|
Voortrekker Fort
Voortrekker Fort/Ohrigstad Fort was constructed before 1847 to act as a refuge for local Voortrekker families due to the constant attacks of local Bantu peoples, Bantu tribes. It is situated in the Ohrigstad area of northern Mpumalanga province which was first settled by Europeans under the leadership of Andries Hendrik Potgieter. History The Voortrekker Fort was built circa. 1847 by early pioneering Voortrekkers in modern day Mpumalanga Province, South Africa. The main purpose of the fortifications were to protect themselves and their families against possible attacks by the local tribes in the general Ohrigstad vicinity. The fort is in the same grounds as the Andries Hendrik Potgieter Gedenksaal. The fort was built using a combination of dry stone walling and mud brick layering with loopholes supported by slate stone lintels, making rifle-fire easier. The site is mostly in ruins today, however it has received Provincial List of heritage sites in Mpumalanga, Heritage status, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ohrigstad
Ohrigstad (Afrikaans for ''Ohrig city''), formerly Andries Orieg Stad, is a small town to the north of Lydenburg in the Limpopo province, South Africa. History A fort was established by a group of Voortrekkers under the leadership of Andries Hendrik Potgieter with the help of a Dutch merchant Gregorius Ohrig. The settlers arrived in 1845 and were soon afterwards decimated by malaria and forced to abandon the area. Settlers only returned once the disease was under control. On the 14 May 1873, the area was proclaimed as a public gold field after the discovery of gold in the Selati River. The Voortrekker, Pieter Willem Prinsloo, who left the Cape between 20 June 1837 and the end of March 1838, registered a farm Dorenhoek in the Ohrigstad area on 16 March 1846.Visagie, Jan C. Voortrekkerstamouers 1835 - 1845. Protea Boekhuis. Pretoria. 2011. Page 406 - 407. Tourism The Echo Caves are situated close to the town. See also *Great trek *Voortrekker Fort *Andries Hendrik Potgieter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
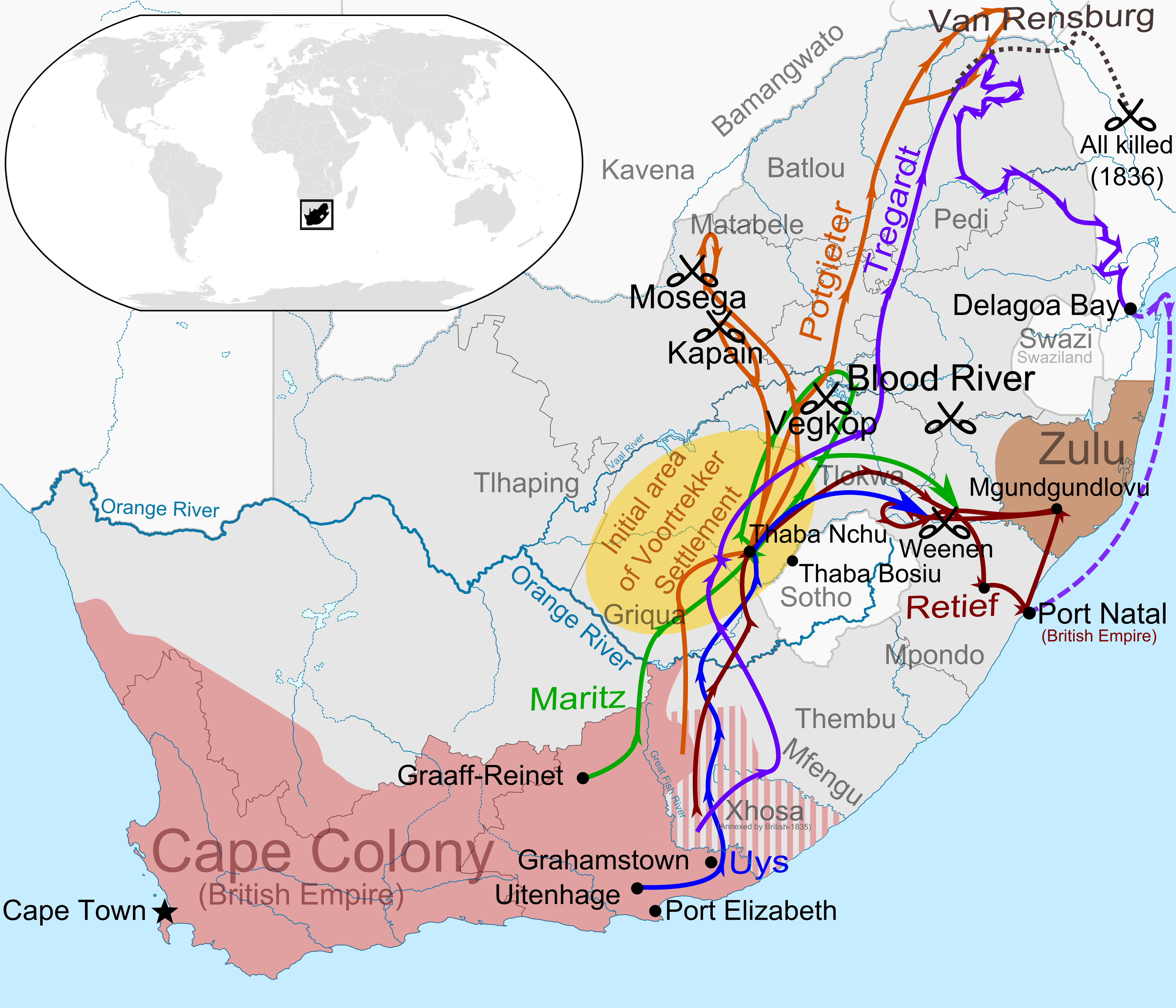
Voortrekker
The Great Trek ( af, Die Groot Trek; nl, De Grote Trek) was a Northward migration of Dutch-speaking settlers who travelled by wagon trains from the Cape Colony into the interior of modern South Africa from 1836 onwards, seeking to live beyond the Cape's British colonial administration. The Great Trek resulted from the culmination of tensions between rural descendants of the Cape's original European settlers, known collectively as ''Boers'', and the British Empire. It was also reflective of an increasingly common trend among individual Boer communities to pursue an isolationist and semi-nomadic lifestyle away from the developing administrative complexities in Cape Town. Boers who took part in the Great Trek identified themselves as ''voortrekkers'', meaning "pioneers", "pathfinders" (literally "fore-trekkers") in Dutch and Afrikaans. The Great Trek led directly to the founding of several autonomous Boer republics, namely the South African Republic (also known simply as the '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Trek
The Great Trek ( af, Die Groot Trek; nl, De Grote Trek) was a Northward migration of Dutch-speaking settlers who travelled by wagon trains from the Cape Colony into the interior of modern South Africa from 1836 onwards, seeking to live beyond the Cape's British colonial administration. The Great Trek resulted from the culmination of tensions between rural descendants of the Cape's original European settlers, known collectively as ''Boers'', and the British Empire. It was also reflective of an increasingly common trend among individual Boer communities to pursue an isolationist and semi-nomadic lifestyle away from the developing administrative complexities in Cape Town. Boers who took part in the Great Trek identified themselves as ''voortrekkers'', meaning "pioneers", "pathfinders" (literally "fore-trekkers") in Dutch and Afrikaans. The Great Trek led directly to the founding of several autonomous Boer republics, namely the South African Republic (also known simply as the '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bantu Peoples
The Bantu peoples, or Bantu, are an ethnolinguistic grouping of approximately 400 distinct ethnic groups who speak Bantu languages. They are native to 24 countries spread over a vast area from Central Africa to Southeast Africa and into Southern Africa. There are several hundred Bantu languages. Depending on the definition of "language" or "dialect", it is estimated that there are between 440 and 680 distinct languages. The total number of speakers is in the hundreds of millions, ranging at roughly 350 million in the mid-2010s (roughly 30% of the population of Africa, or roughly 5% of the total world population). About 60 million speakers (2015), divided into some 200 ethnic or tribal groups, are found in the Democratic Republic of the Congo alone. The larger of the individual Bantu groups have populations of several million, e.g. the people of Rwanda and Burundi (25 million), the Bagandapeople of Uganda (10 million as of 2019), the Shona of Zimbabwe (15 million ), the Zulu of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mpumalanga
Mpumalanga () is a province of South Africa. The name means "East", or literally "The Place Where the Sun Rises" in the Swazi, Xhosa, Ndebele and Zulu languages. Mpumalanga lies in eastern South Africa, bordering Eswatini and Mozambique. It constitutes 6.5% of South Africa's land area. It shares borders with the South African provinces of Limpopo to the north, Gauteng to the west, the Free State to the southwest, and KwaZulu-Natal to the south. The capital is Mbombela. Mpumalanga was formed in 1994, when the area that was the Eastern Transvaal was merged with the former bantustans KaNgwane, KwaNdebele and parts of Lebowa and Gazankulu. Although the contemporary borders of the province were only formed at the end of apartheid, the region and its surroundings has a history that extends back thousands of years. Much of its history, and current significance is as a region of trade. History Precolonial Era Archeological sites in the Mpumalanga region indicate settlement b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Europeans
Europeans are the focus of European ethnology, the field of anthropology related to the various ethnic groups that reside in the states of Europe. Groups may be defined by common genetic ancestry, common language, or both. Pan and Pfeil (2004) count 87 distinct "''peoples of Europe''", of which 33 form the majority population in at least one sovereign state, while the remaining 54 constitute ethnic minorities. The total number of national minority populations in Europe is estimated at 105 million people, or 14% of 770 million Europeans.Christoph Pan, Beate Sibylle Pfeil (2002), Minderheitenrechte in Europa. Handbuch der europäischen Volksgruppen', Braumüller, (Google Books, snippet view). Als2006 reprint by Springer(Amazon, no preview) . The Russians are the most populous among Europeans, with a population of roughly 120 million. There are no universally accepted and precise definitions of the terms " ethnic group" and "nationality". In the context of European ethnography in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andries Hendrik Potgieter
Andries Hendrik Potgieter, known as Hendrik Potgieter (19 December 1792 – 16 December 1852) was a Voortrekker leader and the last known Champion of the Potgieter family. He served as the first head of state of Potchefstroom from 1840 and 1845 and also as the first head of state of Zoutpansberg from 1845 to 1852. Beyond the Orange River Potgieter and his party moved inland to the present Free State, where they signed a treaty with the leader of the Barolong, Moroka. The treaty stipulated that Potgieter would protect the Baralong against the Matabele raiders, in exchange for land. The tract of land was from the Vet River to the Vaal River. The Matabele leader, Mzilikazi, was threatened by the white incursion into what he saw as his sphere of influence, which led to the Matabele's attack on the Potgieter laager in October 1836, at Vegkop, near the present-day town of Heilbron. The attack was beaten off, but the Matabele made off with most of the trekker oxen, crucial draught ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Heritage Sites In Mpumalanga
This is a list of the heritage sites in Mpumalanga as recognized by the South African Heritage Resources Agency. References {{Lists of South African Heritage Resources Tourist attractions in Mpumalanga Mpumalanga Heritage sites A national heritage site is a heritage site having a value that has been registered by a governmental agency as being of national importance to the cultural heritage or history of that country. Usually such sites are listed in a heritage regist ... Lime kilns in South Africa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Trek
The Great Trek ( af, Die Groot Trek; nl, De Grote Trek) was a Northward migration of Dutch-speaking settlers who travelled by wagon trains from the Cape Colony into the interior of modern South Africa from 1836 onwards, seeking to live beyond the Cape's British colonial administration. The Great Trek resulted from the culmination of tensions between rural descendants of the Cape's original European settlers, known collectively as ''Boers'', and the British Empire. It was also reflective of an increasingly common trend among individual Boer communities to pursue an isolationist and semi-nomadic lifestyle away from the developing administrative complexities in Cape Town. Boers who took part in the Great Trek identified themselves as ''voortrekkers'', meaning "pioneers", "pathfinders" (literally "fore-trekkers") in Dutch and Afrikaans. The Great Trek led directly to the founding of several autonomous Boer republics, namely the South African Republic (also known simply as the '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |