|
Vein (band) Albums
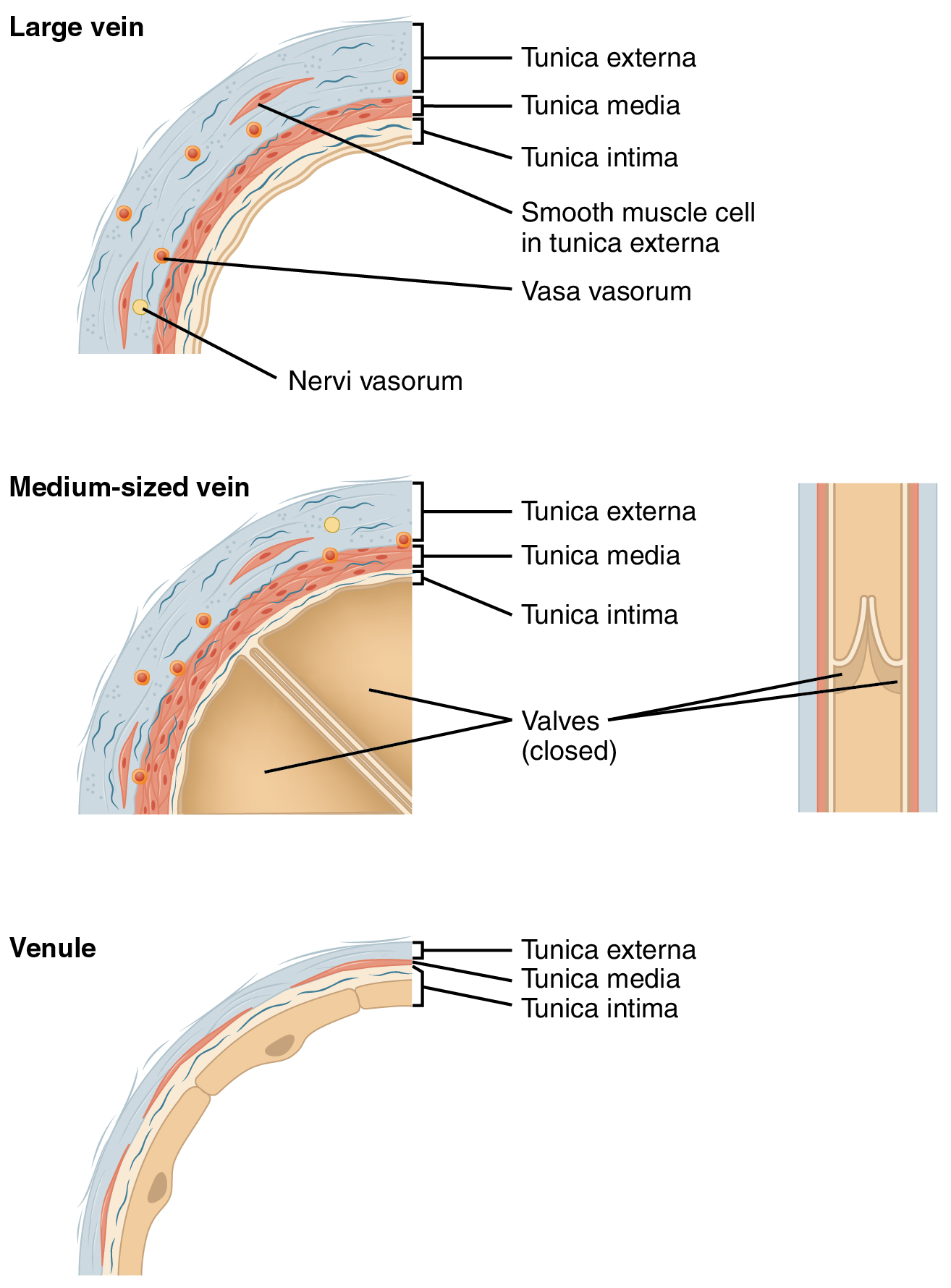
Veins are blood vessels in the circulatory system of humans and most other animals that carry blood toward the heart. Most veins carry deoxygenated blood from the tissues back to the heart; exceptions are those of the pulmonary and fetal circulations which carry oxygenated blood to the heart. In the systemic circulation arteries carry oxygenated blood away from the heart, and veins return deoxygenated blood to the heart. There are three sizes of veins, large, medium, and small. Smaller veins are called venules, and the smallest the post-capillary venules are microscopic that make up the veins of the microcirculation. Veins have less smooth muscle, and connective tissue than arteries, and are often closer to the skin. Because of the thinner walls in veins they are able to expand and can hold more blood. At any time, nearly 70% of the total volume of blood in the human body is in the veins. In medium and large sized veins the flow of blood is maintained by one-way (un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Connective Tissue
Connective tissue is one of the four primary types of animal tissue, along with epithelial tissue, muscle tissue, and nervous tissue. It develops from the mesenchyme derived from the mesoderm the middle embryonic germ layer. Connective tissue is found in between other tissues everywhere in the body, including the nervous system. The three meninges, membranes that envelop the brain and spinal cord are composed of connective tissue. Most types of connective tissue consists of three main components: elastic and collagen fibers, ground substance, and cells. Blood, and lymph are classed as specialized fluid connective tissues that do not contain fiber. All are immersed in the body water. The cells of connective tissue include fibroblasts, adipocytes, macrophages, mast cells and leucocytes. The term "connective tissue" (in German, ''Bindegewebe'') was introduced in 1830 by Johannes Peter Müller. The tissue was already recognized as a distinct class in the 18th century. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skeletal Muscle Pump
The skeletal muscle pump or musculovenous pump is a collection of skeletal muscles that aid the heart in the circulation of blood. It is especially important in increasing venous return to the heart, but may also play a role in arterial blood flow. General The skeletal muscle pump is vital in negating orthostatic intolerance when standing. When moving upright, the blood volume moves to the peripheral parts of the body. To combat this, the muscles involved in standing contract and help to bring venous blood volume to the heart. The pump is important in affecting the central and local supply of blood output. Venous return, cardiac output, and stroke volume were all increased during exercise experiments, as well as affecting the local muscle being used, blood volume. Arterial blood pumping Between muscle relaxations, intramuscular pressure transiently returns to a level below the venous blood pressure. This allows blood from the capillary system to refill the veins until th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Venule
A venule is a very small blood vessel in the microcirculation that allows blood to return from the capillary beds to drain into the larger blood vessels, the veins. Venules range from 7μm to 1mm in diameter. Veins contain approximately 70% of total blood volume, while about 25% is contained in the venules. Many venules unite to form a vein. Structure Venule walls have three layers: An inner endothelium composed of squamous endothelial cells that act as a membrane, a middle layer of muscle and elastic tissue and an outer layer of fibrous connective tissue. The middle layer is poorly developed so that venules have thinner walls than arterioles. They are porous so that fluid and blood cells can move easily from the bloodstream through their walls. Short portal venules between the neural and anterior pituitary lobes provide an avenue for rapid hormonal exchange via the blood. Specifically within and between the pituitary lobes is anatomical evidence for confluent interlobe ve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
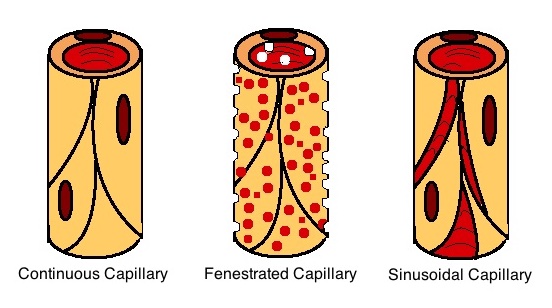
Capillaries
A capillary is a small blood vessel from 5 to 10 micrometres (μm) in diameter. Capillaries are composed of only the tunica intima, consisting of a thin wall of simple squamous endothelial cells. They are the smallest blood vessels in the body: they convey blood between the arterioles and venules. These microvessels are the site of exchange of many substances with the interstitial fluid surrounding them. Substances which cross capillaries include water, oxygen, carbon dioxide, urea, glucose, uric acid, lactic acid and creatinine. Lymph capillaries connect with larger lymph vessels to drain lymphatic fluid collected in the microcirculation. During early embryonic development, new capillaries are formed through vasculogenesis, the process of blood vessel formation that occurs through a '' de novo'' production of endothelial cells that then form vascular tubes. The term ''angiogenesis'' denotes the formation of new capillaries from pre-existing blood vessels and already present endo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Capillary Bed
A capillary is a small blood vessel from 5 to 10 micrometres (μm) in diameter. Capillaries are composed of only the tunica intima, consisting of a thin wall of simple squamous endothelial cells. They are the smallest blood vessels in the body: they convey blood between the arterioles and venules. These microvessels are the site of exchange of many substances with the interstitial fluid surrounding them. Substances which cross capillaries include water, oxygen, carbon dioxide, urea, glucose, uric acid, lactic acid and creatinine. Lymph capillaries connect with larger lymph vessels to drain lymphatic fluid collected in the microcirculation. During early embryonic development, new capillaries are formed through vasculogenesis, the process of blood vessel formation that occurs through a '' de novo'' production of endothelial cells that then form vascular tubes. The term ''angiogenesis'' denotes the formation of new capillaries from pre-existing blood vessels and already present endo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Visual Cortex
The visual cortex of the brain is the area of the cerebral cortex that processes visual information. It is located in the occipital lobe. Sensory input originating from the eyes travels through the lateral geniculate nucleus in the thalamus and then reaches the visual cortex. The area of the visual cortex that receives the sensory input from the lateral geniculate nucleus is the primary visual cortex, also known as visual area 1 ( V1), Brodmann area 17, or the striate cortex. The extrastriate areas consist of visual areas 2, 3, 4, and 5 (also known as V2, V3, V4, and V5, or Brodmann area 18 and all Brodmann area 19). Both hemispheres of the brain include a visual cortex; the visual cortex in the left hemisphere receives signals from the right visual field, and the visual cortex in the right hemisphere receives signals from the left visual field. Introduction The primary visual cortex (V1) is located in and around the calcarine fissure in the occipital lobe. Each hemisphere's V1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Visual Perception
Visual perception is the ability to interpret the surrounding environment through photopic vision (daytime vision), color vision, scotopic vision (night vision), and mesopic vision (twilight vision), using light in the visible spectrum reflected by objects in the environment. This is different from visual acuity, which refers to how clearly a person sees (for example "20/20 vision"). A person can have problems with visual perceptual processing even if they have 20/20 vision. The resulting perception is also known as vision, sight, or eyesight (adjectives ''visual'', ''optical'', and ''ocular'', respectively). The various physiological components involved in vision are referred to collectively as the visual system, and are the focus of much research in linguistics, psychology, cognitive science, neuroscience, and molecular biology, collectively referred to as vision science. Visual system In humans and a number of other mammals, light enters the eye through the cornea and is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Venous Valve
Veins are blood vessels in humans and most other animals that carry blood towards the heart. Most veins carry deoxygenated blood from the tissues back to the heart; exceptions are the pulmonary and umbilical veins, both of which carry oxygenated blood to the heart. In contrast to veins, arteries carry blood away from the heart. Veins are less muscular than arteries and are often closer to the skin. There are valves (called ''pocket valves'') in most veins to prevent backflow. Structure Veins are present throughout the body as tubes that carry blood back to the heart. Veins are classified in a number of ways, including superficial vs. deep, pulmonary vs. systemic, and large vs. small. *Superficial veins are those closer to the surface of the body, and have no corresponding arteries. *Deep veins are deeper in the body and have corresponding arteries. *Perforator veins drain from the superficial to the deep veins. These are usually referred to in the lower limbs and feet. *Communica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Systolic
Systole ( ) is the part of the cardiac cycle during which some chambers of the heart contract after refilling with blood. The term originates, via New Latin, from Ancient Greek (''sustolē''), from (''sustéllein'' 'to contract'; from ''sun'' 'together' + ''stéllein'' 'to send'), and is similar to the use of the English term ''to squeeze''. The mammalian heart has four chambers: the left atrium above the left ventricle (lighter pink, see graphic), which two are connected through the mitral (or bicuspid) valve; and the right atrium above the right ventricle (lighter blue), connected through the tricuspid valve. The atria are the receiving blood chambers for the circulation of blood and the ventricles are the discharging chambers. In late ventricular diastole, the atrial chambers contract and send blood to the larger, lower ventricle chambers. This flow fills the ventricles with blood, and the resulting pressure closes the valves to the atria. The ventricles now perform i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tunica Intima
The tunica intima (New Latin "inner coat"), or intima for short, is the innermost tunica (layer) of an artery or vein. It is made up of one layer of endothelial cells and is supported by an internal elastic lamina. The endothelial cells are in direct contact with the blood flow. The three layers of a blood vessel are an inner layer (the tunica intima), a middle layer (the tunica media), and an outer layer (the tunica externa). In dissection, the inner coat (tunica intima) can be separated from the middle (tunica media) by a little maceration, or it may be stripped off in small pieces; but, because of its friability, it cannot be separated as a complete membrane. It is a fine, transparent, colorless structure which is highly elastic, and, after death, is commonly corrugated into longitudinal wrinkles. Structure The structure of the tunica intima depends on the blood vessel type. Elastic arteries – A single layer of Endothelial and a supporting layer of elastin-rich collagen. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tunica Media
The tunica media (New Latin "middle coat"), or media for short, is the middle tunica (layer) of an artery or vein. It lies between the tunica intima on the inside and the tunica externa on the outside. Artery Tunica media is made up of smooth muscle cells, elastic tissue and collagen. It lies between the tunica intima on the inside and the tunica externa on the outside. The middle coat (tunica media) is distinguished from the inner (tunica intima) by its color and by the transverse arrangement of its fibers. * In the ''smaller arteries'' it consists principally of smooth muscle fibers in fine bundles, arranged in lamellæ and disposed circularly around the vessel. These lamellæ vary in number according to the size of the vessel; the smallest arteries having only a single layer, and those slightly larger three or four layers - up to a maximum of six layers. It is to this coat that the thickness of the wall of the artery is mainly due. * In the ''larger arteries'', as the ilia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tunica Externa
The tunica externa (New Latin "outer coat"), also known as the tunica adventitia (New Latin "additional coat"), is the outermost tunica (layer) of a blood vessel, surrounding the tunica media. It is mainly composed of collagen and, in arteries, is supported by external elastic lamina. The collagen serves to anchor the blood vessel to nearby organs, giving it stability. The three layers of the blood vessels are: an inner tunica intima, a middle tunica media, and an outer tunica externa. Structure The tunica externa is made from collagen and elastic fibers in a loose connective tissue. This is secreted by fibroblasts. Function The tunica externa provides basic structural support to blood vessels. It prevents vessels from expanding too much from internal blood pressure, particularly arteries. It is also relevant in controlling vascular flow in the lungs. Clinical significance A common pathological disorder concerning the tunica externa is scurvy, also known as vitamin C defici ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |