software development on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Software development is the process of
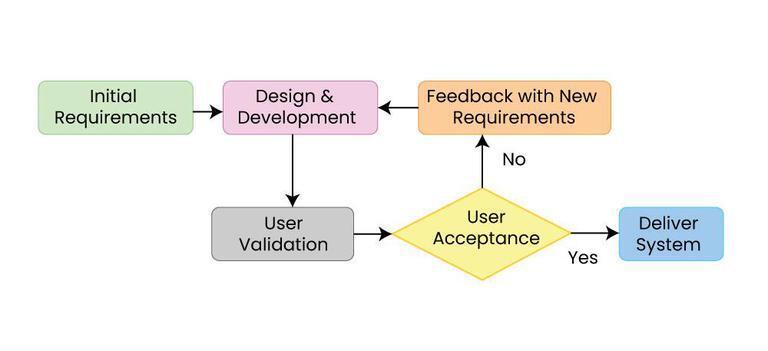 Each of the available methodologies are best suited to specific kinds of projects, based on various technical, organizational, project, and team considerations.
*The simplest methodology is the "code and fix", typically used by a single programmer working on a small project. After briefly considering the purpose of the program, the programmer codes it and runs it to see if it works. When they are done, the product is released. This methodology is useful for prototypes but cannot be used for more elaborate programs.
*In the top-down waterfall model, feasibility, analysis,
Each of the available methodologies are best suited to specific kinds of projects, based on various technical, organizational, project, and team considerations.
*The simplest methodology is the "code and fix", typically used by a single programmer working on a small project. After briefly considering the purpose of the program, the programmer codes it and runs it to see if it works. When they are done, the product is released. This methodology is useful for prototypes but cannot be used for more elaborate programs.
*In the top-down waterfall model, feasibility, analysis,
 An
An
 A
A
''Concepts for Automating Systems Integration''
NIST 2003.
designing
A design is the concept or proposal for an object, process, or system. The word ''design'' refers to something that is or has been intentionally created by a thinking agent, and is sometimes used to refer to the inherent nature of something ...
and implementing a software
Software consists of computer programs that instruct the Execution (computing), execution of a computer. Software also includes design documents and specifications.
The history of software is closely tied to the development of digital comput ...
solution to satisfy a user. The process is more encompassing than programming, writing code
In communications and information processing, code is a system of rules to convert information—such as a letter, word, sound, image, or gesture—into another form, sometimes shortened or secret, for communication through a communicati ...
, in that it includes conceiving the goal, evaluating feasibility, analyzing requirements
In engineering, a requirement is a condition that must be satisfied for the output of a work effort to be acceptable. It is an explicit, objective, clear and often quantitative description of a condition to be satisfied by a material, design, pro ...
, design
A design is the concept or proposal for an object, process, or system. The word ''design'' refers to something that is or has been intentionally created by a thinking agent, and is sometimes used to refer to the inherent nature of something ...
, testing and release
Release may refer to:
* Art release, the public distribution of an artistic production, such as a film, album, or song
* Legal release, a legal instrument
* News release, a communication directed at the news media
* Release (ISUP), a code to i ...
. The process is part of software engineering
Software engineering is a branch of both computer science and engineering focused on designing, developing, testing, and maintaining Application software, software applications. It involves applying engineering design process, engineering principl ...
which also includes organizational management, project management
Project management is the process of supervising the work of a Project team, team to achieve all project goals within the given constraints. This information is usually described in project initiation documentation, project documentation, crea ...
, configuration management
Configuration management (CM) is a management process for establishing and maintaining consistency of a product's performance, functional, and physical attributes with its requirements, design, and operational information throughout its life. ...
and other aspects.
Software development involves many skills and job specializations including programming, testing, documentation
Documentation is any communicable material that is used to describe, explain or instruct regarding some attributes of an object, system or procedure, such as its parts, assembly, installation, maintenance, and use. As a form of knowledge managem ...
, graphic design
Graphic design is a profession, academic discipline and applied art that involves creating visual communications intended to transmit specific messages to social groups, with specific objectives. Graphic design is an interdisciplinary branch of ...
, user support, marketing
Marketing is the act of acquiring, satisfying and retaining customers. It is one of the primary components of Business administration, business management and commerce.
Marketing is usually conducted by the seller, typically a retailer or ma ...
, and fundraising
Fundraising or fund-raising is the process of seeking and gathering voluntary financial contributions by engaging individuals, businesses, charitable foundations, or governmental agencies. Although fundraising typically refers to efforts to gathe ...
.
Software development involves many tools
A tool is an object that can extend an individual's ability to modify features of the surrounding environment or help them accomplish a particular task. Although many animals use simple tools, only human beings, whose use of stone tools dates ...
including: compiler
In computing, a compiler is a computer program that Translator (computing), translates computer code written in one programming language (the ''source'' language) into another language (the ''target'' language). The name "compiler" is primaril ...
, integrated development environment
An integrated development environment (IDE) is a Application software, software application that provides comprehensive facilities for software development. An IDE normally consists of at least a source-code editor, build automation tools, an ...
(IDE), version control
Version control (also known as revision control, source control, and source code management) is the software engineering practice of controlling, organizing, and tracking different versions in history of computer files; primarily source code t ...
, computer-aided software engineering
Computer-aided software engineering (CASE) is a domain of software tools used to design and implement applications. CASE tools are similar to and are partly inspired by computer-aided design (CAD) tools used for designing hardware products. CASE ...
, and word processor A word processor (WP) is a device or computer program that provides for input, editing, formatting, and output of text, often with some additional features.
Early word processors were stand-alone devices dedicated to the function, but current word ...
.
The details of the process used for a development effort varies. The process may be confined to a formal, documented standard, or it can be customized and emergent for the development effort. The process may be sequential, in which each major phase (i.e. design, implement and test) is completed before the next begins, but an iterative approach where small aspects are separately designed, implemented and tested can reduce risk and cost and increase quality.
Methodologies
 Each of the available methodologies are best suited to specific kinds of projects, based on various technical, organizational, project, and team considerations.
*The simplest methodology is the "code and fix", typically used by a single programmer working on a small project. After briefly considering the purpose of the program, the programmer codes it and runs it to see if it works. When they are done, the product is released. This methodology is useful for prototypes but cannot be used for more elaborate programs.
*In the top-down waterfall model, feasibility, analysis,
Each of the available methodologies are best suited to specific kinds of projects, based on various technical, organizational, project, and team considerations.
*The simplest methodology is the "code and fix", typically used by a single programmer working on a small project. After briefly considering the purpose of the program, the programmer codes it and runs it to see if it works. When they are done, the product is released. This methodology is useful for prototypes but cannot be used for more elaborate programs.
*In the top-down waterfall model, feasibility, analysis, design
A design is the concept or proposal for an object, process, or system. The word ''design'' refers to something that is or has been intentionally created by a thinking agent, and is sometimes used to refer to the inherent nature of something ...
, development, quality assurance
Quality assurance (QA) is the term used in both manufacturing and service industries to describe the systematic efforts taken to assure that the product(s) delivered to customer(s) meet with the contractual and other agreed upon performance, design ...
, and implementation occur sequentially in that order. This model requires one step to be complete before the next begins, causing delays, and makes it impossible to revise previous steps if necessary.
*With iterative processes these steps are interleaved with each other for improved flexibility, efficiency, and more realistic scheduling. Instead of completing the project all at once, one might go through most of the steps with one component at a time. Iterative development also lets developers prioritize the most important features, enabling lower priority ones to be dropped later on if necessary. Agile is one popular method, originally intended for small or medium sized projects, that focuses on giving developers more control over the features that they work on to reduce the risk of time or cost overruns. Derivatives of agile include extreme programming
Extreme programming (XP) is a software development methodology intended to improve software quality and responsiveness to changing customer requirements. As a type of agile software development,"Human Centred Technology Workshop 2006 ", 2006, ...
and Scrum. Open-source software development typically uses agile methodology with concurrent design, coding, and testing, due to reliance on a distributed network of volunteer contributors.
*Beyond agile, some companies integrate information technology
Information technology (IT) is a set of related fields within information and communications technology (ICT), that encompass computer systems, software, programming languages, data processing, data and information processing, and storage. Inf ...
(IT) operations with software development, which is called DevOps
DevOps is the integration and automation of the software development and information technology operations. DevOps encompasses necessary tasks of software development and can lead to shortening development time and improving the development life ...
or DevSecOps including computer security
Computer security (also cybersecurity, digital security, or information technology (IT) security) is a subdiscipline within the field of information security. It consists of the protection of computer software, systems and computer network, n ...
. DevOps includes continuous development, testing, integration of new code in the version control system, deployment of the new code, and sometimes delivery of the code to clients. The purpose of this integration is to deliver IT services more quickly and efficiently.
Another focus in many programming methodologies is the idea of trying to catch issues such as security vulnerabilities and bugs as early as possible ( shift-left testing) to reduce the cost of tracking and fixing them.
In 2009, it was estimated that 32 percent of software projects were delivered on time and budget, and with the full functionality. An additional 44 percent were delivered, but missing at least one of these features. The remaining 24 percent were cancelled prior to release.
Steps
Software development life cycle
In software engineering, a software development process or software development life cycle (SDLC) is a process of planning and managing software development. It typically involves dividing software development work into smaller, parallel, or s ...
refers to the systematic process of developing applications.Feasibility
The sources of ideas for software products are plentiful. These ideas can come frommarket research
Market research is an organized effort to gather information about target markets and customers. It involves understanding who they are and what they need. It is an important component of business strategy and a major factor in maintaining com ...
including the demographics
Demography () is the statistical study of human populations: their size, composition (e.g., ethnic group, age), and how they change through the interplay of fertility (births), mortality (deaths), and migration.
Demographic analysis examin ...
of potential new customers, existing customers, sales prospects who rejected the product, other internal software development staff, or a creative third party. Ideas for software products are usually first evaluated by marketing
Marketing is the act of acquiring, satisfying and retaining customers. It is one of the primary components of Business administration, business management and commerce.
Marketing is usually conducted by the seller, typically a retailer or ma ...
personnel for economic feasibility, fit with existing channels of distribution, possible effects on existing product lines, required features, and fit with the company's marketing objectives. In the marketing evaluation phase, the cost and time assumptions become evaluated. The feasibility analysis estimates the project's return on investment
Return on investment (ROI) or return on costs (ROC) is the ratio between net income (over a period) and investment (costs resulting from an investment of some resources at a point in time). A high ROI means the investment's gains compare favorab ...
, its development cost and timeframe. Based on this analysis, the company can make a business decision to invest in further development. After deciding to develop the software, the company is focused on delivering the product at or below the estimated cost and time, and with a high standard of quality (i.e., lack of bugs) and the desired functionality. Nevertheless, most software projects run late and sometimes compromises are made in features or quality to meet a deadline.
Analysis
Software analysis begins with a requirements analysis to capture the business needs of the software. Challenges for the identification of needs are that current or potential users may have different and incompatible needs, may not understand their own needs, and change their needs during the process of software development. Ultimately, the result of analysis is a detailed specification for the product that developers can work from. Software analysts often decompose the project into smaller objects, components that can be reused for increased cost-effectiveness, efficiency, and reliability. Decomposing the project may enable a multi-threaded implementation that runs significantly faster on multiprocessor computers. During the analysis and design phases of software development, structured analysis is often used to break down the customer's requirements into pieces that can be implemented by software programmers. The underlying logic of the program may be represented in data-flow diagrams, data dictionaries, pseudocode, state transition diagrams, and/orentity relationship diagram
An entity is something that Existence, exists as itself. It does not need to be of material existence. In particular, abstractions and legal fictions are usually regarded as entities. In general, there is also no presumption that an entity is Lif ...
s. If the project incorporates a piece of legacy software that has not been modeled, this software may be modeled to help ensure it is correctly incorporated with the newer software.Design
Design involves choices about the implementation of the software, such as whichprogramming language
A programming language is a system of notation for writing computer programs.
Programming languages are described in terms of their Syntax (programming languages), syntax (form) and semantics (computer science), semantics (meaning), usually def ...
s and database software to use, or how the hardware and network communications will be organized. Design may be iterative with users consulted about their needs in a process of trial and error. Design often involves people expert in aspect such as database design, screen architecture, and the performance of servers and other hardware. Designers often attempt to find patterns in the software's functionality to spin off distinct modules that can be reused with object-oriented programming
Object-oriented programming (OOP) is a programming paradigm based on the concept of '' objects''. Objects can contain data (called fields, attributes or properties) and have actions they can perform (called procedures or methods and impl ...
. An example of this is the model–view–controller
Model–view–controller (MVC) is a software architectural pattern commonly used for developing user interfaces that divides the related program logic into three interconnected elements. These elements are:
* the model, the internal representat ...
, an interface between a graphical user interface
A graphical user interface, or GUI, is a form of user interface that allows user (computing), users to human–computer interaction, interact with electronic devices through Graphics, graphical icon (computing), icons and visual indicators such ...
and the backend.
Programming
The central feature of software development is creating and understanding the software that implements the desired functionality. There are various strategies for writing the code. Cohesive software has various components that are independent from each other. Coupling is the interrelation of different software components, which is viewed as undesirable because it increases the difficulty ofmaintenance
The technical meaning of maintenance involves functional checks, servicing, repairing or replacing of necessary devices, equipment, machinery, building infrastructure and supporting utilities in industrial, business, and residential installa ...
. Often, software programmers do not follow industry best practices, resulting in code that is inefficient, difficult to understand, or lacking documentation
Documentation is any communicable material that is used to describe, explain or instruct regarding some attributes of an object, system or procedure, such as its parts, assembly, installation, maintenance, and use. As a form of knowledge managem ...
on its functionality. These standards are especially likely to break down in the presence of deadlines. As a result, testing, debugging, and revising the code becomes much more difficult. Code refactoring
In computer programming and software design, code refactoring is the process of restructuring existing source code—changing the '' factoring''—without changing its external behavior. Refactoring is intended to improve the design, structure, ...
, for example adding more comments to the code, is a solution to improve the understandability of code.
Testing
Testing is the process of ensuring that the code executes correctly and without errors.Debugging
In engineering, debugging is the process of finding the Root cause analysis, root cause, workarounds, and possible fixes for bug (engineering), bugs.
For software, debugging tactics can involve interactive debugging, control flow analysis, Logf ...
is performed by each software developer on their own code to confirm that the code does what it is intended to. In particular, it is crucial that the software executes on all inputs, even if the result is incorrect. Code review
Code review (sometimes referred to as peer review) is a software quality assurance activity in which one or more people examine the source code of a computer program, either after implementation or during the development process. The persons perf ...
s by other developers are often used to scrutinize new code added to the project, and according to some estimates dramatically reduce the number of bugs persisting after testing is complete. Once the code has been submitted, quality assurance
Quality assurance (QA) is the term used in both manufacturing and service industries to describe the systematic efforts taken to assure that the product(s) delivered to customer(s) meet with the contractual and other agreed upon performance, design ...
—a separate department of non-programmers for most large companies—test the accuracy of the entire software product. Acceptance tests derived from the original software requirements are a popular tool for this. Quality testing also often includes stress and load checking (whether the software is robust to heavy levels of input or usage), integration testing (to ensure that the software is adequately integrated with other software), and compatibility testing (measuring the software's performance across different operating systems or browsers). When tests are written before the code, this is called test-driven development.Production
Production is the phase in which software is deployed to the end user. During production, the developer may create technical support resources for users or a process for fixing bugs and errors that were not caught earlier. There might also be a return to earlier development phases if user needs changed or were misunderstood.Workers
Software development is performed by software developers, usually working on a team. Efficient communications between team members is essential to success. This is more easily achieved if the team is small, used to working together, and located near each other. Communications also help identify problems at an earlier state of development and avoid duplicated effort. Many development projects avoid the risk of losing essential knowledge held by only one employee by ensuring that multiple workers are familiar with each component. Software development involves professionals from various fields, not just software programmers but also product managers who set the strategy and roadmap for the product, individuals specialized in testing, documentation writing,graphic design
Graphic design is a profession, academic discipline and applied art that involves creating visual communications intended to transmit specific messages to social groups, with specific objectives. Graphic design is an interdisciplinary branch of ...
, user support, marketing
Marketing is the act of acquiring, satisfying and retaining customers. It is one of the primary components of Business administration, business management and commerce.
Marketing is usually conducted by the seller, typically a retailer or ma ...
, and fundraising. Although workers for proprietary software are paid, most contributors to open-source software
Open-source software (OSS) is Software, computer software that is released under a Open-source license, license in which the copyright holder grants users the rights to use, study, change, and Software distribution, distribute the software an ...
are volunteers. Alternately, they may be paid by companies whose business model
A business model describes how a Company, business organization creates, delivers, and captures value creation, value,''Business Model Generation'', Alexander Osterwalder, Yves Pigneur, Alan Smith, and 470 practitioners from 45 countries, self-pub ...
does not involve selling the software, but something else—such as services and modifications to open source software.
Models and tools
Computer-aided software engineering
Computer-aided software engineering
Computer-aided software engineering (CASE) is a domain of software tools used to design and implement applications. CASE tools are similar to and are partly inspired by computer-aided design (CAD) tools used for designing hardware products. CASE ...
(CASE) is tools for the partial automation
Automation describes a wide range of technologies that reduce human intervention in processes, mainly by predetermining decision criteria, subprocess relationships, and related actions, as well as embodying those predeterminations in machine ...
of software development. CASE enables designers to sketch out the logic of a program, whether one to be written, or an already existing one to help integrate it with new code or reverse engineer it (for example, to change the programming language
A programming language is a system of notation for writing computer programs.
Programming languages are described in terms of their Syntax (programming languages), syntax (form) and semantics (computer science), semantics (meaning), usually def ...
).Documentation
Documentation comes in two forms that are usually kept separate—that intended for software developers, and that made available to the end user to help them use the software. Most developer documentation is in the form of code comments for each file,class
Class, Classes, or The Class may refer to:
Common uses not otherwise categorized
* Class (biology), a taxonomic rank
* Class (knowledge representation), a collection of individuals or objects
* Class (philosophy), an analytical concept used d ...
, and method
Method (, methodos, from μετά/meta "in pursuit or quest of" + ὁδός/hodos "a method, system; a way or manner" of doing, saying, etc.), literally means a pursuit of knowledge, investigation, mode of prosecuting such inquiry, or system. In re ...
that cover the application programming interface
An application programming interface (API) is a connection between computers or between computer programs. It is a type of software Interface (computing), interface, offering a service to other pieces of software. A document or standard that des ...
(API)—how the piece of software can be accessed by another—and often implementation details. This documentation is helpful for new developers to understand the project when they begin working on it. In agile development, the documentation is often written at the same time as the code. User documentation is more frequently written by technical writers.Effort estimation
Accurate estimation is crucial at the feasibility stage and in delivering the product on time and within budget. The process of generating estimations is often delegated by theproject manager
A project manager is a professional in the field of project management. Project managers have the responsibility of the Project planning, planning, procurement and execution of a project, in any undertaking that has a defined scope, defined star ...
. Because the effort estimation is directly related to the size of the complete application, it is strongly influenced by addition of features in the requirements—the more requirements, the higher the development cost. Aspects not related to functionality, such as the experience of the software developers and code reusability, are also essential to consider in estimation. , most of the tools for estimating the amount of time and resources for software development were designed for conventional applications and are not applicable to web application
A web application (or web app) is application software that is created with web technologies and runs via a web browser. Web applications emerged during the late 1990s and allowed for the server to dynamically build a response to the request, ...
s or mobile applications.Integrated development environment
 An
An integrated development environment
An integrated development environment (IDE) is a Application software, software application that provides comprehensive facilities for software development. An IDE normally consists of at least a source-code editor, build automation tools, an ...
(IDE) supports software development with enhanced features compared to a simple text editor
A text editor is a type of computer program that edits plain text. An example of such program is "notepad" software (e.g. Windows Notepad). Text editors are provided with operating systems and software development packages, and can be used to c ...
. IDEs often include automated compiling
In computing, a compiler is a computer program that translates computer code written in one programming language (the ''source'' language) into another language (the ''target'' language). The name "compiler" is primarily used for programs tha ...
, syntax highlighting of errors, debugging assistance, integration with version control
Version control (also known as revision control, source control, and source code management) is the software engineering practice of controlling, organizing, and tracking different versions in history of computer files; primarily source code t ...
, and semi-automation of tests.
Version control
Version control is a popular way of managing changes made to the software. Whenever a new version is checked in, the software saves abackup
In information technology, a backup, or data backup is a copy of computer data taken and stored elsewhere so that it may be used to restore the original after a data loss event. The verb form, referring to the process of doing so, is "wikt:back ...
of all modified files. If multiple programmers are working on the software simultaneously, it manages the merging of their code changes. The software highlights cases where there is a conflict between two sets of changes and allows programmers to fix the conflict.View model
view model
Acornsoft was the software arm of Acorn Computers, and a major publisher of software for the BBC Micro and Acorn Electron. As well as games, it also produced a large number of educational titles, extra computer languages and business and ut ...
is a framework that provides the viewpoints on the system
A system is a group of interacting or interrelated elements that act according to a set of rules to form a unified whole. A system, surrounded and influenced by its open system (systems theory), environment, is described by its boundaries, str ...
and its environment, to be used in the software development process
In software engineering, a software development process or software development life cycle (SDLC) is a process of planning and managing software development. It typically involves dividing software development work into smaller, parallel, or s ...
. It is a graphical representation of the underlying semantics of a view.
The purpose of viewpoints and views is to enable human engineers to comprehend very complex system
A complex system is a system composed of many components that may interact with one another. Examples of complex systems are Earth's global climate, organisms, the human brain, infrastructure such as power grid, transportation or communication sy ...
s and to organize the elements of the problem around domains of expertise
An expert is somebody who has a broad and deep understanding and competence in terms of knowledge, skill and experience through practice and education in a particular field or area of study. Informally, an expert is someone widely recognized a ...
. In the engineering
Engineering is the practice of using natural science, mathematics, and the engineering design process to Problem solving#Engineering, solve problems within technology, increase efficiency and productivity, and improve Systems engineering, s ...
of physically intensive systems, viewpoints often correspond to capabilities and responsibilities within the engineering organization.Edward J. Barkmeyer ea (2003)''Concepts for Automating Systems Integration''
NIST 2003.
Fitness functions
Fitness functions are automated and objective tests to ensure that the new developments don't deviate from the established constraints, checks and compliance controls.Intellectual property
Intellectual property
Intellectual property (IP) is a category of property that includes intangible creations of the human intellect. There are many types of intellectual property, and some countries recognize more than others. The best-known types are patents, co ...
can be an issue when developers integrate open-source
Open source is source code that is made freely available for possible modification and redistribution. Products include permission to use and view the source code, design documents, or content of the product. The open source model is a decentrali ...
code or libraries into a proprietary product, because most open-source licenses used for software require that modifications be released under the same license. As an alternative, developers may choose a proprietary alternative or write their own software module.
References
Further reading
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *External links
* {{Authority control Development Computer occupations Product development