|
Vibrio Anguillarum
''Vibrio anguillarum'' is a species of Gram-negative bacteria with a curved-rod shape and one polar flagellum. It is damaging to the economy of aquaculture sector and fishing industries. See also * '' Vibrio fischerii'' * ''Vibrio harveyi'' * '' Vibrio ordalii'' * '' Vibrio tubiashii'' * ''Vibrio vulnificus'' * Serotype * Virulence Virulence is a pathogen's or microorganism's ability to cause damage to a host. In most, especially in animal systems, virulence refers to the degree of damage caused by a microbe to its host. The pathogenicity of an organism—its ability to ca ... References External linksType strain of ''Vibrio anguillarum'' at Bac''Dive'' - the Bacterial Diversity Metadatabase {{Taxonbar, from=Q7924678 Vibrionales Bacterial diseases of fish Bacteria described in 1854 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gram-negative Bacteria
Gram-negative bacteria are bacteria that do not retain the crystal violet stain used in the Gram staining method of bacterial differentiation. They are characterized by their cell envelopes, which are composed of a thin peptidoglycan cell wall sandwiched between an inner cytoplasmic cell membrane and a bacterial outer membrane. Gram-negative bacteria are found in virtually all environments on Earth that support life. The gram-negative bacteria include the model organism ''Escherichia coli'', as well as many pathogenic bacteria, such as ''Pseudomonas aeruginosa'', '' Chlamydia trachomatis'', and ''Yersinia pestis''. They are a significant medical challenge as their outer membrane protects them from many antibiotics (including penicillin), detergents that would normally damage the inner cell membrane, and lysozyme, an antimicrobial enzyme produced by animals that forms part of the innate immune system. Additionally, the outer leaflet of this membrane comprises a complex lipopol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacteria
Bacteria (; singular: bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one biological cell. They constitute a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria were among the first life forms to appear on Earth, and are present in most of its habitats. Bacteria inhabit soil, water, acidic hot springs, radioactive waste, and the deep biosphere of Earth's crust. Bacteria are vital in many stages of the nutrient cycle by recycling nutrients such as the fixation of nitrogen from the atmosphere. The nutrient cycle includes the decomposition of dead bodies; bacteria are responsible for the putrefaction stage in this process. In the biological communities surrounding hydrothermal vents and cold seeps, extremophile bacteria provide the nutrients needed to sustain life by converting dissolved compounds, such as hydrogen sulphide and methane, to energy. Bacteria also live in symbiotic and parasitic relationsh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flagellum
A flagellum (; ) is a hairlike appendage that protrudes from certain plant and animal sperm cells, and from a wide range of microorganisms to provide motility. Many protists with flagella are termed as flagellates. A microorganism may have from one to many flagella. A gram-negative bacterium ''Helicobacter pylori'' for example uses its multiple flagella to propel itself through the mucus lining to reach the stomach epithelium, where it may cause a gastric ulcer to develop. In some bacteria the flagellum can also function as a sensory organelle, being sensitive to wetness outside the cell. Across the three domains of Bacteria, Archaea, and Eukaryota the flagellum has a different structure, protein composition, and mechanism of propulsion but shares the same function of providing motility. The Latin word means " whip" to describe its lash-like swimming motion. The flagellum in archaea is called the archaellum to note its difference from the bacterial flagellum. Eukaryotic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
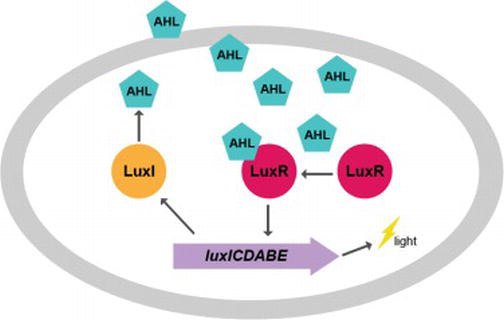
Aliivibrio Fischeri
''Aliivibrio fischeri'' (also called ''Vibrio fischeri'') is a Gram-negative, rod-shaped bacterium found globally in marine environments. This species has bioluminescent properties, and is found predominantly in symbiosis with various marine animals, such as the Hawaiian bobtail squid. It is heterotrophic, oxidase-positive, and motile by means of a single polar flagella. Free-living ''A. fischeri'' cells survive on decaying organic matter. The bacterium is a key research organism for examination of microbial bioluminescence, quorum sensing, and bacterial-animal symbiosis. It is named after Bernhard Fischer, a German microbiologist. Ribosomal RNA comparison led to the reclassification of this species from genus ''Vibrio'' to the newly created ''Aliivibrio'' in 2007. However, the name change is not generally accepted by most researchers, who still publish ''Vibrio fischeri'' (see Google Scholar for 2018-2019). Genome The genome for ''A. fischeri'' was completely sequenced i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vibrio Harveyi
''Vibrio harveyi'' is a Gram-negative, bioluminescent, marine bacterium in the genus ''Vibrio''. ''V. harveyi'' is rod-shaped, motile (via polar flagella), facultatively anaerobic, halophilic, and competent for both fermentative and respiratory metabolism. It does not grow below 4 °C ( optimum growth: 30° to 35 °C). ''V. harveyi'' can be found free-swimming in tropical marine waters, commensally in the gut microflora of marine animals, and as both a primary and opportunistic pathogen of marine animals, including Gorgonian corals, oysters, prawns, lobsters, the common snook, barramundi, turbot, milkfish, and seahorses. It is responsible for luminous vibriosis, a disease that affects commercially farmed penaeid prawns. Additionally, based on samples taken by ocean-going ships, ''V. harveyi'' is thought to be the cause of the milky seas effect, in which, during the night, a uniform blue glow is emitted from the seawater. Some glows can cover nearly . Quorum sen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vibrio Ordalii
''Vibrio ordalii'' is a Gram-negative, rod-shaped bacterium. It causes vibriosis ''Vibrio'' is a genus of Gram-negative bacteria, possessing a curved-rod (comma) shape, several species of which can cause foodborne infection, usually associated with eating undercooked seafood. Being highly salt tolerant and unable to survive ... in fish. Its type strain is ATCC 33509 (=DF3K =Dom F3 kid). References Further reading * *Mutharia, Lucy M., and Paul A. Amor. "Monoclonal antibodies against'' Vibrio anguillarum'' O2 and'' Vibrio ordalii'' identify antigenic differences in lipopolysaccharide O-antigens." FEMS Microbiology Letters 123.3 (1994): 289–298. *Rubio, Andrés Silva, and Rubén Avendaño Herrera. "Vibriosis en Chile: Caracterización de los Agentes Etiológicos, una Necesidad para el Desarrollo de Medidas Eficaces de Prevención Vibriosis in Chile: Characterization of the Etiological Agents, a Need to Develop Prevention Strategies." *Akayli, T., et al. "Identification and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vibrio Tubiashii
''Vibrio tubiashii'' is a Gram-negative, rod-shaped (0.5 um-1.5 um) marine bacterium that uses a single polar flagellum for motility. It has been implicated in several diseases of marine organisms. Discovery ''Vibrio tubiashii'' was originally isolated from juvenile and larval bivalve mollusks suffering from bacillary necrosis, now called vibriosis. It was originally discovered by Tubiash et al in 1965, hence the name, but not properly described until Hada et al in 1984. Since its discovery and identification, ''V. tubiashii'' has been implicated in shellfish vibriosis across the globe, and more recently, coral diseases. Pathogenicity Like many ''Vibrio'' spp., ''V. tubiashii'' produces extracellular enzymes, specifically a zinc-metalloprotease and a cytolysin/hemolysin that are nearly identical to those produced by other pathogenic ''Vibrio'' strains.(Sussman et al 2009). This being said, only the zinc-metalloprotease elicited disease symptoms in ''Crasso ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vibrio Vulnificus
''Vibrio vulnificus'' is a species of Gram-negative, motile, curved rod-shaped (bacillus), pathogenic bacteria of the genus ''Vibrio''. Present in marine environments such as estuaries, brackish ponds, or coastal areas, ''V. vulnificus'' is related to '' ''V. cholerae'''', the causative agent of cholera. At least one strain of ''V. vulnificus'' is bioluminescent. Infection with ''V. vulnificus'' leads to rapidly expanding cellulitis or sepsis. It was first isolated as a source of disease in 1976. Signs and symptoms ''Vibrio vulnificus'' is an extremely virulent bacterium that can cause three types of infections: * Acute gastroenteritis from eating raw or undercooked shellfish: ''V. vulnificus'' causes an infection often incurred after eating seafood, especially raw or undercooked oysters. It does not alter the appearance, taste, or odor of oysters. Symptoms include vomiting, diarrhea, and abdominal pain. * Necrotizing wound infections can occur in injured skin exposed to contam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serotype
A serotype or serovar is a distinct variation within a species of bacteria or virus or among immune cells of different individuals. These microorganisms, viruses, or cells are classified together based on their surface antigens, allowing the epidemiologic classification of organisms to the subspecies level. A group of serovars with common antigens is called a serogroup or sometimes ''serocomplex''. Serotyping often plays an essential role in determining species and subspecies. The ''Salmonella'' genus of bacteria, for example, has been determined to have over 2600 serotypes. ''Vibrio cholerae'', the species of bacteria that causes cholera, has over 200 serotypes, based on cell antigens. Only two of them have been observed to produce the potent enterotoxin that results in cholera: O1 and O139. Serotypes were discovered by the American microbiologist Rebecca Lancefield in 1933. Role in organ transplantation The immune system is capable of discerning a cell as being 'self' or 'n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Virulence
Virulence is a pathogen's or microorganism's ability to cause damage to a host. In most, especially in animal systems, virulence refers to the degree of damage caused by a microbe to its host. The pathogenicity of an organism—its ability to cause disease—is determined by its virulence factors. In the specific context of gene for gene systems, often in plants, virulence refers to a pathogen's ability to infect a resistant host. The noun ''virulence'' derives from the adjective ''virulent'', meaning disease severity. The word ''virulent'' derives from the Latin word ''virulentus'', meaning "a poisoned wound" or "full of poison." From an ecological standpoint, virulence is the loss of fitness induced by a parasite upon its host. Virulence can be understood in terms of proximate causes—those specific traits of the pathogen that help make the host ill—and ultimate causes—the evolutionary pressures that lead to virulent traits occurring in a pathogen strain. Virulent ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vibrionales
The Vibrionaceae are a family of Pseudomonadota given their own order, Vibrionales. Inhabitants of fresh or salt water, several species are pathogenic, including the type species ''Vibrio cholerae'', which is the agent responsible for cholera. Most bioluminescent bacteria belong to this family, and are typically found as symbionts of deep-sea animals. Vibrionaceae are Gram-negative organisms and facultative anaerobes, capable of fermentation. They contain oxidase and have one or more flagella, which are generally polar. Originally, these characteristics defined the family, which was divided into four genera. Two of these, '' Vibrio'' and ''Photobacterium'', correspond to the modern group, although several new genera have been defined. Genetic studies have shown the other two original members—''Aeromonas'' and '' Plesiomonas''—belong to separate families. The family Vibrionaceae currently comprises eight validly published genera: ''Aliivibrio'', ''Catenococcus'', ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacterial Diseases Of Fish
Bacteria (; singular: bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one Cell (biology), biological cell. They constitute a large domain (biology), domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria were among the first life forms to appear on Earth, and are present in most of its habitats. Bacteria inhabit soil, water, Hot spring, acidic hot springs, radioactive waste, and the deep biosphere of Earth's crust. Bacteria are vital in many stages of the nutrient cycle by recycling nutrients such as the nitrogen fixation, fixation of nitrogen from the Earth's atmosphere, atmosphere. The nutrient cycle includes the decomposition of cadaver, dead bodies; bacteria are responsible for the putrefaction stage in this process. In the biological communities surrounding hydrothermal vents and cold seeps, extremophile bacteria provide the nutrients needed to sustain life by converting dissolved compounds, such as hydrogen sulp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |