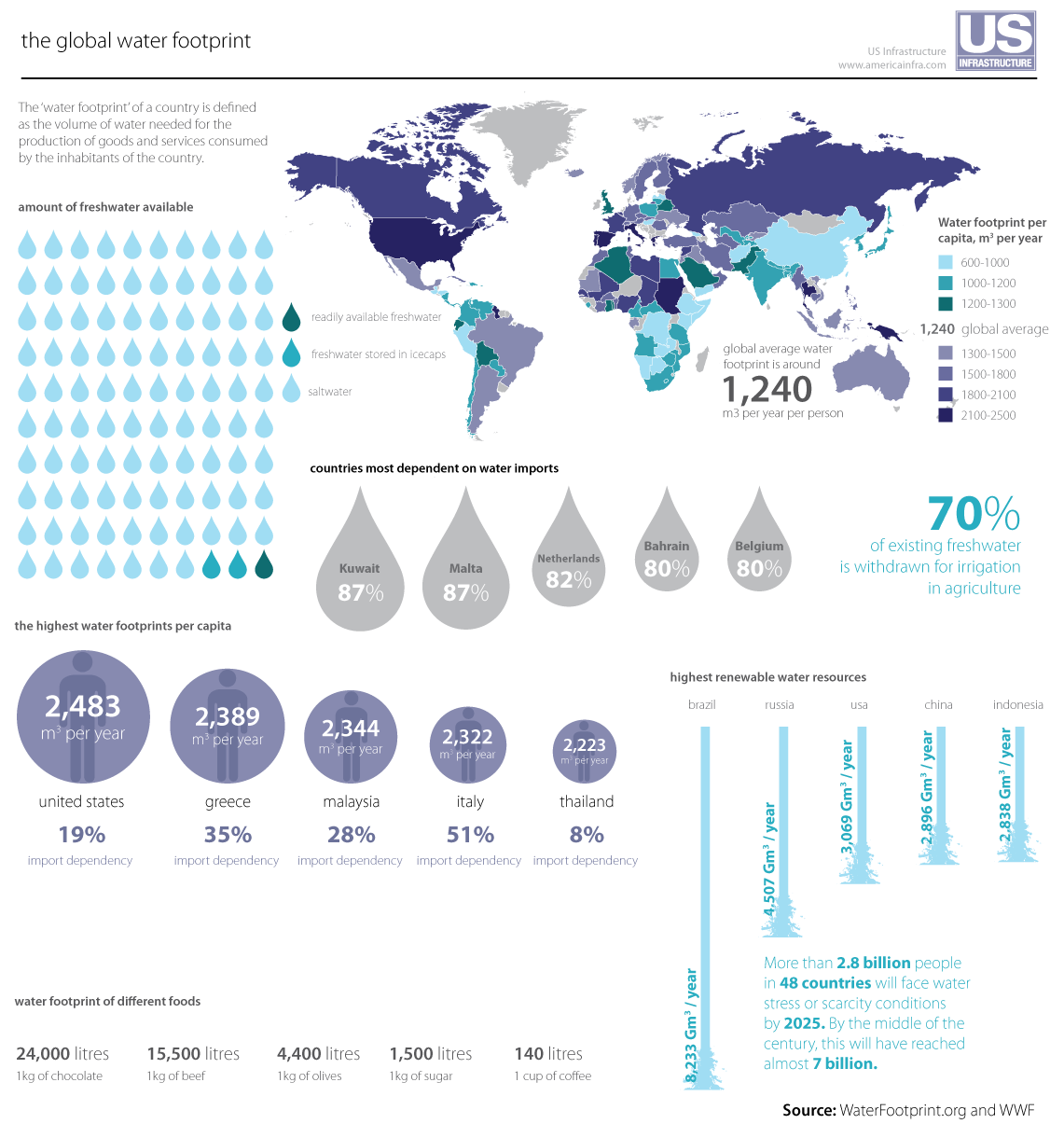
|
Water Use
A water footprint shows the extent of water use in relation to consumption by people. The water footprint of an individual, community, or business is defined as the total volume of fresh water used to produce the goods and services consumed by the individual or community or produced by the business. Water use is measured in water volume consumed ( evaporated) and/or polluted per unit of time. A water footprint can be calculated for any well-defined group of consumers (e.g., an individual, family, village, city, province, state, or nation) or producers (e.g., a public organization, private enterprise, or economic sector), for a single process (such as growing rice) or for any product or service. Traditionally, water use has been approached from the production side, by quantifying the following three columns of water use: water withdrawals in the agricultural, industrial, and domestic sector. While this does provide valuable data, it is a limited way of looking at water use in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World Water Footprint
In its most general sense, the term "world" refers to the totality of entities, to the whole of reality or to everything that is. The nature of the world has been conceptualized differently in different fields. Some conceptions see the world as unique while others talk of a "plurality of worlds". Some treat the world as one simple object while others analyze the world as a complex made up of many parts. In ''scientific cosmology'' the world or universe is commonly defined as " e totality of all space and time; all that is, has been, and will be". '' Theories of modality'', on the other hand, talk of possible worlds as complete and consistent ways how things could have been. ''Phenomenology'', starting from the horizon of co-given objects present in the periphery of every experience, defines the world as the biggest horizon or the "horizon of all horizons". In ''philosophy of mind'', the world is commonly contrasted with the mind as that which is represented by the mind. ''Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surface Water
Surface water is water located on top of land forming terrestrial (inland) waterbodies, and may also be referred to as ''blue water'', opposed to the seawater and waterbodies like the ocean. The vast majority of surface water is produced by precipitation. As the climate warms in the spring, snowmelt runs off towards nearby streams and rivers contributing towards a large portion of human drinking water. Levels of surface water lessen as a result of evaporation as well as water moving into the ground becoming ground-water. Alongside being used for drinking water, surface water is also used for irrigation, wastewater treatment, livestock, industrial uses, hydropower, and recreation. For USGS water-use reports, surface water is considered freshwater when it contains less than 1,000 milligrams per liter (mg/L) of dissolved solids. There are three major types of surface water. Permanent (perennial) surface waters are present year round, and includes lakes, rivers and wetlands (mar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volumetric Flow Rate
In physics and engineering, in particular fluid dynamics, the volumetric flow rate (also known as volume flow rate, or volume velocity) is the volume of fluid which passes per unit time; usually it is represented by the symbol (sometimes ). It contrasts with mass flow rate, which is the other main type of fluid flow rate. In most contexts a mention of ''rate of fluid flow'' is likely to refer to the volumetric rate. In hydrometry, the volumetric flow rate is known as ''discharge''. Volumetric flow rate should not be confused with volumetric flux, as defined by Darcy's law and represented by the symbol , with units of m3/(m2·s), that is, m·s−1. The integration of a flux over an area gives the volumetric flow rate. The SI unit is cubic metres per second (m3/s). Another unit used is standard cubic centimetres per minute (SCCM). In US customary units and imperial units, volumetric flow rate is often expressed as cubic feet per second (ft3/s) or gallons per minute (e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mass Flux
In physics and engineering, mass flux is the rate of mass flow. Its SI units are kg m−2 s−1. The common symbols are ''j'', ''J'', ''q'', ''Q'', ''φ'', or Φ (Greek lower or capital Phi), sometimes with subscript ''m'' to indicate mass is the flowing quantity. Mass flux can also refer to an alternate form of flux in Fick's law that includes the molecular mass, or in Darcy's law that includes the mass density. Sometimes the defining equation for mass flux in this article is used interchangeably with the defining equation in mass flow rate. For example, ''Fluid Mechanics, Schaum's et al'' uses the definition of mass flux as the equation in the mass flow rate article. Definition Mathematically, mass flux is defined as the limit j_m = \lim_ \frac, where I_m = \lim_ \frac = \frac is the mass current (flow of mass per unit time ) and is the area through which the mass flows. For mass flux as a vector , the surface integral of it over a surface ''S'', followed by an integra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Measures Of Pollutant Concentration
Measures of pollutant concentration are used to determine risk assessment in public health. Industry is continually synthesizing new chemicals, the regulation of which requires evaluation of the potential danger for human health and the environment. Risk assessment is nowadays considered essential for making these decisions on a scientifically sound basis. Measures or defined limits include: * ''no-observed-adverse-effect level'' (NOAEL), also called ''no-effect concentration'' (NEC), ''no-observed-effect concentration'' (NOEC) or similarly * '' lowest-observed-adverse-effect level'' (LOAEL) * ''acceptable operator exposure level'' (AOEL) * ECx (in percentage). No-effect concentration ''No-effect concentration'' (NEC) is a risk assessment parameter that represents the concentration of a pollutant that will not harm the species involved, with respect to the effect that is studied. It is often the starting point for environmental policy. There is not much debate on the existence ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Urban Runoff
Urban runoff is surface runoff of rainwater, landscape irrigation, and car washing created by urbanization. Impervious surfaces (roads, parking lots and sidewalks) are constructed during land development. During rain , storms and other precipitation events, these surfaces (built from materials such as asphalt and concrete), along with rooftops, carry polluted stormwater to storm drains, instead of allowing the water to percolate through soil. This causes lowering of the water table (because groundwater recharge is lessened) and flooding since the amount of water that remains on the surface is greater.Water Environment Federation Alexandria, VA; an American Society of Civil Engineers Reston, VA [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nonpoint Source Pollution
Nonpoint source (NPS) pollution refers to diffuse contamination (or pollution) of water or air that does not originate from a single discrete source. This type of pollution is often the cumulative effect of small amounts of contaminants gathered from a large area. It is in contrast to point source pollution which results from a single source. Nonpoint source pollution generally results from land runoff, precipitation, atmospheric deposition, drainage, seepage, or hydrological modification (rainfall and snowmelt) where tracing pollution back to a single source is difficult. Nonpoint source water pollution affects a water body from sources such as polluted runoff from agricultural areas draining into a river, or wind-borne debris blowing out to sea. Nonpoint source air pollution affects air quality, from sources such as smokestacks or car tailpipes. Although these pollutants have originated from a point source, the long-range transport ability and multiple sources of the pollutant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Water Pollution
Water pollution (or aquatic pollution) is the contamination of water bodies, usually as a result of human activities, so that it negatively affects its uses. Water bodies include lakes, rivers, oceans, aquifers, reservoirs and groundwater. Water pollution results when contaminants are introduced into these water bodies. Water pollution can be attributed to one of four sources: sewage discharges, industrial activities, agricultural activities, and urban runoff including stormwater. It can be grouped into surface water pollution (either fresh water pollution or marine pollution) or groundwater pollution. For example, releasing inadequately treated wastewater into natural waters can lead to degradation of these aquatic ecosystems. Water pollution can also lead to water-borne diseases for people using polluted water for drinking, bathing, washing or irrigation. Water pollution reduces the ability of the body of water to provide the ecosystem services (such as drinking water ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Forestry
Forestry is the science and craft of creating, managing, planting, using, conserving and repairing forests, woodlands, and associated resources for human and environmental benefits. Forestry is practiced in plantations and natural stands. The science of forestry has elements that belong to the biological, physical, social, political and managerial sciences. Forest management play essential role of creation and modification of habitats and affect ecosystem services provisioning. Modern forestry generally embraces a broad range of concerns, in what is known as multiple-use management, including: the provision of timber, fuel wood, wildlife habitat, natural water quality management, recreation, landscape and community protection, employment, aesthetically appealing landscapes, biodiversity management, watershed management, erosion control, and preserving forests as "sinks" for atmospheric carbon dioxide. Forest ecosystems have come to be seen as the most important comp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Horticulture
Horticulture is the branch of agriculture that deals with the art, science, technology, and business of plant cultivation. It includes the cultivation of fruits, vegetables, nuts, seeds, herbs, sprouts, mushrooms, algae, flowers, seaweeds and non-food crops such as grass and ornamental trees and plants. It also includes plant conservation, landscape restoration, landscape and garden design, construction, and maintenance, and arboriculture, ornamental trees and lawns. The study and practice of horticulture have been traced back thousands of years. Horticulture contributed to the transition from nomadic human communities to sedentary, or semi-sedentary, horticultural communities.von Hagen, V.W. (1957) The Ancient Sun Kingdoms Of The Americas. Ohio: The World Publishing Company Horticulture is divided into several categories which focus on the cultivation and processing of different types of plants and food items for specific purposes. In order to conserve the science of horticultur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Evapotranspiration
Evapotranspiration (ET) is the combined processes by which water moves from the earth’s surface into the atmosphere. It covers both water evaporation (movement of water to the air directly from soil, canopies, and water bodies) and transpiration (movement of water from the soil, through roots and bodies of vegetation, on leaves and then into the air). Evapotranspiration is an important part of the local water cycle and climate, as well as measurement of it plays a key role in agricultural irrigation and water resource management. Definition Evapotranspiration is a combination of evaporation and transpiration, measured in order to better understand crop water requirements, irrigation scheduling, and watershed management. The two key components of evapotranspiration are: * Evaporation: the movement of water directly to the air from sources such as the soil and water bodies. It can be affected by factors including heat, humidity, and wind speed. * Transpiration: the mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Precipitation
In meteorology, precipitation is any product of the condensation of atmospheric water vapor that falls under gravitational pull from clouds. The main forms of precipitation include drizzle, rain, sleet, snow, ice pellets, graupel and hail. Precipitation occurs when a portion of the atmosphere becomes saturated with water vapor (reaching 100% relative humidity), so that the water condenses and "precipitates" or falls. Thus, fog and mist are not precipitation but colloids, because the water vapor does not condense sufficiently to precipitate. Two processes, possibly acting together, can lead to air becoming saturated: cooling the air or adding water vapor to the air. Precipitation forms as smaller droplets coalesce via collision with other rain drops or ice crystals within a cloud. Short, intense periods of rain in scattered locations are called showers. Moisture that is lifted or otherwise forced to rise over a layer of sub-freezing air at the surface may be condens ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |