|
Villa González Ortega
Villa González Ortega is a municipality in the Mexican state of Zacatecas, located approximately southeast of the state capital of Zacatecas City. It is named after Jesús González Ortega. Geography The municipality of Villa González Ortega is located at an elevation between on the Mexican Plateau in southeastern Zacatecas. It borders the Zacatecan municipalities of Noria de Ángeles to the south, Ojocaliente to the southwest, and General Pánfilo Natera to the northwest. It also borders the municipalities of Villa de Ramos and Salinas in the state of San Luis Potosí to the north and east respectively. The municipality covers an area of and comprises 0.6% of the state's area. As of 2009, 45.7% of the land in Villa González Ortega is used for agriculture. The remainder of the land comprises matorral (51.8%), urban areas (1.3%), and grassland (1.0%). The municipality lies in the endorheic basin of El Salado. Its generally flat terrain is interrupted by small hills and pla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Municipalities Of Mexico
Municipalities (''municipios'' in Spanish language, Spanish) are the second-level administrative divisions of Mexico, where the first-level administrative division is the ''states of Mexico, state'' (Spanish: estado). They should not be confused with cities or towns that may share the same name as they are distinct entities and do not share geographical boundaries. As of January 2021, there are 2,454 municipalities in Mexico, excluding the 16 Boroughs of Mexico City, boroughs of Mexico City. Since the 2015 Intercensal Survey, two municipalities have been created in Campeche, three in Chiapas, three in Morelos, one in Quintana Roo and one in Baja California. The internal political organization and their responsibilities are outlined in the 115th article of the Constitution of Mexico, 1917 Constitution and detailed in the constitutions of the states to which they belong. are distinct from , a form of Mexican Localities of Mexico, locality, and are divided into ''Colonia (Mexico ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Villa De Ramos
Villa de Ramos is a municipio or municipality to the northwest of San Luis Potosi, Mexico History The foundation of Villa de Ramos is attributed to Fr. Jeronimo de Pangua. A rich mine was discovered around this place in the year 1608 and the population settled until 1610. In 1612, a church was built but later destroyed due to the discovery of a rich mine. A few years later, silver and other minerals extracted from this place were exhausting and exploration projects were halted. Gradually, the y indigenous people coming from the northern region. During 1794, a few mines were being exploited on that place, the biggest was Don Juan de Dious Galindo's San Vicente. Days later, a fabulous discovery was made, one inhabitant of the place was digging on his kitchen, he gathered a certain amount of grains of native silver. During Mexico's War of Independence, Villa de Ramos was again declining in terms of population. El Real de Ramos, as it was called at that time, lay on ruins and va ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Camino Real De Tierra Adentro
The Camino Real de Tierra Adentro ( en, Royal Road of the Interior Land), also known as the Silver Route, was a Spanish road between Mexico City and San Juan Pueblo (''Ohkay Owingeh''), New Mexico, USA, that was used from 1598 to 1882. It was the northernmost of the four major "royal roads" that linked Mexico City to its major tributaries during and after the Spanish colonial era. In 2010, 55 sites and five existing UNESCO World Heritage Sites along the Mexican section of the route were collectively added to the World Heritage List, including historic cities, towns, bridges, haciendas and other monuments along the route between the Historic Center of Mexico City (an independent World Heritage Site) and the town of Valle de Allende, Chihuahua. The section of the route within the United States was proclaimed the El Camino Real de Tierra Adentro National Historic Trail, a part of the National Historic Trail system, on October 13, 2000. The historic route is overseen by both t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World Heritage Site
A World Heritage Site is a landmark or area with legal protection by an international convention administered by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO). World Heritage Sites are designated by UNESCO for having cultural, historical, scientific or other form of significance. The sites are judged to contain " cultural and natural heritage around the world considered to be of outstanding value to humanity". To be selected, a World Heritage Site must be a somehow unique landmark which is geographically and historically identifiable and has special cultural or physical significance. For example, World Heritage Sites might be ancient ruins or historical structures, buildings, cities, deserts, forests, islands, lakes, monuments, mountains, or wilderness areas. A World Heritage Site may signify a remarkable accomplishment of humanity, and serve as evidence of our intellectual history on the planet, or it might be a place of great natural beauty. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization is a specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) aimed at promoting world peace and security through international cooperation in education, arts, sciences and culture. It has 193 member states and 12 associate members, as well as partners in the non-governmental, intergovernmental and private sector. Headquartered at the World Heritage Centre in Paris, France, UNESCO has 53 regional field offices and 199 national commissions that facilitate its global mandate. UNESCO was founded in 1945 as the successor to the League of Nations's International Committee on Intellectual Cooperation.English summary). Its constitution establishes the agency's goals, governing structure, and operating framework. UNESCO's founding mission, which was shaped by the Second World War, is to advance peace, sustainable development and human rights by facilitating collaboration and dialogue among nations. It pursues this objective t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hacienda
An ''hacienda'' ( or ; or ) is an estate (or ''finca''), similar to a Roman ''latifundium'', in Spain and the former Spanish Empire. With origins in Andalusia, ''haciendas'' were variously plantations (perhaps including animals or orchards), mines or factories, with many ''haciendas'' combining these activities. The word is derived from Spanish ''hacer'' (to make, from Latin ''facere'') and ''haciendo'' (making), referring to productive business enterprises. The term ''hacienda'' is imprecise, but usually refers to landed estates of significant size, while smaller holdings were termed ''estancias'' or ''ranchos''. All colonial ''haciendas'' were owned almost exclusively by Spaniards and criollos, or rarely by mestizo individuals. In Mexico, as of 1910, there were 8,245 haciendas in the country. In Argentina, the term ''estancia'' is used for large estates that in Mexico would be termed ''haciendas''. In recent decades, the term has been used in the United States for an archi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
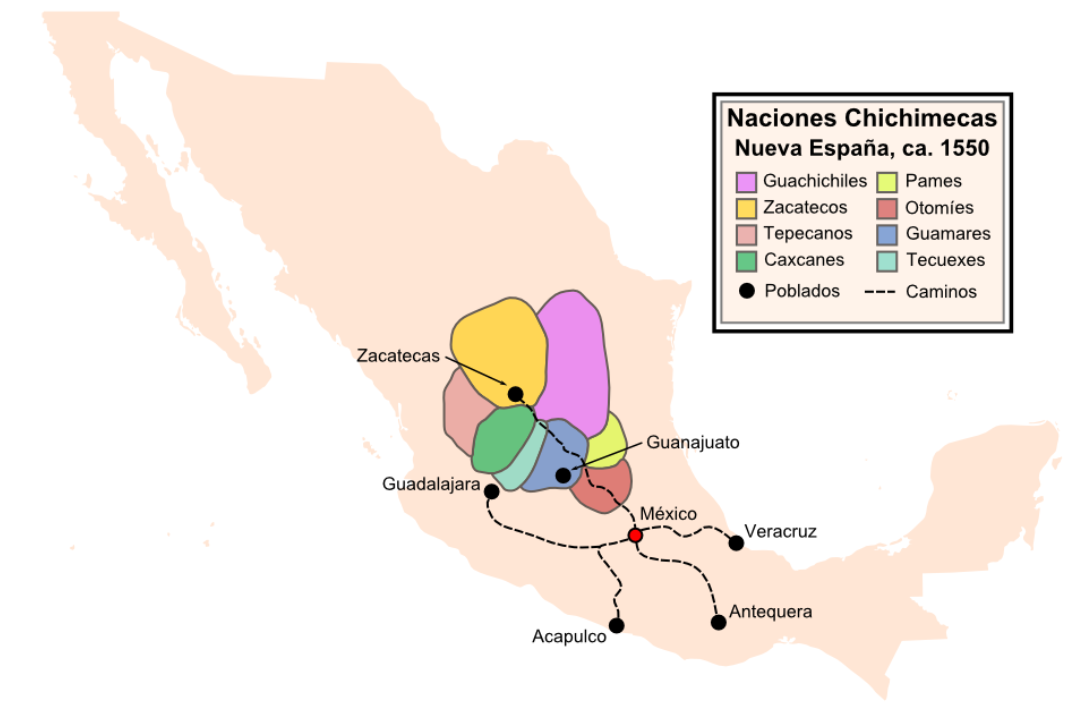
Chichimeca
Chichimeca () is the name that the Nahua peoples of Mexico generically applied to nomadic and semi-nomadic peoples who were established in present-day Bajio region of Mexico. Chichimeca carried the meaning as the Roman term "barbarian" that described Germanic tribes. The name, with its pejorative sense, was adopted by the Spanish Empire. For the Spanish, in the words of scholar Charlotte M. Gradie, "the Chichimecas were a wild, nomadic people who lived north of the Valley of Mexico. They had no fixed dwelling places, lived by hunting, wore little clothes and fiercely resisted foreign intrusion into their territory, which happened to contain silver mines the Spanish wished to exploit." In spite of not having temples or idols, they practiced animal sacrifice, and they were feared for their expertise and brutality in war. The Spanish invasion resulted in a "drastic population decline of all the peoples known collectively as Chichimecas, and to the eventual disappearance as peoples ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guachichil
The Guachichil, Cuauchichil, or Quauhchichitl, are an Indigenous people of Mexico. Pre-contact, they occupied the most extensive territory of all the indigenous Chichimeca Nations tribes in pre-Columbian Central Mexico. The Guachichiles roamed through a large region of Zacatecas; as well as portions of San Luis Potosí, Guanajuato, and northeastern Jalisco; south to the northern corners of Michoacán; and north to Saltillo in Coahuila. The Guachichil Nation continues to exist in the city of San Luis Potosi, San Luis Potosi, Mexico, and is recognized by the city and state. They have tribal members in Mexico and the United States. History Considered both warlike and brave, the Guachichiles played a major role in provoking the other Chichimeca tribes to resist the Spanish settlement. The historian Philip Wayne Powell wrote: :::" ''Their strategic position in relation to Spanish mines and highways, made them especially effective in raiding and in escape from Spanish reprisal''." ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Servicio Meteorológico Nacional (Mexico)
The Servicio Meteorológico Nacional (SMN) is Mexico's national weather organization. It collects data and issues forecasts, advisories, and warnings for the entire country. History A presidential decree founded El Observatorio Meteorológico y Astrónomico de México (The Meteorological and Astronomical Observatory of Mexico) on February 6, 1877 as part of the Geographic Exploring of the National Territory commission. By 1880, it became an independent agency located at Chapultepec Castle, then encompassing six observatories. In 1901, the Servicio Meteorologia Nacional was formed with 31 sections for each state and 18 independent observatories which reported back to the central office in Tacubaya via telegraph. It joined the World Meteorological Organization in 1947. By 1980, the organization included 72 observatories, of which eight launched weather balloons and radiosondes, and five radars serviced the country. In 1989, it became a subagency of the General de Administracion d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
INAFED {{R from other capitalisation ...
#REDIRECT Instituto Nacional para el Federalismo y el Desarrollo Municipal #REDIRECT Instituto Nacional para el Federalismo y el Desarrollo Municipal #REDIRECT Instituto Nacional para el Federalismo y el Desarrollo Municipal {{R from other capitalisation ... {{R from other capitalisation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Llanos El Salado
{{Short description, Endorheic basin in Mexico Llanos el Salado is a large endorheic basin of central Mexico. It is located on the Mexican Plateau, and covers portions of several Mexican states, including eastern and northeastern Zacatecas, Northern San Luis Potosí, western Tamaulipas, southwestern Nuevo León, and southeastern Coahuila. El Salado blends into the Bolsón de Mapimí, another endorheic basin, on the north. The basin has an arid climate and is covered by deserts and xeric shrublands. Mexico's National Institute of Statistics and Geography (INEGI) divides the Llanos el Salado region into several basins: * Fresnillo-Yesca * Matehuala * Presa San José-Los Pilares y Otras * San Pablo y Otras * Sierra Madre * Sierra Madre Oriental * Sierra de Rodriguez References * Olson, D., Dinerstein, E., Canevari, P., Davidson, I., Castro, G., Morisset, V., Abell, R., and Toledo, E.; eds. (1998). ''Freshwater biodiversity of Latin America and the Caribbean: A conservation assessm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endorheic Basin
An endorheic basin (; also spelled endoreic basin or endorreic basin) is a drainage basin that normally retains water and allows no outflow to other external bodies of water, such as rivers or oceans, but drainage converges instead into lakes or swamps, permanent or seasonal, that equilibrate through evaporation. They are also called closed or terminal basins, internal drainage systems, or simply basins. Endorheic regions contrast with exorheic regions. Endorheic water bodies include some of the largest lakes in the world, such as the Caspian Sea, the world's largest inland body of water. Basins with subsurface outflows which eventually lead to the ocean are generally not considered endorheic; they are cryptorheic. Endorheic basins constitute local base levels, defining a limit of erosion and deposition processes of nearby areas. Etymology The term was borrowed from French ''endor(rh)éisme'', coined from the combining form ''endo-'' (from grc, ἔνδον ''éndon'' 'wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |