|
Vamps (2011 Film)
The VaMP driverless car was one of the first truly autonomous cars a 2007 book by Ernst D. Dickmanns along with its twin vehicle, the VITA-2. They were able to drive in heavy traffic for long distances without human intervention, using to recognize rapidly moving obstacles such as other cars, and automatically avoid and pass them. 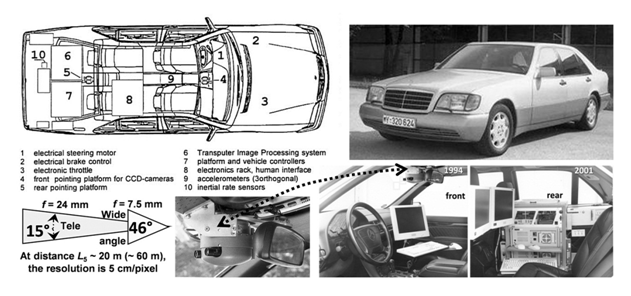 The VaMP was constructed by the team of
The VaMP was constructed by the team of
|
Driverless Car
A self-driving car, also known as an autonomous car, driver-less car, or robotic car (robo-car), is a car that is capable of traveling without human input.Xie, S.; Hu, J.; Bhowmick, P.; Ding, Z.; Arvin, F.,Distributed Motion Planning for Safe Autonomous Vehicle Overtaking via Artificial Potential Field IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2022. Self-driving cars use sensors to perceive their surroundings, such as optical and thermographic cameras, radar, lidar, ultrasound/sonar, GPS, odometry and inertial measurement units. Control systems interpret sensory information to create a three-dimensional model of the surroundings. Based on the model, the car identifies appropriate navigation paths, and strategies for managing traffic controls (stop signs, etc.) and obstacles.Hu, J.; Bhowmick, P.; Jang, I.; Arvin, F.; Lanzon, A.,A Decentralized Cluster Formation Containment Framework for Multirobot Systems IEEE Transactions on Robotics, 2021. Once the techn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uncertainty
Uncertainty refers to epistemic situations involving imperfect or unknown information. It applies to predictions of future events, to physical measurements that are already made, or to the unknown. Uncertainty arises in partially observable or stochastic environments, as well as due to ignorance, indolence, or both. It arises in any number of fields, including insurance, philosophy, physics, statistics, economics, finance, medicine, psychology, sociology, engineering, metrology, meteorology, ecology and information science. Concepts Although the terms are used in various ways among the general public, many specialists in decision theory, statistics and other quantitative fields have defined uncertainty, risk, and their measurement as: Uncertainty The lack of certainty, a state of limited knowledge where it is impossible to exactly describe the existing state, a future outcome, or more than one possible outcome. ;Measurement of uncertainty: A set of possible states or outc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
VIAC
VIAC, the VisLab Intercontinental Autonomous Challenge, is the challenge conceived by VisLab as an extreme test of autonomous vehicles. It ran from July 20, 2010 to October 28, 2010, involving four driverless vehicles driving with virtually no human intervention on an almost trip from Parma, Italy to Shanghai, China."Without driver or map, vans go from Italy to China" Elaine Kurtenbac, AP.COM Jo Ling Kent, CNN.COM Overview The |
Driverless Car
A self-driving car, also known as an autonomous car, driver-less car, or robotic car (robo-car), is a car that is capable of traveling without human input.Xie, S.; Hu, J.; Bhowmick, P.; Ding, Z.; Arvin, F.,Distributed Motion Planning for Safe Autonomous Vehicle Overtaking via Artificial Potential Field IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2022. Self-driving cars use sensors to perceive their surroundings, such as optical and thermographic cameras, radar, lidar, ultrasound/sonar, GPS, odometry and inertial measurement units. Control systems interpret sensory information to create a three-dimensional model of the surroundings. Based on the model, the car identifies appropriate navigation paths, and strategies for managing traffic controls (stop signs, etc.) and obstacles.Hu, J.; Bhowmick, P.; Jang, I.; Arvin, F.; Lanzon, A.,A Decentralized Cluster Formation Containment Framework for Multirobot Systems IEEE Transactions on Robotics, 2021. Once the techn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Munich
Munich ( ; german: München ; bar, Minga ) is the capital and most populous city of the States of Germany, German state of Bavaria. With a population of 1,558,395 inhabitants as of 31 July 2020, it is the List of cities in Germany by population, third-largest city in Germany, after Berlin and Hamburg, and thus the largest which does not constitute its own state, as well as the List of cities in the European Union by population within city limits, 11th-largest city in the European Union. The Munich Metropolitan Region, city's metropolitan region is home to 6 million people. Straddling the banks of the River Isar (a tributary of the Danube) north of the Northern Limestone Alps, Bavarian Alps, Munich is the seat of the Bavarian Regierungsbezirk, administrative region of Upper Bavaria, while being the population density, most densely populated municipality in Germany (4,500 people per km2). Munich is the second-largest city in the Bavarian dialects, Bavarian dialect area, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deutsches Museum
The Deutsches Museum (''German Museum'', officially (English: ''German Museum of Masterpieces of Science and Technology'')) in Munich, Germany, is the world's largest museum of science and technology, with about 28,000 exhibited objects from 50 fields of science and technology. It receives about 1.5 million visitors per year. The museum was founded on 28 June 1903, at a meeting of the Association of German Engineers (VDI) as an initiative of Oskar von Miller. It is the largest museum in Munich. For a period of time the museum was also used to host pop and rock concerts including The Who, Jimi Hendrix and Elton John. Museumsinsel The main site of the Deutsches Museum is a small island in the Isar river, which had been used for rafting wood since the Middle Ages. The island did not have any buildings before 1772 because it was regularly flooded prior to the building of the Sylvensteinspeicher. In 1772 the Isar barracks were built on the island and, after the flooding of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Global Positioning System
The Global Positioning System (GPS), originally Navstar GPS, is a satellite-based radionavigation system owned by the United States government and operated by the United States Space Force. It is one of the global navigation satellite systems (GNSS) that provides geolocation and time information to a GPS receiver anywhere on or near the Earth where there is an unobstructed line of sight to four or more GPS satellites. It does not require the user to transmit any data, and operates independently of any telephonic or Internet reception, though these technologies can enhance the usefulness of the GPS positioning information. It provides critical positioning capabilities to military, civil, and commercial users around the world. Although the United States government created, controls and maintains the GPS system, it is freely accessible to anyone with a GPS receiver. The GPS project was started by the U.S. Department of Defense in 1973. The first prototype spacecraft was lau ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arithmetic Mean
In mathematics and statistics, the arithmetic mean ( ) or arithmetic average, or just the ''mean'' or the ''average'' (when the context is clear), is the sum of a collection of numbers divided by the count of numbers in the collection. The collection is often a set of results of an experiment or an observational study, or frequently a set of results from a survey. The term "arithmetic mean" is preferred in some contexts in mathematics and statistics, because it helps distinguish it from other means, such as the geometric mean and the harmonic mean. In addition to mathematics and statistics, the arithmetic mean is used frequently in many diverse fields such as economics, anthropology and history, and it is used in almost every academic field to some extent. For example, per capita income is the arithmetic average income of a nation's population. While the arithmetic mean is often used to report central tendencies, it is not a robust statistic, meaning that it is greatly influe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Autobahn
The (; German plural ) is the federal controlled-access highway system in Germany. The official German term is (abbreviated ''BAB''), which translates as 'federal motorway'. The literal meaning of the word is 'Federal Auto(mobile) Track'. German are widely known for having no federally mandated general speed limit for some classes of vehicles. However, limits are posted and enforced in areas that are urbanised, substandard, accident-prone, or under construction. On speed-unrestricted stretches, an advisory speed limit () of applies. While driving faster is not illegal as such in the absence of a speed limit, it can cause an increased liability in the case of a collision (which mandatory auto insurance has to cover); courts have ruled that an "ideal driver" who is exempt from absolute liability for "inevitable" tort under the law would not exceed . A 2017 report by the Federal Road Research Institute reported that in 2015, 70.4% of the Autobahn network had only the advis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated between the Baltic and North seas to the north, and the Alps to the south; it covers an area of , with a population of almost 84 million within its 16 constituent states. Germany borders Denmark to the north, Poland and the Czech Republic to the east, Austria and Switzerland to the south, and France, Luxembourg, Belgium, and the Netherlands to the west. The nation's capital and most populous city is Berlin and its financial centre is Frankfurt; the largest urban area is the Ruhr. Various Germanic tribes have inhabited the northern parts of modern Germany since classical antiquity. A region named Germania was documented before AD 100. In 962, the Kingdom of Germany formed the bulk of the Holy Roman Empire. During the 16th ce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Copenhagen
Copenhagen ( or .; da, København ) is the capital and most populous city of Denmark, with a proper population of around 815.000 in the last quarter of 2022; and some 1.370,000 in the urban area; and the wider Copenhagen metropolitan area has 2,057,142 people. Copenhagen is on the islands of Zealand and Amager, separated from Malmö, Sweden, by the Øresund strait. The Øresund Bridge connects the two cities by rail and road. Originally a Viking fishing village established in the 10th century in the vicinity of what is now Gammel Strand, Copenhagen became the capital of Denmark in the early 15th century. Beginning in the 17th century, it consolidated its position as a regional centre of power with its institutions, defences, and armed forces. During the Renaissance the city served as the de facto capital of the Kalmar Union, being the seat of monarchy, governing the majority of the present day Nordic region in a personal union with Sweden and Norway ruled by the Danis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Traffic
Traffic comprises pedestrians, vehicles, ridden or herded animals, trains, and other conveyances that use public ways (roads) for travel and transportation. Traffic laws govern and regulate traffic, while rules of the road include traffic laws and informal rules that may have developed over time to facilitate the orderly and timely flow of traffic. Organized traffic generally has well-established priorities, lanes, right-of-way, and traffic control at intersections. Traffic is formally organized in many jurisdictions, with marked lanes, junctions, intersections, interchanges, traffic signals, or signs. Traffic is often classified by type: heavy motor vehicle (e.g., car, truck), other vehicle (e.g., moped, bicycle), and pedestrian. Different classes may share speed limits and easement, or may be segregated. Some jurisdictions may have very detailed and complex rules of the road while others rely more on drivers' common sense and willingness to cooperate. Organization ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





