|
William Duncan Strong
William Duncan Strong (1899–1962) was an American archaeologist and anthropologist noted for his application of the direct historical approach to the study of indigenous peoples of North and South America. Early life and education Strong was born in Portland, Oregon. He initially studied zoology, but he changed his focus to anthropology at the University of California, Berkeley, under the influence of Alfred L. Kroeber, who became his "principal teacher, mentor, and friend". Strong completed his doctorate in 1926. Career Strong's doctoral dissertation, "An Analysis of Southwestern Society", was published in ''American Anthropologist''. A related study of his, ''Aboriginal Society in Southern California'', presenting his detailed fieldwork among the Serrano, Luiseño, Cupeño, and Cahuilla peoples, has been characterized as "one of the earliest and one of the best efforts by a United States anthropologist to combine structural-functional analysis with historical data and inte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaeologist
Archaeology or archeology is the scientific study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeological record consists of artifacts, architecture, biofacts or ecofacts, sites, and cultural landscapes. Archaeology can be considered both a social science and a branch of the humanities. It is usually considered an independent academic discipline, but may also be classified as part of anthropology (in North America – the four-field approach), history or geography. Archaeologists study human prehistory and history, from the development of the first stone tools at Lomekwi in East Africa 3.3 million years ago up until recent decades. Archaeology is distinct from palaeontology, which is the study of fossil remains. Archaeology is particularly important for learning about prehistoric societies, for which, by definition, there are no written records. Prehistory includes over 99% of the human past, from the Paleolithic until the adve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Waldo Rudolph Wedel
Waldo Rudolph Wedel (September 10, 1908 – August 27, 1996) was an American archaeologist and a central figure in the study of the prehistory of the Great Plains. He was born in Newton, Kansas to a family of Mennonites. In 1939 he married Mildred Mott, a fellow archaeologist and ethnohistorian. Wedel died in 1996 in Boulder, Colorado, about one year after Mildred's death. Education Wedel began studying at Bethel College in Newton, Kansas. In 1928, he transferred to the University of Arizona to study under archaeologist Byron Cummings and visiting professor William Morris Davis. In 1930 he received his BA from the University of Arizona. He then transferred to the University of Nebraska for a M.A. degree and studied under William Duncan Strong. In 1931 Wedel received his M.A. degree. His thesis utilized Strong's direct historical approach to studying Pawnee archaeological materials. During the next four field seasons he was involved with excavations under the Unive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ai Apaec
Ai apaec (from the Mochica Aiapæc [a.ja.pøk] or [aiapøk]), was the chief deity of the Moche (culture), Mochica culture. The most feared and adored of all punitive gods, it was also referred to as the “headsman”. Ai Apaec was worshipped as the creator god, protector of the Moche, a provider of water, food and military triumphs. Aiapaec means 'maker' in the Moche (culture), Mochica language. Representations The most common representation of Ai Apaec is the one seen in the murals of the Temples of the Sun and the Moon, which present an anthropomorphic face with feline fangs, surrounded by ocean waves. Ai apaec was represented in several ways, depending on the period, place, and medium used. In metallurgy, for example, Ai apaec is often seen as a spider with eight legs and an anthropomorphic face with jaguar fangs. In ceramics the divinity is often more anthropomorphic, usually with his head in his hands and sometimes with two snakes sprouting from his head. In sculpture ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pottery
Pottery is the process and the products of forming vessels and other objects with clay and other ceramic materials, which are fired at high temperatures to give them a hard and durable form. Major types include earthenware, stoneware and porcelain. The place where such wares are made by a ''potter'' is also called a ''pottery'' (plural "potteries"). The definition of ''pottery'', used by the ASTM International, is "all fired ceramic wares that contain clay when formed, except technical, structural, and refractory products". In art history and archaeology, especially of ancient and prehistoric periods, "pottery" often means vessels only, and sculpted figurines of the same material are called "terracottas". Pottery is one of the oldest human inventions, originating before the Neolithic period, with ceramic objects like the Gravettian culture Venus of Dolní Věstonice figurine discovered in the Czech Republic dating back to 29,000–25,000 BC, and pottery vessels that were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seriation (archaeology)
In archaeology, seriation is a relative dating method in which assemblages or artifacts from numerous sites in the same culture are placed in chronological order. Where absolute dating methods, such as radio carbon, cannot be applied, archaeologists have to use relative dating methods to date archaeological finds and features. Seriation is a standard method of dating in archaeology. It can be used to date stone tools, pottery fragments, and other artifacts. In Europe, it has been used frequently to reconstruct the chronological sequence of graves in a cemetery (e.g. Jørgensen 1992; Müssemeier, Nieveler et al. 2003). Contextual and frequency seriation Two different variants of seriation have been applied: contextual seriation and frequency seriation (Renfrew and Bahn 1996, pp. 116–117). Whereas contextual seriation is based on the presence or absence of a design style, frequency seriation relies on measuring the proportional abundance or frequency of a design sty ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peru
, image_flag = Flag of Peru.svg , image_coat = Escudo nacional del Perú.svg , other_symbol = Great Seal of the State , other_symbol_type = Seal (emblem), National seal , national_motto = "Firm and Happy for the Union" , national_anthem = "National Anthem of Peru" , march = "March of Flags" , image_map = PER orthographic.svg , map_caption = , image_map2 = , capital = Lima , coordinates = , largest_city = capital , official_languages = Peruvian Spanish, Spanish , languages_type = Co-official languages , languages = , ethnic_groups = , ethnic_groups_year = 2017 , demonym = Peruvians, Peruvian , government_type = Unitary state, Unitary Semi-presidential system, semi-presidential republic , leader_title1 = President of Peru, President ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
La Ciudad Blanca
La Ciudad Blanca (, Spanish for "The White City") is a legendary settlement said to be located in the Mosquitia region of the Gracias a Dios Department in eastern Honduras. It is also known by the Pech name Kahã Kamasa ("White Town"). This extensive area of rainforest, which includes the Río Plátano Biosphere Reserve, has long been the subject of multidisciplinary research. Archaeologists refer to it as being a part of the Isthmo-Colombian Area of the Americas, one in which the predominant indigenous languages have included those in the Chibchan and Misumalpan families. Due to the many variants of the story in the region, most professional archaeologists doubt that it refers to any one actual settlement, much less one representing a city of the Pre-Columbian era. They point out that there are multiple large archaeological sites in the region and that references to the legendary White City cannot be proven to refer to any single place. Spanish conquistador Hernán Cortés re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Honduras
Honduras, officially the Republic of Honduras, is a country in Central America. The republic of Honduras is bordered to the west by Guatemala, to the southwest by El Salvador, to the southeast by Nicaragua, to the south by the Pacific Ocean at the Gulf of Fonseca, and to the north by the Gulf of Honduras, a large inlet of the Caribbean Sea. Its capital and largest city is Tegucigalpa. Honduras was home to several important Mesoamerican cultures, most notably the Maya, before the Spanish Colonization in the sixteenth century. The Spanish introduced Catholicism and the now predominant Spanish language, along with numerous customs that have blended with the indigenous culture. Honduras became independent in 1821 and has since been a republic, although it has consistently endured much social strife and political instability, and remains one of the poorest countries in the Western Hemisphere. In 1960, the northern part of what was the Mosquito Coast was transferred from Nicara ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pacific Northwest
The Pacific Northwest (sometimes Cascadia, or simply abbreviated as PNW) is a geographic region in western North America bounded by its coastal waters of the Pacific Ocean to the west and, loosely, by the Rocky Mountains to the east. Though no official boundary exists, the most common conception includes the U.S. states of Oregon, Washington (state), Washington, and Idaho, and the Canadian province of British Columbia. Some broader conceptions reach north into Alaska and Yukon, south into northern California, and east into western Montana. Other conceptions may be limited to the coastal areas west of the Cascade Mountains, Cascade and Coast Mountains, Coast mountains. The variety of definitions can be attributed to partially overlapping commonalities of the region's history, culture, geography, society, ecosystems, and other factors. The Northwest Coast is the coastal region of the Pacific Northwest, and the Northwest Plateau (also commonly known as "British Columbia Interi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
San Joaquin Valley
The San Joaquin Valley ( ; es, Valle de San Joaquín) is the area of the Central Valley of the U.S. state of California that lies south of the Sacramento–San Joaquin River Delta and is drained by the San Joaquin River. It comprises seven counties of Northern and one of Southern California, including, in the north, all of San Joaquin and Kings counties, most of Stanislaus, Merced, and Fresno counties, and parts of Madera and Tulare counties, along with a majority of Kern County, in Southern California. Although the valley is predominantly rural, it has densely populated urban centers: Fresno, Bakersfield, Stockton, Modesto, Tulare, Visalia, Hanford, and Merced. The first European to enter the valley was Pedro Fages in 1772. The San Joaquin Valley was originally inhabited by the Yokuts and Miwok peoples. The Tejon Indian Tribe of California is a federally recognized tribe of Kitanemuk, Yokuts, and Chumash indigenous people of California. Their ancestral homeland ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dismal River (Nebraska)
The Dismal River is a winding U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map , accessed March 30, 2011 river in the state of Nebraska. It is formed by the confluence of two forks, one of which has its origins in Grant County and the other in Hooker County. The forks meet near Nebraska Highway 97 between Mullen and Tryon. From here the Dismal River flows east-southeast into Thomas County, crossing U.S. Highway 83 south of Thedford. Passing just south of the Nebraska National Forest (once the Dismal River National Forest), it turns slightly to the northeast before its confluence with the Middle Loup River just East of Dunning in Blaine County. Most of the land along the river is privately owned and used for ranching. The water comes from the Ogallala Aquifer and boils up beneath the river in places, sometimes creating areas of quicksand Quicksand is a colloid consisting of fine granular material (such as sand, silt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
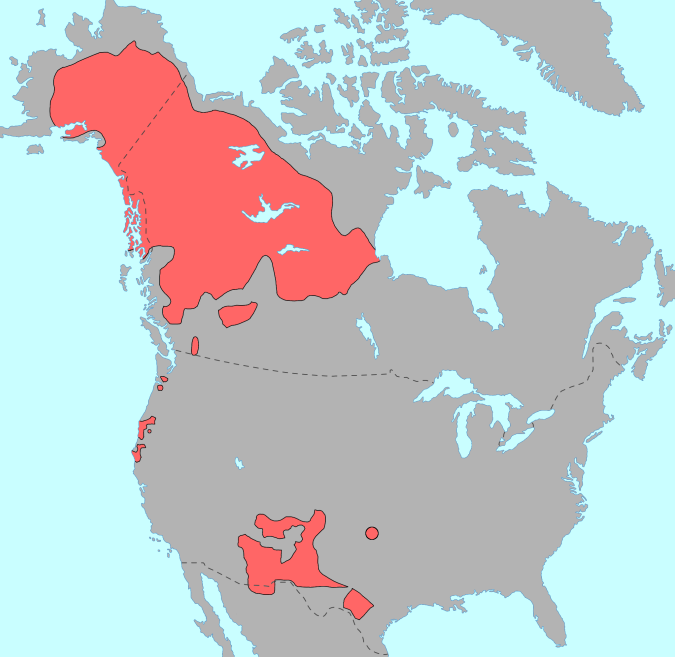
Dismal River Culture
The Dismal River culture refers to a set of cultural attributes first seen in the Dismal River area of Nebraska in the 1930s by archaeologists William Duncan Strong, Waldo Rudolph Wedel and A. T. Hill. Also known as Dismal River aspect and Dismal River complex, dated between 1650-1750 A.D., is different from other prehistoric Central Plains and Woodland traditions of the western Plains. The Dismal River people are believed to have spoken an Athabascan language and to have been part of the people later known to Europeans as Apaches.Gibbon, Guy E.; Ames, Kenneth M. (1998''Archaeology of Prehistoric Native America: An Encyclopedia''.p. 212. .Gibbon, Guy E.; Ames, Kenneth M. (1998''Archaeology of Prehistoric Native America: An Encyclopedia''.pp. 213, 768. . Western Plains Dismal River culture sites have been found in Nebraska, Kansas, Colorado and South Dakota. 18 sites were located in Hayes, Hooker, Cherry, Thomas and Lincoln counties in the Sand Hills of Nebraska. Notable ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)