|
Wahbarz
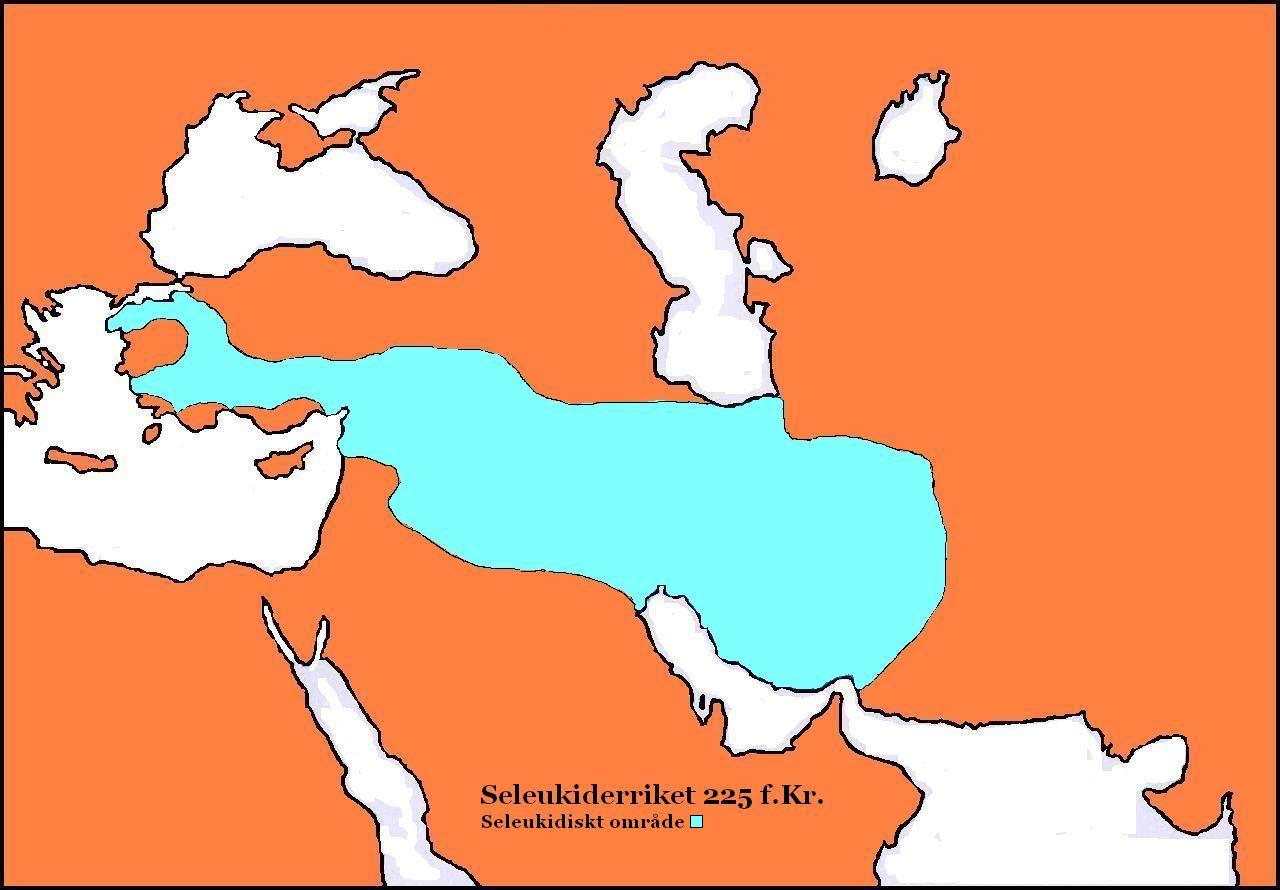
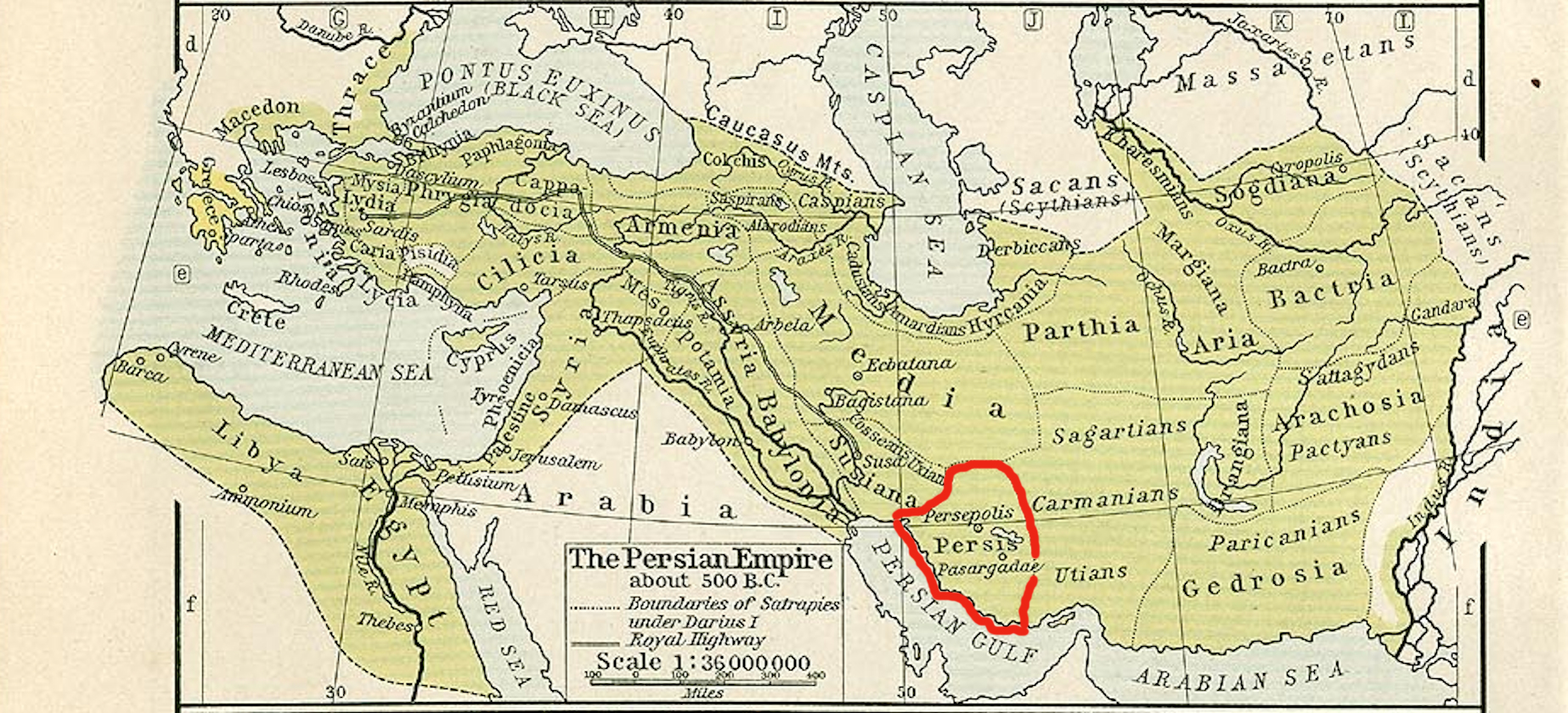
Wahbarz (also spelled Vahbarz), known in Greek language, Greek sources as Oborzos, was a dynast (''frataraka'') of Persis in the 1st half of the 2nd century BC, ruling from possibly to 164 BC. His reign was marked by his efforts to establish Persis as a kingdom independent from Seleucid Empire, Seleucid authority. He was able to reign independently for three decades, and even expanded to the west, seizing the Seleucid province of Characene. In 164 BC, the Seleucids repelled Wahbarz's forces from Characene, forcing him to re-submit as a Seleucid vassal. He was succeeded by Baydad. Background Since the end of the 3rd or the beginning of the 2nd century BCE, Persis had been ruled by local dynasts subject to the Seleucid Empire. They held the ancient Persian title of ''frataraka'' ("leader, governor, forerunner"), which is also attested in the Achaemenid-era. The Achaemenid Empire, which had a century earlier ruled most of the Near East, originated from the region. The ''frataraka' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ardakhshir I
Ardakhshir I (also spelled Artaxerxes I; Aramaic: ''rtḥštry'') was a dynast (''frataraka'') of Persis in the late 3rd-century BC, ruling sometime after 220 to . Name ''Ardakhshir'' (''Ardashir'') is the Middle Persian form of the Old Persian ''Ṛtaxšira'' (also spelled ''Artaxšaçā'', meaning "whose reign is through truth"). The Latin variant of the name is '. Three kings of the Achaemenid Empire were known to have the same name. Reign Since the end of the 3rd or the beginning of the 2nd century BCE, Persis had been ruled by local dynasts subject to the Seleucid Empire. They held the ancient Persian title of ''frataraka'' ("leader, governor, forerunner"), which is also attested in the Achaemenid-era. The Achaemenid Empire, which had a century earlier ruled most of the Near East, originated from the region. The ''frataraka'' themselves emphasized their close affiliation with the prominent Achaemenid king of kings, and their court was probably at the former Achaemenid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baydad
Baydad (also spelled Bagdates), was a dynast (''frataraka'') of Persis from 164 to 146 BC. Background Since the end of the 3rd or the beginning of the 2nd century BCE, Persis had been ruled by local dynasts subject to the Seleucid Empire. They held the ancient Persian title of ''frataraka'' ("leader, governor, forerunner"), which is also attested in the Achaemenid-era. The Achaemenid Empire, which had a century earlier ruled most of the Near East, originated from the region. The ''frataraka'' themselves emphasized their close affiliation with the prominent Achaemenid King of Kings, and their court was probably at the former Achaemenid capital of Persepolis, where they financed construction projects on and near the Achaemenid plateau. The ''frataraka'' had traditionally been regarded as priestly dynasts or advocates of religious (and political) opposition to Hellenism, however, this is no longer considered the case. Chronology of the ''frataraka'' The traditional view of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fire Temple
A fire temple, Agiary, Atashkadeh ( fa, آتشکده), Atashgah () or Dar-e Mehr () is the place of worship for the followers of Zoroastrianism, the ancient religion of Iran (Persia). In the Zoroastrian religion, fire (see ''atar''), together with clean water (see ''aban''), are agents of ritual purity. Clean, white "ash for the purification ceremonies sregarded as the basis of ritual life", which "are essentially the rites proper to the tending of a domestic fire, for the temple ireis that of the hearth fire raised to a new solemnity". For, one "who sacrifices unto fire with fuel in his hand ..., is given happiness". , there were 167 fire temples in the world, of which 45 were in Mumbai, 105 in the rest of India, and 17 in other countries. Of these only 9 (1 in Iran and 8 in India) are the main temples known as '' atash behrams'' and the remaining are the smaller temples known as ''agiarys''. History and development Concept First evident in the 9th century BCE, the Zoroastr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sagdodonacus
Sagdodonacus was an Iranian officer, who served as the governor of Characene from to 164 BC under suzerainty of the Frataraka rulers of Persis. He was the father of Hyspaosines. Name The name of ''Sagdodonacus'' ("to hold, to keep") is seemingly Bactrian and he was presumably of Bactrian origin himself. He was called Saxt in the accounts of the 10th-century historian Hamza al-Isfahani. Biography The Frataraka rulers of Persis were local rulers subject to the Seleucid Empire since the 2nd-century BC. After the death of Antiochus III the Great in 187 BC, however, Seleucid rule weakened in its southern provinces, which allowed Persis under Wahbarz to not only declare independence, but also expand over the region of Characene, appointing Sagdodonacus as its governor. The precise date of the Persis conquest of Characene and Sagdodonacus' appointment is unknown. It may have been in the summer 184 BC, when Seleucid authority over its southern provinces seem to have been further wea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tiara
A tiara (from la, tiara, from grc, τιάρα) is a jeweled head ornament. Its origins date back to ancient Greece and Rome. In the late 18th century, the tiara came into fashion in Europe as a prestigious piece of jewelry to be worn by women at formal occasions. The basic shape of the modern tiara is a (semi-)circle, usually made of silver, gold or platinum, and richly decorated with precious stones, pearls or cameos. Tiaras were extremely popular during the late 19th century and were worn at events where the dress code was white tie. After World War I, wearing a tiara gradually fell out of fashion, except for official occasions at a royal court. Interest in tiaras has increased again since the beginning of the 21st century. The word "tiara" is often used interchangeably with the word "diadem". Description The basic shape of the modern tiara is a (semi-)circle, usually made of silver, gold or platinum. Tiaras have also been made from tortoiseshell, coral and quartz, and in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wadfradad II
Wadfradad II (also spelled Autophradates II) was a dynast (''frataraka'') of Persis in the late 2nd-century BC, ruling sometime after 138 BC. He was appointed as ''frataraka'' by the Parthian king Mithridates I (), who granted him more autonomy, most likely in an effort to maintain healthy relations with Persis as the Parthian Empire was under constant conflict with the Saka, Seleucids, and Characene. The coinage of Wadfradad I shows influence from the coins minted under Mithridates I. Wadfradad I was succeeded by Darayan I, the first of the Kings of Persis The Kings of Persis, also known as the Darayanids, were a series of Persian kings, who ruled the region of Persis in southwestern Iran, from the 2nd century BCE to 224 CE. They ruled as sub-kings of the Parthian Empire, until they toppled them an .... References Sources * . * * * * * {{Fratarakas of Persis 2nd-century BC Iranian people History of Fars Province 2nd-century BC rulers in Asia Vassal rule ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coin Of Wahbarz Killing A Greek
A coin is a small, flat (usually depending on the country or value), round piece of metal or plastic used primarily as a medium of exchange or legal tender. They are standardized in weight, and produced in large quantities at a mint in order to facilitate trade. They are most often issued by a government. Coins often have images, numerals, or text on them. ''Obverse'' and its opposite, ''reverse'', refer to the two flat faces of coins and medals. In this usage, ''obverse'' means the front face of the object and ''reverse'' means the back face. The obverse of a coin is commonly called ''heads'', because it often depicts the head of a prominent person, and the reverse ''tails''. Coins are usually made of metal or an alloy, or sometimes of man-made materials. They are usually disc shaped. Coins, made of valuable metal, are stored in large quantities as bullion coins. Other coins are used as money in everyday transactions, circulating alongside banknotes. Usually the highest value ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polyaenus
Polyaenus or Polyenus ( ; see ae (æ) vs. e; grc-gre, Πoλύαινoς, Polyainos, "much-praised") was a 2nd-century CE Greek author, known best for his ''Stratagems in War'' ( grc-gre, Στρατηγήματα, Strategemata), which has been preserved. He was born in Bithynia. The ''Suda'' calls him a rhetorician, and Polyaenus himself writes that he was accustomed to plead causes before the Roman emperor. Polyaenus dedicated ''Stratagems in War'' to the two emperors Marcus Aurelius () and Lucius Verus (), while they were engaged in the Roman–Parthian War of 161–166, about 163, at which time he was too old to accompany them in their campaigns. Stratagems This work is divided into eight books: the first six contain accounts of the stratagems of the most celebrated Greek generals, the seventh book contains stratagems of non Greeks and Romans, and the eighth book those of the Romans and of illustrious women. Parts, however, of the sixth and seventh books are lost, so that of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greeks
The Greeks or Hellenes (; el, Έλληνες, ''Éllines'' ) are an ethnic group and nation indigenous to the Eastern Mediterranean and the Black Sea regions, namely Greece, Cyprus, Albania, Italy, Turkey, Egypt, and, to a lesser extent, other countries surrounding the Mediterranean Sea. They also form a significant diaspora (), with Greek communities established around the world.. Greek colonies and communities have been historically established on the shores of the Mediterranean Sea and Black Sea, but the Greek people themselves have always been centered on the Aegean and Ionian seas, where the Greek language has been spoken since the Bronze Age.. Until the early 20th century, Greeks were distributed between the Greek peninsula, the western coast of Asia Minor, the Black Sea coast, Cappadocia in central Anatolia, Egypt, the Balkans, Cyprus, and Constantinople. Many of these regions coincided to a large extent with the borders of the Byzantine Empire of the late 11th cent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antiochus III The Great
Antiochus III the Great (; grc-gre, Ἀντίoχoς Μέγας ; c. 2413 July 187 BC) was a Greek Hellenistic king and the 6th ruler of the Seleucid Empire, reigning from 222 to 187 BC. He ruled over the region of Syria and large parts of the rest of western Asia towards the end of the 3rd century BC. Rising to the throne at the age of eighteen in 222 BC, his early campaigns against the Ptolemaic Kingdom were unsuccessful, but in the following years Antiochus gained several military victories and substantially expanded the empire's territory. His traditional designation, ''the Great'', reflects an epithet he assumed. He also assumed the title ''Basileus Megas'' (Greek for "Great King"), the traditional title of the Persian kings. A militarily active ruler, Antiochus restored much of the territory of the Seleucid Empire, before suffering a serious setback, towards the end of his reign, in his war against Rome. Declaring himself the "champion of Greek freedom against Roman domina ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Republic
The Roman Republic ( la, Res publica Romana ) was a form of government of Rome and the era of the classical Roman civilization when it was run through public representation of the Roman people. Beginning with the overthrow of the Roman Kingdom (traditionally dated to 509 BC) and ending in 27 BC with the establishment of the Roman Empire, Rome's control rapidly expanded during this period—from the city's immediate surroundings to hegemony over the entire Mediterranean world. Roman society under the Republic was primarily a cultural mix of Latin and Etruscan societies, as well as of Sabine, Oscan, and Greek cultural elements, which is especially visible in the Roman Pantheon. Its political organization developed, at around the same time as direct democracy in Ancient Greece, with collective and annual magistracies, overseen by a senate. The top magistrates were the two consuls, who had an extensive range of executive, legislative, judicial, military, and religious powers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
%2C_governor%2C_c._mid_3rd_century_BC.jpg)