|
Untitled Text
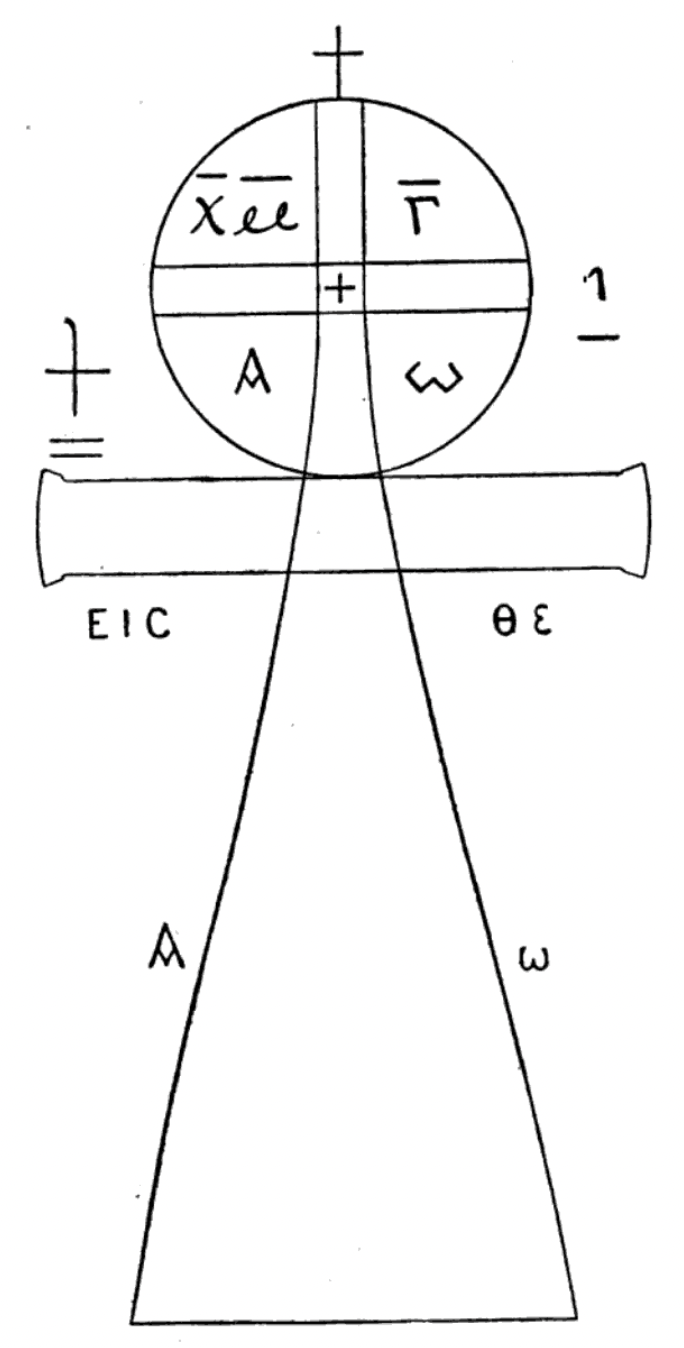
The ''Untitled Text'' in the Bruce Codex—also called the ''Untitled Treatise'', the ''Untitled Apocalypse'', and ''The Gnosis of the Light''—is a Gnostic text. When James Bruce acquired the codex in Egypt in 1769, "very little knowledge" was available about this period of Gnostic Christianity. It was one of the few known surviving Gnostic works until the discovery of the Nag Hammadi library in 1945. Carl Schmidt described the text's author as having "full knowledge of Greek philosophy" and being "full of the doctrine of the Platonic ideas." Background James Bruce purchased the Bruce Codex near Medinet Habu, Upper Egypt, around 1769. It contained text in Coptic, Arabic, and Geʽez. Carl Gottfried Woide transcribed the entire codex in 1776. The Bodleian Library obtained the codex in 1848, and in 1886 they bound the texts together. Between Woide's transcription of the codex and the 1970s, seven leaves disappeared altogether, and there is significant damage throughout the man ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bruce Codex
The Bruce Codex (Latin: ) is a codex that contains Coptic, Arabic, and Ethiopic manuscripts. It contains rare Gnostic works; the Bruce Codex is the only known surviving copy of the Books of Jeu and another work simply called Untitled Text or the Untitled Apocalypse. In 1769, James Bruce purchased the codex in Upper Egypt. It currently resides in the Bodleian Library (Bruce 96), where it has been since 1848. History The Scottish traveler James Bruce purchased the codex around 1769 while in Upper Egypt, near Medinet Habu. It had supposedly been found in the ruins of a building once inhabited by Egyptian monks. The codex came to the attention of Carl Gottfried Woide, who made a copy of the Coptic Gnostic texts within, as well as discussed the codex in a work on Egyptian copies of the Bible and other religious manuscripts. In 1848, both Woide's transcript of the text as well as the original codex were acquired by the Bodleian Library and classified as "Bruce 96". took t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Books Of Jeu
The Books of Jeu are two Gnostic texts. Though independent works, both the First Book of Jeu and the Second Book of Jeu appear, in Sahidic Coptic, in the Bruce Codex. They are a combination of a gospel and an esoteric revelation; the work professes to record conversations Jesus had with both the male apostles and his female disciples, and the secret knowledge (gnosis) revealed in these conversations. Authorship and date The date of the Bruce Codex, which contains the sole surviving copy of the work, is unknown and disputed, with estimates ranging from the 3rd to the 10th century. It is believed that the Sahidic Coptic of the Codex version is a translation, however, and the original was written in Koine Greek in the early 3rd century. This estimate is because the Pistis Sophia mentions the two books of Jeu twice (158.18 and 228.35), suggesting that the Books of Jeu were written before it, and the Pistis Sophia is dated to the late 3rd or early 4th century. The author is unknow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ennead
The Ennead or Great Ennead was a group of nine deities in Egyptian mythology worshipped at Heliopolis: the sun god Atum; his children Shu and Tefnut; their children Geb and Nut; and their children Osiris, Isis, Set, and Nephthys. The Ennead sometimes includes Horus, the son of Osiris and Isis. Status within ancient Egypt The Great Ennead was only one of several such groupings of nine deities in ancient Egypt. Its claims to preeminence by its Heliopolitan priests were not respected throughout Egypt. As close as Memphis (also within modern Cairo), the priests of Ptah celebrated him as superior to the Nine. In addition to Memphis having its own creation myth, the Ogdoad (of the city of Hermopolis) centered around physical creation and eight primordial gods was another creation story that existed at the same time. Name in Egyptian, Greek, and Latin The English name ''ennead'' is a borrowing via Latin of the Greek name ''enneás'' (), meaning "the nine". The term ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monad (philosophy)
The term ''monad'' () is used in some cosmic philosophy and cosmogony to refer to a most basic or original substance. As originally conceived by the Pythagoreans, the Monad is the Supreme Being, divinity or the totality of all things. In the philosophy of Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz, there are infinite monads, which are the basic and immaterial elementary particles, or simplest units, that make up the universe. Historical background According to Hippolytus, the worldview was inspired by the Pythagoreans, who called the first thing that came into existence the "monad", which begat (bore) the dyad (from the Greek word for two), which begat the numbers, which begat the point, begetting lines or finiteness, etc. It meant divinity, the first being, or the totality of all beings, referring in cosmogony (creation theories) variously to source acting alone and/or an indivisible origin and equivalent comparators. Pythagorean and Platonic philosophers like Plotinus and Porphyry c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jesus
Jesus, likely from he, יֵשׁוּעַ, translit=Yēšūaʿ, label=Hebrew/Aramaic ( AD 30 or 33), also referred to as Jesus Christ or Jesus of Nazareth (among other names and titles), was a first-century Jewish preacher and religious leader; he is the central figure of Christianity, the world's largest religion. Most Christians believe he is the incarnation of God the Son and the awaited Messiah (the Christ) prophesied in the Hebrew Bible. Virtually all modern scholars of antiquity agree that Jesus existed historically. Research into the historical Jesus has yielded some uncertainty on the historical reliability of the Gospels and on how closely the Jesus portrayed in the New Testament reflects the historical Jesus, as the only detailed records of Jesus' life are contained in the Gospels. Jesus was a Galilean Jew who was circumcised, was baptized by John the Baptist, began his own ministry and was often referred to as "rabbi". Jesus debated with fellow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adam
Adam; el, Ἀδάμ, Adám; la, Adam is the name given in Genesis 1-5 to the first human. Beyond its use as the name of the first man, ''adam'' is also used in the Bible as a pronoun, individually as "a human" and in a collective sense as "mankind". tells of God's creation of the world and its creatures, including ''adam'', meaning humankind; in God forms "Adam", this time meaning a single male human, out of "the dust of the ground", places him in the Garden of Eden, and forms a woman, Eve, as his helpmate; in Adam and Eve eat the fruit of the tree of knowledge and God condemns Adam to labour on the earth for his food and to return to it on his death; deals with the birth of Adam's sons, and lists his descendants from Seth to Noah. The Genesis creation myth was adopted by both Christianity and Islam, and the name of Adam accordingly appears in the Christian scriptures and in the Quran. He also features in subsequent folkloric and mystical elaborations in later Judaism, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
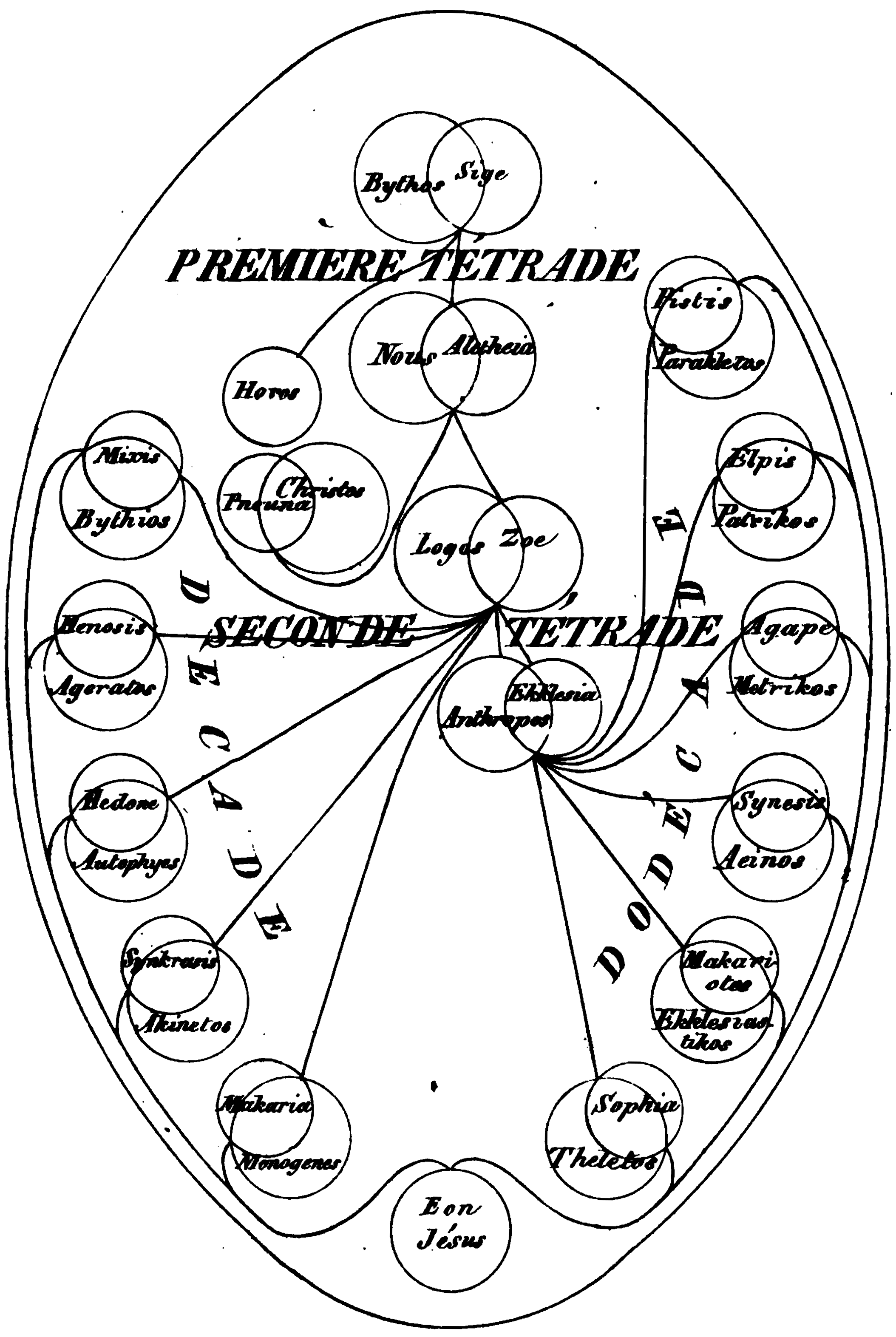
Pleroma
Pleroma ( grc-koi, πλήρωμα, literally "fullness") generally refers to the totality of divine powers. It is used in Christian theological contexts, especially in Gnosticism. The term also appears in the Epistle to the Colossians, which is traditionally attributed to Paul the Apostle. The word is used 17 times in the New Testament. The word literally means "fullness", from the verb (, "to fill"), from ( πλήρης, "full"). Svenska Akademiens ordbok, search on the word ''Pleroma'/ref> Christianity New Testament The word itself is a relative term, capable of many shades of meaning, according to the subject with which it is joined and the antithesis to which it is contrasted. It denotes the result of the action of the verb ''pleroun;'' but ''pleroun'' is either *to fill up an empty thing (''e.g.'' ), or *to complete an incomplete thing (''e.g.'' ); and the verbal substantive in -''ma'' may express either #the objective accusative after the verb, 'the thing filled or c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aeon (Gnosticism)
In many Gnostic systems, various emanations of God are known by such names as One, Monad, ''Aion teleos'' (αἰών τέλεος "The Broadest Aeon"), Bythos (, "depth" or "profundity"), ''Proarkhe'' ("before the beginning", ), ''Arkhe'' ("the beginning", ), and Aeons. In different systems these emanations are differently named, classified, and described, but emanation theory is common to all forms of Gnosticism. In Basilidian Gnosis they are called sonships (υἱότητες ''huiotetes''; sing.: υἱότης ''huiotes''); according to Marcus, they are numbers and sounds; in Valentinianism they form male/female pairs called syzygies (Greek , from σύζυγοι ''syzygoi'', lit. "yokings together"). This source of all being is an Aeon, in which an inner being dwells, known as ''Ennoea'' ("thought, intent", Greek ), ''Charis'' ("grace", Greek ), or ''Sige'' ("silence", Greek ). The split perfect being conceives the second Aeon, ''Nous'' ("mind", Greek Νους), within its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Demiurge
In the Platonic, Neopythagorean, Middle Platonic, and Neoplatonic schools of philosophy, the demiurge () is an artisan-like figure responsible for fashioning and maintaining the physical universe. The Gnostics adopted the term ''demiurge''. Although a fashioner, the demiurge is not necessarily the same as the Creator figure in the monotheistic sense, because the demiurge itself and the material from which the demiurge fashions the universe are both considered consequences of something else. Depending on the system, they may be considered either uncreated and eternal or the product of some other entity. The word ''demiurge'' is an English word derived from ''demiurgus'', a Latinised form of the Greek or . It was originally a common noun meaning "craftsman" or "artisan", but gradually came to mean "producer", and eventually "creator". The philosophical usage and the proper noun derive from Plato's ''Timaeus'', written 360 BC, where the demiurge is presented as the c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Papyrus
Papyrus ( ) is a material similar to thick paper that was used in ancient times as a writing surface. It was made from the pith of the papyrus plant, '' Cyperus papyrus'', a wetland sedge. ''Papyrus'' (plural: ''papyri'') can also refer to a document written on sheets of such material, joined side by side and rolled up into a scroll, an early form of a book. Papyrus is first known to have been used in Egypt (at least as far back as the First Dynasty), as the papyrus plant was once abundant across the Nile Delta. It was also used throughout the Mediterranean region. Apart from a writing material, ancient Egyptians employed papyrus in the construction of other artifacts, such as reed boats, mats, rope, sandals, and baskets. History Papyrus was first manufactured in Egypt as far back as the fourth millennium BCE.H. Idris Bell and T.C. Skeat, 1935"Papyrus and its uses"(British Museum pamphlet). The earliest archaeological evidence of papyrus was excavated in 2012 an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uncial Script
Uncial is a majuscule Glaister, Geoffrey Ashall. (1996) ''Encyclopedia of the Book''. 2nd edn. New Castle, DE, and London: Oak Knoll Press & The British Library, p. 494. script (written entirely in capital letters) commonly used from the 4th to 8th centuries AD by Latin and Greek scribes. Uncial letters were used to write Greek and Latin, as well as Gothic and Coptic. Development Early uncial script most likely developed from late rustic capitals. Early forms are characterized by broad single-stroke letters using simple round forms taking advantage of the new parchment and vellum surfaces, as opposed to the angular, multiple-stroke letters, which are more suited for rougher surfaces, such as papyrus. In the oldest examples of uncial, such as the fragment of '' De bellis macedonicis'' in the British Library, of the late 1st-early 2nd century, all of the letters are disconnected from one another, and word separation is typically not used. Word separation, however, is char ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leaf (books)
'''' is the "right" or "front" side and ''verso'' is the "left" or "back" side when text is written or printed on a leaf of paper () in a bound item such as a codex, book, broadsheet, or pamphlet. Etymology The terms are shortened from Latin: and ' (which translate as "on the right side of the leaf" and "on the back side of the leaf"). The two opposite pages themselves are called ' and ' in Latin, and the ablative ', ' already imply that the text on the page (and not the physical page itself) are referred to. Usage In codicology, each physical sheet (', abbreviated ''fol.'' or ''f.'') of a manuscript is numbered, and the sides are referred to as ' and ', abbreviated as ''r'' and ''v'' respectively. Editions of manuscripts will thus mark the position of text in the original manuscript in the form ''fol. 1r'', sometimes with the ''r'' and ''v'' in superscript, as in ''1r'', or with a superscript ''o'' indicating the ablative ', ', as in ''1ro''. This terminology has been st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |