|
Ermanaric
Ermanaric; la, Ermanaricus or ''Hermanaricus''; ang, Eormanrīc ; on, Jǫrmunrekkr , gmh, Ermenrîch (died 376) was a Greuthungian Gothic king who before the Hunnic invasion evidently ruled a sizable portion of Oium, the part of Scythia inhabited by the Goths at the time. He is mentioned in two Roman sources: the contemporary writings of Ammianus Marcellinus, and in ''Getica'' by the sixth-century historian Jordanes. He also appears in a fictionalized form in later Germanic heroic legends. Modern historians disagree on the size of Ermanaric's realm. Herwig Wolfram postulates that he at one point ruled a realm stretching from the Baltic Sea to the Black Sea as far eastwards as the Ural Mountains. Peter Heather is skeptical of the claim that Ermanaric ruled all Goths except the Tervingi, and furthermore points to the fact that such an enormous empire would have been larger than any known Gothic political unit, that it would have left bigger traces in the sources and that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amali Dynasty
The Amali – also called Amals, Amalings or Amalungs – were a leading dynasty of the Goths, a Germanic people who confronted the Roman Empire during the decline of the Western Roman Empire. They eventually became the royal house of the Ostrogoths and founded the Ostrogothic Kingdom of Italy. Origin The Amal clan was claimed to have descended from the divine. Jordanes writes: Now the first of these heroes, as they themselves relate in their legends, was Gapt, who begat Hulmul. And Hulmul begat Augis; and Augis begat him who was called Amal, from whom the name of the Amali comes. Athal begat Achiulf and Oduulf. Now Achiulf begat Ansila and Ediulf, Vultuulf and Ermanaric. This provides the following stemma for the earliest rulers of the Goths, before outlining in more detail the two divisions that arose from the son, Achiulf of Athal, the last in this early lineage : Gapt or Gaut is the Scandinavian god of war. Hulmul or Humli-Hulmul, is considered the divine father of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Germanic Heroic Legend
Germanic heroic legend (german: germanische Heldensage) is the heroic literary tradition of the Germanic-speaking peoples, most of which originates or is set in the Migration Period (4th-6th centuries AD). Stories from this time period, to which others were added later, were transmitted orally, traveled widely among the Germanic speaking peoples, and were known in many variants. These legends typically reworked historical events or personages in the manner of oral poetry, forming a heroic age. Heroes in these legends often display a heroic ethos emphasizing honor, glory, and loyalty above other concerns. Like Germanic mythology, heroic legend is a genre of Germanic folklore. Heroic legends are attested in Anglo-Saxon England, medieval Scandinavia, and medieval Germany. Many take the form of Germanic heroic poetry (german: germanische Heldendichtung): shorter pieces are known as heroic lays, whereas longer pieces are called Germanic heroic epic (). The early Middle Ages preserve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Goths
The Goths ( got, 𐌲𐌿𐍄𐌸𐌹𐌿𐌳𐌰, translit=''Gutþiuda''; la, Gothi, grc-gre, Γότθοι, Gótthoi) were a Germanic people who played a major role in the fall of the Western Roman Empire and the emergence of medieval Europe. In his book '' Getica'' (c. 551), the historian Jordanes writes that the Goths originated in southern Scandinavia, but the accuracy of this account is unclear. A people called the ''Gutones''possibly early Gothsare documented living near the lower Vistula River in the 1st century, where they are associated with the archaeological Wielbark culture. From the 2nd century, the Wielbark culture expanded southwards towards the Black Sea in what has been associated with Gothic migration, and by the late 3rd century it contributed to the formation of the Chernyakhov culture. By the 4th century at the latest, several Gothic groups were distinguishable, among whom the Thervingi and Greuthungi were the most powerful. During this time, Wulfila bega ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vithimiris
Vithimiris was a king of the Greuthungi, ruling for some unspecified time in the area of present-day southern Ukraine. He succeeded to Ermanaric, meaning that he probably reigned in 376. Ammianus Marcellinus, the only known source on him, states that after Ermanaric's death he tried to resist the Alani, who were allied with the Huns, with the help of other Huns hired as mercenaries. He did so "for some time" (), but eventually, "after many defeats" (), he died in battle. It is then assumed that he most probably ruled in 376, possibly also in 375. According to Herwig Wolfram, Vithimiris was "certainly not" the son of Ermanaric. His son Viderichus was too young at that time to rule, so the actual reign was in the hands of Alatheus and Saphrax, his subordinate commanders, as Michael Kulikowski labels them. There is also a parallel story of these events, told by Jordanes, the only other author to mention Ermanaric. However, Jordanes does not know Vithimiris; he narrates that after ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Svanhildr
Svanhild is the beautiful daughter of Sigurd and Gudrun in Germanic heroic legend, whose grisly death at the hands of her jealous royal husband Ermanaric was told in many northern European stories, including the Old Norse ''Poetic Edda'' (''Hamðismál'' and '' Guðrúnarhvöt''), ''Prose Edda'', and ''Völsunga Saga''; the skaldic poem ''Ragnarsdrápa''; the Danish Latin ''Gesta Danorum''; and the German Latin '' Annals of Quedlinburg''. She was "the most beautiful of all women," and was married to Ermanaric (''Jörmunrekkr'') the king of the Goths. She was accused of infidelity with the king's son, Randver. Because of this Ermanaric had her trampled to death under horses. Her mother made her half-brothers Hamdir and Sörli exact revenge for her death, a story which is retold in ''Hamðismál'' and '' Guðrúnarhvöt'', Bragi Boddason's ''Ragnarsdrápa'', in the ''Völsunga saga'' and in ''Gesta Danorum''. Jimmy Joe''Svanhild (Swanhild)'' (Völsunga Saga) ''Norse Myths''. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greuthungi
The Greuthungi (also spelled Greutungi) were a Gothic people who lived on the Pontic steppe between the Dniester and Don rivers in what is now Ukraine, in the 3rd and the 4th centuries. They had close contacts with the Tervingi, another Gothic people, who lived west of the Dniester River. To the east of the Greuthungi, living near the Don river, were the Alans. When the Huns arrived in the European Steppe region in the late 4th century, first the Alans were forced to join them, and then a part of the Greuthungi. Alans and Goths became an important part of Attila's forces, together with other eastern European peoples. Many Greuthungi, together with some Alans and Huns, crossed the Lower Danube to join a large group of Tervingi who had entered the Roman Empire in 376. These peoples defeated an imperial army in the Battle of Adrianople in 378, and came to a settlement agreement within the Roman empire by 382 AD. The original tribal names of the Goths fell out of use within the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oium
Oium was a name for Scythia, or a fertile part of it, roughly in modern Ukraine, where the Goths, under a legendary King Filimer, settled after leaving Gothiscandza, according to the ''Getica'' by Jordanes, written around 551. It is generally assumed that the story reproduced by Jordanes contains a historical core, although several scholars have suggested that parts of it are fictional. Name etymology Jordanes does not give an etymology, but many scholars interpret this word as a dative plural to a noun, widespread in the Germanic languages, whose Proto-Germanic reconstruction is *''awjō'' and which means 'well-watered meadow' or 'island'. (The same noun is also found in ''Scatinauia'', the Latinised name of an island in Northern Europe mentioned in Pliny the Elder's ''Naturalis historia'', from which the names of Scandinavia and Scania originate.) This noun is generally derived from the Proto-Germanic word *''ahwō'' 'water; stream, river' (whence Gothic 'river'), wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tervingi
The Thervingi, Tervingi, or Teruingi (sometimes pluralised Tervings or Thervings) were a Gothic people of the plains north of the Lower Danube and west of the Dniester River in the 3rd and the 4th centuries. They had close contacts with the Greuthungi, another Gothic people from east of the Dniester, as well as the Roman Empire. They were one of the main components of the large movement of Goths and other peoples over the Danube in 376, and they are seen as one of the most important ancestral groups of the Visigoths. Etymology According to a proposal made by Moritz Schönfeld in 1911, and still widely cited, the name ''Tervingi'' was probably related to the Gothic word "''triu''", equivalent to English "tree", and thus means "forest people".Wolfram, ''History of the Goths'', trans. T. J. Dunlop (Berkeley, University of California Press, 1988), p. 25. Herwig Wolfram agrees with the older position of Franz Altheim that such geographical names were used to distinguish Gothic pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Germania
Germania ( ; ), also called Magna Germania (English: ''Great Germania''), Germania Libera (English: ''Free Germania''), or Germanic Barbaricum to distinguish it from the Roman province of the same name, was a large historical region in north-central Europe during the Roman era, which was associated by Roman authors with the Germanic peoples. The region stretched roughly from the Middle and Lower Rhine in the west to the Vistula in the east. It also extended as far south as the Upper and Middle Danube and Pannonia, and to the known parts of Scandinavia in the north. Archaeologically, these peoples correspond roughly to the Roman Iron Age of those regions. While apparently dominated by Germanic peoples, Magna Germania was also inhabited by Celts. The Latin name ''Germania'' means "land of the Germani", but the etymology of the name ''Germani'' itself is uncertain. During the Gallic Wars of the 1st century BC, the Roman general Julius Caesar encountered peoples originating fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexander The Great
Alexander III of Macedon ( grc, Ἀλέξανδρος, Alexandros; 20/21 July 356 BC – 10/11 June 323 BC), commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the ancient Greek kingdom of Macedon. He succeeded his father Philip II to the throne in 336 BC at the age of 20, and spent most of his ruling years conducting a lengthy military campaign throughout Western Asia and Egypt. By the age of thirty, he had created one of the largest empires in history, stretching from Greece to northwestern India. He was undefeated in battle and is widely considered to be one of history's greatest and most successful military commanders. Until the age of 16, Alexander was tutored by Aristotle. In 335 BC, shortly after his assumption of kingship over Macedon, he campaigned in the Balkans and reasserted control over Thrace and Illyria before marching on the city of Thebes, which was subsequently destroyed in battle. Alexander then led the League of Corinth, and used his authori ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
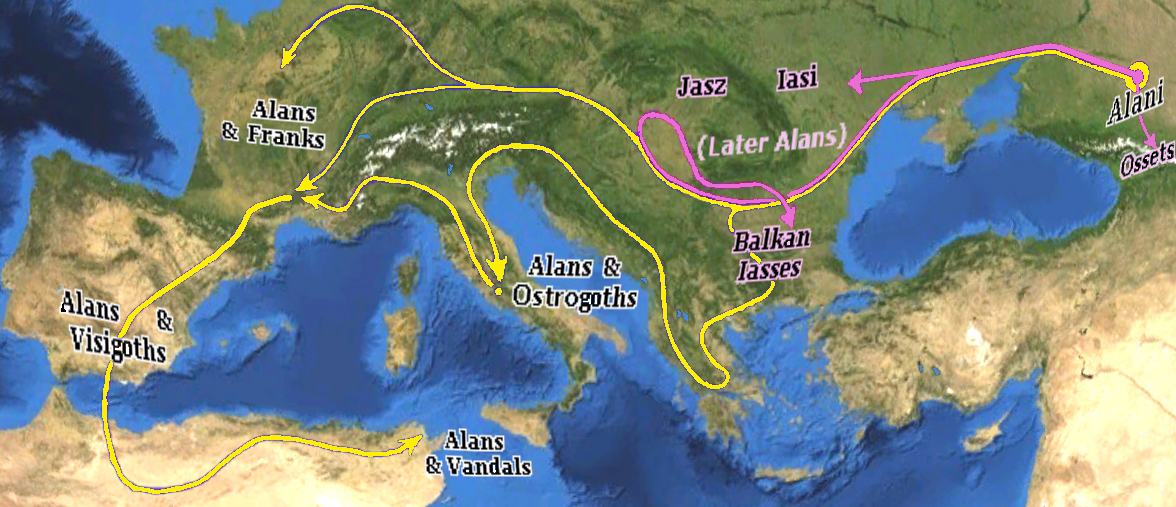
Alans
The Alans (Latin: ''Alani'') were an ancient and medieval Iranian nomadic pastoral people of the North Caucasus – generally regarded as part of the Sarmatians, and possibly related to the Massagetae. Modern historians have connected the Alans with the Central Asian Yancai of Chinese sources and with the Aorsi of Roman sources. Having migrated westwards and becoming dominant among the Sarmatians on the Pontic–Caspian steppe, the Alans are mentioned by Roman sources in the . At that time they had settled the region north of the Black Sea and frequently raided the Parthian Empire and the Caucasian provinces of the Roman Empire. From the Goths broke their power on the Pontic Steppe. Upon the Hunnic defeat of the Goths on the Pontic Steppe around , many of the Alans migrated westwards along with various Germanic tribes. They crossed the Rhine in 406CE along with the Vandals and Suebi, settling in Orléans and Valence. Around 409 CE they joined the Vandals and Suebi i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suicide
Suicide is the act of intentionally causing one's own death. Mental disorders (including depression, bipolar disorder, schizophrenia, personality disorders, anxiety disorders), physical disorders (such as chronic fatigue syndrome), and substance abuse (including alcoholism and the use of and withdrawal from benzodiazepines) are risk factors. Some suicides are impulsive acts due to stress (such as from financial or academic difficulties), relationship problems (such as breakups or divorces), or harassment and bullying. Those who have previously attempted suicide are at a higher risk for future attempts. Effective suicide prevention efforts include limiting access to methods of suicide such as firearms, drugs, and poisons; treating mental disorders and substance abuse; careful media reporting about suicide; and improving economic conditions. Although crisis hotlines are common resources, their effectiveness has not been well studied. The most commonly adopted m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)

.jpg)