|
Usman Bengali
Usman Bengali ( bn, ওসমান বাঙ্গালী, fa, ; d. 1570s) was a 16th-century Islamic scholar of Bengal. He is mostly associated for his great teaching in the town of Sambhal during the Mughal period. His name is mentioned in the works of ʽAbd al-Qadir Badayuni and Abd al-Hayy al-Lucknawi, where he is described as one of the most famous of the Hanafi ulama of that period. Biography Usman was born and raised in Bengal. He completed his education relating to Islamic studies and Qur'an, eventually earning the title of '' Mawlana''. He later migrated to Sambhal in Hindustan where he studied under the renowned poet Miyan Hatim Sambhali. Intending to seek further knowledge, he proceeded to Gujarat where he became a student of Wajihuddin Alvi who was the teacher of Yusuf Bengali. According to the ''Asrariyah'' treatise written by Kamal Muhammad Sambhali, Usman then went back to Sambhal where he permanently settled. During his old age, his students would regularl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hanafis
The Hanafi school ( ar, حَنَفِية, translit=Ḥanafiyah; also called Hanafite in English), Hanafism, or the Hanafi fiqh, is the oldest and one of the four traditional major Sunni schools (maddhab) of Islamic Law (Fiqh). It is named after the 8th century Kufan scholar, Abu Hanifa, a Tabi‘i of Persian origin whose legal views were preserved primarily by his two most important disciples, Imam Abu Yusuf and Muhammad al-Shaybani. It is considered one of the most widely accepted maddhab amongst Sunni Muslim community and is called the ''Madhhab of Jurists'' (maddhab ahl al-ray). The importance of this maddhab lies in the fact that it is not just a collection of rulings or sayings of Imam Abu Hanifa alone, but rather the rulings and sayings of the council of judges he established belong to it. It had a great excellence and advantage over the establishment of Sunni Islamic legal science. No one before Abu Hanifa preceded in such works. He was the first to solve the cases and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
16th-century Bengalis
The 16th century begins with the Julian year 1501 ( MDI) and ends with either the Julian or the Gregorian year 1600 ( MDC) (depending on the reckoning used; the Gregorian calendar introduced a lapse of 10 days in October 1582). The 16th century is regarded by historians as the century which saw the rise of Western civilization and the Islamic gunpowder empires. The Renaissance in Italy and Europe saw the emergence of important artists, authors and scientists, and led to the foundation of important subjects which include accounting and political science. Copernicus proposed the heliocentric universe, which was met with strong resistance, and Tycho Brahe refuted the theory of celestial spheres through observational measurement of the 1572 appearance of a Milky Way supernova. These events directly challenged the long-held notion of an immutable universe supported by Ptolemy and Aristotle, and led to major revolutions in astronomy and science. Galileo Galilei became a champion ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muntakhab-ut-Tawarikh
''Muntakhab-ut-Tawarikh (منتخب التواریخ) or'' ''Tarikh-i-Bada'uni'' (تاریخ بداؤنی), ''Selection of Chronicles'' by `Abd al-Qadir Bada'uni (1540–1605) is a book describing the early Mughal history of India, covering the period from the days of Ghaznavid reign until the fortieth regnal year of Mughal Emperor Akbar. Overview ''Muntakhab-ut-Tawarikh'' is a general history of the Muslims in India from Sabuktigin to 1595, commenced in 1590 followed by biographies of shaykhs, scholars, physicians and poets. `Abd al-Qadir Bada'uni began writing this history in the first half of 1590. The book was completed by October 1595. Its comprises on the 618 solar year's historic events. ''Muntakhab-ut-Tawarikh'' is based largely on Khawaja Nīzām-ud-Din Ahmad Sirhindi's Tabakāt-i-Akbar Shāhi (also known as Tabakāt-i-Akbari), with characteristic asides by `Abd al-Qadir Bada'uni. The work contains three volumes. The first volume contains historic accounts about th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wolseley Haig
Sir Thomas Wolseley Haig KCIE CSI CMG CBE (7 August 1865 – 28 April 1938) was a civil servant in British India, then Professor at Trinity College, Dublin, and later a Scottish herald. Early life Haig was the son of Major Robert Wolseley Haig RA, FRS, (1830–72) the military astronomer, and Maria Georgina Brown. His maternal great grandfather was Charles James Blomfield, Bishop of London. He was also descended from the Haigs of Bonnington, branch of the Border house of Haig of Bemersyde, and was thus related to the first Lord Haig. He was educated at Wellington College, and then Sandhurst. Army career Haig joined the Seaforth Highlanders in 1884 and was transferred to the Indian Army in 1887 where he served in Upper Burma (1887–89) fighting "dacoits" (bandits). He won a medal and clasp for his service. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grand Mufti Of India
The Grand Mufti of India is the most senior and influential religious authority of the Barelvi Muslim Community of India. The incumbent is Sheikh Abubakr Ahmad, general secretary of All India Sunni Jamiyyathul Ulama, who was conferred the title in February 2019 at the Gareeb Nawaz Peace Conference held at Ramlila Maidan, New Delhi, organised by the All India Tanzeem Ulama-e-Islam. Role The Grand Mufti is the most senior religious authority in the country. His main role is to give opinions (''fatawa'') on Islamic legal matters and social affairs. The Grand Mufti is traditionally chosen from the Barelvi school of Sunni Islam. History Mughal period The first Grand Mufti of India, Shah Fazle Rasool Badayuni was appointed by the final Mughal Emperor, Bahadur Shah Zafar. Badayuni was a Hanafi scholar who had deep knowledge of Islamic jurisprudence. His Urdu statements on Islamic subjects were published as ''Tariqi Fatwa,'' which later became famous. His grandson `Abd al-Qad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kamal Muhammad Sambhali , Australian Malaysian singer
{{disambiguation ...
Kamal may refer to: *Kamal (name), a male given name and surname with multiple origins *Kamal (navigation), a navigational instrument for measuring latitude *Kamal, Jhapa, a rural municipality in Nepal *Alfa Romeo Kamal, an SUV by Alfa Romeo *Operation Kamala, name given to corrupt political practices by BJP in India See also *Kamala (other) *Kamahl Kandiah Kamalesvaran ( ta, கந்தையா கமலேஸ்வரன்; born 13 November 1934), better known by his stage name Kamahl, is a Malaysian-born Australian singer and recording artist. His highest charting Australian single, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yusuf Bengali
Mufti Yūsuf Bangālī ( bn, ইঊসুফ বাঙ্গালী, fa, ) was a 16th-century Sufi pir of the Shattari order. He was a prominent teacher during the reign of the Farooqui dynasty and Mughal emperor Akbar. Background Yusuf originated from Bengal. He travelled across the subcontinent for further Islamic studies, eventually becoming a student and disciple of Wajihuddin Alvi, who was also the teacher of Usman Bengali. After gaining sufficient training from Alvi, he was permitted to migrate to Burhanpur where he maintained a khanqah as well as a madrasa. Yusuf became one of the most prominent scholars of the Shattari order of Bengali descent, others being Ali Sher of Sylhet and Shah Manjhan of Lakhnauti. Pir Muhammad bin Abdul Halim was a longtime student of Yusuf, and Isa Burhanpuri was another notable student of Yusuf Bengali. Yusuf would also circumcise Muslim children after their birth, and most notably, Yusuf circumcised Sakah Ji Burhanpuri who would later ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gujarat
Gujarat (, ) is a state along the western coast of India. Its coastline of about is the longest in the country, most of which lies on the Kathiawar peninsula. Gujarat is the fifth-largest Indian state by area, covering some ; and the ninth-most populous state, with a population of 60.4 million. It is bordered by Rajasthan to the northeast, Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu to the south, Maharashtra to the southeast, Madhya Pradesh to the east, and the Arabian Sea and the Pakistani province of Sindh to the west. Gujarat's capital city is Gandhinagar, while its largest city is Ahmedabad. The Gujaratis are indigenous to the state and their language, Gujarati, is the state's official language. The state encompasses 23 sites of the ancient Indus Valley civilisation (more than any other state). The most important sites are Lothal (the world's first dry dock), Dholavira (the fifth largest site), and Gola Dhoro (where 5 uncommon seals were found). Lothal i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
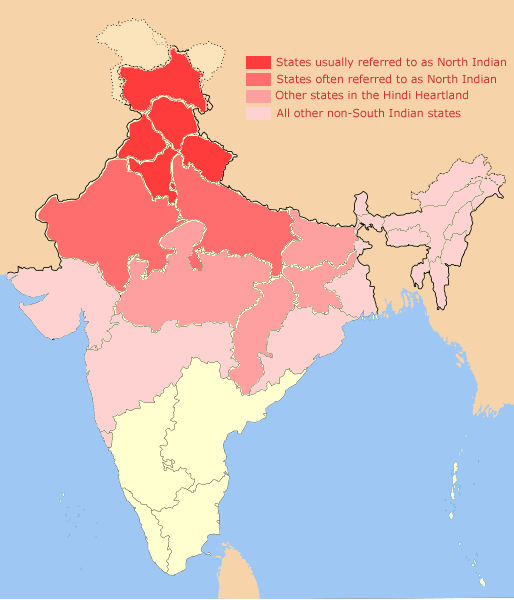
North India
North India is a loosely defined region consisting of the northern part of India. The dominant geographical features of North India are the Indo-Gangetic Plain and the Himalayas, which demarcate the region from the Tibetan Plateau and Central Asia. The term North India has varying definitions. The Ministry of Home Affairs in its Northern Zonal Council Administrative division included the states of Haryana, Himachal Pradesh, Punjab and Rajasthan and Union Territories of Chandigarh, Delhi, Jammu and Kashmir and Ladakh. The Ministry of Culture in its ''North Culture Zone'' includes the state of Uttarakhand but excludes Delhi whereas the Geological Survey of India includes Uttar Pradesh and Delhi but excludes Rajasthan and Chandigarh. Other states sometimes included are Bihar, Gujarat, Jharkhand, Madhya Pradesh and West Bengal. North India has been the historical centre of the Mughal Empire, the Delhi Sultanate and the British Indian Empire. It has a diverse culture, and includ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qur'an
The Quran (, ; Standard Arabic: , Quranic Arabic: , , 'the recitation'), also romanized Qur'an or Koran, is the central religious text of Islam, believed by Muslims to be a revelation from God. It is organized in 114 chapters (pl.: , sing.: ), which consist of verses (pl.: , sing.: , cons.: ). In addition to its religious significance, it is widely regarded as the finest work in Arabic literature, and has significantly influenced the Arabic language. Muslims believe that the Quran was orally revealed by God to the final prophet, Muhammad, through the archangel Gabriel incrementally over a period of some 23 years, beginning in the month of Ramadan, when Muhammad was 40; and concluding in 632, the year of his death. Muslims regard the Quran as Muhammad's most important miracle; a proof of his prophethood; and the culmination of a series of divine messages starting with those revealed to Adam, including the Torah, the Psalms and the Gospel. The word ''Quran'' occurs so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Islamic Studies
Islamic studies refers to the academic study of Islam, and generally to academic multidisciplinary "studies" programs—programs similar to others that focus on the history, texts and theologies of other religious traditions, such as Eastern Christian Studies or Jewish Studies but also fields such as (environmental studies, Middle East studies, race studies, urban studies, etc.)—where scholars from diverse disciplines (history, culture, literature, art) participate and exchange ideas pertaining to the particular field of study. Carole Hillenbrand describes Islamic studies as "a discipline that seeks to explain what the Islamic world has achieved in the past and what the future holds for it." Many academic Islamic Studies programs include the historical study of Islam, Islamic civilization, history of the Muslim world, historiography, Islamic law, Islamic theology and Islamic philosophy. Specialists in Islamic Studies concentrate on the detailed, academic study of tex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |