|
Utba Ibn Ghazwan Al-Mazini
Utba ibn Ghazwan al-Mazini ( ar, عُتبة بن غَزْوان المازني, ʿUtba ibn Ghazwān al-Māzinī) (–638) was a well-known companion of the Islamic prophet Muhammad. He was the seventh person to convert to Islam and participated in the ''hijra'' to Abyssinia, but returned to stay with Muhammad in Mecca before making the second ''hijrah'' to Medina. He fought at the battle of Badr (624), the battle of Uhud (625), the Battle of the Trench (627) and many others, including the battles of Yamamah. During the caliphate of Umar (r. 634–644), Utba commanded a force of 2,000 men in a campaign against Ubullah which lasted from June through September 635. Once Uballah was occupied, Utba sent a force across the Tigris River which occupied the district of Furat, followed by Meisan and Abarqubaz. He was soon appointed governor of Basra (Iraq) by the caliph. In 639 Utba left for the Hijaz to perform hajj and to request Umar to relieve him of his office as governor. Umar re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caliph
A caliphate or khilāfah ( ar, خِلَافَة, ) is an institution or public office under the leadership of an Islamic steward with the title of caliph (; ar, خَلِيفَة , ), a person considered a political-religious successor to the Islamic prophet Muhammad and a leader of the entire Muslim world (ummah). Historically, the caliphates were polities based on Islam which developed into multi-ethnic trans-national empires. During the medieval period, three major caliphates succeeded each other: the Rashidun Caliphate (632–661), the Umayyad Caliphate (661–750), and the Abbasid Caliphate (750–1258). In the fourth major caliphate, the Ottoman Caliphate, the rulers of the Ottoman Empire claimed caliphal authority from 1517. Throughout the history of Islam, a few other Muslim states, almost all hereditary monarchies such as the Mamluk Sultanate (Cairo) and Ayyubid Caliphate, have claimed to be caliphates. The first caliphate, the Rashidun Caliphate, was established in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Al-Mada'ini
Abū l-Ḥasan ʿAlī ibn Muḥammad ibn ʿAbdallāh ibn Abī Sayf al-Qurashī l-Madāʾinī () (752/3–843), better known by his ''nisba'' of al-Madāʾinī ("from al-Mada'in"), was a scholar of Iranian descent who wrote in Arabic and was active under the early Abbasids in Iraq in the first half of the 9th century. A scholar of many interests, he wrote over 200 works, but is best known as a historian. Life Little is known about al-Mada'ini's life. The second edition of the ''Encyclopaedia of Islam'' notes that according to his own account, he was born in 752. However the third edition of the ''Encyclopaedia of Islam'' notes that according to other sources (citing al-Marzubani), he was born in 752/3, which can be treated as "his approximate year of birth". Al-Mada'ini and his family were of Iranian descent, and, according to sources attributed to him, he knew Persian. He was most likely born in Basra, and for most of his life remained in various cities in Iraq. Al-Mada'ini and h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Al-Baladhuri
ʾAḥmad ibn Yaḥyā ibn Jābir al-Balādhurī ( ar, أحمد بن يحيى بن جابر البلاذري) was a 9th-century Muslim historian. One of the eminent Middle Eastern historians of his age, he spent most of his life in Baghdad and enjoyed great influence at the court of the caliph al-Mutawakkil. He travelled in Syria and Iraq, compiling information for his major works. His full name was Ahmad Bin Yahya Bin Jabir Al-Baladhuri ( ar, أحمد بن يحيى بن جابر البلاذري), Balazry Ahmad Bin Yahya Bin Jabir Abul Hasan or Abi al-Hassan Baladhuri. Biography Al-Baladhuri's ethnicity has been described as Arab and Persian, although his sympathies seem to have been strongly with the Arabs, for Masudi refers to one of his works in which he rejects Baladhuri's condemnation of non-Arab nationalism Shu'ubiyya. He lived at the court of the caliphs al-Mutawakkil and Al-Musta'in and was tutor to the son of al-Mutazz. He died in 892 as the result of a drug called ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Banu Thaqif
The Banu Thaqif ( ar, بنو ثقيف, Banū Thaqīf) is an Tribes of Arabia, Arab tribe which inhabited, and still inhabits, the city of Ta'if and its environs, in modern Saudi Arabia, and played a prominent role in early Islamic history. During the pre-Islamic Arabia, pre-Islamic period, the Thaqif rivaled and cooperated with the Quraysh tribe of Mecca in trade and land ownership. The tribe initially opposed the Islamic prophet Muhammad, but following the Muslim siege of Ta'if in 630, they came to terms and embraced Islam. The Thaqif's inter-tribal networks and their relatively high education helped them quickly advance in the nascent Muslim state. They took on an especially important role in the conquest and administration of Iraq, providing the Rashidun Caliphate, Rashidun and Umayyad Caliphate, Umayyad caliphs capable and powerful governors for that province and the eastern Caliphate. Among their notable governors in Iraq were al-Mughira ibn Shu'ba (638, 642–645), Ziyad i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Al-Harith Ibn Kalada
Al-Harith ibn Kalada ( ar, الحارث بن كلدة; d. 13 AH/634–35) was an Arab physician and a companion of the Islamic prophet Muhammad. He is said to have traveled to Gundeshapur in search of medical knowledge before the advent of Islam Islam (; ar, ۘالِإسلَام, , ) is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic Monotheism#Islam, monotheistic religion centred primarily around the Quran, a religious text considered by Muslims to be the direct word of God in Islam, God (or .... References Further reading * C. Pellat, "al-Harith B. Kalada," EI2, supplement (1980). External links * {{DEFAULTSORT:Harith ibn Kalada Banu Thaqif Companions of the Prophet Physicians of the medieval Islamic world 7th-century physicians 630s deaths Year of birth unknown Hejaz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Expeditions Of Muhammad
__NOTOC__ The list of expeditions of Muhammad includes the expeditions undertaken by the Muslim community during the lifetime of the Islamic prophet Muhammad. Some sources use the word ''ghazwa'' and a related plural ''maghazi'' in a narrow technical sense to refer to the expeditions in which Muhammad took part, while using the word ''sariyya'' (pl. ''saraya'') for those early Muslim expeditions where he was not personally present. Other sources use the terms ''ghazwa'' and ''maghazi'' generically to refer to both types of expeditions. Early Islamic sources contain significant divergences in the chronology of expeditions. Unless noted otherwise, the dates given in this list are based on ''Muhammad at Medina'' by Montgomery Watt, who in turn follows the chronology proposed by Leone Caetani. List of expeditions ; Type legend References {{Muhammad2 Expeditions of Muhammad Military expeditions A military, also known collectively as armed forces, is a heavily armed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
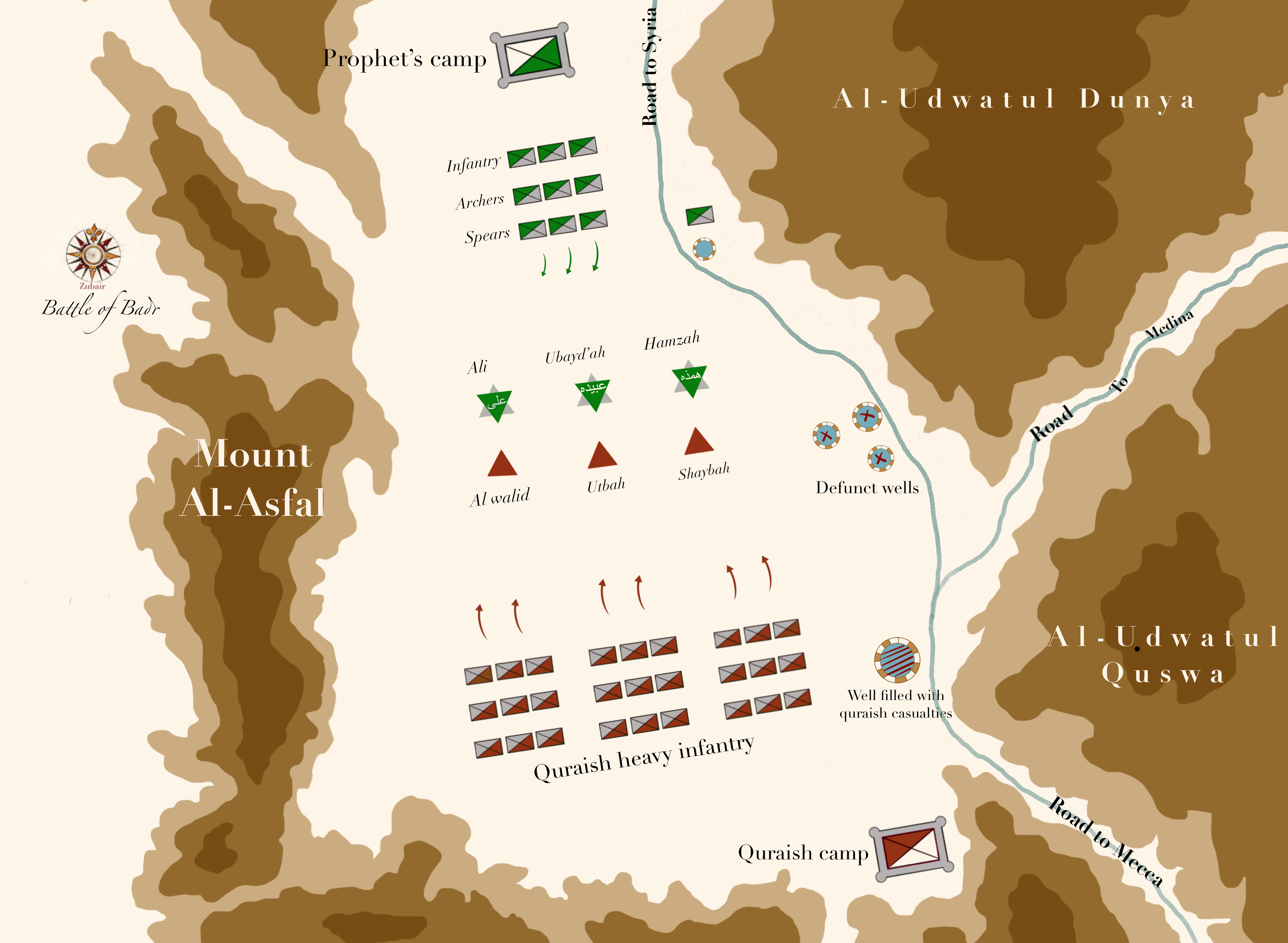
Battle Of Badr
The Battle of Badr ( ar, غَزْوَةُ بَدِرْ ), also referred to as The Day of the Criterion (, ) in the Quran, Qur'an and by Muslims, was fought on 13 March 624 CE (17 Ramadan (calendar month), Ramadan, 2 Anno Hegirae, AH), near the present-day city of Badr, Saudi Arabia, Badr, Madinah Province, Al Madinah Province in Saudi Arabia. Muhammad, commanding an army of his Companions of the Prophet, Sahaba, defeated an army of the Quraysh led by Amr ibn Hishām, better known as Abu Jahl. The battle marked the beginning of the six-year war between Muhammad and his tribe. Prior to the battle, the Muslims and the Meccans had fought several smaller skirmishes in late 623 and early 624. Muhammad took keen interest in capturing Meccan caravans after Hegira, his migration to Medina, seeing it as repayment for his people, the Muhajirun. A few days before the battle, when he learnt of a Makkan caravan returning from the Levant led by Abu Sufyan ibn Harb, Muhammad gathered a small E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quraysh
The Quraysh ( ar, قُرَيْشٌ) were a grouping of Arab clans that historically inhabited and controlled the city of Mecca and its Kaaba. The Islamic prophet Muhammad was born into the Hashim clan of the tribe. Despite this, many of the Quraysh staunchly opposed Muhammad, until converting to Islam ''en masse'' in CE. Afterwards, leadership of the Muslim community traditionally passed to a member of the Quraysh, as was the case with the Rashidun, Umayyad, Abbasid, and purportedly the Fatimid caliphates. Name Sources differ as to the etymology of Quraysh, with one theory holding that it was the diminutive form of ''qirsh'' (shark).Watt 1986, p. 435. The 9th-century genealogist Hisham ibn al-Kalbi asserted that there was no eponymous founder of Quraysh;Peters 1994, p. 14. rather, the name stemmed from ''taqarrush'', an Arabic word meaning "a coming together" or "association". The Quraysh gained their name when Qusayy ibn Kilab, a sixth-generation descendant of Fihr ibn Malik, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Banu Nawfal
) , type = Qurayshi / Adnanite Arab Tribe , image = , alt = , caption = Banner of Banu Taym , nisba = Al-Nawfal () , location = Western Arabian Peninsula, especially in Mecca (present-day Saudi Arabia) , descended = Nawfal ibn Abd Manaf , branches = , religion = Islam Banu Nawfal ( ar, بنو نوفل) is a notable Arabic sub-clan of the Quraish tribe. Its progenitor is Nawfal ibn Abd Manaf. References Nawfal {{islam-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hejaz
The Hejaz (, also ; ar, ٱلْحِجَاز, al-Ḥijāz, lit=the Barrier, ) is a region in the west of Saudi Arabia. It includes the cities of Mecca, Medina, Jeddah, Tabuk, Yanbu, Taif, and Baljurashi. It is also known as the "Western Province" in Saudi Arabia.Mackey, p. 101. "The Western Province, or the Hejaz .. It is bordered in the west by the Red Sea, in the north by Jordan, in the east by the Najd, and in the south by the 'Asir Region. Its largest city is Jeddah (the second largest city in Saudi Arabia), with Mecca and Medina being the fourth and fifth largest cities respectively in the country. The Hejaz is the most cosmopolitan region in the Arabian Peninsula. The Hejaz is significant for being the location of the Islamic holy cities of Mecca and Medina, the first and second holiest sites in Islam, respectively. As the site of the two holiest sites in Islam, the Hejaz has significance in the Arab and Islamic historical and political landscape. The region of Hejaz is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qays
Qays ʿAylān ( ar, قيس عيلان), often referred to simply as Qays (''Kais'' or ''Ḳays'') were an Arab tribal confederation that branched from the Mudar group. The tribe does not appear to have functioned as a unit in the pre-Islamic era (pre-630). However, by the early Umayyad period (661-750), its constituent tribes consolidated into one of the main tribo-political factions of the caliphate. The major constituent tribes or tribal groupings of the Qays were the Ghatafan, Hawazin, Amir, Thaqif, Sulaym, Ghani, Bahila and Muharib. Many of these tribes or their clans migrated from the Arabian Peninsula and established themselves in Jund Qinnasrin (military district of northern Syria) and the Jazira (Upper Mesopotamia), which long became their abode. From there they governed on behalf of the caliphs or rebelled against them. The power of the Qays as a unified group diminished with the rise of the Abbasid Caliphate which did not derive its military strength solely from the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)