|
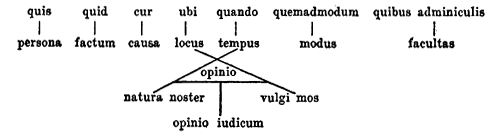
Five Ws
The Five Ws (sometimes referred to as Five Ws and How, 5W1H, or Six Ws) are questions whose answers are considered basic in information gathering or problem solving. They are often mentioned in journalism (''cf.'' news style), research, and police investigations. According to the principle of the Five Ws, a report can only be considered complete if it answers these questions starting with an interrogative word: * Who * What * When * Where * Why Some others commonly add ''how'' to the list. Each question should have a factual answer—facts necessary to include for a report to be considered complete. Importantly, none of these questions can be answered with a simple "yes" or "no". In the United Kingdom (excluding Scotland), the Five Ws are used in Key Stage 2 and Key Stage 3 lessons (ages 7–14). Origin The Five Ws and How were long attributed to Hermagoras of Temnos. But in 2010, it was established that Aristotle's Nicomachean Ethics are in fact the source of the element ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
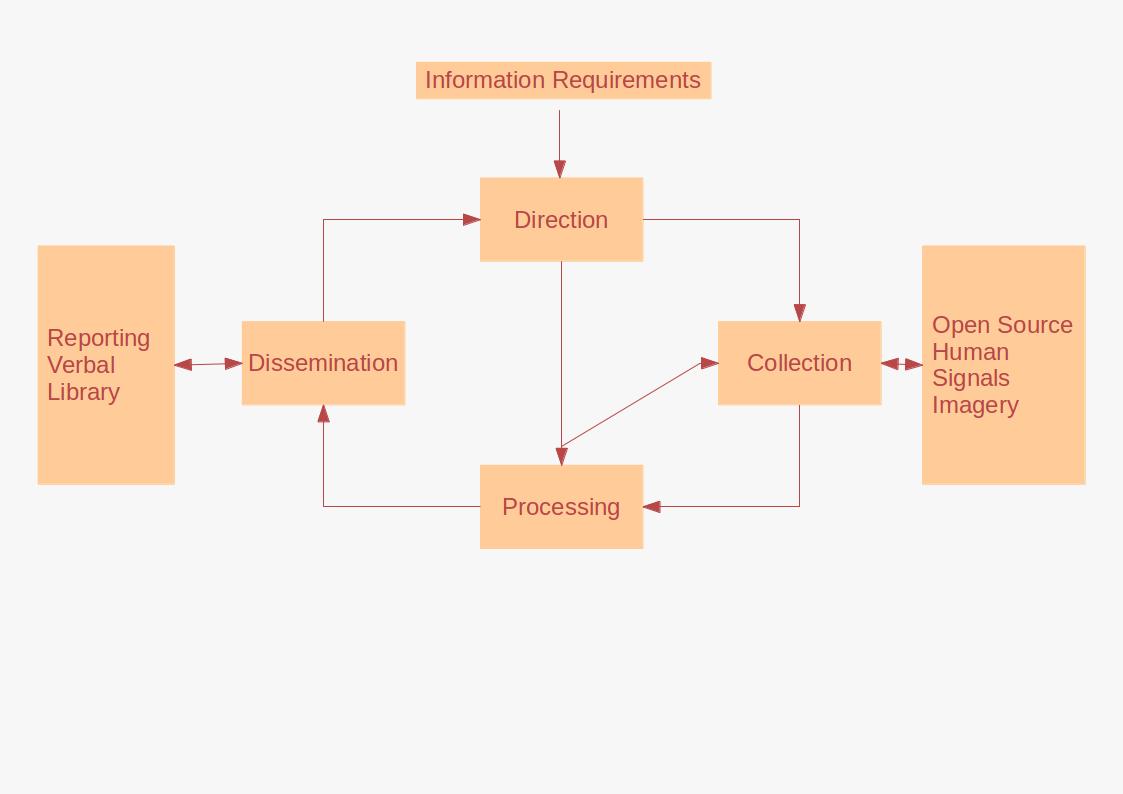
Information Gathering
Intelligence assessment, or simply intel, is the development of behavior forecasts or recommended courses of action to the leadership of an organisation, based on wide ranges of available overt and covert information (intelligence). Assessments develop in response to leadership declaration requirements to inform decision-making. Assessment may be executed on behalf of a state, military or commercial organisation with ranges of information sources available to each. An intelligence assessment reviews available information and previous assessments for relevance and currency. Where there requires additional information, the analyst may direct some collection. Intelligence studies is the academic field concerning intelligence assessment, especially relating to international relations and military science. Process Intelligence assessment is based on a customer requirement or need, which may be a standing requirement or tailored to a specific circumstance or a Request for Informa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Locus (rhetoric)
''Inventio'', one of the five canons of rhetoric, is the method used for the ''discovery of arguments'' in Western rhetoric and comes from the Latin word, meaning "invention" or "discovery". ''Inventio'' is the central, indispensable canon of rhetoric, and traditionally means a systematic search for arguments. A speaker uses ''Inventio'' when they begin the thought process to form and develop an effective argument. Often, the invention phase can be seen as the first step in an attempt to generate ideas or create an argument that is convincing and compelling. The other four canons of classical rhetoric (namely dispositio, elocutio, memoria, and pronuntiatio) rely on their interrelationship with invention. Purpose According to Crowley and Hawhee, invention is the division of rhetoric that investigates the possible means by which proofs can be discovered. It supplies the speaker and writers with sets of instructions or ideas that help them to find and compose arguments that are ap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert De Sorbon
Robert de Sorbon (; 9 October 1201 – 15 August 1274) was a French theologian, the chaplain of Louis IX of France, and founder of the Sorbonne college in Paris. Biography Born into a poor family in Sorbon, in what is now the Ardennes ''département'', Robert de Sorbon entered the Church and was educated in Reims and Paris. He was noted for his piety and attracted the patronage of the Comte d'Artois and King Louis IX of France, later known as Saint Louis. He became the canon of Cambrai around 1251 before being appointed canon of Paris and the king's confessor in 1258. Sorbon began to teach around 1253 and in 1257 established the ''Maison de Sorbonne'', a college in Paris originally intended to teach theology to twenty poor students. It was sponsored by King Louis and received the endorsement of Pope Alexander IV in 1259. He was assisted by Peter of Limoges. It subsequently grew into a major centre of learning and became the core of what would become the University of Paris. So ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Summa Theologica
The ''Summa Theologiae'' or ''Summa Theologica'' (), often referred to simply as the ''Summa'', is the best-known work of Thomas Aquinas (1225–1274), a scholasticism, scholastic theologian and Doctor of the Church. It is a compendium of all of the main theology, theological teachings of the Catholic Church, intended to be an instructional guide for theology students, including Seminary, seminarians and the literate laity. Presenting the reasoning for almost all points of Christian theology in the West, topics of the ''Summa'' follow the following cycle: God; Creation, Man; teleology, Man's purpose; Christ; the Sacraments; and back to God. Thomas Aquinas#Late career and cessation of writing (1272–1274), Although unfinished, it is "one of the classics of the history of philosophy and one of the most influential works of Western literature." Moreover, the ''Summa'' remains Aquinas' "most perfect work, the fruit of his mature years, in which the thought of his whole life is con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexander De Stavenby
Alexander de Stavenby (or Alexander of Stainsby; died 26 December 1238) was a medieval Bishop of Coventry and Lichfield. Alexander was probably a native of Stainsby, Lincolnshire, and had two brothers, William and Gilbert, who held land there. He may have studied under Stephen Langton, later Archbishop of Canterbury, as Langton was from a village less than 10 miles away.Vincent "Stainsby , Alexander of" ''Oxford Dictionary of National Biography'' Alexander taught theology at Toulouse before his appointment to the episcopate.Moorman ''Church Life in England'' p. 163 He may have been a teacher of Dominic, the founder of the Dominican Order, at Toulouse.Moorman ''Church Life in England'' p. 368 He also taught at Bologna and was named a chamber clerk for Pope Honorius III. Alexander was nominated as bishop about 13 April 1224, and consecrated on 14 April 1224.Fryde, et al. ''Handbook of British Chronology'' p. 253 While bishop, Alexander urged the people in his diocese to receive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fourth Lateran Council
The Fourth Council of the Lateran or Lateran IV was convoked by Pope Innocent III in April 1213 and opened at the Lateran Palace in Rome on 11 November 1215. Due to the great length of time between the Council's convocation and meeting, many bishops had the opportunity to attend what is considered by the Roman Catholic Church to have been the twelfth ecumenical council. Background Innocent III first mooted organizing an ecumenical council in November 1199. In his letter titled ''Vineam Domini'', dated 19 April 1213, the Pope writes of the urgent need to recover the Holy Land and reform the Church. The letter, which also served as a summons to an ecumenical council, was included alongside the Pope's papal bull '' Quia maior''. In preparing for the council, the Pope spearheaded the extensive refurbishment of the old St. Peter's Basilica, which he designated as the "centrepiece for display and decoration" during the council. The lunette of the main door leading to the tomb of St. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Penance
Penance is any act or a set of actions done out of Repentance (theology), repentance for Christian views on sin, sins committed, as well as an alternate name for the Catholic Church, Catholic, Lutheran, Eastern Orthodox, and Oriental Orthodox sacrament of Reconciliation or Confession. It also plays a part in confession among Anglicanism, Anglicans and Methodism, Methodists, in which it is a Sacrament, rite, as well as among other Protestants. The word ''penance'' derives from Old French and Latin ''paenitentia'', both of which derive from the same root meaning repentance, the desire to be Forgiveness, forgiven (in English see contrition). Penance and repentance, similar in their derivation and original sense, have come to symbolize conflicting views of the essence of repentance, arising from the controversy as to the respective merits of Faith in Christianity, "faith" and "good works". Word derivations occur in many languages. According to dictionary definitions, the primary mea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Of Salisbury
John of Salisbury (late 1110s – 25 October 1180), who described himself as Johannes Parvus ("John the Little"), was an English author, philosopher, educationalist, diplomat and bishop of Chartres. Early life and education Born at Salisbury, England, he was of Anglo-Saxon rather than of Norman extraction, and therefore apparently a clerk from a modest background, whose career depended upon his education. Beyond that, and that he applied to himself the cognomen of ''Parvus'', meaning "short" or "small", few details are known regarding his early life. From his own statements it is gathered that he crossed to France about 1136, and began regular studies in Paris under Peter Abelard,Guilfoy, Kevin"John of Salisbury" The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy (Spring 2015 Edition), Edward N. Zalta (ed.). who had for a brief period re-opened his famous school there on Montagne Sainte-Geneviève. His vivid accounts of teachers and students provide some of the most valuable insights into ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thierry De Chartres
Thierry of Chartres (''Theodoricus Chartrensis'') or Theodoric the Breton (''Theodericus Brito'') (died before 1155, probably 1150) was a twelfth-century philosophy, philosopher working at Chartres and Paris, France. The cathedral school at Chartres promoted scholarship before the first university was founded in France. Thierry was a major figure in twelfth-century philosophy and learning, and, like many twelfth-century scholars, is notable for his embrace of Plato's ''Timaeus (dialogue), Timaeus'' and his application of philosophy to theological issues. Some modern scholars believed Thierry to have been a brother of Bernard of Chartres who had founded the school of Chartres, but later research has shown that this is unlikely. Thierry became chancellor of Chartres after his predecessor, Gilbert of Poitiers, returned to his native city in 1141. John of Salisbury, Herman of Carinthia, and Clarembald of Arras were among Thierry's students. Works ''Hexaemeron'' The ''Hexaemeron'' in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boethius
Anicius Manlius Severinus Boethius, commonly known as Boethius (; Latin: ''Boetius''; 480 – 524 AD), was a Roman senator, consul, ''magister officiorum'', historian, and philosopher of the Early Middle Ages. He was a central figure in the translation of the Greek classics into Latin, a precursor to the Scholastic movement, and, along with Cassiodorus, one of the two leading Christian scholars of the 6th century. The local cult of Boethius in the Diocese of Pavia was sanctioned by the Sacred Congregation of Rites in 1883, confirming the diocese's custom of honouring him on the 23 October. Boethius was born in Rome a few years after the collapse of the Western Roman Empire. A member of the Anicii family, he was orphaned following the family's sudden decline and was raised by Quintus Aurelius Memmius Symmachus, a later consul. After mastering both Latin and Greek in his youth, Boethius rose to prominence as a statesman during the Ostrogothic Kingdom: becoming a senator by a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Julius Victor
Gaius Julius Victor (4th century AD) was a Roman writer of rhetoric, possibly of Gaulish origin. His extant manual is of some importance as facilitating the textual criticism of Quintilian, whom he closely follows in many places. References Attribution: * *''Rhetores Latini minores'', Karl Halm Karl Felix Halm (also ''Carl''; ''Karl Felix Ritter von Halm'' after 1872; 5 April 1809 – 5 October 1882), was a German classical scholar and critic. Life He was born at Munich. In 1849, having held appointments at Speyer and Hadamar, he ... (ed.), Lipsiae in aedibus B. G. Teubneri, 1863pp. 371-448 * ''C. Julii Victoris Ars rhetorica'', Remo Giomini; Maria Silvana Celentano (eds.) Leipzig: Teubner, 1980. {{DEFAULTSORT:Julius Victor, Gaius 4th-century Romans 4th-century Latin writers Ancient Roman rhetoricians Victor, Gaius ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Victorinus
Marcus Piavonius VictorinusSome of the inscriptions record his name as M. Piavvonius Victorinus, as does the first release of coins from the Colonia mint. A mosaic from Augusta Treverorum (Trier) lists him as Piaonius. was emperor in the Gallic provinces from 268 to 270Martindale, p. 965 or 269 to 271,Polfer, ''Victorinus'' following the brief reign of Marius. He was murdered by a jealous husband whose wife he had tried to seduce. Reign Hailing from Gaul, Victorinus was born to a family of great wealth, and was a soldier under Postumus, the first of the so-called Gallic emperors. He showed considerable ability, as he held the title of tribunus praetorianorum (tribune of the praetorians) in 266/267, and rose swiftly to become co-consul with Postumus in 268.Southern, p. 118 It is also possible that Postumus then elevated him to the post of praetorian prefect.Potter, p. 266 Shortly after putting down a rebellion by Laelianus in 269, Postumus was murdered by his own troops, who a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |