Tibet, flows northwest through the disputed region of Kashmir, Quote: "Kashmir, region of the northwestern Indian subcontinent. It is bounded by the Uygur Autonomous Region of Xinjiang to the northeast and the Tibet Autonomous Region to the east (both parts of China), by the Indian states of Himachal Pradesh and Punjab to the south, by Pakistan to the west, and by Afghanistan to the northwest. The northern and western portions are administered by Pakistan and comprise three areas: Azad Kashmir, Gilgit, and Baltistan, ... The southern and southeastern portions constitute the Indian state of Jammu and Kashmir. The Indian- and Pakistani-administered portions are divided by a "line of control" agreed to in 1972, although neither country recognizes it as an international boundary. In addition, China became ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lake Manasarovar
Lake Manasarovar (Sanskrit: मानसरोवर), also called Mapam Yutso (;) locally, is a high altitude freshwater lake fed by the Kailash Glaciers near Mount Kailash in Burang County, Ngari Prefecture, Tibet Autonomous Region, China. The lake along with Mount Kailash to its north are sacred sites in four religions: Bön, Buddhism, Hinduism and Jainism. Etymology The Sanskrit word "''Manasarovar''" (मानसरोवर) is a combination of two Sanskrit words; "''Mānas''" (मानस्) meaning "mind (in its widest sense as applied to all the mental powers), intellect, intelligence, understanding, perception, sense, conscience''" while "''sarovara''" (सरोवर) means "''a lake or a large pond deep enough for a lotus''". Geography It is located about 50 kilometers to the northwest of Nepal, about 100 kilometers east of Uttarakhand, and in the southwest region of Tibet. The lake lies at above mean sea level, a relatively high elevation for a large freshw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cashmere Wool
Cashmere wool, usually simply known as cashmere, is a fiber obtained from cashmere goats, pashmina goats, and some other breeds of goat. It has been used to make yarn, textiles and clothing for hundreds of years. Cashmere is closely associated with the Kashmir shawl, the word "cashmere" deriving from an anglicisation of ''Kashmir'', when the Kashmir shawl reached Europe in the 19th century. Both the soft undercoat and the guard hairs may be used; the softer hair is reserved for textiles, while the coarse guard hair is used for brushes and other non-apparel purposes. A number of countries produce cashmere and have improved processing techniques over the years but China and Mongolia are two of the leading producers as of 2019. Afghanistan is ranked third. Some yarns and clothing marketed as containing cashmere have been found to contain little to no cashmere fiber, so more stringent testing has been requested to make sure items are fairly represented. Poor land management and o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pashmina (material)
Pashmina (, ) refers to, depending on the source, a term for cashmere wool of the Changthangi cashmere goat,Janet Rizvi: ''Pashmina: The Kashmir Shawl and Beyond''. Marg Foundation, 2009. ISBN 978-8185026909. for fine Indian cashmere woolRobert R. Franck: ''Silk, Mohair, Cashmere and Other Luxury Fibres''. Volume 19 of ''Woodhead Publishing Series in Textiles'', Elsevier Science, 2001. ISBN 978-1855735408. p. 142. or a synonym for cashmere wool. The word ''pashm'' means "wool" in Persian, but in Kashmir, ''pashm'' referred to the raw unspun wool of domesticated Changthangi goats. In common parlance today, ''pashmina'' may refer either to the material or to the variant of the Kashmir shawl that is made from it. Both cashmere and pashmina come from the same goat but typical cashmere ranges from 12 to 21 microns in diameter, whereas ''pashmina'' can also refer to a cashmere and silk blend (70 % / 30 %) that has a typical fiber range from 12 to 16 microns. History Samples of wool fi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gartok
