|
Jira (software)
Jira ( ) is a software product developed by Atlassian that allows bug tracking, issue tracking and agile project management. Jira is used by a large number of clients and users globally for project, time, requirements, task, bug, change, code, test, release, sprint management. Naming The product name comes from the second and third syllables of the Japanese word pronounced as ''Gojira'', which is Japanese for Godzilla. The name originated from a nickname Atlassian developers used to refer to Bugzilla, which was previously used internally for bug-tracking. Description According to Atlassian, Jira is used for issue tracking and project management. Some of the organizations that have used Jira at some point in time for bug-tracking and project management include Fedora Commons, Hibernate, and the Apache Software Foundation, which uses both Jira and Bugzilla. Jira includes tools allowing migration from competitor Bugzilla. Jira is offered in three packages: * Jira Softwar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atlassian
Atlassian Corporation () is an Australia, Australian-United States, American proprietary software company that specializes in collaboration tools designed primarily for software development and project management. Domicile (law), Domiciled in the United States as Atlassian Corporation Plc., the company is globally headquartered in Sydney, Australia, with a US headquarters in San Francisco, and over 12,000 employees across 14 countries. Atlassian currently serves over 300,000 customers in over 200 countries across the globe. History In 2001, Mike Cannon-Brookes sent an email to his University of New South Wales classmates asking if any of them were interested in helping him launch a tech startup after graduation. Scott Farquhar was the only one who replied, and together they founded Atlassian in 2002. They Entrepreneurship#Bootstrapping, bootstrapped the company for several years, financing the startup with a $10,000 credit card debt. The name was derived from the Greek mytho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jira Studio
Jira Studio was an integrated, hosted software development suite developed by Atlassian Software Systems. Jira Studio included Subversion for revision control, Jira for issue tracking and bug tracking, Confluence for content management, Jira Agile (previously known as GreenHopper) for agile planning and management, Bamboo for continuous integration, Crucible for code review and FishEye for source code repository browsing. Jira Studio was retired in February 2013. The Atlassian Cloud offers the same SaaS hosted model, integrations, and plugin capability, but is licensed per product. Integration Jira Studio supported Atlassian's IDE connectors for Eclipse, Visual Studio and IntelliJ IDEA. Information in Jira Studio could be displayed in external systems using OpenSocial gadgets, and project information could be externally accessed using Activity Streams.{{cite web, url=https://www.proggio.com/blog/using-jira-for-project-management/, title= Jira Project Management Monday, 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Team Foundation Server
Azure DevOps Server, formerly known as Team Foundation Server (TFS) and Visual Studio Team System (VSTS), is a Microsoft product that provides version control (either with Team Foundation Version Control (TFVC) or Git), reporting, requirements management, project management (for both agile software development and waterfall teams), automated builds, testing and release management capabilities. It covers the entire application lifecycle and enables DevOps capabilities. Azure DevOps can be used as a back-end to numerous integrated development environments (IDEs) but is tailored for Microsoft Visual Studio and Eclipse on all platforms. On-premises vs. online Azure DevOps is available in two different forms: on-premises ("Server") and online ("Services"). The latter form is called Azure DevOps Services (formerly Visual Studio Online before it was renamed to Visual Studio Team Services in 2015). The cloud service is backed by the Microsoft Azure cloud platform. It uses the same ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apache Subversion
Apache Subversion (often abbreviated SVN, after its command name ''svn'') is a version control system distributed as open source under the Apache License. Software developers use Subversion to maintain current and historical versions of files such as source code, web pages, and documentation. Its goal is to be a mostly compatible successor to the widely used Concurrent Versions System (CVS). The open source community has used Subversion widely: for example, in projects such as Apache Software Foundation, FreeBSD, SourceForge, and from 2006 to 2019, GCC. CodePlex was previously a common host for Subversion repositories. Subversion was created by CollabNet Inc. in 2000, and is now a top-level Apache project being built and used by a global community of contributors. History CollabNet founded the Subversion project in 2000 as an effort to write an open-source version-control system which operated much like CVS but which fixed the bugs and supplied some features missing in CVS ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perforce
Perforce Software, Inc. is an American developer of software used for developing and running applications, including version control software, web-based repository management, developer collaboration, application lifecycle management, web application servers, debugging tools, platform automation, and agile planning software. The company is based in Minneapolis, Minnesota, and is equally owned by private equity firms Clearlake Capital and Francisco Partners. History Perforce was founded in 1995 in Alameda, California by Christopher Seiwald, a software developer and computer science graduate from UC Berkeley. Its first product was also called Perforce, and was a version control system allowing companies to collaborate on large software projects by keeping track of changes to both the source code and binary files. In June 2013, the company released P4 Code Review (formerly Helix Swarm), a tool for developers working in different geographic areas to collaborate on code review. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
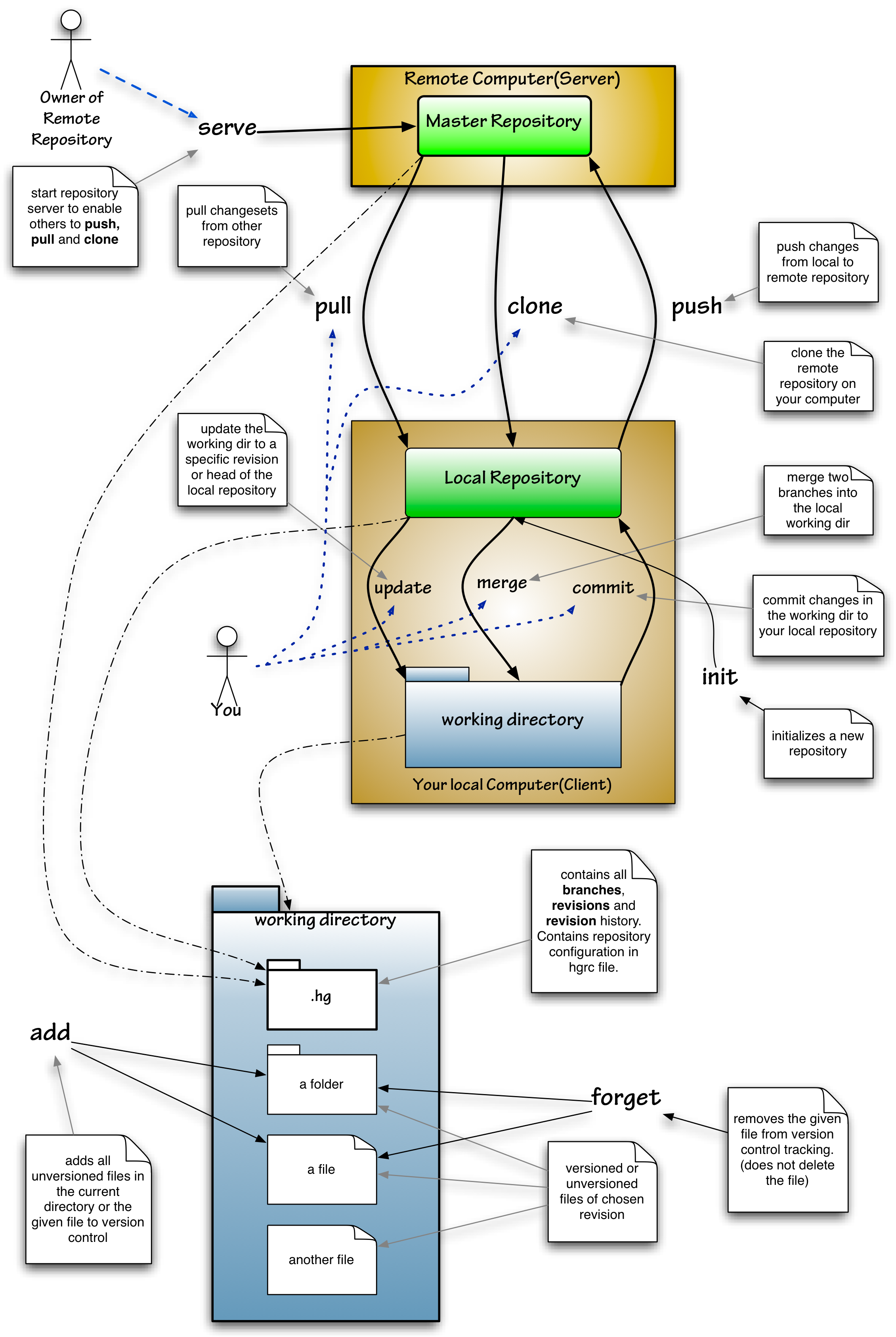
Mercurial
Mercurial is a distributed revision control tool for software developers. It is supported on Microsoft Windows, Linux, and other Unix-like systems, such as FreeBSD and macOS. Mercurial's major design goals include high performance and scalability, decentralization, fully distributed collaborative development, robust handling of both plain text and binary files, and advanced branching and merging capabilities, while remaining conceptually simple. It includes an integrated web-interface. Mercurial has also taken steps to ease the transition for users of other version control systems, particularly Subversion. Mercurial is primarily a command-line driven program, but graphical user interface extensions are available, e.g. TortoiseHg, and several IDEs offer support for version control with Mercurial. All of Mercurial's operations are invoked as arguments to its driver program hg (a reference to Hg – the chemical symbol of the element mercury). Olivia Mackall originated Mercu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Concurrent Versions System
Concurrent Versions System (CVS, or Concurrent Versioning System) is a version control system originally developed by Dick Grune in July 1986. Design CVS operates as a front end to Revision Control System (RCS), an older version control system that manages individual files but not whole projects. It expands upon RCS by adding support for repository-level change tracking, and a client-server model. Files are tracked using the same history format as in RCS, with a hidden directory containing a corresponding history file for each file in the repository. CVS uses delta compression for efficient storage of different versions of the same file. This works well with large text files with few changes from one version to the next. This is usually the case for source code files. On the other hand, when CVS is told to store a file as binary, it will keep each individual version on the server. This is typically used for non-text files such as executable images where it is difficult ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IBM DevOps Code ClearCase
IBM DevOps Code ClearCase (also known as IBM Rational ClearCase) is a family of computer software tools that supports software configuration management (SCM) of source code and other software development assets. It also supports design-data management of electronic design artifacts, thus enabling hardware and software co-development. ClearCase includes revision control and forms the basis for configuration management at large and medium-sized businesses, accommodating projects with hundreds or thousands of developers. It is developed by IBM. ClearCase supports two configuration management models: UCM (Unified Change Management) and base ClearCase. UCM provides an out-of-the-box model while base ClearCase provides a basic infrastructure (UCM is built on base ClearCase). Both can be customized to support a wide variety of needs. ClearCase can accommodate large binary files, a large number of files, and large repository sizes. It supports branching and labeling. It enables the correc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Revision Control
Version control (also known as revision control, source control, and source code management) is the software engineering practice of controlling, organizing, and tracking different versions in history of computer files; primarily source code text files, but generally any type of file. Version control is a component of software configuration management. A ''version control system'' is a software tool that automates version control. Alternatively, version control is embedded as a feature of some systems such as word processors, spreadsheets, collaborative web docs, and content management systems, e.g., Wikipedia's page history. Version control includes viewing old versions and enables reverting a file to a previous version. Overview As teams develop software, it is common to deploy multiple versions of the same software, and for different developers to work on one or more different versions simultaneously. Bugs or features of the software are often only present in ce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
XML-RPC
XML-RPC is a remote procedure call (RPC) protocol which uses XML to encode its calls and HTTP as a transport mechanism.Simon St. Laurent, Joe Johnston, Edd Dumbill. (June 2001) ''Programming Web Services with XML-RPC.'' O'Reilly. First Edition. History The XML-RPC protocol was created in 1998 by Dave Winer of UserLand Software and Microsoft, with Microsoft seeing the protocol as an essential part of scaling up its efforts in business-to-business e-commerce. As new functionality was introduced, the standard evolved into what is now SOAP. UserLand supported XML-RPC from version 5.1 of its Frontier web content management system, released in June 1998. XML-RPC's idea of a human-readable-and-writable, script-parsable standard for HTTP-based requests and responses has also been implemented in competing specifications such as Allaire's Web Distributed Data Exchange (WDDX) and webMethod's Web Interface Definition Language (WIDL). Prior art wrapping COM, CORBA, and Java RMI obje ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SOAP
Soap is a salt (chemistry), salt of a fatty acid (sometimes other carboxylic acids) used for cleaning and lubricating products as well as other applications. In a domestic setting, soaps, specifically "toilet soaps", are surfactants usually used for washing, bathing, and other types of housekeeping. In industrial settings, soaps are used as thickeners, components of some lubricants, emulsifiers, and catalysts. Soaps are often produced by mixing fats and oils with a Base (chemistry), base. Humans have used soap for millennia; evidence exists for the production of soap-like materials in ancient Babylon around 2800 BC. Types Toilet soaps In a domestic setting, "soap" usually refers to what is technically called a toilet soap, used for household and personal cleaning. Toilet soaps are salts of fatty acids with the general formula (Carboxylate ion, RCO2−)M+, where M is Sodium, Na (sodium) or Potassium, K (potassium). When used for cleaning, soap solubilizes particles and g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
REST
REST (Representational State Transfer) is a software architectural style that was created to describe the design and guide the development of the architecture for the World Wide Web. REST defines a set of constraints for how the architecture of a distributed, Internet-scale hypermedia system, such as the Web, should behave. The REST architectural style emphasises uniform API, interfaces, independent deployment of Software component, components, the scalability of interactions between them, and creating a Multitier architecture, layered architecture to promote caching to reduce user-perceived latency (engineering), latency, enforce computer security, security, and encapsulate legacy systems. REST has been employed throughout the software industry to create stateless protocol, stateless, reliable, web application, web-based applications. An application that adheres to the #Architectural constraints, REST architectural constraints may be informally described as ''RESTful'', althoug ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |