|
Wehrmachtbericht
''Wehrmachtbericht'' (literally: "Armed forces report", usually translated as Wehrmacht communiqué or Wehrmacht report) was the daily Wehrmacht High Command mass-media communiqué and a key component of Nazi propaganda during World War II. Produced by the Propaganda Department of the OKW (Wehrmacht Propaganda Troops), it covered Germany's military situation and was broadcast daily on the Reich Broadcasting Corporation of Nazi Germany. All broadcasts were authorized by the Reich Ministry of Propaganda under Joseph Goebbels. Despite the latter's attempts to temper excessive optimism, they often exaggerated the success of the German armed forces, the Wehrmacht, leading historian Aristotle Kallis to describe their tone as "triumphalist". Both civilian and military authorities considered the ''Wehrmachtbericht'' to be a vital instrument of German home-front mobilisation, the civilian contribution to the German war effort, especially after the defeat in the Battle of Stalingrad. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nazi Propaganda
The propaganda used by the German Nazi Party in the years leading up to and during Adolf Hitler's dictatorship of Nazi Germany, Germany from 1933 to 1945 was a crucial instrument for acquiring and maintaining power, and for the implementation of Nazism, Nazi policies. Themes Nazi propaganda promoted Nazi ideology by demonizing the enemies of the Nazi Party, notably Jews and Communism, communists, but also Capitalism, capitalists and intellectuals. It promoted the values asserted by the Nazis, including heroic death, ''Führerprinzip'' (leader principle), ''Volksgemeinschaft'' (people's community), ''Blood and Soil, Blut und Boden'' (blood and soil) and pride in the Germanic ''Herrenvolk'' (master race). Propaganda was also used to maintain the cult of personality around Nazi leader Adolf Hitler, and to promote campaigns for Nazi eugenics, eugenics and the Heim ins Reich, annexation of German-speaking areas. After the outbreak of World War II, Nazi propaganda vilified Germany's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wehrmacht Propaganda Troops
Propaganda Troops (german: Wehrmachtpropaganda, abbreviated as ') was a branch of service of the and the of Nazi Germany during World War II. Subordinated to the High Command of the (the '), its function was to produce and disseminate propaganda materials aimed at the German troops and the population. Planning and formation The planning for propaganda activities by the Wehrmacht began in 1938. Joseph Goebbels, the head of Ministry of Propaganda, sought to establish effective cooperation with the Wehrmacht to ensure a smooth flow of propaganda materials from the front. He deferred to the military in setting up and controlling the propaganda companies, but provided assistance in supplying personnel. Function and operation The service was subordinated to the OKW Chief of Operation Staff, General Alfred Jodl. Commanded by General Hasso von Wedel, the department oversaw the numerous propaganda companies (''Propagandakompanie'' or PK) of the Wehrmacht and the Waffen-SS, attach ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bundesarchiv Bild 183-B00548, Berlin, PK-Führer Bei Joseph Goebbels
, type = Archive , seal = , seal_size = , seal_caption = , seal_alt = , logo = Bundesarchiv-Logo.svg , logo_size = , logo_caption = , logo_alt = , image = Bundesarchiv Koblenz.jpg , image_caption = The Federal Archives in Koblenz , image_alt = , formed = , preceding1 = , preceding2 = , dissolved = , superseding1 = , superseding2 = , agency_type = , jurisdiction = , status = Active , headquarters = PotsdamerStraße156075Koblenz , coordinates = , motto = , employees = , budget = million () , chief1_name = Michael Hollmann , chief1_position = President of the Federal Archives , chief2_name = Dr. Andrea Hänger , chief2_position ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hasso Von Wedel (general)
Hasso von Wedel (20 November 1898 – 3 January 1961) was a German general who commanded the Wehrmacht Propaganda Troops during World War II. He was directly subordinate to the head of OKW Operations Staff (''Wehrmachtführungsstab, WFSt.''), General Alfred Jodl. Wedel's Propaganda Department had control over the propaganda units and served to mediate between them and the Reich Propaganda Ministry of Joseph Goebbels. After the capitulation of Nazi Germany, Wedel was taken prisoner by US troops on 6 May 1945 and released on 18 May 1946. Wedel described his experience on war propaganda in an apologetic account written between 1957 and 1958 and published after his death under the title ''Die Propagandatruppen der Deutschen Wehrmacht'' ("The Wehrmacht's Propaganda Troops"). For example, he described the relations between the Wehrmacht and civilian propaganda organizations as allegedly problematic, while they cooperated successfully and effectively throughout the war. Wedel and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schutzstaffel
The ''Schutzstaffel'' (SS; also stylized as ''ᛋᛋ'' with Armanen runes; ; "Protection Squadron") was a major paramilitary organization under Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party in Nazi Germany, and later throughout German-occupied Europe during World War II. It began with a small guard unit known as the ''Saal-Schutz'' ("Hall Security") made up of party volunteers to provide security for party meetings in Munich. In 1925, Heinrich Himmler joined the unit, which had by then been reformed and given its final name. Under his direction (1929–1945) it grew from a small paramilitary formation during the Weimar Republic to one of the most powerful organizations in Nazi Germany. From the time of the Nazi Party's rise to power until the regime's collapse in 1945, the SS was the foremost agency of security, surveillance, and terror within Germany and German-occupied Europe. The two main constituent groups were the '' Allgemeine SS'' (General SS) and ''Waffen-SS'' (Armed SS). The ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sicherheitsdienst
' (, ''Security Service''), full title ' (Security Service of the ''Reichsführer-SS''), or SD, was the intelligence agency of the SS and the Nazi Party in Nazi Germany. Established in 1931, the SD was the first Nazi intelligence organization and the Gestapo (formed in 1933) was considered its sister organization through the integration of SS members and operational procedures. The SD was administered as an independent SS office between 1933 and 1939. That year, the SD was transferred over to the Reich Security Main Office (''Reichssicherheitshauptamt''; RSHA), as one of its seven departments. Its first director, Reinhard Heydrich, intended for the SD to bring every single individual within the Third Reich's reach under "continuous supervision". Following Germany's defeat in World War II, the tribunal at the Nuremberg trials officially declared that the SD was a criminal organisation, along with the rest of Heydrich's RSHA (including the Gestapo) both individually and as branch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
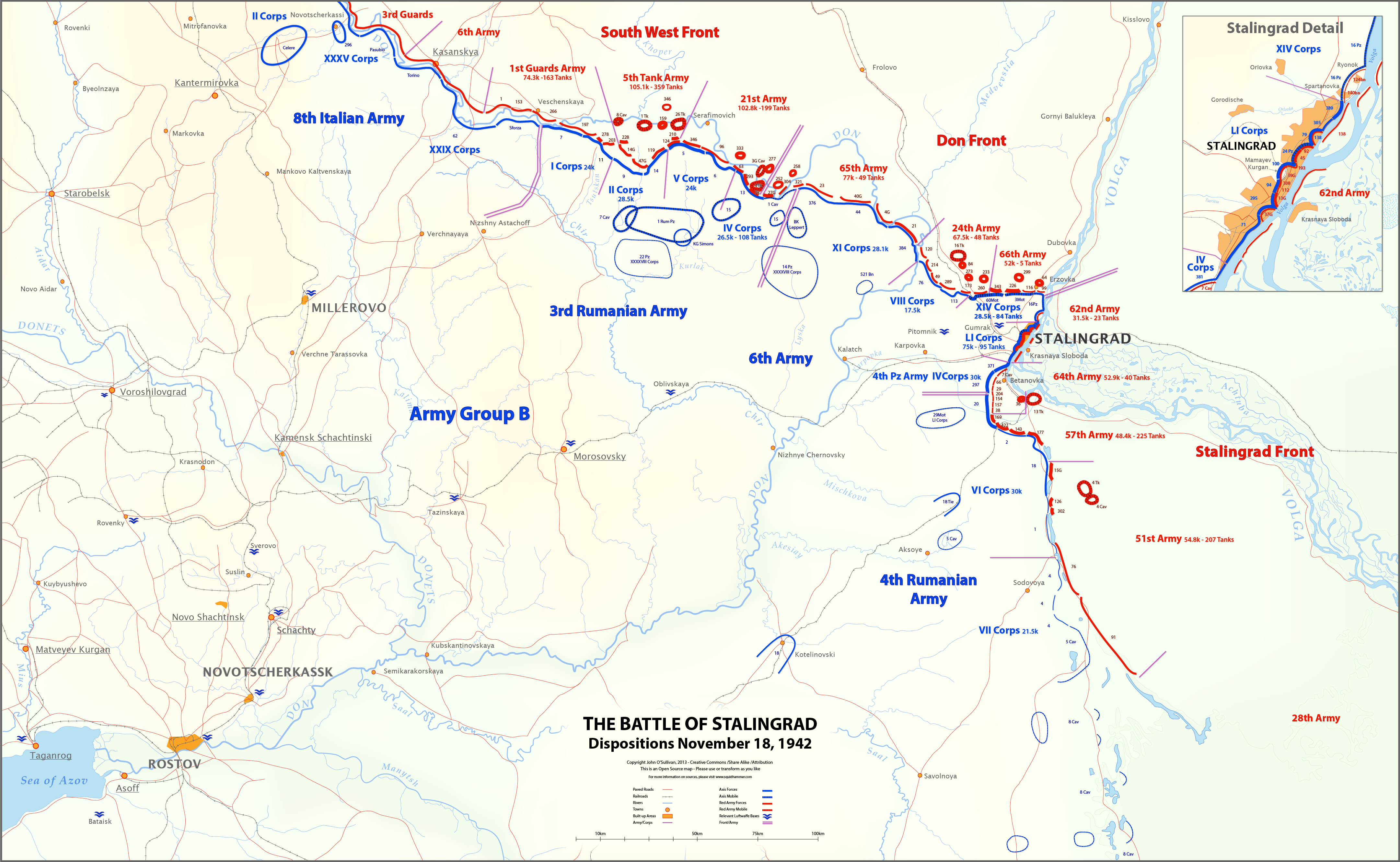
6th Army (Wehrmacht)
The 6th Army was a field army unit of the German Wehrmacht during World War II (1939–1945). It was widely remembered for being the most highly decorated German army unit until its defeat by the Red Army at the Battle of Stalingrad in the winter of 1942–1943. It also acquired a reputation for the war crimes (such as the massacre of more than 30,000 Jews at Babi Yar in September 1941) that it committed under the command of Field Marshal Walther von Reichenau during Operation Barbarossa. Western campaigns Originally numbered as the 10th Army, this Army formed on 10 October 1939 with General Walther von Reichenau in command. Its primary mission was to guard the western defenses of Germany against British and French attacks during the Polish campaign. During the invasion of the Low Countries the 6th Army saw active service linking up with paratroopers and destroying fortifications at Eben Emael, Liège, and Namur during the Battle of Belgium. The 6th Army was then involved in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Operation Uranus
Operation Uranus (russian: Опера́ция «Ура́н», Operatsiya "Uran") was the codename of the Soviet Red Army's 19–23 November 1942 strategic operation on the Eastern Front of World War II which led to the encirclement of Axis forces in the vicinity of Stalingrad: the German Sixth Army, the Third and Fourth Romanian armies, and portions of the German Fourth Panzer Army. The Red Army carried out the operation at roughly the midpoint of the five-month long Battle of Stalingrad, aiming to destroy German forces in and around Stalingrad. Planning for Operation Uranus had commenced in September 1942, and developed simultaneously with plans to envelop and destroy German Army Group Center (Operation Mars) and German forces in the Caucasus. Due to the length of the front lines created by the German 1942 summer offensive, which had aimed at taking the Caucasus oil fields and the city of Stalingrad, German and other Axis forces were over-extended. The German ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Operation Typhoon
The Battle of Moscow was a military campaign that consisted of two periods of strategically significant fighting on a sector of the Eastern Front during World War II. It took place between September 1941 and January 1942. The Soviet defensive effort frustrated Hitler's attack on Moscow, the capital and largest city of the Soviet Union. Moscow was one of the primary military and political objectives for Axis forces in their invasion of the Soviet Union. The German Strategic Offensive, named Operation Typhoon, called for two pincer offensives, one to the north of Moscow against the Kalinin Front by the 3rd and 4th Panzer Armies, simultaneously severing the Moscow–Leningrad railway, and another to the south of Moscow Oblast against the Western Front south of Tula, by the 2nd Panzer Army, while the 4th Army advanced directly towards Moscow from the west. Initially, the Soviet forces conducted a strategic defence of the Moscow Oblast by constructing three defensive belts, d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Otto Dietrich
Jacob Otto Dietrich (31 August 1897 – 22 November 1952) was a German SS officer during the Nazi era, who served as the Press Chief of the Nazi regime and was a confidant of Adolf Hitler. Biography Otto Dietrich was born in Essen, he served as a soldier during World War I and was awarded the Iron Cross (First Class). Afterwards he studied at the universities of Munich, Frankfurt am Main and Freiburg, from which he graduated with a doctorate in political science in 1921. Dietrich worked for newspapers in Essen and Munich. In 1929 he became a member of the Nazi Party (NSDAP) as a Personal Press Referent. Here he was able to introduce Hitler to numerous important officials within different sects of the mining industry to help secure funding for the Nazi Party. On 1 August 1931 he was appointed Press Chief of the NSDAP, and the following year joined the SS. On 2 June 1933 Hitler appointed Dietrich a ''Reichsleiter'', the second highest political rank in the Nazi Party. On 1 Novemb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Kiev (1941)
The First Battle of Kiev was the German name for the operation that resulted in a huge encirclement of Soviet troops in the vicinity of Kiev during World War II. This encirclement is considered the largest encirclement in the history of warfare (by number of troops). The operation ran from 7 July to 26 September 1941, as part of Operation Barbarossa, the Axis invasion of the Soviet Union. Much of the Southwestern Front of the Red Army (commanded by Mikhail Kirponos) was encircled, but small groups of Red Army troops managed to escape the pocket days after the German panzers met east of the city, including the headquarters of Marshal Semyon Budyonny, Marshal Semyon Timoshenko and Commissar Nikita Khrushchev. Kirponos was trapped behind German lines and was killed while trying to break out. The battle was an unprecedented defeat for the Red Army, exceeding even the Battle of Białystok–Minsk of June–July 1941. The encirclement trapped 452,700 soldiers, 2,642 guns and mort ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Smolensk
Smolensk ( rus, Смоленск, p=smɐˈlʲensk, a=smolensk_ru.ogg) is a city and the administrative center of Smolensk Oblast, Russia, located on the Dnieper River, west-southwest of Moscow. First mentioned in 863, it is one of the oldest cities in Russia. Population: The city has been destroyed several times throughout its long history because it was on the invasion routes of various empires. Smolensk is known for its electronics, textiles, food processing, and diamond faceting industries. Etymology The name of the city is derived from the name of the Smolnya River. Smolnya river flows through Karelian and Murmansk areas of north-western Russia. The origin of the river's name is less clear. One possibility is the old Slavic word () for black soil, which might have colored the waters of the Smolnya. An alternative origin could be the Russian word (), which means resin, tar, or pitch. Pine trees grow in the area, and the city was once a center of resin processing and t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |