|
User Stories
In software development and product management, a user story is an informal, natural language description of features of a software system. They are written from the perspective of an end user or user of a system, and may be recorded on index cards, Post-it notes, or digitally in project management software. Depending on the project, user stories may be written by different stakeholders like client, user, manager, or development team. User stories are a type of boundary object. They facilitate sensemaking and communication; and may help software teams document their understanding of the system and its context. History * 1997: Kent Beck introduces user stories at the Chrysler C3 project in Detroit. * 1998: Alistair Cockburn visited the C3 project and coined the phrase "A user story is a promise for a conversation." * 1999: Kent Beck published the first edition of the book ''Extreme Programming Explained'', introducing Extreme Programming (XP), and the usage of user stories in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Software Development
Software development is the process of conceiving, specifying, designing, programming, documenting, testing, and bug fixing involved in creating and maintaining applications, frameworks, or other software components. Software development involves writing and maintaining the source code, but in a broader sense, it includes all processes from the conception of the desired software through to the final manifestation of the software, typically in a planned and structured process. Software development also includes research, new development, prototyping, modification, reuse, re-engineering, maintenance, or any other activities that result in software products. Methodologies One system development methodology is not necessarily suitable for use by all projects. Each of the available methodologies are best suited to specific kinds of projects, based on various technical, organizational, project, and team considerations. Software development activities Identification of need The sou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scrum (development)
Scrum is a framework for project management with an initial emphasis on software development, although it has been used in other fields including research, sales, marketing and advanced technologies. It is designed for teams of ten or fewer members who break their work into goals that can be completed within time-boxed iterations, called ''sprints'', no longer than one month and most commonly two weeks. The scrum team assesses progress in time-boxed daily meetings of 15 minutes or fewer, called daily scrums (a form of stand-up meeting). At the end of the sprint, the team holds two further meetings: one sprint review intended to demonstrate the work done for stakeholders and elicit feedback, and one sprint retrospective intended to enable the team to reflect and improve. Name The term ''scrum'' is borrowed from rugby, where it is a formation of players. The term ''scrum'' was chosen by the paper's authors because it implies teamwork. The software development term ''scru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
User Story Mapping , a user of a commercial product or service
{{disambiguation ...
Ancient Egyptian roles * User (ancient Egyptian official), an ancient Egyptian nomarch (governor) of the Eighth Dynasty * Useramen, an ancient Egyptian vizier also called "User" Other uses * User (computing), a person (or software) using an information system * User (telecommunications), an entity using a telecommunications system * User, a slang term for a freeloader See also * Drug user (other), a person who uses drugs * End user In product development, an end user (sometimes end-user) is a person who ultimately uses or is intended to ultimately use a product. The end user stands in contrast to users who support or maintain the product, such as sysops, system administrat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
To-do List
Time management is the process of planning and exercising conscious control of time spent on specific activities, especially to increase effectiveness, efficiency, and productivity. It involves of various demands upon a person relating to Employment, work, Interpersonal relationship, social life, family, hobby, hobbies, personal interests, and commitments with the finite nature of time. Using time effectively gives the person "choice" on spending or managing activities at their own time and expediency. Time management may be aided by a range of skills, tools, and techniques used to management, manage time when accomplishing specific tasks, projects, and goals complying with a due date. Initially, time management referred to just business or work activities, but eventually, the term broadened to include personal activities as well. A time management system is a designed combination of processes, tools, techniques, and methods. Time management is usually a necessity in any project man ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hierarchy
A hierarchy (from Greek: , from , 'president of sacred rites') is an arrangement of items (objects, names, values, categories, etc.) that are represented as being "above", "below", or "at the same level as" one another. Hierarchy is an important concept in a wide variety of fields, such as architecture, philosophy, design, mathematics, computer science, organizational theory, systems theory, systematic biology, and the social sciences (especially political philosophy). A hierarchy can link entities either directly or indirectly, and either vertically or diagonally. The only direct links in a hierarchy, insofar as they are hierarchical, are to one's immediate superior or to one of one's subordinates, although a system that is largely hierarchical can also incorporate alternative hierarchies. Hierarchical links can extend "vertically" upwards or downwards via multiple links in the same direction, following a path. All parts of the hierarchy that are not linked vertically to one ano ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jira (software)
Jira ( ) is a proprietary software, proprietary issue tracking system, issue tracking product developed by Atlassian that allows bug tracking system, bug tracking and agile software development, agile project management. Naming The product name comes from the second and third syllables of the Japanese word pronounced as ''Gojira'', which is Japanese for Godzilla. The name originated from a nickname Atlassian developers used to refer to Bugzilla, which was previously used internally for bug-tracking. Description According to Atlassian, Jira is used for issue tracking and project management by over 180,000 customers in 190 countries. Some of the organizations that have used Jira at some point in time for bug-tracking and project management include Fedora Commons, Hibernate (Java), Hibernate, and the The Apache Software Foundation, Apache Software Foundation, which uses both Jira and Bugzilla. Jira includes tools allowing migration from competitor Bugzilla. Jira is offered in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
User Story Map In Action , a user of a commercial product or service
{{disambiguation ...
Ancient Egyptian roles * User (ancient Egyptian official), an ancient Egyptian nomarch (governor) of the Eighth Dynasty * Useramen, an ancient Egyptian vizier also called "User" Other uses * User (computing), a person (or software) using an information system * User (telecommunications), an entity using a telecommunications system * User, a slang term for a freeloader See also * Drug user (other), a person who uses drugs * End user In product development, an end user (sometimes end-user) is a person who ultimately uses or is intended to ultimately use a product. The end user stands in contrast to users who support or maintain the product, such as sysops, system administrat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Given-When-Then
Given-When-Then (GWT) is a semi-structured way to write down test cases. They can either be tested manually or automated as browser tests with tools like Selenium and Cucumber. It derives its name from the three clauses used, which start with the words given, when and then. Given describes the preconditions and initial state before the start of a test and allows for any pre-test setup that may occur. When describes actions taken by a user during a test. Then describes the outcome resulting from actions taken in the when clause. The Given-When-Then was proposed by Dan North in 2006, as part of behavior-driven development. See also * Acceptance test-driven development * Acceptance testing * Behavior-driven development * Cucumber syntax * Hoare triple Hoare logic (also known as Floyd–Hoare logic or Hoare rules) is a formal system with a set of logical rules for reasoning rigorously about the correctness of computer programs. It was proposed in 1969 by the British comput ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fibonacci Scale (agile)
In Agile software development, the Fibonacci scale consists of a sequence of numbers used for estimating the relative size of user stories in points. Agile Scrum is based on the concept of working iteratively in short sprints, typically two weeks long, where the requirements and development are continuously being improved. The Fibonacci sequence consists of numbers that are the summation of the two preceding numbers, starting with , 1 Agile uses the Fibonacci sequence to achieve better results by reducing complexity, effort, and doubt when determining the development time required for a task, which can range from a few minutes to several weeks. Procedure It is easier to determine the relative complexity of a task rather than figuring out how much time it requires. Due to this, when working with agile, a revised Fibonacci scale is used in terms of points to estimate the work, as opposed to the traditional measurement of time. In one method commonly used to calculate the size ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extreme Programming Practices
Extreme programming (XP) is an agile software development methodology used to implement software projects. This article details the practices used in this methodology. Extreme programming has 12 practices, grouped into four areas, derived from the best practices of software engineering.Beck, K. ''Extreme Programming Explained: Embrace Change'' 2nd. ed. Addison-Wesley, 2000 pp. 54 Fine scale feedback Pair programming Pair programming means that all the codes which is produced by two people programming on one task on one workstation. One programmer has control over the workstation and is thinking mostly about the coding in detail. The other programmer is more focused on the big picture, and is continually reviewing the code that is being produced by the first programmer. Programmers trade roles after minute to hour periods. The pairs are not fixed; programmers switch partners frequently, so that everyone knows what everyone is doing, and everybody remains familiar with the whole ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extreme Programming
Extreme programming (XP) is a software development methodology intended to improve software quality and responsiveness to changing customer requirements. As a type of agile software development,"Human Centred Technology Workshop 2006 ", 2006, PDFHuman Centred Technology Workshop 2006 /ref> it advocates frequent Software release life cycle, releases in short development cycles, intended to improve productivity and introduce checkpoints at which new customer requirements can be adopted. Other elements of extreme programming include: programming Pair programming, in pairs or doing extensive code review, unit testing of all code, You aren't gonna need it, not programming features until they are actually needed, a flat management structure, code simplicity and clarity, expecting changes in the customer's requirements as time passes and the problem is better understood, and frequent communication with the customer and among programmers. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
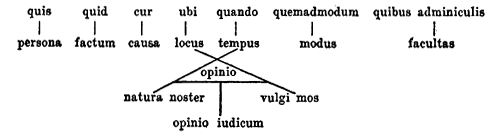
Five Ws
The Five Ws (sometimes referred to as Five Ws and How, 5W1H, or Six Ws) are questions whose answers are considered basic in information gathering or problem solving. They are often mentioned in journalism (''cf.'' news style), research, and police investigations. According to the principle of the Five Ws, a report can only be considered complete if it answers these questions starting with an interrogative word: * Who * What * When * Where * Why Some others commonly add ''how'' to the list. Each question should have a factual answer—facts necessary to include for a report to be considered complete. Importantly, none of these questions can be answered with a simple "yes" or "no". In the United Kingdom (excluding Scotland), the Five Ws are used in Key Stage 2 and Key Stage 3 lessons (ages 7–14). Origin The Five Ws and How were long attributed to Hermagoras of Temnos. But in 2010, it was established that Aristotle's Nicomachean Ethics are in fact the source of the element ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |