Aeon (Gnosticism) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
In many
 In the system of Valentinus, as expounded by Irenaeus (i. 1), the origin of things was traced to two eternal co-existent principles, a male and a female. The male was called Bythos or Proarche, or Propator, etc.; the female had the names Ennoea, Charis and Sige. The whole Aeonology of Valentinus was based on a theory of syzygies, or pairs of Aeons, each Aeon being provided with a consort; and the supposed need of the co-operation of a male and female principle for the generation of new ones, was common to Valentinus and some earlier Gnostic systems. But it was a disputed point in these systems whether the First Principle of all was thus twofold. There were those, both in earlier systems, and even among the Valentinians who held, that the origin of things was to be traced to a single Principle, which some described as
In the system of Valentinus, as expounded by Irenaeus (i. 1), the origin of things was traced to two eternal co-existent principles, a male and a female. The male was called Bythos or Proarche, or Propator, etc.; the female had the names Ennoea, Charis and Sige. The whole Aeonology of Valentinus was based on a theory of syzygies, or pairs of Aeons, each Aeon being provided with a consort; and the supposed need of the co-operation of a male and female principle for the generation of new ones, was common to Valentinus and some earlier Gnostic systems. But it was a disputed point in these systems whether the First Principle of all was thus twofold. There were those, both in earlier systems, and even among the Valentinians who held, that the origin of things was to be traced to a single Principle, which some described as
by Alison Veneto, SMRT TV, April 24, 2006, "...Aeon Flux has a serious Gnostic bent. The ancient mystery religion is where they got the concepts of aeons and the demiurge, amongst other things."
May 18, 2008, The Alien Next Door
Nina Munteanu
!-- Author is a science-fiction writer -->
Tertullian's account against the Valentinians
is the source text for much of what we know about the Æons.
Gnosis.org
- The Gnostic Society Library Gnostic deities Gnosticism
Gnostic
Gnosticism (from grc, γνωστικός, gnōstikós, , 'having knowledge') is a collection of religious ideas and systems which coalesced in the late 1st century AD among Jewish and early Christian sects. These various groups emphasized pe ...
systems, various emanations of God
In monotheism, monotheistic thought, God is usually viewed as the supreme being, creator deity, creator, and principal object of Faith#Religious views, faith.Richard Swinburne, Swinburne, R.G. "God" in Ted Honderich, Honderich, Ted. (ed)''The Ox ...
are known by such names as One, Monad
Monad may refer to:
Philosophy
* Monad (philosophy), a term meaning "unit"
**Monism, the concept of "one essence" in the metaphysical and theological theory
** Monad (Gnosticism), the most primal aspect of God in Gnosticism
* ''Great Monad'', a ...
, ''Aion teleos'' (αἰών τέλεος "The Broadest Aeon"), Bythos The Monad in Gnosticism is an adaptation of concepts of the Monad in Greek philosophy to Christian gnostic belief systems.
Overview
The term ''monad'' comes from the Greek feminine noun ''monas'' ( nominative singular, μονάς), "one unit," whe ...
(, "depth" or "profundity"), ''Proarkhe'' ("before the beginning", ), ''Arkhe'' ("the beginning", ), and Aeons. In different systems these emanations are differently named, classified, and described, but emanation theory is common to all forms of Gnosticism. In Basilidian Gnosis they are called sonships (υἱότητες ''huiotetes''; sing.: υἱότης ''huiotes''); according to Marcus, they are numbers and sounds; in Valentinianism
Valentinianism was one of the major Gnostic Christian movements. Founded by Valentinus in the 2nd century AD, its influence spread widely, not just within Rome but also from Northwest Africa to Egypt through to Asia Minor and Syria in the East. ...
they form male/female pairs called syzygies (Greek , from σύζυγοι ''syzygoi'', lit. "yokings together").
This source of all being is an Aeon, in which an inner being dwells, known as ''Ennoea'' ("thought, intent", Greek ), ''Charis'' ("grace", Greek ), or ''Sige'' ("silence", Greek ). The split perfect being conceives the second Aeon, ''Nous'' ("mind", Greek Νους), within itself. Complex hierarchies of Aeons are thus produced, sometimes to the number of thirty. These Aeons belong to a purely ideal, noumenal
In philosophy, a noumenon (, ; ; noumena) is a posited object or an event that exists independently of human sense and/or perception. The term ''noumenon'' is generally used in contrast with, or in relation to, the term ''phenomenon'', which ...
, intelligible, or supersensible world; they are immaterial, they are hypostatic ideas. Together with the source from which they emanate, they form ''Pleroma
Pleroma ( grc-koi, πλήρωμα, literally "fullness") generally refers to the totality of divine powers. It is used in Christian theological contexts, especially in Gnosticism. The term also appears in the Epistle to the Colossians, which is t ...
'' ("fullness", Greek ). The lowest regions of Pleroma are closest to darkness—that is, the physical world.
The transition from immaterial to material, from noumenal to sensible, is created by a flaw, passion, or sin in an Aeon. According to Basilides
Basilides (Greek: Βασιλείδης) was an early Christian Gnostic religious teacher in Alexandria, Egypt who taught from 117 to 138 AD, notes that to prove that the heretical sects were "later than the catholic Church," Clement of Alexandri ...
, it is a flaw in the last sonship; according to others the sin of the Great Archon
''Archon'' ( gr, ἄρχων, árchōn, plural: ἄρχοντες, ''árchontes'') is a Greek word that means "ruler", frequently used as the title of a specific public office. It is the masculine present participle of the verb stem αρχ-, mean ...
, or Aeon-Creator, of the Universe; according to others it is the passion of the female Aeon Sophia, who emanates without her partner Aeon, resulting in the ''Demiurge
In the Platonic, Neopythagorean, Middle Platonic, and Neoplatonic schools of philosophy, the demiurge () is an artisan-like figure responsible for fashioning and maintaining the physical universe. The Gnostics adopted the term ''demiurge''. Al ...
'' (Greek ), a creature that should never have been. This creature does not belong to Pleroma, and the One emanates two savior Aeons, ''Christ
Jesus, likely from he, יֵשׁוּעַ, translit=Yēšūaʿ, label=Hebrew/Aramaic ( AD 30 or 33), also referred to as Jesus Christ or Jesus of Nazareth (among other Names and titles of Jesus in the New Testament, names and titles), was ...
'' and ''the Holy Spirit
In Judaism, the Holy Spirit is the divine force, quality, and influence of God over the Universe or over his creatures. In Nicene Christianity, the Holy Spirit or Holy Ghost is the third person of the Trinity. In Islam, the Holy Spirit acts as ...
'', to save humanity from the Demiurge. Christ then took a human form (''Jesus''), to teach humanity how to achieve Gnosis
Gnosis is the common Greek noun for knowledge ( γνῶσις, ''gnōsis'', f.). The term was used among various Hellenistic religions and philosophies in the Greco-Roman world. It is best known for its implication within Gnosticism, where it ...
. The ultimate end of all Gnosis is ''metanoia'' (Greek μετάνοια), or repentance—undoing the sin of material existence and returning to Pleroma.
Aeons bear a number of similarities to Judaeo-Christian angels, including roles as servants and emanations of God, and existing as beings of light. In fact, certain Gnostic Angels, such as Armozel, are also Aeons. The Gnostic Gospel of Judas
The Gospel of Judas is a non-canonical Gnostic gospel. The content consists of conversations between Jesus and Judas Iscariot. Given that it includes late 2nd-century theology, it is widely thought to have been composed in the 2nd century (prio ...
, found in 2006, purchased, held, and translated by the National Geographic Society
The National Geographic Society (NGS), headquartered in Washington, D.C., United States, is one of the largest non-profit scientific and educational organizations in the world.
Founded in 1888, its interests include geography, archaeology, and ...
, also mentions Aeons and speaks of Jesus' teachings about them.
Valentinus
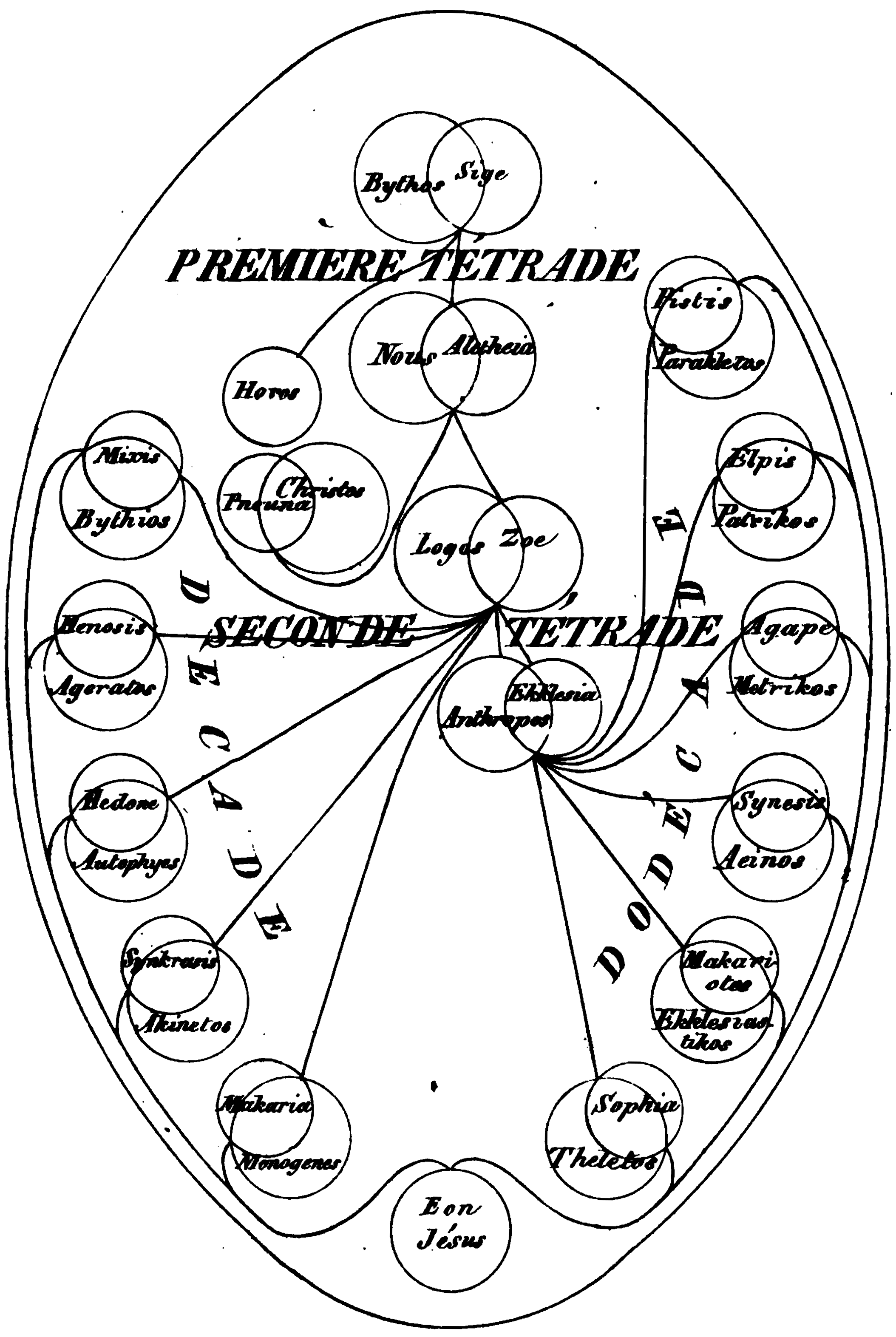
Valentinus assumed, as the beginning of all things, the Primal Being or Bythos, who after ages of silence and contemplation, gave rise to other beings by a process of emanation. The first series of beings, the Aeons, were thirty in number, representing fifteen syzygies or pairs sexually complementary. One common form is outlined below:Tertullian
Tertullian (; la, Quintus Septimius Florens Tertullianus; 155 AD – 220 AD) was a prolific early Christian author from Carthage in the Roman province of Africa. He was the first Christian author to produce an extensive corpus of L ...
's ''Against the Valentinians'' gives a slightly different sequence. The first eight of these Aeons, corresponding to generations one through four below, are referred to as the '' Ogdoad.''
*First generation
**''Bythos'' Βύθος (the One) and ''Sige'' Σιγή (Silence, Charis, Ennoea, etc.)
*Second generation
**''Nous'' Νοΰς (Nus, Mind) and ''Aletheia'' Άλήθεια (Veritas, Truth)
*Third generation, emanated from Nous and Aletheia
**''Sermo'' (the Word; ''Logos'' Λόγος) and ''Vita'' (the Life; ''Zoe'' Ζωή)
*Fourth generation, emanated from Sermo and Vita
**''Anthropos'' Άνθρωπος (Homo, Man) and ''Ecclesia'' Έκκλησία (Church)
*Fifth generation
**Emanated from Sermo and Vita:
***''Bythios'' (Profound) and ''Mixis'' (Mixture)
***''Ageratos'' (Never old) and ''Henosis'' (Union)
***''Autophyes'' (Essential nature) and ''Hedone'' (Pleasure)
***''Acinetos'' (Immovable) and ''Syncrasis'' (Commixture)
***''Monogenes'' (Only-begotten) and ''Macaria'' (Happiness)
**Emanated from Anthropos and Ecclesia
***''Paracletus'' (Comforter) and ''Pistis'' (Faith)
***''Patricas'' (Paternal) and ''Elpis'' (Hope)
***''Metricos'' (Maternal) and ''Agape'' (Love)
***''Ainos'' (Praise) and ''Synesis'' (Intelligence)
***''Ecclesiasticus'' (Son of Ecclesia) and ''Macariotes'' (Blessedness)
***''Theletus'' (Perfect) and ''Sophia'' (Wisdom)
Ptolemy and Colorbasus
According toIrenaeus
Irenaeus (; grc-gre, Εἰρηναῖος ''Eirēnaios''; c. 130 – c. 202 AD) was a Greek bishop noted for his role in guiding and expanding Christian communities in the southern regions of present-day France and, more widely, for the dev ...
, the followers of the Gnostics
Gnosticism (from grc, γνωστικός, gnōstikós, , 'having knowledge') is a collection of religious ideas and systems which coalesced in the late 1st century AD among Jewish and early Christian sects. These various groups emphasized pe ...
Ptolemy
Claudius Ptolemy (; grc-gre, Πτολεμαῖος, ; la, Claudius Ptolemaeus; AD) was a mathematician, astronomer, astrologer, geographer, and music theorist, who wrote about a dozen scientific treatises, three of which were of importanc ...
and Colorbasus
In Christian Gnostic religious history, the Colarbasians (from Gk. Colarbasus, Hippol., Ps. Tert.; Colorbasus, Iren., Epiph., Theodoret, Philast. cod., Aug.; ''C. Bassus'' Philast. codd.) were a supposed sect of the 2nd century, deemed heretics, ...
had Aeons that differ from those of Valentinus. Logos is created when Anthropos
Anthropos (ἄνθρωπος) is Greek for human.
Anthropos may also refer to:
* Anthropos, in Gnosticism, the first human being, also referred to as ''Adamas'' (from Hebrew meaning ''earth'') or ''Geradamas''
* ′Anthropos′ as a part of an ...
learns to speak. The first four are called the ''Tetrad'', and the eight are the ''Ogdoad'' deities
A deity or god is a supernatural being who is considered divine or sacred. The ''Oxford Dictionary of English'' defines deity as a god or goddess, or anything revered as divine. C. Scott Littleton defines a deity as "a being with powers greate ...
of the Ancient Egyptian pantheon.
*First generation
**''Bythos'' Βύθος (the One) and ''Sige'' Σιγή (Silence, Charis, Ennoea, etc.)
*Second generation (conceived by the One):
**''Ennoea'' (Thought) and ''Thelesis'' (Will)
*Third generation, emanated from Ennoea and Thelesis:
**''Nous'' Νοΰς (or ''Monogenes'') and ''Aletheia'' Άλήθεια
*Fourth generation, emanated from Nous and Aletheia:
**''Anthropos'' Άνθρωπος (Homo, Man) and ''Ecclesia'' Έκκλησία (Church)
*Fifth generation, emanated from Anthropos and Ecclesia:
**''Logos'' Λόγος and ''Zoe'' Ζωή
*Sixth generation:
**Emanated from Logos and Zoe:
***''Bythius'' and ''Mixis''
***''Ageratos'' and ''Henosis''
***''Autophyes'' and ''Hedone''
***''Acinetos'' and ''Syncrasis''
***''Monogenes'' and ''Macaria''
**Emanated from Anthropos and Ecclesia:
***''Paracletus'' and ''Pistis''
***''Patricos'' and ''Elpis''
***''Metricos'' and ''Agape''
***''Ainos'' and ''Synesis''
***''Ecclesiasticus'' and ''Macariotes''
***''Theletos'' and ''Sophia''
The order of Anthropos and Ecclesia versus Logos and Zoe is somewhat debated; different sources give different accounts. Logos and Zoe are unique to this system as compared to the previous, and may be an evolved version of the first, totalling 32 Aeons, but it is not clear if the first two were actually regarded Aeons.
Modern interpretations
According to Myther, "The total number of Aeons, being 32, reflects the similarity of the mechanism to theTree of Life
The tree of life is a fundamental archetype in many of the world's mythological, religious, and philosophical traditions. It is closely related to the concept of the sacred tree.Giovino, Mariana (2007). ''The Assyrian Sacred Tree: A History ...
, which, as suggested in the Zohar
The ''Zohar'' ( he, , ''Zōhar'', lit. "Splendor" or "Radiance") is a foundational work in the literature of Jewish mystical thought known as Kabbalah. It is a group of books including commentary on the mystical aspects of the Torah (the five ...
, incorporates 10 Sephirot
Sefirot (; he, סְפִירוֹת, translit=Səfīrōt, Tiberian: '), meaning '' emanations'', are the 10 attributes/emanations in Kabbalah, through which Ein Sof (The Infinite) reveals itself and continuously creates both the physical realm an ...
h and 22 paths interconnecting these 10 Sephiroth; while 10 Aeons are created during the first five generations from which come the other 22 Aeons later during the sixth generation."
Sige
 In the system of Valentinus, as expounded by Irenaeus (i. 1), the origin of things was traced to two eternal co-existent principles, a male and a female. The male was called Bythos or Proarche, or Propator, etc.; the female had the names Ennoea, Charis and Sige. The whole Aeonology of Valentinus was based on a theory of syzygies, or pairs of Aeons, each Aeon being provided with a consort; and the supposed need of the co-operation of a male and female principle for the generation of new ones, was common to Valentinus and some earlier Gnostic systems. But it was a disputed point in these systems whether the First Principle of all was thus twofold. There were those, both in earlier systems, and even among the Valentinians who held, that the origin of things was to be traced to a single Principle, which some described as
In the system of Valentinus, as expounded by Irenaeus (i. 1), the origin of things was traced to two eternal co-existent principles, a male and a female. The male was called Bythos or Proarche, or Propator, etc.; the female had the names Ennoea, Charis and Sige. The whole Aeonology of Valentinus was based on a theory of syzygies, or pairs of Aeons, each Aeon being provided with a consort; and the supposed need of the co-operation of a male and female principle for the generation of new ones, was common to Valentinus and some earlier Gnostic systems. But it was a disputed point in these systems whether the First Principle of all was thus twofold. There were those, both in earlier systems, and even among the Valentinians who held, that the origin of things was to be traced to a single Principle, which some described as hermaphrodite
In reproductive biology, a hermaphrodite () is an organism that has both kinds of reproductive organs and can produce both gametes associated with male and female sexes.
Many Taxonomy (biology), taxonomic groups of animals (mostly invertebrate ...
; others said was above all sex. And among the Valentinians who counted thirty Aeons, there were those who counted Bythos and Sige as the first pair; others who asserted the Single Principle excluded Bythos from the number, and made out the number of thirty without reckoning him. Thus Irenaeus says of the Valentinians (I. ii. 4. p. 10), "For they maintain that sometimes the Father acts in conjunction with Sige, but that at other times he shows himself independent both of male and female." And ( I. xi. 5) "For some declare him to be without a consort, and neither male nor female, and, in fact, nothing at all; while others affirm him to be masculo-feminine, assigning to him the nature of a hermaphrodite; others, again, allot Sige to him as a spouse, that thus may be formed the first conjunction."
Hippolytus supposes Valentinus to have derived his system from that of Simon
Simon may refer to:
People
* Simon (given name), including a list of people and fictional characters with the given name Simon
* Simon (surname), including a list of people with the surname Simon
* Eugène Simon, French naturalist and the genus ...
; and in that as expounded in the '' Apophasis Megale'', from which he gives extracts, the origin of things is derived from six roots, divided into three pairs; but all these roots spring from a single independent Principle, which is without consort. The name Sige occurs in the description which Hippolytus (vi. 18) quotes from the ''Apophasis'', how from the supreme Principle there arise the male and female offshoots ''nous'' and '' epinoia''. The name Sige is there given not to either of the offshoots but to the supreme Principle itself: however, in the description, these offshoots appear less as distinct entities than as different aspects of the same Being.
Cyril of Jerusalem (''Catech''. vi. 17) makes Sige the daughter of Bythos and by him the mother of Logos, a fable which he classes with the incests which heathen mythology attributed to Jupiter. Irenaeus ( II. xii.) ridicules the absurdity of the later form of Valentinian theory, in which Sige and Logos are represented as coexistent Aeons in the same Pleroma. "Where there is Silence" he says, "there will not be Word; and where there is Word, there cannot be Silence". He goes on ( ii. 14) to trace the invention of Sige to the heathen poets, quoting Antiphanes, who in his Theogony makes Chaos
Chaos or CHAOS may refer to:
Arts, entertainment and media Fictional elements
* Chaos (''Kinnikuman'')
* Chaos (''Sailor Moon'')
* Chaos (''Sesame Park'')
* Chaos (''Warhammer'')
* Chaos, in ''Fabula Nova Crystallis Final Fantasy''
* Cha ...
the offspring of Night and Silence.
Ennoea
In the attempts made by the framers of different Gnostic systems to explain the origin of the existing world, the first stage in the process was usually made by personifying the conception in the divine mind of that which was to emanate from Him. We learn fromJustin Martyr
Justin Martyr ( el, Ἰουστῖνος ὁ μάρτυς, Ioustinos ho martys; c. AD 100 – c. AD 165), also known as Justin the Philosopher, was an early Christian apologist and philosopher.
Most of his works are lost, but two apologies and ...
(''Ap''. I. 26), and from Irenaeus ( I. 23), that the word Ennoea was used in a technical sense in the system of Simon
Simon may refer to:
People
* Simon (given name), including a list of people and fictional characters with the given name Simon
* Simon (surname), including a list of people with the surname Simon
* Eugène Simon, French naturalist and the genus ...
. The Latin translation of Irenaeus either retains the word, or renders "mentis conceptio." Tertullian has "injectio" (''De Anima'', 34). In the '' Apophasis Megale'' cited by Hippolytus (''Ref''. vi. 18, 19, p. 174), the word used is not ''Ennoia'' but ''Epinoia''. Irenaeus states ( I. 23) that the word Ennoea passed from the system of Simon into that of Menander. In the Barbeliot system which Irenaeus also counts as derived from that of Simon ( I. 29), Ennoea appears as one of the first in the series of emanations from the unnameable Father.
In the system of Valentinus ( Iren. I. i.) Ennoea is one of several alternative names for the consort of the primary Aeon Bythos. For the somewhat different form in which Ptolemaeus presented this part of the system see Irenaeus ( I. xii.). Irenaeus criticises this part of the system ( II. xiii.). The name Ennoea is similarly used in the Ophite system described by Irenaeus ( I. xxx.).
Charis
Charis, in the system of Valentinus, was an alternative name, with Ennoea and Sige, for the consort of the primary Aeon Bythos ( Iren. i. 4). The name expresses that aspect of the absolute Greatness in which it is regarded not as a solitary monad, but as imparting from its perfection to beings of which it is the ultimate source; and this is the explanation given in the Valentinian fragment preserved by Epiphanius (''Haer''. xxxi. 6), ''dia to epikechoregekenai auten thesaurismata tou Megethous tois ek tou Megethous''. The use of the word Charis enabled Ptolemaeus (quoted by Irenaeus, i. 8) to find in the first tetrad of Aeons, viz., Pater, Monogenes, Charis, Aletheia. The suspicion arises that it was with a view to such an identification that names to be found in the prologue of St. John's Gospel were added as alternative appellations to the original names of the Aeons. But this is a point on which we have no data to pronounce. Charis has an important place in the system of Marcus ( Irenaeus, i. 13). The name Charis appears also in the system of the Barbelitae ( Irenaeus, i. 29), but as denoting a later emanation than in the Valentinian system. The word has possibly also a technical meaning in the Ophite prayers preserved by Origen ( ''Contra Celsum'', vi. 31), all of which end with the invocation .Nous
Ecclesia
This higher Ecclesia was held to be the archetype of the lower Ecclesia constituted by the spiritual seed on earth ( Iren. I. v. 6, p. 28). In a Gnostic system described by Irenaeus ( I. xxx. p. 109) we have also a heavenly church, not, however, as a separate Aeon, but as constituted by the harmony of the first existing beings. According to Hippolytus (v. 6, p. 95), theNaassenes
The Naassenes (Greek ''Naasseni,'' possibly from Hebrew נָחָשׁ ''naḥaš'', snake) were a Christian Gnostic sect known only through the writings of Hippolytus of Rome.
The Naassenes claimed to have been taught their doctrines by Mariamne, ...
counted three Ecclesiae.
It is especially in the case of the church that we find in Christian speculation prior to Valentinus traces of the conception, which lies at the root of the whole doctrine of Aeons, that earthly things have their archetypes in preexistent heavenly things. Hermas Hermas is a masculine given name. Notable people with the name include:
* Hermas of Dalmatia (1st century), one of the Seventy Disciples, feast day April 8
* Hermas of Philippopolis (1st century), one of the Seventy Disciples, feast day May 31
* H ...
(''Vis''. ii. 4) speaks of the church as created before all things and of the world as formed for her sake; and in the newly discovered portion of the so-called Second Epistle of Clement
The Second Epistle of Clement ( grc, Κλήμεντος πρὸς Κορινθίους, Klēmentos pros Korinthious, from Clement to Corinthians), often referred to as 2 Clement (pronounced "Second Clement"), is an early Christian writing. It was ...
to the Corinthians (c. 14) the writer speaks of the spiritual church as created before the sun and moon, as pre-existent like Christ Himself, and like him manifested in the last days for men's salvation; and he even uses language which, if it were not sufficiently accounted for by what is said in the Epistle to the Ephesians as to the union between Christ and His church, might be supposed to have affinity with the Valentinian doctrine of the relation between Anthropos and Ecclesia.
The author of the Epistle to the Hebrews
The Epistle to the Hebrews ( grc, Πρὸς Ἑβραίους, Pros Hebraious, to the Hebrews) is one of the books of the New Testament.
The text does not mention the name of its author, but was traditionally attributed to Paul the Apostle. Mos ...
quotes the direction to Moses to make the tabernacle after the pattern shewn him on the Mount (a passage cited in ), and his argument dwells on the inference that the various parts of the Jewish service were but copies of better heavenly archetypes. This same heavenly tabernacle appears as part of the imagery of the book of the Revelation (, ). In the same book the church appears as the Lamb's wife, the new Jerusalem descending from heaven; and St. Paul's teaching () might be thrown into the form that the church existed in God's election before the foundation of the world.
Anthropos
As the world is an image of the living Aeon (), so is man an image of the pre-existent man of the . Valentinus, according to Clemens Alexandrinus ( ''Valentini homil. ap. Clem. Strom.'' iv. 13, 92), spoke of the Sophia as an artist (''zographos'') making this visible lower world a picture of the glorious Archetype, but the hearer or reader would as readily understand the heavenly wisdom of the Book of Proverbs to be meant by this Sophia, as the 12th and fallen Aeon. Under her (according to Valentinus) stand the world-creative angels, whose head is the Demiurge. Her formation (''plasma'') is Adam created in the name of the . In him thus made a higher power puts the seed of the heavenly pneumatic essence (). Thus furnished with higher insight, Adam excites the fears of the angels; for even as ''kosmikoi anthropoi'' are seized with fear of the images made by their own hands to bear the name of God, ''i.e.'' the idols, so these angels cause the images they have made to disappear ( ''Ep. ad amicos ap. Clem. Alex. Strom.'' ii. 8, 36).Horos
According to the doctrine of Valentinus, as described by Irenaeus i. 2, the youngest Aeon Sophia, in her passion to comprehend the Father of all, runs the danger of being absorbed into his essence, from which she is saved by coming into contact with the limiting power ''Horos'', whose function it is to strengthen all things outside the ineffable Greatness, by confining each to its appointed place. According to this version Horos was a previously existing power; but according to another, and apparently a later account, Horos is an Aeon only generated on this occasion at the request of all the Aeons, who implored the Father to avert a danger that threatened to affect them all. Then (as Hippolytus tells the story, vi. 31) he directs the production of a new pair of Aeons, Christ and the Holy Spirit, who restore order by separating from the Pleroma the unformed offspring of Sophia. After this Horos is produced in order to secure the permanence of the order thus produced. Irenaeus (''u. s.'') reverses this order, and Horos is produced first, afterwards the other pair. The Valentinian fragment in Epiphanius (''Haer''. 31, p. 171), which seems to give a more ancient form of this heresy, knows nothing of Horos, but it relates as the last spiritual birth the generation of five beings without consorts, whose names are used in the Irenaean version as titles for the supernumerary Aeon Horos. But besides, this Aeon has a sixth name, which in the version of Hippolytus is made his primary title ''Stauros
''Stauros'' () is a Greek word for a stake or an implement of capital punishment. The Greek New Testament uses the word ''stauros'' for the instrument of Jesus' crucifixion, and it is generally translated ''cross'' in Christian contexts. This arti ...
;'' and it is explained ( Irenaeus, i. 3) that besides his function as a separator, in respect of which he is called Horos, this Aeon does the work of stablishing and settling, in respect of which he is called Stauros. A derivation from is hinted at.
The literal earthly crucifixion of the Saviour (that seen by the psychic
A psychic is a person who claims to use extrasensory perception (ESP) to identify information hidden from the normal senses, particularly involving telepathy or clairvoyance, or who performs acts that are apparently inexplicable by natural laws, ...
church, which only believes in the ''historical'' Jesus) was meant to represent an ''archetypal'' scene in the world of Aeons, when the younger Sophia, Achamoth, is healed through the Savior's instrumentation.
The distinction just explained as to the different use of the names Horos and Stauros was not carefully observed by Valentinians. Thus the last word is sometimes used when the function of separation and division is spoken of (''Excerpt. ex Script. Theodot.'' 22 and 42, Clem. Alex. ii. pp. 974, 979), it being remarked in the latter passage that the cross separates the faithful from the unbelievers; and Clem. Alex., who occasionally uses Valentinian language in an orthodox sense, speaks in the same way (''Paed''. iii. 12, p. 303, and ''Strom''. ii. 20, p. 486).
In the Valentinian theory there is a double Horos, or at least a double function discharged by Horos.
On the one hand, he discharges as already described, a function within the Pleroma, separating the other Aeons from the ineffable Bythos, and saving them from absorption into his essence. On the other hand, Horos is the outside boundary of the Pleroma itself, giving it permanence and stability by guarding it against the intrusion of any foreign element.
Cultural references
The animated TV series ''Æon Flux
''Æon Flux'' is an American avant-garde science fiction adventure animated television series that aired on MTV from November 30, 1991, until October 10, 1995, with film, comic book, and video game adaptations following thereafter. It premiered ...
'' draws its name and some of its iconography from Gnosticism, notably aeons (the two main characters forming a syzygy) and a demiurge.Aeon Flux: All You've Ever Needed From Sci-Fiby Alison Veneto, SMRT TV, April 24, 2006, "...Aeon Flux has a serious Gnostic bent. The ancient mystery religion is where they got the concepts of aeons and the demiurge, amongst other things."
May 18, 2008, The Alien Next Door
Nina Munteanu
!-- Author is a science-fiction writer -->
See also
*Aion (deity)
Aion ( el, Αἰών) is a Hellenistic deity associated with time, the orb or circle encompassing the universe, and the zodiac.
The "time" which Aion represents is perpetual, unbounded, ritual, and cyclic: The future is a returning version o ...
* Nous
''Nous'', or Greek νοῦς (, ), sometimes equated to intellect or intelligence, is a concept from classical philosophy for the faculty of the human mind necessary for understanding what is true or real.
Alternative English terms used in p ...
* Archon (Gnosticism)
Archons are, in Gnosticism and religions closely related to it, the builders of the physical universe. Among the Archontics, Ophites, Sethians and in the writings of Nag Hammadi library, the archons are rulers, each related to one of seven planets ...
* Luminary (Gnosticism)
In Sethian Gnosticism, a luminary is an angel-like being (or heavenly dwelling place in the ''Apocryphon of John''). Four luminaries are typically listed in Sethian Gnostic texts, such as the ''Secret Book of John'', the '' Holy Book of the Great ...
References
Bibliography
* ;Attribution * * * * * * * *{{Catholic, wstitle=ÆonsExternal links
Tertullian's account against the Valentinians
is the source text for much of what we know about the Æons.
- The Gnostic Society Library Gnostic deities Gnosticism