|
White Huns
The "White Huns", also known as the White Hunas, in Iranian as the ''Spet Xyon'' and in Sanskrit as the ''Sveta-huna'', were a sub-group of the Huna and/or Xionites. The White Huns are sometimes regarded as synonymous with the Hephthalites, but may have included other tribes as well. They are well known for their conquest and occupation of North India, particularly the Punjab region. History The "White Huns," or Hephthalites, were reported by Byzantine, Indian, Chinese, Arab-Persian, Armenian and other written sources. Despite the abundance of information, a number of questions of the history of the states created by the Hephthalites are considered by scientists from different and often opposite points of view. Well-informed authors of Chinese chronicles call the regions of East Turkestan (Turfan) the homeland of the Hephthalites. According to this information, the eftalnts were driven out of there as a result of clashes with the neighboring tribes of the Juan-Juan. Hephthalites ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iranian Languages
The Iranian languages or Iranic languages are a branch of the Indo-Iranian languages in the Indo-European language family that are spoken natively by the Iranian peoples, predominantly in the Iranian Plateau. The Iranian languages are grouped in three stages: Old Iranian (until 400 BCE), Middle Iranian (400 BCE–900 CE) and New Iranian (since 900 CE). The two directly-attested Old Iranian languages are Old Persian (from the Achaemenid Empire) and Old Avestan (the language of the Avesta). Of the Middle Iranian languages, the better understood and recorded ones are Middle Persian (from the Sasanian Empire), Parthian (from the Parthian Empire), and Bactrian (from the Kushan and Hephthalite empires). , there were an estimated 150–200 million native speakers of the Iranian languages. '' Ethnologue'' estimates that there are 86 languages in the group, with the largest among them being Persian (Farsi, Dari, and Tajik dialects), Pashto, Kurdish, Luri, and Balochi. Terminol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cadusii
The Cadusii (also called Cadusians; grc, Καδούσιοι, ''Kadoúsioi''; Latin: ''Cadusii'') were an ancient Iranian tribe that lived in the mountains between Media and the shore of the Caspian Sea. The area that the Cadusii lived in bordered that of the Anariacae and Albani. The Dareitai and Pantimati people may have been part of the Cadusii. According to tradition, the legendary Assyrian king Ninus subdued the Cadusii. The Greek physician and historian Ctesias () was highly interested in the Cadusii, incorporating them in his invented history of an early Median dynasty. The Cadusii later voluntarily submitted to Cyrus the Great (), the first ruler of the Achaemenid Empire (550 BC–330 BC). According to Xenophon, as Cyrus was about to pass away, he appointed his younger son Tanaoxares (Bardiya) as satrap over the Medes, Armenians, and Cadusii. The Cadusii were most likely part of the satrapy of Media, and perhaps occasionally that of Hyrcania. Although they fought on side o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ghazar Parpetsi
Ghazar Parpetsi ( hy, Ղազար Փարպեցի, translit=Łazar P῾arpec῾i) was a 5th to 6th century Armenian chronicler and historian. He had close ties with the powerful Mamikonian noble family and is most prominent for writing a history of Armenia, ''History of Armenia'', sometime in the early sixth century. Life Ghazar was born in the village of Parpi (near the town of Ashtarak in Armenia, then under Sasanian rule), and was raised by a princess of the Mamikonian family. Melik-Bakhshyan, Stepan. ''«Ղազար Փարպեցի»'' (Ghazar Parpetsi). Soviet Armenian Encyclopedia. vol. vii. Yerevan: Armenian Academy of Sciences, 1981, pp. 19–20. Owing to the close ties he held with the Mamikonian family, following the defeat of the Armenians at the battle of Avarayr in 451, Ghazar moved to the Mamikonian Prince Ashusah's castle in Gugark, where he received his primary education. Studying under the auspices of Aghan Artstruni, he befriended Vahan Mamikonian; he was an excellent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ferdowsi
Abul-Qâsem Ferdowsi Tusi ( fa, ; 940 – 1019/1025 CE), also Firdawsi or Ferdowsi (), was a Persians, Persian poet and the author of ''Shahnameh'' ("Book of Kings"), which is one of the world's longest epic poetry, epic poems created by a single poet, and the greatest epic of Persian-speaking people, Persian-speaking countries. Ferdowsi is celebrated as one of the most influential figures of Persian literature and one of the greatest in the history of literature. Name Except for his kunya (Arabic), kunya ( – ) and his laqab ( – ''Ferdowsī'', meaning 'Paradise, paradisic'), nothing is known with any certainty about his full name. From an early period on, he has been referred to by different additional names and titles, the most common one being / ("philosopher"). Based on this, his full name is given in Persian language, Persian sources as / . Due to the non-standardized transliteration from Persian alphabet, Persian into English language, English, different spellings ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Al-Masudi
Al-Mas'udi ( ar, أَبُو ٱلْحَسَن عَلِيّ ٱبْن ٱلْحُسَيْن ٱبْن عَلِيّ ٱلْمَسْعُودِيّ, '; –956) was an Arab historian, geographer and traveler. He is sometimes referred to as the "Herodotus of the Arabs". A polymath and prolific author of over twenty works on theology, history (Islamic and universal), geography, natural science and philosophy, his celebrated magnum opus '' Murūj al-Dhahab wa-Ma'ādin al-Jawhar'' ( ar, مُرُوج ٱلذَّهَب وَمَعَادِن ٱلْجَوْهَر, link=no), combines universal history with scientific geography, social commentary and biography, and is published in English in a multi-volume series as '' The Meadows of Gold and Mines of Gems''. Birth, travels and literary output Apart from what Al-Mas'udi writes of himself little is known. Born in Baghdad, he was descended from Abdullah Ibn Mas'ud, a companion of Muhammad. He mentions many scholar associates met on his travels thr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Al-Tabari
( ar, أبو جعفر محمد بن جرير بن يزيد الطبري), more commonly known as al-Ṭabarī (), was a Muslim historian and scholar from Amol, Tabaristan. Among the most prominent figures of the Islamic Golden Age, al-Tabari is known for his historical works and his expertise in Qur'anic exegesis (), but he has also been described as "an impressively prolific polymath".Lindsay Jones (ed.), ''Encyclopedia of religion'', volume 13, Macmillan Reference USA, 2005, p. 8943 He wrote works on a diverse range of subjects, including world history, poetry, lexicography, grammar, ethics, mathematics, and medicine. His most influential and best known works are his Quranic commentary, known in Arabic as , and his historical chronicle called ''History of the Prophets and Kings'' (), often referred to as ("al-Tabari's History"). Al-Tabari followed the Shafi'i madhhab for nearly a decade before he developed his own interpretation of Islamic jurisprudence. His understanding ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amu Darya
The Amu Darya, tk, Amyderýa/ uz, Amudaryo// tg, Амударё, Amudaryo ps, , tr, Ceyhun / Amu Derya grc, Ὦξος, Ôxos (also called the Amu, Amo River and historically known by its Latin language, Latin name or Greek ) is a major river in Central Asia and Afghanistan. Rising in the Pamir Mountains, north of the Hindu Kush, the Amu Darya is formed by the confluence of the Vakhsh River, Vakhsh and Panj River, Panj rivers, in the Tigrovaya Balka Nature Reserve on the border between Afghanistan and Tajikistan, and flows from there north-westwards into the South Aral Sea, southern remnants of the Aral Sea. In its upper course, the river forms part of Afghanistan's northern border with Tajikistan, Uzbekistan, and Turkmenistan. In ancient history, the river was regarded as the boundary of Greater Iran with "Turan", which roughly corresponded to present-day Central Asia.B. SpulerĀmū Daryā in Encyclopædia Iranica, online ed., 2009 The Amu Darya has a flow of about 70 cubic k ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transcaspian Oblast
The Transcaspian Oblast (russian: Закаспійская область), or just simply Transcaspia (russian: Закаспія), was the section of Russian Empire and early Soviet Russia to the east of the Caspian Sea during the second half of the 19th century until 1924. It was bounded to the south by Iran's Khorasan Province and Afghanistan, to the north by the former Russian province of Uralsk, and to the northeast by the former Russian protectorates of Khiva and Bukhara. Area, 212,545 sq. miles. Part of Russian Turkestan, Transcaspian Oblast corresponds roughly to the territory of present-day Turkmenistan and southwestern of Kazakhstan. The name of the oblast (literally, "Beyond Caspian") is explained by the fact that until the construction of the Trans-Aral Railway in the early 20th century the easiest way to reach this oblast from central Russia (or from Russian Transcaucasia) was across the Caspian Sea, by boat from Astrakhan or Baku. Former administrative division ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maskut
The Maskut (also spelled Mazkut) were a group of Massagetaen-Sarmato-Alanian tribes located in the eastern part of the Caucasus, along the western coast of the Caspian Sea. They lived between Derbent and Shaporan, which corresponds to present-day northeast Azerbaijan and southeast Dagestan (Russia). The name "Maskut" is also sometimes used to refer to a geographic area, rather than an ethnic group. The first wave of these tribes arrived in the 3rd-century from the Volga–Don Canal and the northern coast of the Caspian Sea. The modern Russian-Dagestani historian Murtazali Gadjiev suggests that these tribes had immigrated as a result of not only climate changes and longing to explore new regions, but as well as due to concurrent conflicts. The Sarmato-Alan burial sites in Dagestan between the 3rd and 5th centuries are regarded as part of the Maskut settlement. In 216, these tribes attacked Armenia, and also participated in the war between Armenia and Sasanian Iran in the mid 3rd-ce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rus' People
The Rusʹ (Old East Slavic: Рѹсь; Belarusian language, Belarusian, Russian language, Russian, Rusyn language, Rusyn, and Ukrainian language, Ukrainian: Русь; Old Norse: ''Garðaríki, Garðar''; Greek language, Greek: Ῥῶς, ''Rhos'') were a people in Early Middle Ages, early medieval eastern Europe. The scholarly consensus holds that they were originally Norsemen, mainly originating from present-day Sweden, who settled and ruled along Trade route from the Varangians to the Greeks, the river-routes between the Baltic and the Black Seas from around the 8th to 11th centuries AD. In the 9th century, they formed the state of Kievan Rusʹ, where the ruling Norsemen along with local Finnic peoples, Finnic tribes gradually assimilated into the East Slavs, East Slavic population, with Old East Slavic becoming the common spoken language. Old Norse language, Old Norse remained familiar to the elite until their complete assimilation by the second half of the 11th century, and i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sarir
Sarir or Serir was a medieval Christian state lasting from the 6th or 7th century to the 12th century in the mountainous regions of modern-day Dagestan. Its name is derived from the Arabic word for "throne" and refers to a golden throne that was viewed as a symbol of royal authority. Origin Sarir was first documented as a political entity in the 6th century AD. The memory of its foundation was transmitted orally among the Caucasian Avars. According to one legend, the kingdom was established by a Persian general who was sent to control the Caucasus by a Sassanian king. This legend is corroborated by the names of local kings, which are normally of Persian or even Syrian etymology. Sarir bordered the Khazars to the north, the Durdzuks to the west and northwest, the Georgians and Derbent to the south. As the state was Christian, Arab historians erroneously viewed it as a dependency of the Byzantine Empire. The capital of Sarir was the city of Humraj, tentatively identified with t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
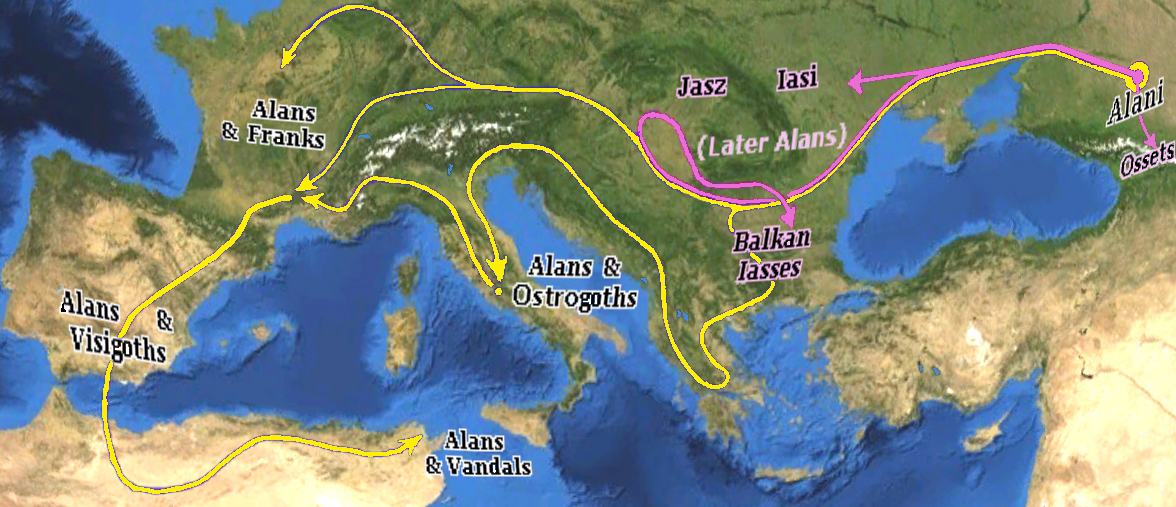
Alans
The Alans (Latin: ''Alani'') were an ancient and medieval Iranian nomadic pastoral people of the North Caucasus – generally regarded as part of the Sarmatians, and possibly related to the Massagetae. Modern historians have connected the Alans with the Central Asian Yancai of Chinese sources and with the Aorsi of Roman sources. Having migrated westwards and becoming dominant among the Sarmatians on the Pontic–Caspian steppe, the Alans are mentioned by Roman sources in the . At that time they had settled the region north of the Black Sea and frequently raided the Parthian Empire and the Caucasian provinces of the Roman Empire. From the Goths broke their power on the Pontic Steppe. Upon the Hunnic defeat of the Goths on the Pontic Steppe around , many of the Alans migrated westwards along with various Germanic tribes. They crossed the Rhine in 406CE along with the Vandals and Suebi, settling in Orléans and Valence. Around 409 CE they joined the Vandals and Suebi in cro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |