|
Volcano Plot
Volcano plot may refer to: * Sabatier principle - a concept in chemical catalysis that relates the optimal concentrations of catalysts and substrates * Volcano plot (statistics) - a type of graph used to relate fold-change to p-value that is commonly used in genomics and other List_of_omics_topics_in_biology, omic experiments involving thousands of data-points {{disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
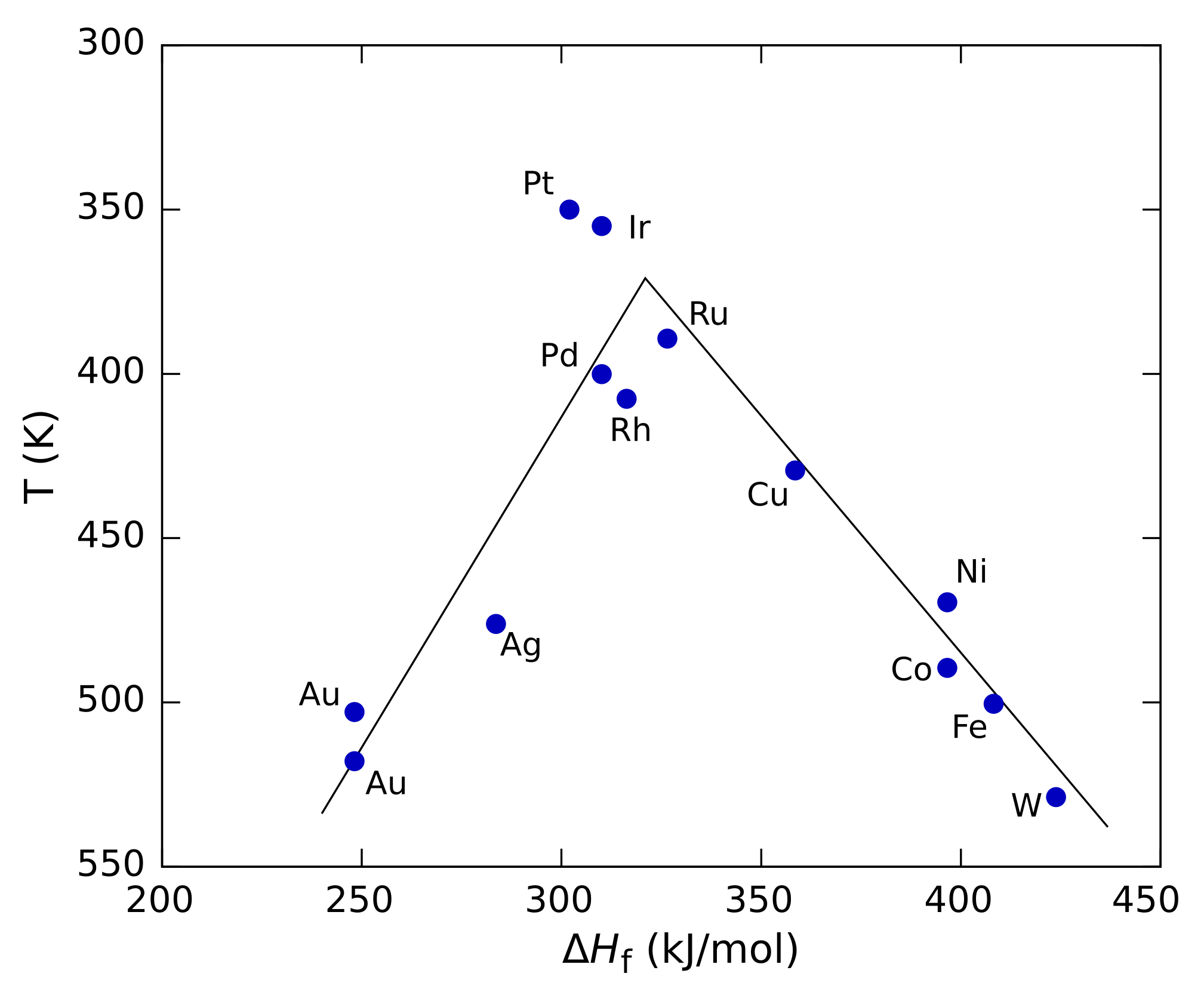
Sabatier Principle
The Sabatier principle is a qualitative concept in chemical heterogeneous catalysis named after the French chemist Paul Sabatier. It states that the interactions between the catalyst and the substrate should be "just right"; that is, neither too strong nor too weak. If the interaction is too weak, the molecule will fail to bind to the catalyst and no reaction will take place. On the other hand, if the interaction is too strong, the product fails to dissociate. The principle can be shown graphically by plotting the reaction rate against a property such as the heat of adsorption of the reactant by the catalyst. Such plots pass through a maximum, looking roughly like a triangle or an inverted parabola, and are called volcano plots because of their shape. Analogous three-dimensional plots can also be built against two different properties, such as the heats of adsorption of the two reactants for a two-component reaction. In that case the plot is generally shown as a contour plot and i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volcano Plot (statistics)
In statistics, a volcano plot is a type of scatter-plot that is used to quickly identify changes in large data sets composed of replicate data. It plots significance versus fold-change on the y and x axes, respectively. These plots are increasingly common in omic experiments such as genomics, proteomics, and metabolomics where one often has a list of many thousands of replicate data points between two conditions and one wishes to quickly identify the most meaningful changes. A volcano plot combines a measure of statistical significance from a statistical test (e.g., a p value from an ANOVA model) with the magnitude of the change, enabling quick visual identification of those data-points (genes, etc.) that display large magnitude changes that are also statistically significant. A volcano plot is constructed by plotting the negative logarithm of the p value on the y axis (usually base 10). This results in data points with low p values (highly significant) appearing toward the t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
P-value
In null-hypothesis significance testing, the ''p''-value is the probability of obtaining test results at least as extreme as the result actually observed, under the assumption that the null hypothesis is correct. A very small ''p''-value means that such an extreme observed outcome would be very unlikely under the null hypothesis. Reporting ''p''-values of statistical tests is common practice in academic publications of many quantitative fields. Since the precise meaning of ''p''-value is hard to grasp, misuse is widespread and has been a major topic in metascience. Basic concepts In statistics, every conjecture concerning the unknown probability distribution of a collection of random variables representing the observed data X in some study is called a ''statistical hypothesis''. If we state one hypothesis only and the aim of the statistical test is to see whether this hypothesis is tenable, but not to investigate other specific hypotheses, then such a test is called a null ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genomics
Genomics is an interdisciplinary field of biology focusing on the structure, function, evolution, mapping, and editing of genomes. A genome is an organism's complete set of DNA, including all of its genes as well as its hierarchical, three-dimensional structural configuration. In contrast to genetics, which refers to the study of ''individual'' genes and their roles in inheritance, genomics aims at the collective characterization and quantification of ''all'' of an organism's genes, their interrelations and influence on the organism. Genes may direct the production of proteins with the assistance of enzymes and messenger molecules. In turn, proteins make up body structures such as organs and tissues as well as control chemical reactions and carry signals between cells. Genomics also involves the sequencing and analysis of genomes through uses of high throughput DNA sequencing and bioinformatics to assemble and analyze the function and structure of entire genomes. Advances in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |