|
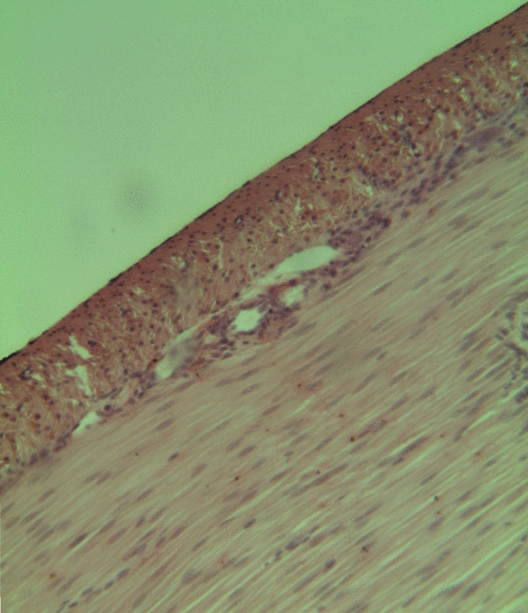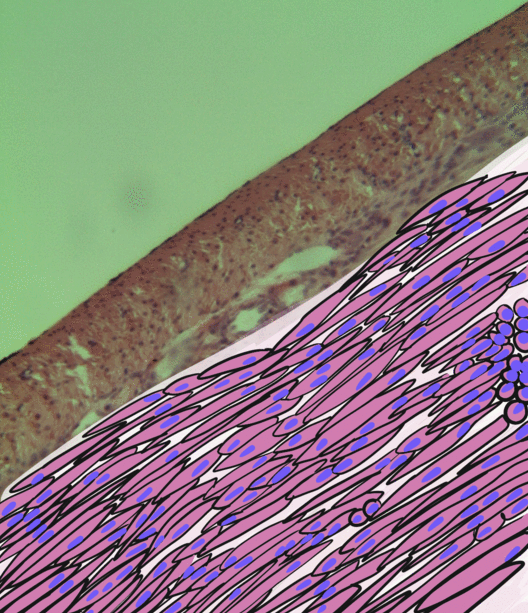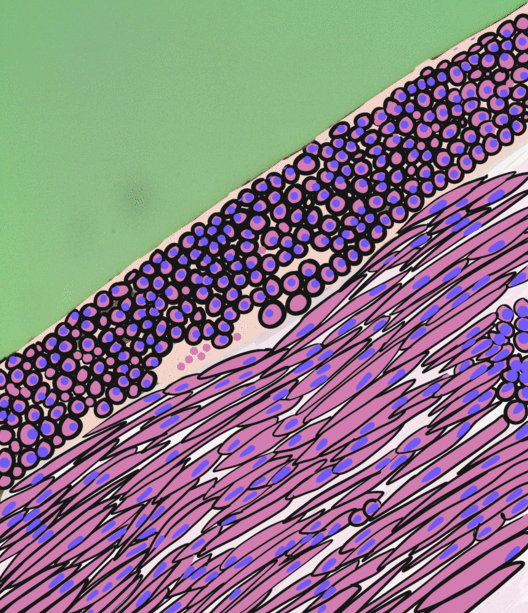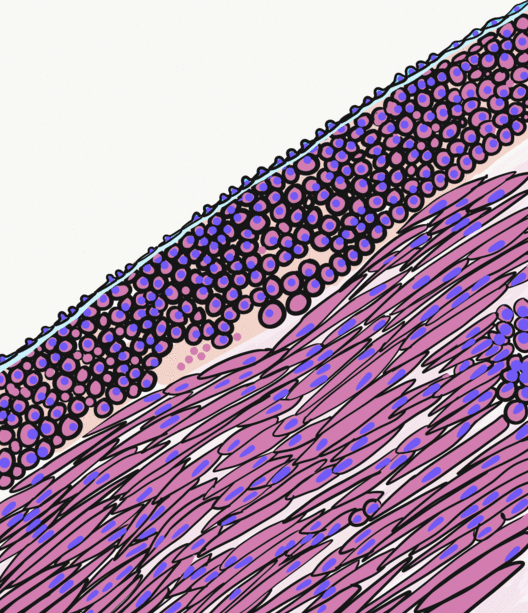
Tunica Media
The tunica media (New Latin "middle coat"), or media for short, is the middle tunica (layer) of an artery or vein. It lies between the tunica intima on the inside and the tunica externa on the outside. Artery Tunica media is made up of smooth muscle cells, elastic tissue and collagen. It lies between the tunica intima on the inside and the tunica externa on the outside. The middle coat (tunica media) is distinguished from the inner (tunica intima) by its color and by the transverse arrangement of its fibers. * In the ''smaller arteries'' it consists principally of smooth muscle fibers in fine bundles, arranged in lamellæ and disposed circularly around the vessel. These lamellæ vary in number according to the size of the vessel; the smallest arteries having only a single layer, and those slightly larger three or four layers - up to a maximum of six layers. It is to this coat that the thickness of the wall of the artery is mainly due. * In the ''larger arteries'', as the ilia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Artery
An artery (plural arteries) () is a blood vessel in humans and most animals that takes blood away from the heart to one or more parts of the body (tissues, lungs, brain etc.). Most arteries carry oxygenated blood; the two exceptions are the pulmonary and the umbilical arteries, which carry deoxygenated blood to the organs that oxygenate it (lungs and placenta, respectively). The effective arterial blood volume is that extracellular fluid which fills the arterial system. The arteries are part of the circulatory system, that is responsible for the delivery of oxygen and nutrients to all cells, as well as the removal of carbon dioxide and waste products, the maintenance of optimum blood pH, and the circulation of proteins and cells of the immune system. Arteries contrast with veins, which carry blood back towards the heart. Structure The anatomy of arteries can be separated into gross anatomy, at the macroscopic level, and microanatomy, which must be studied with a microscop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Collagen
Collagen () is the main structural protein in the extracellular matrix found in the body's various connective tissues. As the main component of connective tissue, it is the most abundant protein in mammals, making up from 25% to 35% of the whole-body protein content. Collagen consists of amino acids bound together to form a triple helix of elongated fibril known as a collagen helix. It is mostly found in connective tissue such as cartilage, bones, tendons, ligaments, and skin. Depending upon the degree of mineralization, collagen tissues may be rigid (bone) or compliant (tendon) or have a gradient from rigid to compliant (cartilage). Collagen is also abundant in corneas, blood vessels, the gut, intervertebral discs, and the dentin in teeth. In muscle tissue, it serves as a major component of the endomysium. Collagen constitutes one to two percent of muscle tissue and accounts for 6% of the weight of the skeletal muscle tissue. The fibroblast is the most common cell that crea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brachiocephalic Artery
The brachiocephalic artery (or brachiocephalic trunk or innominate artery) is an artery of the mediastinum that supplies blood to the right arm and the head and neck. It is the first branch of the aortic arch. Soon after it emerges, the brachiocephalic artery divides into the right common carotid artery and the right subclavian artery. There is no brachiocephalic artery for the left side of the body. The left common carotid, and the left subclavian artery, come directly off the aortic arch. However, there are two brachiocephalic veins. Structure The brachiocephalic artery arises, on a level with the upper border of the second right costal cartilage, from the start of the aortic arch, on a plane anterior to the origin of the left carotid artery. It ascends obliquely upward, backward, and to the right to the level of the upper border of the right sternoclavicular articulation, where it divides into the right common carotid artery and right subclavian arteries. The artery then cros ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aorta
The aorta ( ) is the main and largest artery in the human body, originating from the left ventricle of the heart and extending down to the abdomen, where it splits into two smaller arteries (the common iliac arteries). The aorta distributes oxygenated blood to all parts of the body through the systemic circulation. Structure Sections In anatomical sources, the aorta is usually divided into sections. One way of classifying a part of the aorta is by anatomical compartment, where the thoracic aorta (or thoracic portion of the aorta) runs from the heart to the diaphragm. The aorta then continues downward as the abdominal aorta (or abdominal portion of the aorta) from the diaphragm to the aortic bifurcation. Another system divides the aorta with respect to its course and the direction of blood flow. In this system, the aorta starts as the ascending aorta, travels superiorly from the heart, and then makes a hairpin turn known as the aortic arch. Following the aortic arch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elastic Fibers
Elastic fibers (or yellow fibers) are an essential component of the extracellular matrix composed of bundles of proteins (elastin) which are produced by a number of different cell types including fibroblasts, endothelial, smooth muscle, and airway epithelial cells. These fibers are able to stretch many times their length, and snap back to their original length when relaxed without loss of energy. Elastic fibers include elastin, elaunin and oxytalan. Elastic tissue is classified as "connective tissue proper". Elastic fibers are formed via elastogenesis, a highly complex process involving several key proteins including fibulin-4, fibulin-5, latent transforming growth factor β binding protein 4, and microfibril associated protein 4. In this process tropoelastin, the soluble monomeric precursor to elastic fibers is produced by elastogenic cells and chaperoned to the cell surface. Following excretion from the cell, tropoelastin self associates into ~200 nm particles by coace ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carotid
In anatomy, the left and right common carotid arteries (carotids) ( in Merriam-Webster Online Dictionary '.) are that supply the head and neck with ; they divide in the neck to form the and |
Femoral Artery
The femoral artery is a large artery in the thigh and the main arterial supply to the thigh and leg. The femoral artery gives off the deep femoral artery or profunda femoris artery and descends along the anteromedial part of the thigh in the femoral triangle. It enters and passes through the adductor canal, and becomes the popliteal artery as it passes through the adductor hiatus in the adductor magnus near the junction of the middle and distal thirds of the thigh. Structure The femoral artery enters the thigh from behind the inguinal ligament as the continuation of the external iliac artery. Here, it lies midway between the anterior superior iliac spine and the symphysis pubis (Mid-inguinal point). Segments In clinical parlance, the femoral artery has the following segments: *The common femoral artery (CFA) is the segment of the femoral artery between the inferior margin of the inguinal ligament and the branching point of the deep femoral artery/profunda femoris artery. Its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Common Iliac Artery
The common iliac artery is a large artery of the abdomen paired on each side. It originates from the aortic bifurcation at the level of the 4th lumbar vertebra. It ends in front of the sacroiliac joint, one on either side, and each bifurcates into the external and internal iliac arteries. Structure The common iliac artery are about 4 cm long in adults and more than a centimeter in diameter. It begins as a branch of the aorta. This is at the level of the 4th lumbar vertebra. It runs inferolaterally, along the medial border of the psoas muscles. It bifurcates into the external iliac artery and the internal iliac artery at the pelvic brim, in front of the sacroiliac joints. The common iliac artery, and all of its branches, exist as paired structures (that is to say, there is one on the left side and one on the right). The distribution of the common iliac artery is basically the pelvis and lower limb (as the femoral artery) on the corresponding side. Relations Both common il ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elastic Tissue
Elastic fibers (or yellow fibers) are an essential component of the extracellular matrix composed of bundles of proteins ( elastin) which are produced by a number of different cell types including fibroblasts, endothelial, smooth muscle, and airway epithelial cells. These fibers are able to stretch many times their length, and snap back to their original length when relaxed without loss of energy. Elastic fibers include elastin, elaunin and oxytalan. Elastic tissue is classified as "connective tissue proper". Elastic fibers are formed via elastogenesis, a highly complex process involving several key proteins including fibulin-4, fibulin-5, latent transforming growth factor β binding protein 4, and microfibril associated protein 4. In this process tropoelastin, the soluble monomeric precursor to elastic fibers is produced by elastogenic cells and chaperoned to the cell surface. Following excretion from the cell, tropoelastin self associates into ~200 nm particles by coac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vein
Veins are blood vessels in humans and most other animals that carry blood towards the heart. Most veins carry deoxygenated blood from the tissues back to the heart; exceptions are the pulmonary and umbilical veins, both of which carry oxygenated blood to the heart. In contrast to veins, arteries carry blood away from the heart. Veins are less muscular than arteries and are often closer to the skin. There are valves (called ''pocket valves'') in most veins to prevent backflow. Structure Veins are present throughout the body as tubes that carry blood back to the heart. Veins are classified in a number of ways, including superficial vs. deep, pulmonary vs. systemic, and large vs. small. * Superficial veins are those closer to the surface of the body, and have no corresponding arteries. *Deep veins are deeper in the body and have corresponding arteries. *Perforator veins drain from the superficial to the deep veins. These are usually referred to in the lower limbs and feet. *Communic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Smooth Muscle
Smooth muscle is an involuntary non-striated muscle, so-called because it has no sarcomeres and therefore no striations (''bands'' or ''stripes''). It is divided into two subgroups, single-unit and multiunit smooth muscle. Within single-unit muscle, the whole bundle or sheet of smooth muscle cells contracts as a syncytium. Smooth muscle is found in the walls of hollow organs, including the stomach, intestines, bladder and uterus; in the walls of passageways, such as blood, and lymph vessels, and in the tracts of the respiratory, urinary, and reproductive systems. In the eyes, the ciliary muscles, a type of smooth muscle, dilate and contract the iris and alter the shape of the lens. In the skin, smooth muscle cells such as those of the arrector pili cause hair to stand erect in response to cold temperature or fear. Structure Gross anatomy Smooth muscle is grouped into two types: single-unit smooth muscle, also known as visceral smooth muscle, and multiunit smooth muscle. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |