|
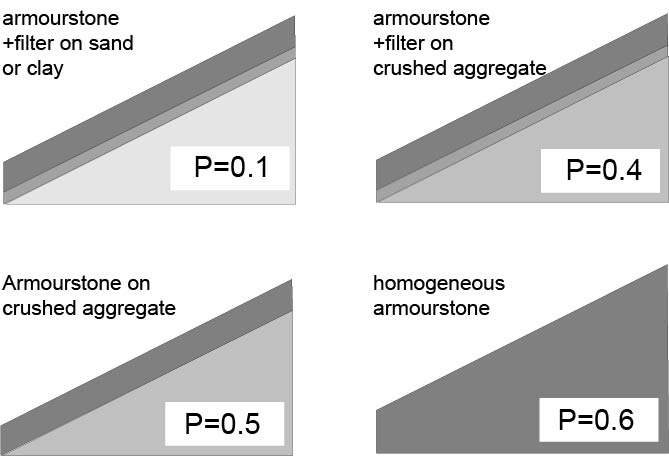
Van Der Meer Formula
The Van der Meer formula is a formula for calculating the required stone weight for armourstone under the influence of (wind) waves. This is necessary for the design of breakwaters and shoreline protection. Around 1985 it was found that the Hudson formula in use at that time had considerable limitations (only valid for permeable breakwaters and steep (storm) waves). That is why the Dutch government agency Rijkswaterstaat commissioned Deltares to start research for a more complete formula. This research, conducted by Jentsje van der Meer, resulted in the Van der Meer formula in 1988, as described in his dissertation. This formula reads :\frac= \begin c_ P^ \left (\frac \right)^ \xi_m^ & \mbox \xi_m < \xi \quad lunging\\ c_ P^ \left (\frac \right)^ \xi_m^ \sqrt & \mbox \xi_m \ge \xi \quad urging ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Armourstone
Armourstone is a generic term for broken stone with stone masses between (very coarse Construction aggregate, aggregate) that is suitable for use in hydraulic engineering. Dimensions and characteristics for armourstone are laid down in European Standard EN13383. In the United States, there are a number of different standards and publications setting out different methodologies for classifying armourstone, ranging from weight-based classifications to gradation curves and size-based classifications. Stone Classes European Practice to EN13383 Armourstone is available in standardised stone classes, defined by both a lower and upper value of the stone mass within these classes. For instance, Class 60-300 signifies that up to 10% of the stones weigh less than and up to 30% weigh more than . The standard also mentions values which shouldn't be exceeded by 5% or 3%. For particular applications like a top layer for a breakwater (structure), breakwater or bank protection, the me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Water Waves
In fluid dynamics, a wind wave, water wave, or wind-generated water wave, is a surface wave that occurs on the free surface of bodies of water as a result from the wind blowing over the water surface. The contact distance in the direction of the wind is known as the ''fetch''. Waves in the oceans can travel thousands of kilometers before reaching land. Wind waves on Earth range in size from small ripples, to waves over high, being limited by wind speed, duration, fetch, and water depth. When directly generated and affected by local wind, a wind wave system is called a wind sea. Wind waves will travel in a great circle route after being generated – curving slightly left in the southern hemisphere and slightly right in the northern hemisphere. After moving out of the area of fetch, wind waves are called '' swells'' and can travel thousands of kilometers. A noteworthy example of this is waves generated south of Tasmania during heavy winds that will travel across the Pacif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Breakwater (structure)
A breakwater is a permanent structure constructed at a coastal area to protect against tides, currents, waves, and storm surges. Part of a coastal management system, breakwaters are installed to minimize erosion, and to protect anchorages, helping isolate vessels within them from marine hazards such as prop washes and wind-driven waves. A breakwater, also known in some contexts as a jetty, may be connected to land or freestanding, and may contain a walkway or road for vehicle access. On beaches where longshore drift threatens the erosion of beach material, smaller structures on the beach, usually perpendicular to the water's edge, may be installed. Their action on waves and current is intended to slow the longshore drift and discourage mobilisation of beach material. In this usage they are more usually referred to as groynes. Purposes Breakwaters reduce the intensity of wave action in inshore waters and thereby provide safe harbourage. Breakwaters may also be small structu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hudson's Equation
Hudson's equation, also known as Hudson formula, is an equation used by coastal engineers to calculate the minimum size of riprap ( armourstone) required to provide ''satisfactory'' stability characteristics for rubble structures such as breakwaters under attack from storm wave conditions. The equation was developed by the United States Army Corps of Engineers, Waterways Experiment Station (WES), following extensive investigations by Hudson (1953, 1959, 1961a, 1961b) Initial equation The equation itself is: :W =\frac where: *''W'' is the design weight of the riprap armor (Newton) *''\gamma_r'' is the specific weight of the armor blocks (N/m3) *''H'' is the design wave height at the toe of the structure (m) *''K''''D'' is a dimensionless stability coefficient, deduced from laboratory experiments for different kinds of armour blocks and for very small damage (a few blocks removed from the armour layer) (-): :* ''K''''D'' = around 3 for natural quarry rock :* ''K''''D'' = around 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rijkswaterstaat
Rijkswaterstaat, founded in 1798 as the ''Bureau voor den Waterstaat'' and formerly translated to Directorate General for Public Works and Water Management, is a Directorate-General of the Ministry of Infrastructure and Water Management of the Netherlands. Its role is the practical execution of the public works and water management, including the construction and maintenance of waterways and roads, and flood protection and prevention. The agency was also involved in the construction of big railway projects such as the Betuweroute and the HSL-Zuid. The mission of the organisation is: "Rijkswaterstaat is de rijksdienst die werkt aan droge voeten, schoon en voldoende water én aan de vlotte en veilige doorstroming van het verkeer" (Rijkswaterstaat is the national agency that provides dry feet, clean and sufficient water and a quick and safe flow of traffic). The agency is divided in 10 regional, 6 specialist services and 2 special services. As of 15 May 2017, the director-general (DG ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deltares
Deltares is a (''Major Technological Institute'') in the Netherlands specialising in Hydraulic engineering, hydraulic engineering research and consulting, along with Water resources, water management, Geotechnical engineering, geotechnics, and infrastructure. The organisation's research mainly focuses on River, rivers and River delta, river deltas, Coast, coastal regions, and Offshore geotechnical engineering, offshore engineering. As of 2020, Deltares employed over 750 full-time equivalent (FTE) staff members from 42 nationalities, located in Delft and Utrecht. The Revenue, turnover in 2020 was €112 million. Deltares operations focus on, among other things: * Water resources, Water management; * Water safety; * Hydraulic engineering; * Groundwater; * Soil management; * Geology; * Ecology; * Water quality; * River morphology, River and coastal morphology. Facilities In addition to desk study research, Deltares undertakes physical model research and development of comput ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)
