|
Venedi
The Vistula Veneti (also called Baltic Veneti) were an Indo-European people that inhabited the region of central Europe east of the Vistula River and the areas around the Bay of Gdańsk. The name first appeared in the 1st century AD in the writings of ancient Romans who differentiated a group of peoples whose manner and language differed from that of the Germanic and Sarmatian tribes. In the 6th century AD, Byzantine sources described the Veneti as the ancestors of the Slavs,Alexander M. Schenker, ''The Dawn of Slavic: An Introduction to Slavic Philology'' (1995), 1.4., including a reference to J. Ochmański, Ochmański, ''Historia Litwy'', 2nd ed. (Wrocław, 1982) who during the second phase of the Migration Period moved south across the northern frontier of the Byzantine Empire. Roman historical sources Pliny the Elder places the Veneti along the Baltic coast. He calls them the Sarmatian Venedi (Latin: ''Sarmatae Venedi''). Thereafter, the 2nd century Greco-Roman geogra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fenni
The Fenni were an ancient people of northeastern Europe, first described by Cornelius Tacitus in '' Germania'' in AD 98. Ancient accounts The Fenni are first mentioned by Cornelius Tacitus in '' Germania'' in 98 A.D. Their location is uncertain, due to the vagueness of Tacitus' account: ''"they (Venedi) overrun in their predatory excursions all the woody and mountainous tracts between the Peucini and the Fenni"''.Tacitus G.46 The Greco-Roman geographer Ptolemy, who produced his '' Geographia'' in ca. 150 AD, mentions a people called the ''Phinnoi'' (Φιννοι), generally believed to be synonymous with the Fenni. He locates them in two different areas: a northern group in northern ''Scandia'' ( Scandinavia), then believed to be an island; and a southern group, apparently dwelling to the East of the upper Vistula river (SE Poland). It remains unclear what was the relationship between the two groups. The next ancient mention of the Fenni/Finni is in the '' Getica'' of 6th-c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antes (people)
The Antes, or Antae ( gr, Ἄνται), were an early East Slavic tribal polity of the 6th century CE. They lived on the lower Danube River, in the northwestern Black Sea region (present-day Moldova and central Ukraine), and in the regions around the Don River (in Middle and Southern Russia). Scholars commonly associate the Antes with the archaeological Penkovka culture. First mentioned in the historical record in 518, the Antes invaded the Diocese of Thrace sometime between the years of 533 and 545. Thereafter, they became Byzantine '' foederati'' and received gold payments and a fort (named "Turris" - the Latin word ''turris'' means 'tower') somewhere north of the Danube at a strategically important location to prevent hostile barbarians from invading Roman lands. Thus from 545 to the 580s, Antean soldiers fought in various Byzantine campaigns. The Pannonian Avars attacked the Antes at the beginning of the 7th century, when the Antes disappeared as a group and became anc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ermanaric
Ermanaric; la, Ermanaricus or ''Hermanaricus''; ang, Eormanrīc ; on, Jǫrmunrekkr , gmh, Ermenrîch (died 376) was a Greuthungian Gothic king who before the Hunnic invasion evidently ruled a sizable portion of Oium, the part of Scythia inhabited by the Goths at the time. He is mentioned in two Roman sources: the contemporary writings of Ammianus Marcellinus, and in ''Getica'' by the sixth-century historian Jordanes. He also appears in a fictionalized form in later Germanic heroic legends. Modern historians disagree on the size of Ermanaric's realm. Herwig Wolfram postulates that he at one point ruled a realm stretching from the Baltic Sea to the Black Sea as far eastwards as the Ural Mountains. Peter Heather is skeptical of the claim that Ermanaric ruled all Goths except the Tervingi, and furthermore points to the fact that such an enormous empire would have been larger than any known Gothic political unit, that it would have left bigger traces in the sources and that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Germanic Peoples
The Germanic peoples were historical groups of people that once occupied Central Europe and Scandinavia during antiquity and into the early Middle Ages. Since the 19th century, they have traditionally been defined by the use of ancient and early medieval Germanic languages and are thus equated at least approximately with Germanic-speaking peoples, although different academic disciplines have their own definitions of what makes someone or something "Germanic". The Romans named the area belonging to North-Central Europe in which Germanic peoples lived '' Germania'', stretching East to West between the Vistula and Rhine rivers and north to south from Southern Scandinavia to the upper Danube. In discussions of the Roman period, the Germanic peoples are sometimes referred to as ''Germani'' or ancient Germans, although many scholars consider the second term problematic since it suggests identity with present-day Germans. The very concept of "Germanic peoples" has become the subj ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Getica
''De origine actibusque Getarum'' (''The Origin and Deeds of the Getae oths'), commonly abbreviated ''Getica'', written in Late Latin by Jordanes in or shortly after 551 AD, claims to be a summary of a voluminous account by Cassiodorus of the origin and history of the Gothic people, which is now lost. However, the extent to which Jordanes actually used the work of Cassiodorus is unknown. It is significant as the only remaining contemporaneous resource that gives an extended account of the origin and history of the Goths, although to what extent it should be considered history or origin mythology is a matter of dispute. Synopsis of the work The ''Getica'' begins with a discussion of a large island named Scandza, which faces the mouth of the Vistula river and had been described by the writers Claudius Ptolemy and Pomponius Mela. Jordanes reports this island to be the original home of many different peoples including the Goths, who have swarmed like bees from there (16-25). Jord ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
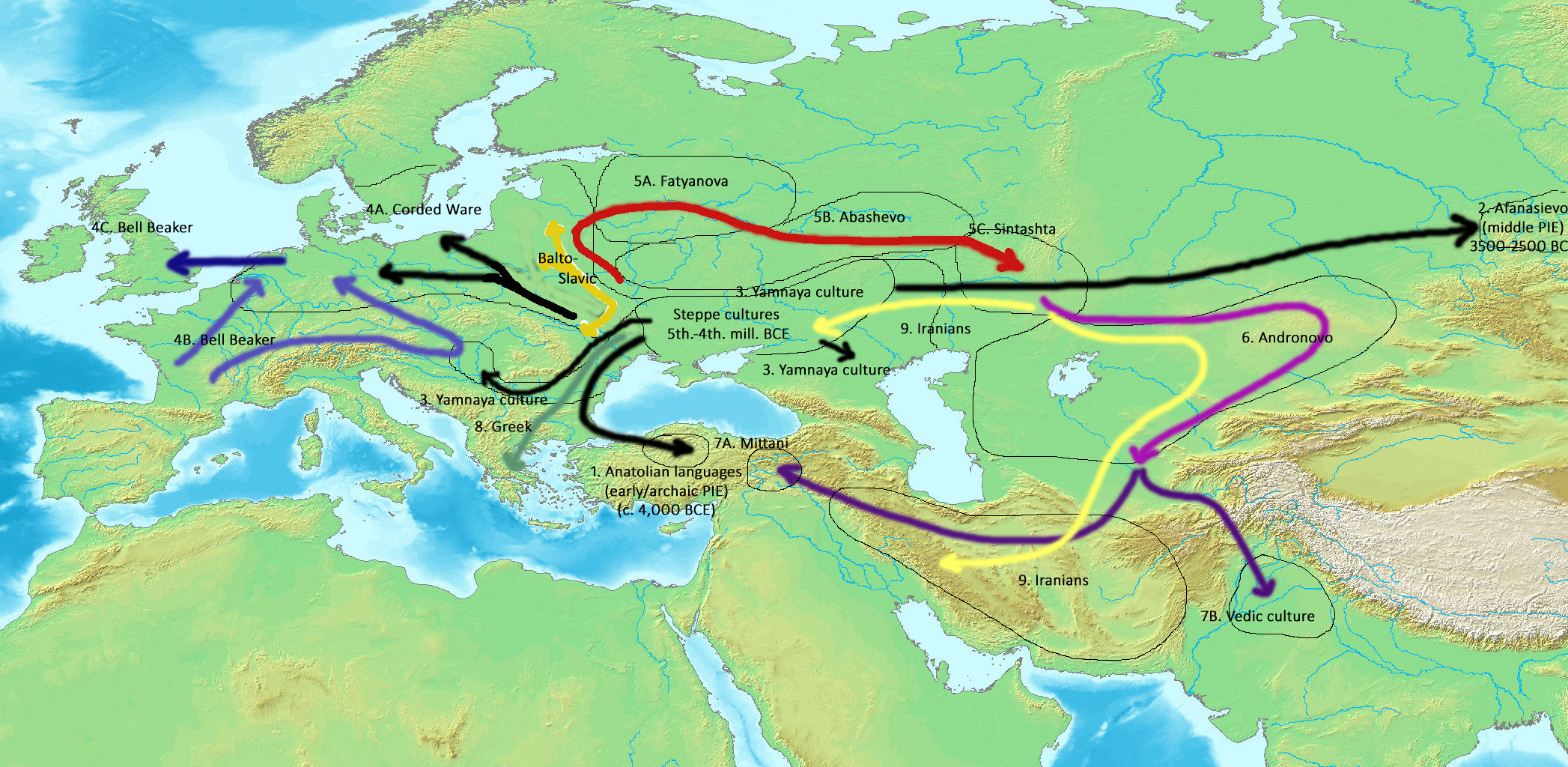
Proto-Indo-Europeans
The Proto-Indo-Europeans are a hypothetical prehistoric population of Eurasia who spoke Proto-Indo-European (PIE), the ancestor of the Indo-European languages according to linguistic reconstruction. Knowledge of them comes chiefly from that linguistic reconstruction, along with material evidence from archaeology and archaeogenetics. The Proto-Indo-Europeans likely lived during the late Neolithic, or roughly the 4th millennium BC. Mainstream scholarship places them in the Pontic–Caspian steppe zone in Eurasia (present-day Ukraine and southern Russia). Some archaeologists would extend the time depth of PIE to the middle Neolithic (5500 to 4500 BC) or even the early Neolithic (7500 to 5500 BC) and suggest alternative location hypotheses. By the early second millennium BC, descendants of the Proto-Indo-Europeans had reached far and wide across Eurasia, including Anatolia (Hittites), the Aegean (the linguistic ancestors of Mycenaean Greece), the north of Europe ( Corded W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Danube
The Danube ( ; ) is a river that was once a long-standing frontier of the Roman Empire and today connects 10 European countries, running through their territories or being a border. Originating in Germany, the Danube flows southeast for , passing through or bordering Austria, Slovakia, Hungary, Croatia, Serbia, Romania, Bulgaria, Moldova, and Ukraine before draining into the Black Sea. Its drainage basin extends into nine more countries. The largest cities on the river are Vienna, Budapest, Belgrade and Bratislava, all of which are the capitals of their respective countries; the Danube passes through four capital cities, more than any other river in the world. Five more capital cities lie in the Danube's basin: Bucharest, Sofia, Zagreb, Ljubljana and Sarajevo. The fourth-largest city in its basin is Munich, the capital of Bavaria, standing on the Isar River. The Danube is the second-longest river in Europe, after the Volga in Russia. It flows through much of Central ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tisa
The Tisza, Tysa or Tisa, is one of the major rivers of Central and Eastern Europe. Once, it was called "the most Hungarian river" because it flowed entirely within the Kingdom of Hungary. Today, it crosses several national borders. The Tisza begins near Rakhiv in Ukraine, at the confluence of the White Tisa and Black Tisa, which is at coordinates 48.07465560782065, 24.24443465360461 (the former springs in the Chornohora mountains; the latter in the Gorgany range). From there, the Tisza flows west, roughly following Ukraine's borders with Romania and Hungary, then shortly as border between Slovakia and Hungary, later into Hungary, and finally into Serbia. It enters Hungary at Tiszabecs. It traverses Hungary from north to south. A few kilometers south of the Hungarian city of Szeged, it enters Serbia. Finally, it joins the Danube near the village of Stari Slankamen in Vojvodina, Serbia. The Tisza drains an area of about and has a length of Its mean annual discharge is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lake Constance
Lake Constance (german: Bodensee, ) refers to three bodies of water on the Rhine at the northern foot of the Alps: Upper Lake Constance (''Obersee''), Lower Lake Constance (''Untersee''), and a connecting stretch of the Rhine, called the Lake Rhine (''Seerhein''). These waterbodies lie within the Lake Constance Basin () in the Alpine Foreland through which the Rhine flows. The lake is situated where Germany, Switzerland, and Austria meet. Its shorelines lie in the German states of Baden-Württemberg and Bavaria, the Swiss cantons of St. Gallen, Thurgau, and Schaffhausen, and the Austrian state of Vorarlberg. The actual location of the border is disputed. The Alpine Rhine forms in its original course the Austro-Swiss border and flows into the lake from the south. The High Rhine flows westbound out of the lake and forms (with the exception of the Canton of Schaffhausen) the German-Swiss border as far as to the city of Basel. The most populous towns on the Upper Lake ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dniestr
The Dniester, ; rus, Дне́стр, links=1, Dnéstr, ˈdⁿʲestr; ro, Nistru; grc, Τύρᾱς, Tyrās, ; la, Tyrās, la, Danaster, label=none, ) ( ,) is a transboundary river in Eastern Europe. It runs first through Ukraine and then through Moldova (from which it more or less separates the breakaway territory of Transnistria), finally discharging into the Black Sea on Ukrainian territory again. Names The name ''Dniester'' derives from Sarmatian ''dānu nazdya'' "the close river." (The Dnieper, also of Sarmatian origin, derives from the opposite meaning, "the river on the far side".) Alternatively, according to Vasily Abaev ''Dniester'' would be a blend of Scythian ''dānu'' "river" and Thracian ''Ister'', the previous name of the river, literally Dān-Ister (River Ister). The Ancient Greek name of Dniester, ''Tyras'' (Τύρας), is from Scythian ''tūra'', meaning "rapid." The names of the Don and Danube are also from the same Indo-Iranian word ''*dānu'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
East Slavs
The East Slavs are the most populous subgroup of the Slavs. They speak the East Slavic languages, and formed the majority of the population of the medieval state Kievan Rus', which they claim as their cultural ancestor.John Channon & Robert Hudson, ''Penguin Historical Atlas of Russia'' (Penguin, 1995), p. 16. Today, the East Slavs consist of Belarusians, Russians, Rusyns, and Ukrainians. History Sources Researchers know relatively little about the Eastern Slavs prior to approximately 859 AD when the first events recorded in the '' Primary Chronicle'' occurred. The Eastern Slavs of these early times apparently lacked a written language. The few known facts come from archaeological digs, foreign travellers' accounts of the Rus' land, and linguistic comparative analyses of Slavic languages. Very few native Rus' documents dating before the 11th century (none before the 10th century) have survived. The earliest major manuscript with information on Rus' history, the '' Prim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South Slavs
South Slavs are Slavic peoples who speak South Slavic languages and inhabit a contiguous region of Southeast Europe comprising the eastern Alps and the Balkan Peninsula. Geographically separated from the West Slavs and East Slavs by Austria, Hungary, Romania, and the Black Sea, the South Slavs today include Bosniaks, Bulgarians, Croats, Macedonians, Montenegrins, Serbs, and Slovenes, respectively the main populations of Bosnia and Herzegovina, Bulgaria, Croatia, North Macedonia, Montenegro, Serbia, and Slovenia. In the 20th century, the country of Yugoslavia (from Serbo-Croatian, literally meaning "South Slavia" or "South Slavdom") united majority of South Slavic peoples and lands—with the exception of Bulgarians and Bulgaria—into a single state. The Pan-Slavic concept of ''Yugoslavia'' emerged in the late 17th century Croatia, at the time party of Habsburg Monarchy, and gained prominence through the 19th-century Illyrian movement. The Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |