|
White Horse (mythology)
White horses have a special significance in the mythologies of cultures around the world. They are often associated with the sun chariot,''The Complete Dictionary of Symbols'' by Jack Tresidder, Chronicle Books, 2005, , page 241Google books copy/ref> with warrior-heroes, with fertility (in both mare and stallion manifestations), or with an end-of-time saviour, but other interpretations exist as well. Both truly white horses and the more common grey horses, with completely white hair coats, were identified as "white" by various religious and cultural traditions. Portrayal in myth From earliest times, white horses have been mythologised as possessing exceptional properties, transcending the normal world by having wings (e.g. Pegasus from Greek mythology), or having horns (the unicorn). As part of its legendary dimension, the white horse in myth may be depicted with seven heads ( Uchaishravas) or eight feet (Sleipnir), sometimes in groups or singly. There are also white horse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
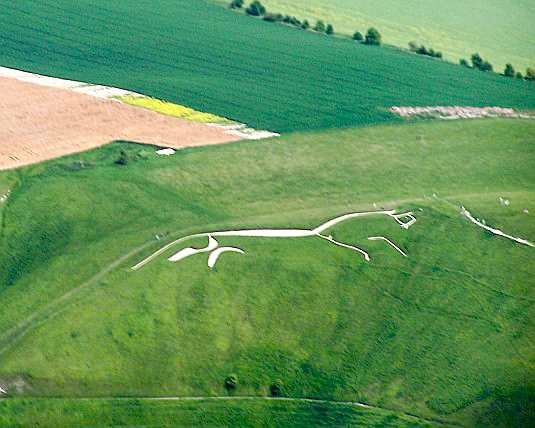
White Horse From Air
White is the lightest color and is achromatic (having no hue). It is the color of objects such as snow, chalk, and milk, and is the opposite of black. White objects fully reflect and scatter all the visible wavelengths of light. White on television and computer screens is created by a mixture of red, blue, and green light. The color white can be given with white pigments, especially titanium dioxide. In ancient Egypt and ancient Rome, priestesses wore white as a symbol of purity, and Romans wore white togas as symbols of citizenship. In the Middle Ages and Renaissance a white unicorn symbolized chastity, and a white lamb sacrifice and purity. It was the royal color of the kings of France, and of the monarchist movement that opposed the Bolsheviks during the Russian Civil War (1917–1922). Greek and Roman temples were faced with white marble, and beginning in the 18th century, with the advent of neoclassical architecture, white became the most common color of new churches ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Patron Saints
A patron saint, patroness saint, patron hallow or heavenly protector is a saint who in Catholicism, Anglicanism, or Eastern Orthodoxy is regarded as the heavenly advocate of a nation, place, craft, activity, class, clan, family, or person. In Christianity Saints often become the patrons of places where they were born or had been active. However, there were cases in Medieval Europe where a city which grew to prominence and obtained for its cathedral the remains or some relics of a famous saint who had lived and was buried elsewhere, thus making them the city's patron saint – such a practice conferred considerable prestige on the city concerned. In Latin America and the Philippines, Spanish and Portuguese explorers often named a location for the saint on whose feast or commemoration day they first visited the place, with that saint naturally becoming the area's patron. Occupations sometimes have a patron saint who had been connected somewhat with it, although some of the con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Loch Neagh
Lough Neagh ( ) is a freshwater lake in Northern Ireland and is the largest lake in the island of Ireland, the United Kingdom and the British Isles. It has a surface area of and supplies 40% of Northern Ireland's water. Its main inflows come from the Upper River Bann and River Blackwater, and its main outflow is the Lower River Bann. Its name comes from Irish , meaning " Eachaidh's lake".Deirdre Flanagan and Laurance Flanagan, Irish Placenames, (Gill & Macmillan Ltd, 1994) The lough is owned by the Earl of Shaftesbury and managed by Lough Neagh Partnership Ltd. Geography With an area of , it is the British Isles' largest lake by area and is ranked 33rd in the list of largest lakes of Europe. Located west of Belfast, it is about long and wide. It is very shallow around the margins and the average depth in the main body of the lake is about , although at its deepest the lough is about deep. Geology Geologically the Lough Neagh Basin is a depression, built from many tecto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Irish Language
Irish ( Standard Irish: ), also known as Gaelic, is a Goidelic language of the Insular Celtic branch of the Celtic language family, which is a part of the Indo-European language family. Irish is indigenous to the island of Ireland and was the population's first language until the 19th century, when English gradually became dominant, particularly in the last decades of the century. Irish is still spoken as a first language in a small number of areas of certain counties such as Cork, Donegal, Galway, and Kerry, as well as smaller areas of counties Mayo, Meath, and Waterford. It is also spoken by a larger group of habitual but non-traditional speakers, mostly in urban areas where the majority are second-language speakers. Daily users in Ireland outside the education system number around 73,000 (1.5%), and the total number of persons (aged 3 and over) who claimed they could speak Irish in April 2016 was 1,761,420, representing 39.8% of respondents. For most of recorded ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Dagda
The Dagda (Old Irish: ''In Dagda,'' ga, An Daghdha, ) is an important god in Irish mythology. One of the Tuatha Dé Danann, the Dagda is portrayed as a father-figure, king, and druid.Koch, John T. ''Celtic Culture: A Historical Encyclopedia''. ABC-CLIO, 2006. pp. 553–54 An Dagda Mary Jones's Celtic Encyclopedia. He is associated with , , manliness and strength, as well as magic, druidry and wisdom.Ó hÓgáin, Dáithí. ''Myth, Legend & Romance: An encyclopaedia of the Irish folk t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Donn
In Irish mythology, Donn ("the dark one", from cel-x-proto, Dhuosnos) is an ancestor of the Gaels and is believed to have been a god of the dead. Donn is said to dwell in Tech Duinn (the "house of Donn" or "house of the dark one"), where the souls of the dead gather. He may have originally been an aspect of the Dagda. Folklore about Donn survived into the modern era in parts of Ireland, in which he is said to be a phantom horseman riding a white horse. Early literary sources A 9th-century poem says that Donn's dying wish was that all his descendants would gather at Donn's house or ''Tech Duinn'' (modern Irish ''Teach Duinn'') after death: "To me, to my house, you shall all come after your deaths". The 10th-century tale ''Airne Fíngein'' ("Fíngen's Vigil") says that Tech Duinn is where the souls of the dead gather. In their translation of ''Acallam na Senórach'', Ann Dooley and Harry Roe commented that "to go to the House of Donn in Irish tradition means to die". This suggest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ann Hyland
Ann Hyland is a writer and historian who specialises in equestrianism and the development of horses. She is also a consultant for the Oxford English Dictionary The ''Oxford English Dictionary'' (''OED'') is the first and foundational historical dictionary of the English language, published by Oxford University Press (OUP). It traces the historical development of the English language, providing a co ....StaffConsultants, advisers, and contributors Oxford English Dictionary Ann Hyland trains horses as well as being a freelance lecturer on equestrian topics.StaffAbout Ann Hyland Greenwood Publishing Select bibliography * ''Beginner's Guide to Western Riding'' (1971)World CatBooks by Ann Hyland World Cat * ''Foal to Five Years'' (1980) * ''The Endurance Horse'' (1988) * ''Riding Long Distance'' (1988) * ''Equus: The Horse in the Roman World'' (1990) * ''The Appaloosa'' (1990) * ''Training the Roman Cavalry'' (1993) * ''The Medieval Warhorse: From Byzantium to the Crusades' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epona
In Gallo-Roman religion, Epona was a protector of horses, ponies, donkeys, and mules. She was particularly a goddess of fertility, as shown by her attributes of a patera, cornucopia, ears of grain and the presence of foals in some sculptures. She and her horses might also have been leaders of the soul in the after-life ride, with parallels in Rhiannon of the Mabinogion. The worship of Epona, "the sole Celtic divinity ultimately worshipped in Rome itself", as the patroness of cavalry, was widespread in the Roman Empire between the first and third centuries AD; this is unusual for a Celtic deity, most of whom were associated with specific localities. Etymology Although known only from Roman contexts, the name Epona ('Great Mare') is from the Gaulish language; it is derived from the inferred Proto-Celtic *''ekʷos'' 'horse', which gives rise to modern Welsh ''ebol'' 'foal', together with the augmentative suffix ''-on'' frequently, though not exclusively, found in theonyms (for exa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mabinogion
The ''Mabinogion'' () are the earliest Welsh prose stories, and belong to the Matter of Britain. The stories were compiled in Middle Welsh in the 12th–13th centuries from earlier oral traditions. There are two main source manuscripts, created c. 1350–1410, as well as a few earlier fragments. The title covers a collection of eleven prose stories of widely different types, offering drama, philosophy, romance, tragedy, fantasy and humour, and created by various narrators over time. There is a classic hero quest, "Culhwch and Olwen"; a historic legend in "Lludd and Llefelys," complete with glimpses of a far off age; and other tales portray a very different King Arthur from the later popular versions. The highly sophisticated complexity of the Four Branches of the Mabinogi defies categorisation. The stories are so diverse that it has been argued that they are not even a true collection. Scholars from the 18th century to the 1970s predominantly viewed the tales as fragmentary p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhiannon
Rhiannon is a major figure in the Mabinogi, the medieval Welsh story collection. She appears mainly in the First Branch of the Mabinogi, and again in the Third Branch. She is a strong-minded Otherworld woman, who chooses Pwyll, prince of Dyfed (west Wales), as her consort, in preference to another man to whom she has already been betrothed. She is intelligent, politically strategic, beautiful, and famed for her wealth and generosity. With Pwyll she has a son, the hero Pryderi, who later inherits the lordship of Dyfed. She endures tragedy when her newborn child is abducted, and she is accused of infanticide. As a widow she marries Manawydan of the British royal family, and has further adventures involving enchantments. Like some other figures of British/Welsh literary tradition, Rhiannon may be a reflection of an earlier Celtic deity. Her name appears to derive from the reconstructed Brittonic form *''Rīgantonā'', a derivative of *''rīgan-'' "queen". In the First Branch of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Welsh Mythology
Welsh mythology (Welsh: ''Mytholeg Cymru'') consists of both folk traditions developed in Wales, and traditions developed by the Celtic Britons elsewhere before the end of the first millennium. As in most of the predominantly oral societies Celtic mythology and history were recorded orally by specialists such as druids ( cy, derwyddon). This oral record has been lost or altered as a result of outside contact and invasion over the years. Much of this altered mythology and history is preserved in medieval Welsh manuscripts, which include the Red Book of Hergest, the White Book of Rhydderch, the Book of Aneirin and the Book of Taliesin. Other works connected to Welsh mythology include the ninth-century Latin historical compilation ''Historia Brittonum'' ("History of the Britons") and Geoffrey of Monmouth's twelfth-century Latin chronicle ''Historia Regum Britanniae'' ("History of the Kings of Britain"), as well as later folklore, such as the materials collected in ''The Welsh Fa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
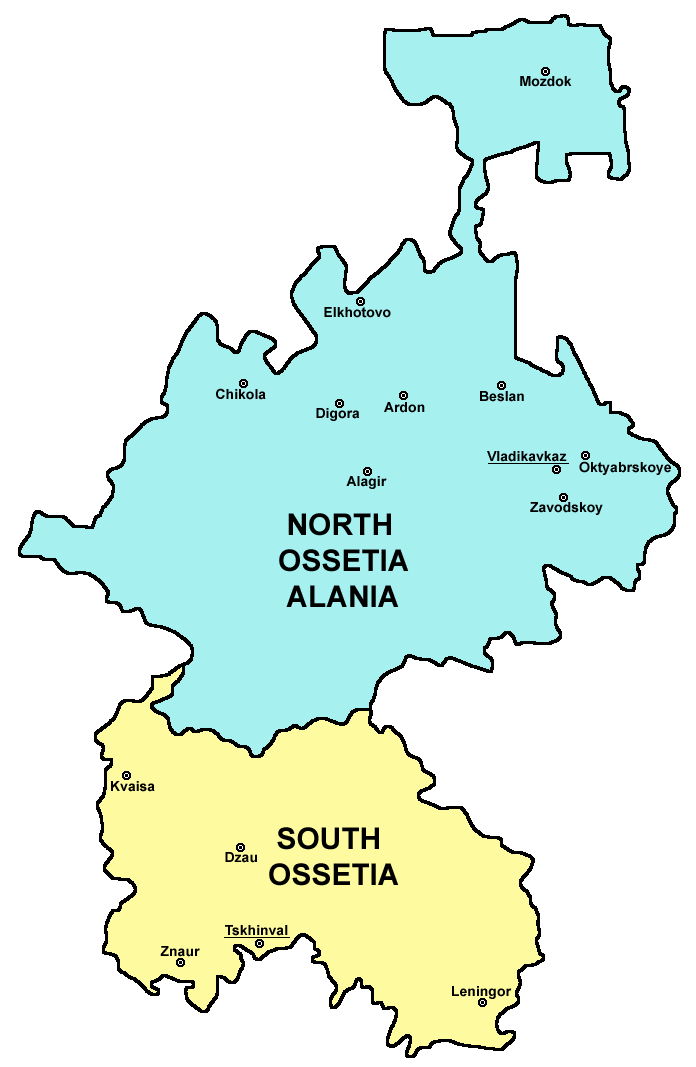
Ossetia
Ossetia ( , ; os, Ирыстон or , or ; russian: Осетия, Osetiya; ka, ოსეთი, translit. ''Oseti'') is an ethnolinguistic region located on both sides of the Greater Caucasus Mountains, largely inhabited by the Ossetians. The Ossetian language is part of the Eastern Iranian branch of the family of Indo-European languages. Most countries recognize the Ossetian-speaking area south of the main Caucasus ridge as lying within the borders of Georgia, but it has come under the control of the ''de facto'' government of the Russian-backed Republic of South Ossetia – the State of Alania. The northern portion of the region consists of the Republic of North Ossetia-Alania within the Russian Federation. Recent history * 1774 — North Ossetia becomes part of the Russian Empire. * 1922 — Creation of the South Ossetian autonomous oblast. North Ossetia remains a part of Russian SFSR, South Ossetia remains a part of Georgian SSR. * 20 September 1990 — South Osse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |






%2C_The_Bull_-_geograph.org.uk_-_284005.jpg)