Gartok (), is made of twin encampment settlements of Gar Günsa and Gar Yarsa (, Wade–Giles: ''Ka-erh-ya-sha'') in the Gar County in the Ngari Prefecture of Tibet. Gar Gunsa served as the winter encampment and Gar Yarsa as the summer encampment. But in British nomenclature, the name Gartok was applied only to Gar Yarsa and the practice continues till date. Gartok was established as Lhasa's administrative headquarters for Western Tibet ( Ngari) after it conquered it from Ladakh in 1684. A senior official called Garpön was stationed here. Gartok (Gar Yarsa) also served as Western Tibet's principal trade-market. But the village itself was small and said to have been quite poor. After the Chinese annexation of Tibet, the headquarters of Western Tibet was moved to Shiquanhe. Gar Yarsa is situated on the bank of the Gartang River, one of the headwaters of the Indus River, at the base of the Kailash Range, at an elevation of . Name Gar () means "encampment". During the 15th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
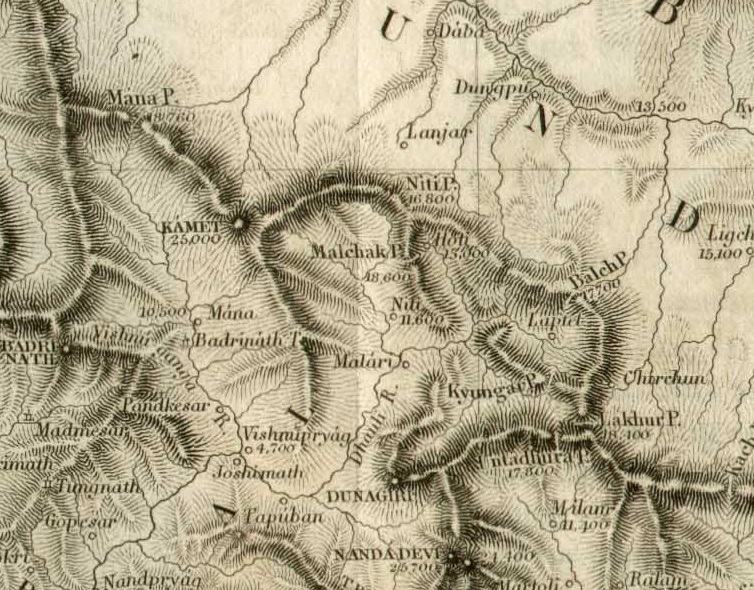
Daba, Tibet
Daba (; ) or Danbab () is a township under the administration of Zanda County in the Tibet region of China, centred at the Daba village. Geography The Daba village is on the bank of the Daba Chu river, a tributary of the Sutlej River. The township of Daba spans both the banks of the Sutlej river, up to the Burang County and the Manasarovar region. It stretches to the south until the Indian border. Daba village and township are close to the Indian border. On the Indian side of the border are Garhwal and Kumaon regions of India's Uttarakhand state. The Niti Pass and the have served as the main historical trade routes. Since 1954, China has disputed the Indian control over the Barahoti region along the border. , the Daba township has two other villages in addition to Daba: * Dongbo Village (, ) * Kyunglung Village (, ) History In the mid-19th century, Henry Strachey mentioned that Daba Dzong was one of the two dzongs in the Guge region of Ngari, the other being Tsaparang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dhauliganga River
The Dhauliganga is a turbulent Himalayan river which rises in the border regions of India and China and flows south into the Garhwal region of Uttarakhand, India. It joins the Alaknanda, the major source stream of the Ganges river. Course Dhauliganga rises in the vicinity of the Niti Pass in the border regions between Garhwal and southwestern Tibet. It flows southwards until it meets the Rishiganga on its left bank at Rini, in the vicinity of Tapovan in Chamoli district. It then flows westwards until it meets the Alaknanda at Vishnuprayag and terminates—the confluence just upstream of the city of Joshimath. The upper Dhauliganga valley parts the East-West Himalayan axis, with Nanda Devi and its subsidiary peaks to its left and Kamet and its subsidiary peaks to its right. Nanda Devi glacier flood On 7 February 2021 a part of Nanda Devi Glacier, a Himalayan glacier in the Nanda Devi National Park, broke away and caused water levels in the Rishiganga and Dh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |