|
Volkert Simon Maarten Van Der Willigen (KNAW)
Volkert Simon Maarten van der Willigen (Rockanje, 9 May 1822 – Haarlem, 19 February 1878), sometimes referred to as Volcardus Simon Martinus van der Willigen, was a Dutch mathematician, physicist and professor.Biografisch Portaal van Nederland on Van der Willigen (Dutch)P.C. Molhuysen en P.J. Blok (red.) Nieuw Nederlandsch Biografisch Woordenboek (NNBW) Deel 10. A.W. Sijthoff, Leiden 1937 – p.1219, F.J.Hoogeveen (Dutch) Life Volkert was son of the minister (Christianity), minister Johannes van der Willigen (1777–1857) and his wife Gerarde Maria Elsabé Bodde (1795–1865). He was the ne ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volkert Simon Maarten Van Der Willigen (KNAW)
Volkert Simon Maarten van der Willigen (Rockanje, 9 May 1822 – Haarlem, 19 February 1878), sometimes referred to as Volcardus Simon Martinus van der Willigen, was a Dutch mathematician, physicist and professor.Biografisch Portaal van Nederland on Van der Willigen (Dutch)P.C. Molhuysen en P.J. Blok (red.) Nieuw Nederlandsch Biografisch Woordenboek (NNBW) Deel 10. A.W. Sijthoff, Leiden 1937 – p.1219, F.J.Hoogeveen (Dutch) Life Volkert was son of the minister (Christianity), minister Johannes van der Willigen (1777–1857) and his wife Gerarde Maria Elsabé Bodde (1795–1865). He was the ne ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anders Ångström
Anders is a male name in Scandinavian languages and Fering North Frisian, an equivalent of the Greek Andreas ("manly") and the English Andrew. It originated from Andres via metathesis. In Sweden, Anders has been one of the most common names for many centuries, earliest attested in 1378. It was common for priests and farmers during medieval times. According to Statistics Sweden, as of 31 December 2002 it ranks 4th among the male names. The great frequency of this name at the point in time (around 1900) when patronymics were converted into family names is the reason why 1 out of every 30 Swedes today is called Andersson. The name day of Anders in the Scandinavian calendar is 30 November, and in the old peasant superstition that day was important for determining what the Christmas weather would be. If it was very cold on 30 November there would be much sleet on Christmas (and vice versa). In Denmark Donald Duck's name is ''Anders And''. The Fering name Anders may have been bor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
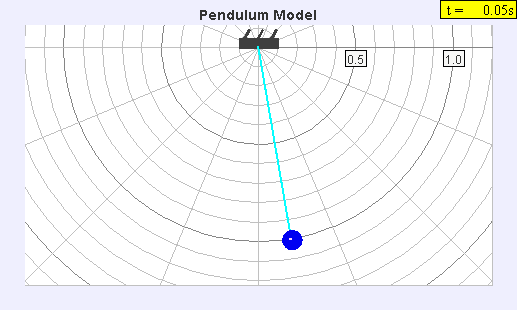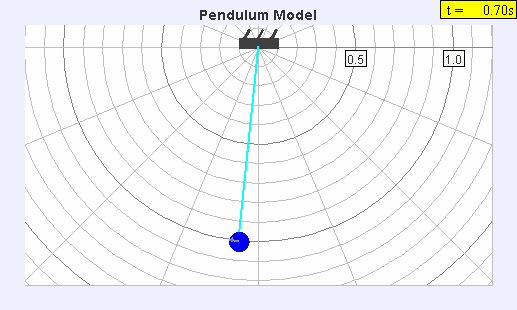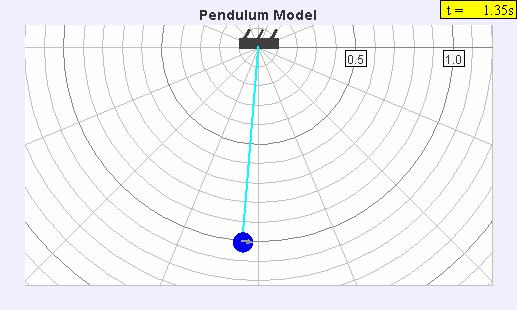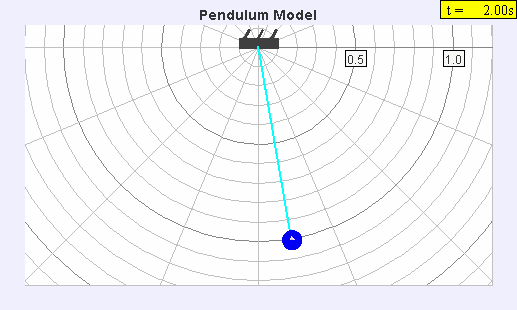
Seconds Pendulum
A seconds pendulum is a pendulum whose period is precisely two seconds; one second for a swing in one direction and one second for the return swing, a frequency of 0.5 Hz. Pendulum A pendulum is a weight suspended from a pivot so that it can swing freely. When a pendulum is displaced sideways from its resting equilibrium position, it is subject to a restoring force due to gravity that will accelerate it back toward the equilibrium position. When released, the restoring force combined with the pendulum's mass causes it to oscillate about the equilibrium position, swinging back and forth. The time for one complete cycle, a left swing and a right swing, is called the period. The period depends on the length of the pendulum, and also to a slight degree on its weight distribution (the moment of inertia about its own center of mass) and the amplitude (width) of the pendulum's swing. For a point mass on a weightless string of length ''L'' swinging with an infinitesimally small ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barometer
A barometer is a scientific instrument that is used to measure air pressure in a certain environment. Pressure tendency can forecast short term changes in the weather. Many measurements of air pressure are used within surface weather analysis to help find surface troughs, pressure systems and frontal boundaries. Barometers and pressure altimeters (the most basic and common type of altimeter) are essentially the same instrument, but used for different purposes. An altimeter is intended to be used at different levels matching the corresponding atmospheric pressure to the altitude, while a barometer is kept at the same level and measures subtle pressure changes caused by weather and elements of weather. The average atmospheric pressure on the earth's surface varies between 940 and 1040 hPa (mbar). The average atmospheric pressure at sea level is 1013 hPa (mbar). Etymology The word ''barometer'' is derived from the Ancient Greek (), meaning "weight", and (), meaning "measure ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermometer
A thermometer is a device that temperature measurement, measures temperature or a temperature gradient (the degree of hotness or coldness of an object). A thermometer has two important elements: (1) a temperature sensor (e.g. the bulb of a mercury-in-glass thermometer or the pyrometric sensor in an infrared thermometer) in which some change occurs with a change in temperature; and (2) some means of converting this change into a numerical value (e.g. the visible scale that is marked on a mercury-in-glass thermometer or the digital readout on an infrared model). Thermometers are widely used in technology and industry to monitor processes, in meteorology, in medicine, and in scientific research. History While an individual thermometer is able to measure degrees of hotness, the readings on two thermometers cannot be compared unless they conform to an agreed scale. Today there is an absolute thermodynamic temperature scale. Internationally agreed temperature scales are designed to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weighing Scale
A scale or balance is a device used to measure weight or mass. These are also known as mass scales, weight scales, mass balances, and weight balances. The traditional scale consists of two plates or bowls suspended at equal distances from a fulcrum. One plate holds an object of unknown mass (or weight), while known masses are added to the other plate until static equilibrium is achieved and the plates level off, which happens when the masses on the two plates are equal. The perfect scale rests at neutral. A spring scale will make use of a spring of known stiffness to determine mass (or weight). Suspending a certain mass will extend the spring by a certain amount depending on the spring's stiffness (or spring constant). The heavier the object, the more the spring stretches, as described in Hooke's law. Other types of scales making use of different physical principles also exist. Some scales can be calibrated to read in units of force (weight) such as newtons instead of unit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Micrometer (device)
A micrometer, sometimes known as a micrometer screw gauge, is a device incorporating a calibrated screw widely used for accurate measurement of components in mechanical engineering and machining as well as most mechanical trades, along with other metrological instruments such as dial, vernier, and digital calipers. Micrometers are usually, but not always, in the form of calipers (opposing ends joined by a frame). The spindle is a very accurately machined screw and the object to be measured is placed between the spindle and the anvil. The spindle is moved by turning the ratchet knob or thimble until the object to be measured is lightly touched by both the spindle and the anvil. Micrometers are also used in telescopes or microscopes to measure the apparent diameter of celestial bodies or microscopic objects. The micrometer used with a telescope was invented about 1638 by William Gascoigne, an English astronomer. History The word ''micrometer'' is a neoclassical coinage ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
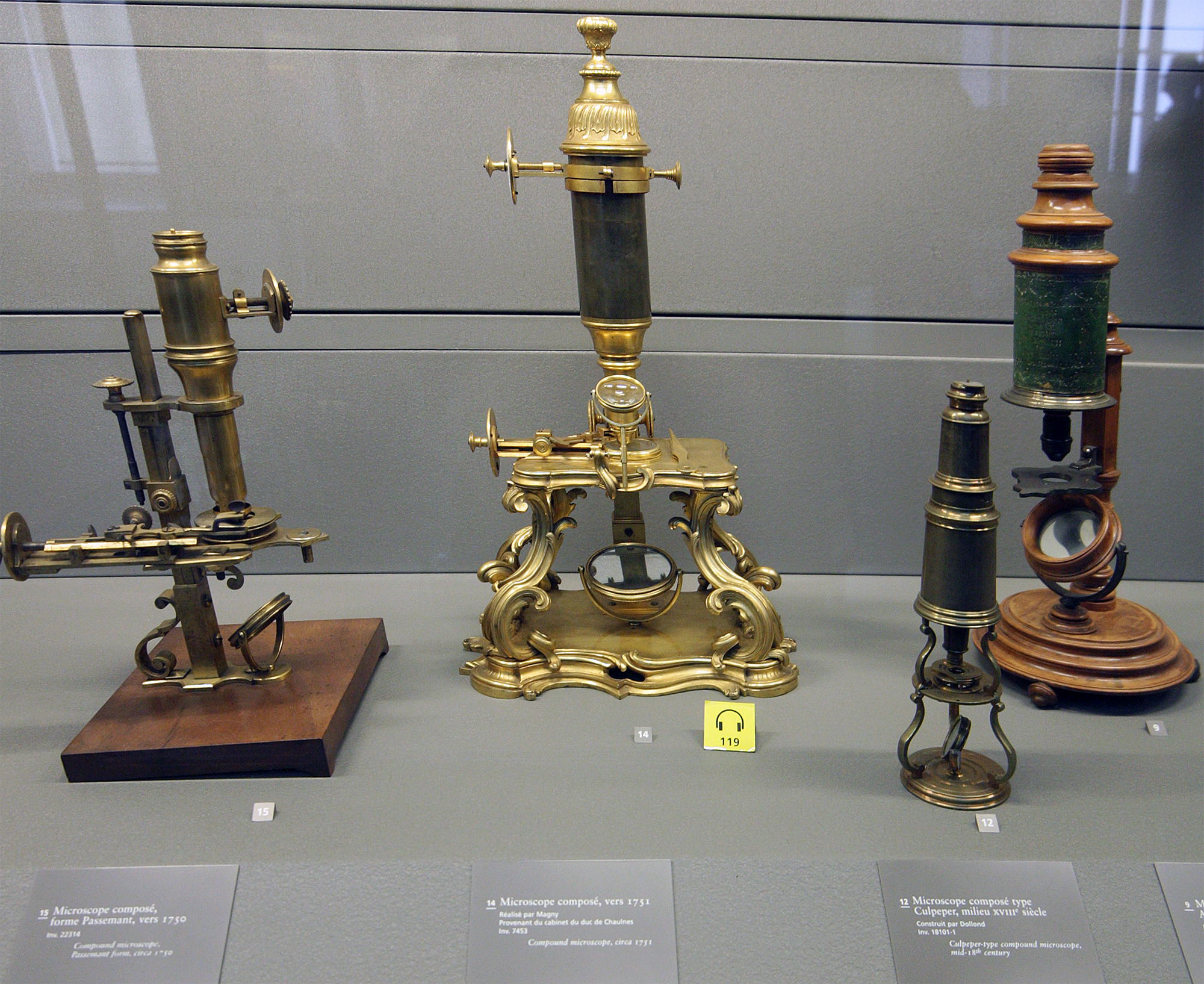
Microscope
A microscope () is a laboratory instrument used to examine objects that are too small to be seen by the naked eye. Microscopy is the science of investigating small objects and structures using a microscope. Microscopic means being invisible to the eye unless aided by a microscope. There are many types of microscopes, and they may be grouped in different ways. One way is to describe the method an instrument uses to interact with a sample and produce images, either by sending a beam of light or electrons through a sample in its optical path, by detecting photon emissions from a sample, or by scanning across and a short distance from the surface of a sample using a probe. The most common microscope (and the first to be invented) is the optical microscope, which uses lenses to refract visible light that passed through a thinly sectioned sample to produce an observable image. Other major types of microscopes are the fluorescence microscope, electron microscope (both the transmi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diffraction Grating
In optics, a diffraction grating is an optical component with a periodic structure that diffracts light into several beams travelling in different directions (i.e., different diffraction angles). The emerging coloration is a form of structural coloration. The directions or diffraction angles of these beams depend on the wave (light) incident angle to the diffraction grating, the spacing or distance between adjacent diffracting elements (e.g., parallel slits for a transmission grating) on the grating, and the wavelength of the incident light. The grating acts as a dispersive element. Because of this, diffraction gratings are commonly used in monochromators and spectrometers, but other applications are also possible such as optical encoders for high precision motion control and wavefront measurement. For typical applications, a reflective grating has ridges or ''rulings'' on its surface while a transmissive grating has transmissive or hollow slits on its surface. Such a grating ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spectroscope
An optical spectrometer (spectrophotometer, spectrograph or spectroscope) is an instrument used to measure properties of light over a specific portion of the electromagnetic spectrum, typically used in spectroscopic analysis to identify materials. The variable measured is most often the light's intensity but could also, for instance, be the polarization state. The independent variable is usually the wavelength of the light or a unit directly proportional to the photon energy, such as reciprocal centimeters or electron volts, which has a reciprocal relationship to wavelength. A spectrometer is used in spectroscopy for producing spectral lines and measuring their wavelengths and intensities. Spectrometers may operate over a wide range of non-optical wavelengths, from gamma rays and X-rays into the far infrared. If the instrument is designed to measure the spectrum on an absolute scale rather than a relative one, then it is typically called a spectrophotometer. The majority o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heliostat
A heliostat (from ''helios'', the Greek word for ''sun'', and ''stat'', as in stationary) is a device that includes a mirror, usually a plane mirror, which turns so as to keep reflecting sunlight toward a predetermined target, compensating for the sun's apparent motions in the sky. The target may be a physical object, distant from the heliostat, or a direction in space. To do this, the reflective surface of the mirror is kept perpendicular to the bisector of the angle between the directions of the sun and the target as seen from the mirror. In almost every case, the target is stationary relative to the heliostat, so the light is reflected in a fixed direction. According to contemporary sources the heliostata, as it was called at first, was invented by Willem 's Gravesande (1688–1742). Other contenders are Giovanni Alfonso Borelli (1608–1679) and Daniel Gabriel Fahrenheit (1686–1736). A Heliostat designed by George Johnstone Storey is in the Science Museum Group collec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astronomical Regulator
A pendulum clock is a clock that uses a pendulum, a swinging weight, as its timekeeping element. The advantage of a pendulum for timekeeping is that it is a harmonic oscillator: It swings back and forth in a precise time interval dependent on its length, and resists swinging at other rates. From its invention in 1656 by Christiaan Huygens, inspired by Galileo Galilei, until the 1930s, the pendulum clock was the world's most precise timekeeper, accounting for its widespread use. Throughout the 18th and 19th centuries, pendulum clocks in homes, factories, offices, and railroad stations served as primary time standards for scheduling daily life, work shifts, and public transportation. Their greater accuracy allowed for the faster pace of life which was necessary for the Industrial Revolution. The home pendulum clock was replaced by less-expensive, synchronous, electric clocks in the 1930s and '40s. Pendulum clocks are now kept mostly for their decorative and antique value. Pend ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |